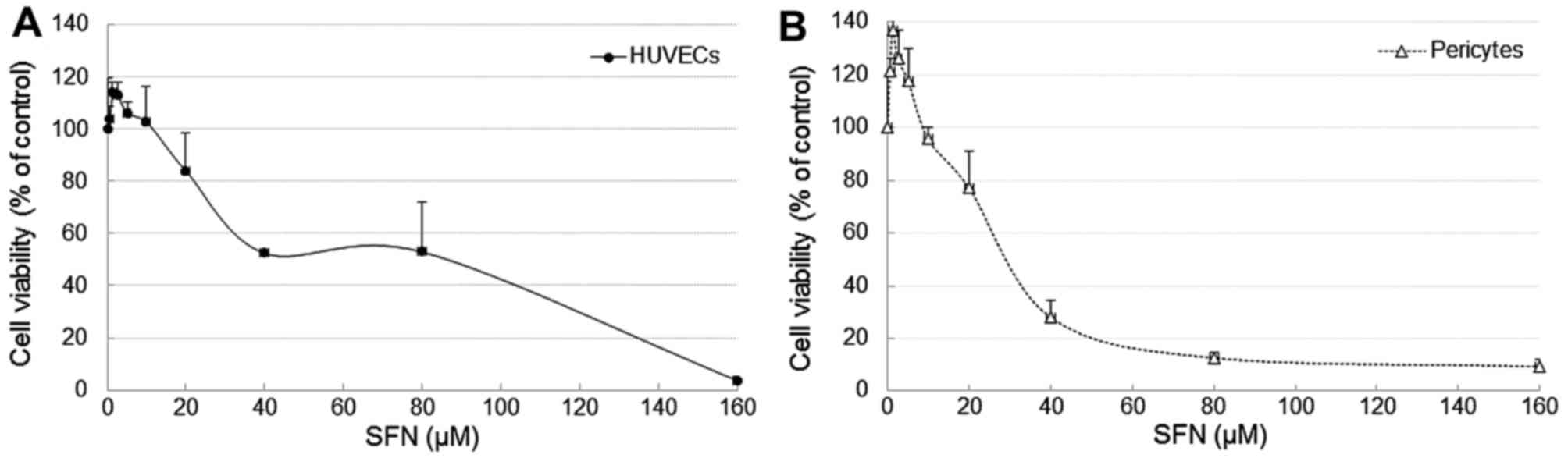
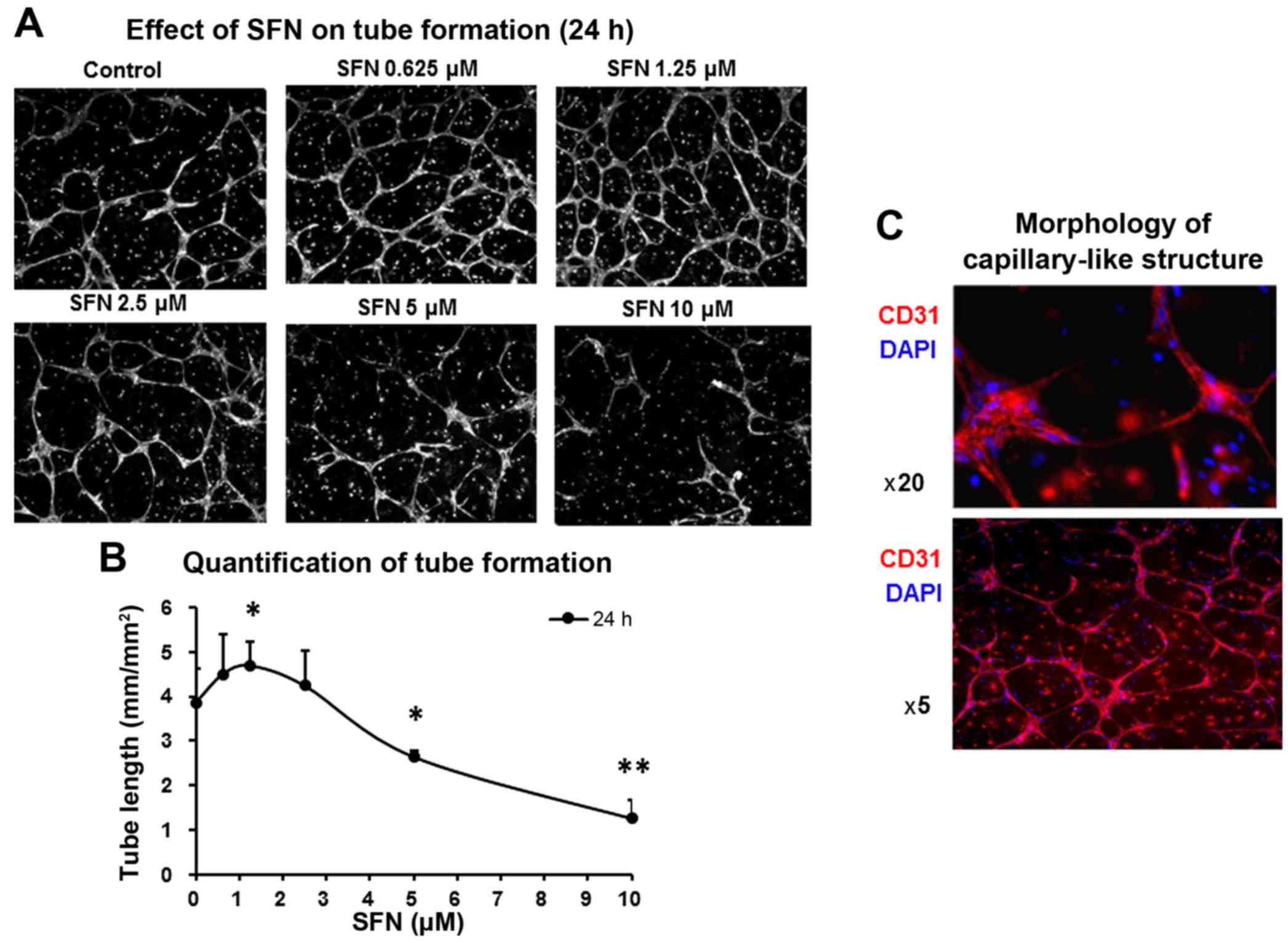
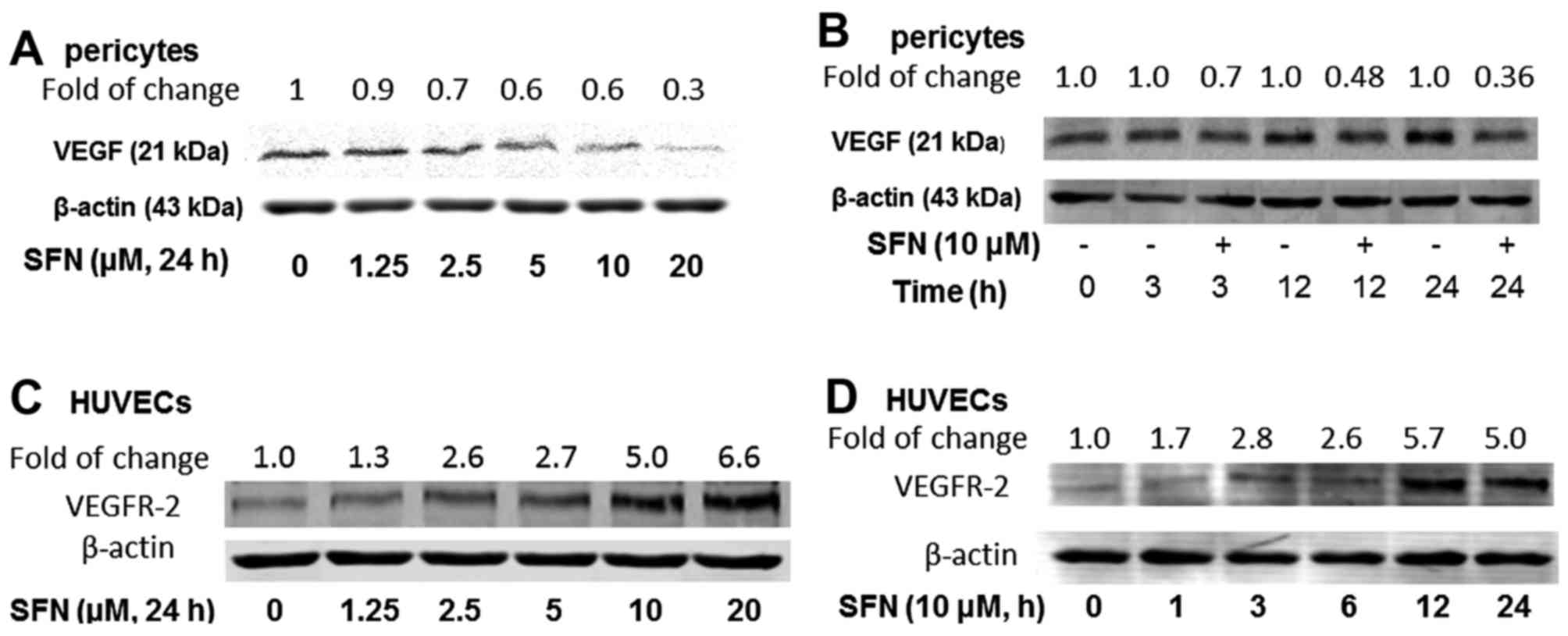
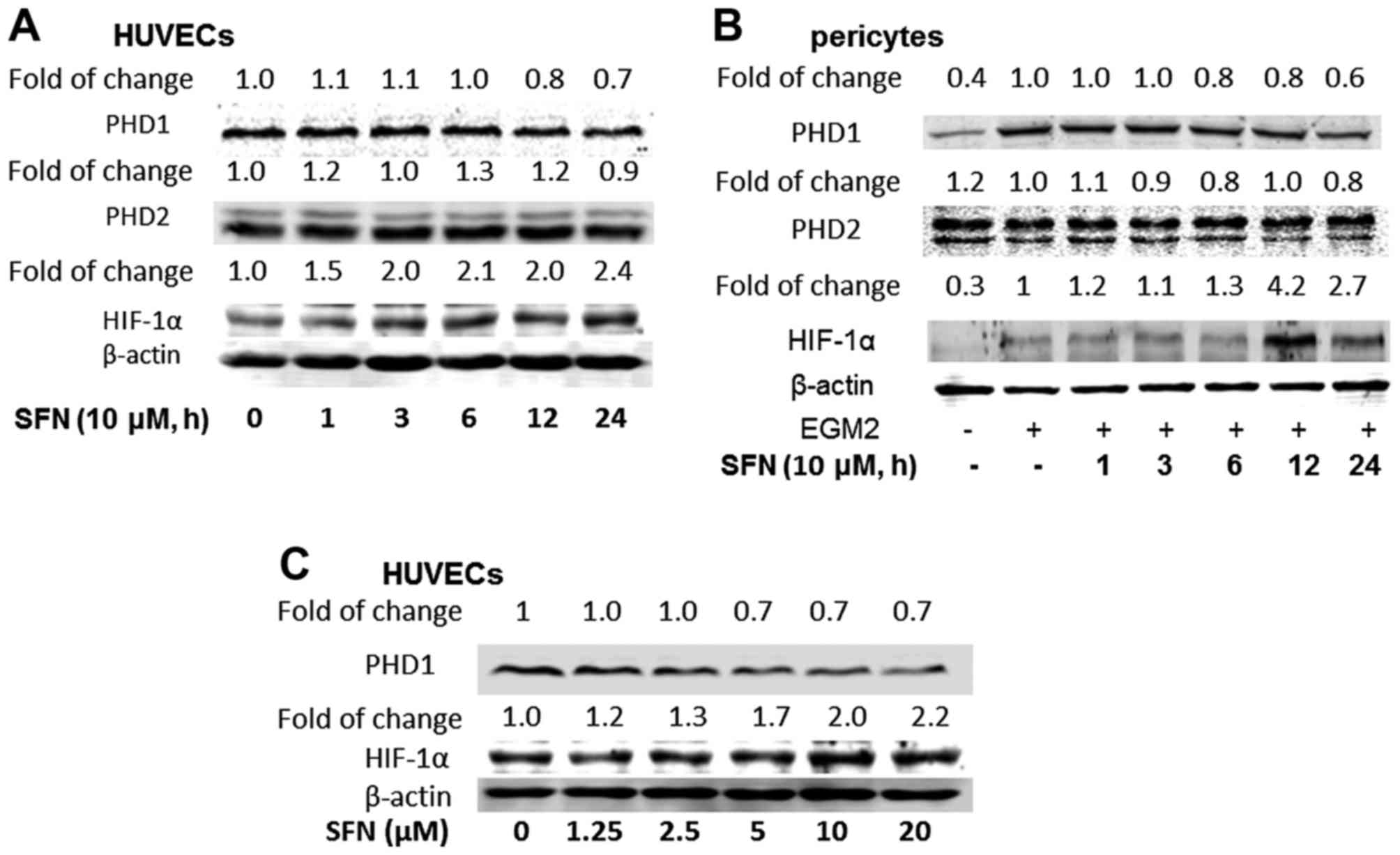
|
1
|
Folkman J: Role of angiogenesis in tumor
growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 29:(Suppl 16). 15–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharma RA, Harris AL, Dalgleish AG,
Steward WP and OByrne KJ: Angiogenesis as a biomarker and target in
cancer chemoprevention. Lancet Oncol. 2:726–732. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Armulik A, Abramsson A and Betsholtz C:
Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ Res. 97:512–523. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N,
Bergsland E and Hanahan D: Benefits of targeting both pericytes and
endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors.
J Clin Invest. 111:1287–1295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: Tumor
angiogenesis: Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med.
17:1359–1370. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Metzen E, Stiehl DP, Doege K, Marxsen JH,
Hellwig-Bürgel T and Jelkmann W: Regulation of the prolyl
hydroxylase domain protein 2 (phd2/egln-1) gene: Identification of
a functional hypoxia-responsive element. Biochem J. 387:711–717.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berra E, Richard DE, Gothié E and
Pouysségur J: HIF-1-dependent transcriptional activity is required
for oxygen-mediated HIF-1alpha degradation. FEBS Lett. 491:85–90.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie K, Wei D, Shi Q and Huang S:
Constitutive and inducible expression and regulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:297–324.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang N, Wang L, Esko J, Giordano FJ, Huang
Y, Gerber HP, Ferrara N and Johnson RS: Loss of HIF-1alpha in
endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven VEGF autocrine loop
necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 6:485–495. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reynolds AR: Potential relevance of
bell-shaped and u-shaped dose-responses for the therapeutic
targeting of angiogenesis in cancer. Dose Response. 8:253–284.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as a
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ellis LM and Hicklin DJ: VEGF-targeted
therapy: Mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:579–591. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rapisarda A and Melillo G: Role of the
VEGF/VEGFR axis in cancer biology and therapy. Adv Cancer Res.
114:237–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Terme M, Pernot S, Marcheteau E, Sandoval
F, Benhamouda N, Colussi O, Dubreuil O, Carpentier AF, Tartour E
and Taieb J: VEGFA-VEGFR pathway blockade inhibits tumor-induced
regulatory T-cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
73:539–549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sessa C, Guibal A, Del Conte G and Rüegg
C: Biomarkers of angiogenesis for the development of antiangiogenic
therapies in oncology: Tools or decorations? Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
5:378–391. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Higdon JV, Delage B, Williams DE and
Dashwood RH: Cruciferous vegetables and human cancer risk:
epidemiologic evidence and mechanistic basis. Pharmacol Res.
55:224–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tse G and Eslick GD: Cruciferous
vegetables and risk of colorectal neoplasms: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Nutr Cancer. 66:128–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yao H, Wang H, Zhang Z, Jiang BH, Luo J
and Shi X: Sulforaphane inhibited expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha in human tongue squamous cancer cells and prostate
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 123:1255–1261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shan Y, Sun C, Zhao X, Wu K, Cassidy A and
Bao Y: Effect of sulforaphane on cell growth,
G0/G1 phase cell progression and apoptosis in
human bladder cancer T24 cells. Int J Oncol. 29:883–888.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shan Y, Wu K, Wang W, Wang S, Lin N, Zhao
R, Cassidy A and Bao Y: Sulforaphane down-regulates COX-2
expression by activating p38 and inhibiting NF-kappaB-DNA-binding
activity in human bladder T24 cells. Int J Oncol. 34:1129–1134.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Dacosta C, Wang W, Zhou Z, Liu M
and Bao Y: Synergy between sulforaphane and selenium in protection
against oxidative damage in colonic CCD841 cells. Nutr Res.
35:610–617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Asakage M, Tsuno NH, Kitayama J, Tsuchiya
T, Yoneyama S, Yamada J, Okaji Y, Kaisaki S, Osada T, Takahashi K,
et al: Sulforaphane induces inhibition of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells proliferation by apoptosis. Angiogenesis.
9:83–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nishikawa T, Tsuno NH, Tsuchiya T,
Yoneyama S, Yamada J, Shuno Y, Okaji Y, Tanaka J, Kitayama J,
Takahashi K, et al: Sulforaphane stimulates activation of
proapoptotic protein bax leading to apoptosis of endothelial
progenitor cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:534–543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nishikawa T, Tsuno NH, Okaji Y, Sunami E,
Shuno Y, Sasaki K, Hongo K, Kaneko M, Hiyoshi M, Kawai K, et al:
The inhibition of autophagy potentiates anti-angiogenic effects of
sulforaphane by inducing apoptosis. Angiogenesis. 13:227–238. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jackson SJ, Singletary KW and Venema RC:
Sulforaphane suppresses angiogenesis and disrupts endothelial
mitotic progression and microtubule polymerization. Vascul
Pharmacol. 46:77–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bertl E, Bartsch H and Gerhäuser C:
Inhibition of angiogenesis and endothelial cell functions are novel
sulforaphane-mediated mechanisms in chemoprevention. Mol Cancer
Ther. 5:575–585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Davis R, Singh KP, Kurzrock R and Shankar
S: Sulforaphane inhibits angiogenesis through activation of FOXO
transcription factors. Oncol Rep. 22:1473–1478. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barrera LN, Cassidy A, Wang W, Wei T,
Belshaw NJ, Johnson IT, Brigelius-Flohé R and Bao Y: TrxR1 and GPx2
are potently induced by isothiocyanates and selenium, and mutually
cooperate to protect Caco-2 cells against free radical-mediated
cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:1914–1924. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Whayne TF Jr, Parinandi N and Maulik N:
Thioredoxins in cardiovascular disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
93:903–911. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cooley LS, Handsley MM, Zhou Z, Lafleur
MA, Pennington CJ, Thompson EW, Pöschl E and Edwards DR: Reversible
transdifferentiation of blood vascular endothelial cells to a
lymphatic-like phenotype in vitro. J Cell Sci. 123:3808–3816. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brachvogel B, Pausch F, Farlie P, Gaipl U,
Etich J, Zhou Z, Cameron T, von der Mark K, Bateman JF and Pöschl
E: Isolated Anxa5+/Sca-1+ perivascular cells
from mouse meningeal vasculature retain their perivascular
phenotype in vitro and in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 313:2730–2743. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou Z, Pausch F, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U,
Brachvogel B and Pöschl E: Induction of initial steps of angiogenic
differentiation and maturation of endothelial cells by pericytes in
vitro and the role of collagen IV. Histochem Cell Biol.
145:511–525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bader BL, Rayburn H, Crowley D and Hynes
RO: Extensive vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and organogenesis
precede lethality in mice lacking all alpha v integrins. Cell.
95:507–519. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Streicher KL, Sylte MJ, Johnson SE and
Sordillo LM: Thioredoxin reductase regulates angiogenesis by
increasing endothelial cell-derived vascular endothelial growth
factor. Nutr Cancer. 50:221–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Griffith LG and Swartz MA: Capturing
complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
7:211–224. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fang C, Man YG, Cuttitta F,
Stetler-Stevenson W, Salomon D, Mazar A, Kulesza P, Rosen S, Avital
I, Stojadinovic A, et al: Novel phenotypic fluorescent
three-dimensional co-culture platforms for recapitulating tumor in
vivo progression and for personalized therapy. J Cancer. 4:755–763.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nascarella MA, Stanek EJ III, Hoffmann GR
and Calabrese EJ: Quantification of hormesis in anticancer-agent
dose-responses. Dose Response. 7:160–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ushio-Fukai M and Nakamura Y: Reactive
oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidase as target for cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 266:37–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pagès G and Pouysségur J: Transcriptional
regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene - a
concert of activating factors. Cardiovasc Res. 65:564–573. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Beaver LM, Buchanan A, Sokolowski EI,
Riscoe AN, Wong CP, Chang JH, Löhr CV, Williams DE, Dashwood RH and
Ho E: Transcriptome analysis reveals a dynamic and differential
transcriptional response to sulforaphane in normal and prostate
cancer cells and suggests a role for Sp1 in chemoprevention. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 58:2001–2013. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ji W, Yang M, Praggastis A, Li Y, Zhou HJ,
He Y, Ghazvinian R, Cincotta DJ, Rice KP and Min W: Carbamoylating
activity associated with the activation of the antitumor agent
laromustine inhibits angiogenesis by inducing ASK1-dependent
endothelial cell death. PLoS One. 9:e1032242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lincoln DT, Emadi Ali EM, Tonissen KF and
Clarke FM: The thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system:
Over-expression in human cancer. Anticancer Res. 23:2425–2433.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li D, Wang W, Shan Y, Barrera LN, Howie
AF, Beckett GJ, Wu K and Bao Y: Synergy between sulforaphane and
selenium in the up-regulation of thioredoxin reductase and
protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in human
hepatocytes. Food Chem. 133:300–307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kim YW and Byzova TV: Oxidative stress in
angiogenesis and vascular disease. Blood. 123:625–631. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bir SC, Shen X, Kavanagh TJ, Kevil CG and
Pattillo CB: Control of angiogenesis dictated by picomolar
superoxide levels. Free Radic Biol Med. 63:135–142. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
García-Quintans N, Sánchez-Ramos C, Prieto
I, Tierrez A, Arza E, Alfranca A, Redondo JM and Monsalve M:
Oxidative stress induces loss of pericyte coverage and vascular
instability in PGC-1α-deficient mice. Angiogenesis. 19:217–228.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li WW, Li VW, Hutnik M and Chiou AS: Tumor
angiogenesis as a target for dietary cancer prevention. J Oncol.
2012:8796232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Radomska-Leśniewska DM, Hevelke A,
Skopiński P, Bałan B, Jóźwiak J, Rokicki D, Skopińska-Różewska E
and Białoszewska A: Reactive oxygen species and synthetic
antioxidants as angiogenesis modulators: Clinical implications.
Pharmacol Rep. 68:462–471. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Campbell L, Howie F, Arthur JR, Nicol F
and Beckett G: Selenium and sulforaphane modify the expression of
selenoenzymes in the human endothelial cell line EAhy926 and
protect cells from oxidative damage. Nutrition. 23:138–144. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shan Y, Zhao R, Geng W, Lin N, Wang X, Du
X and Wang S: Protective effect of sulforaphane on human vascular
endothelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
damage. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 10:139–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|