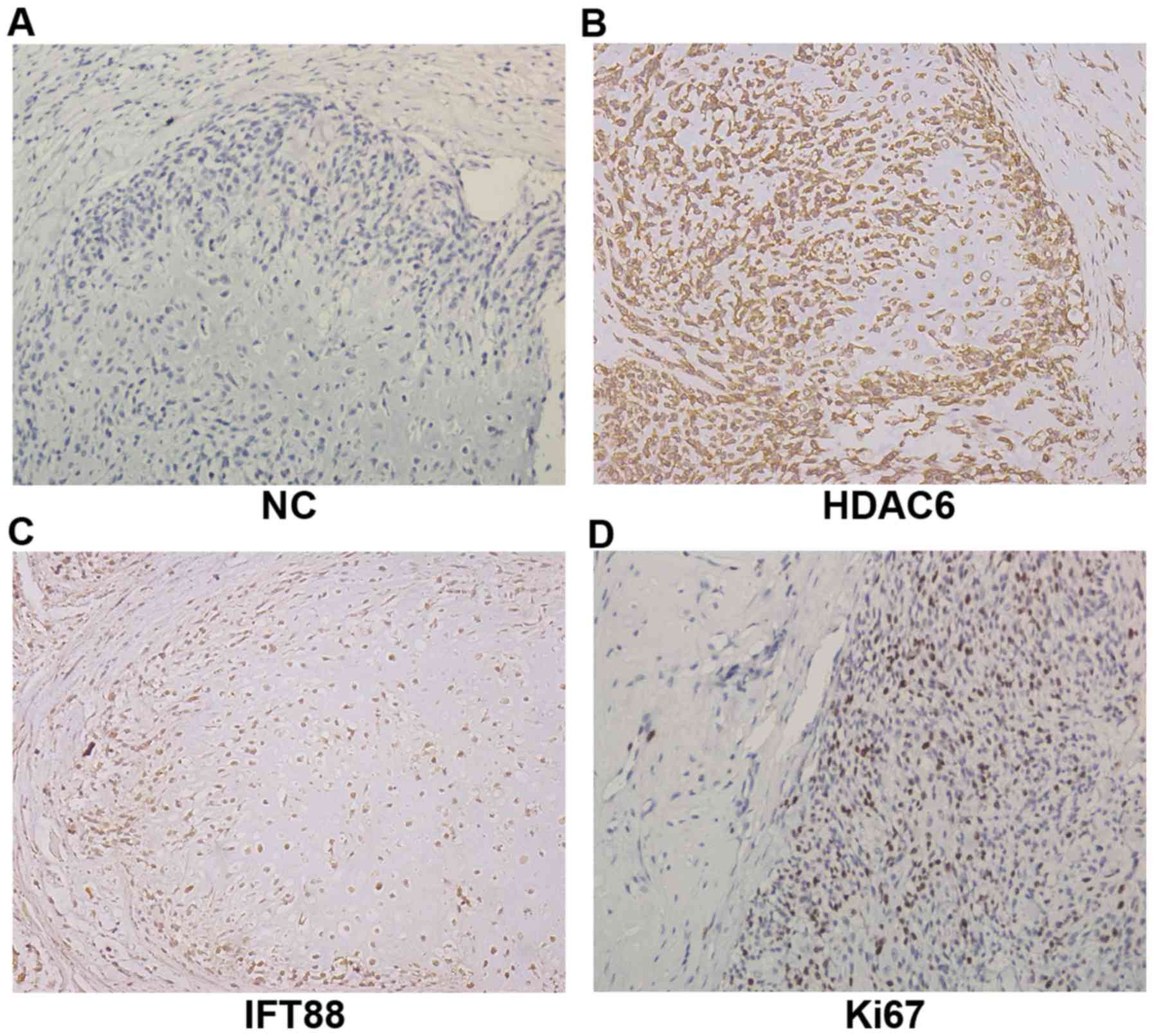
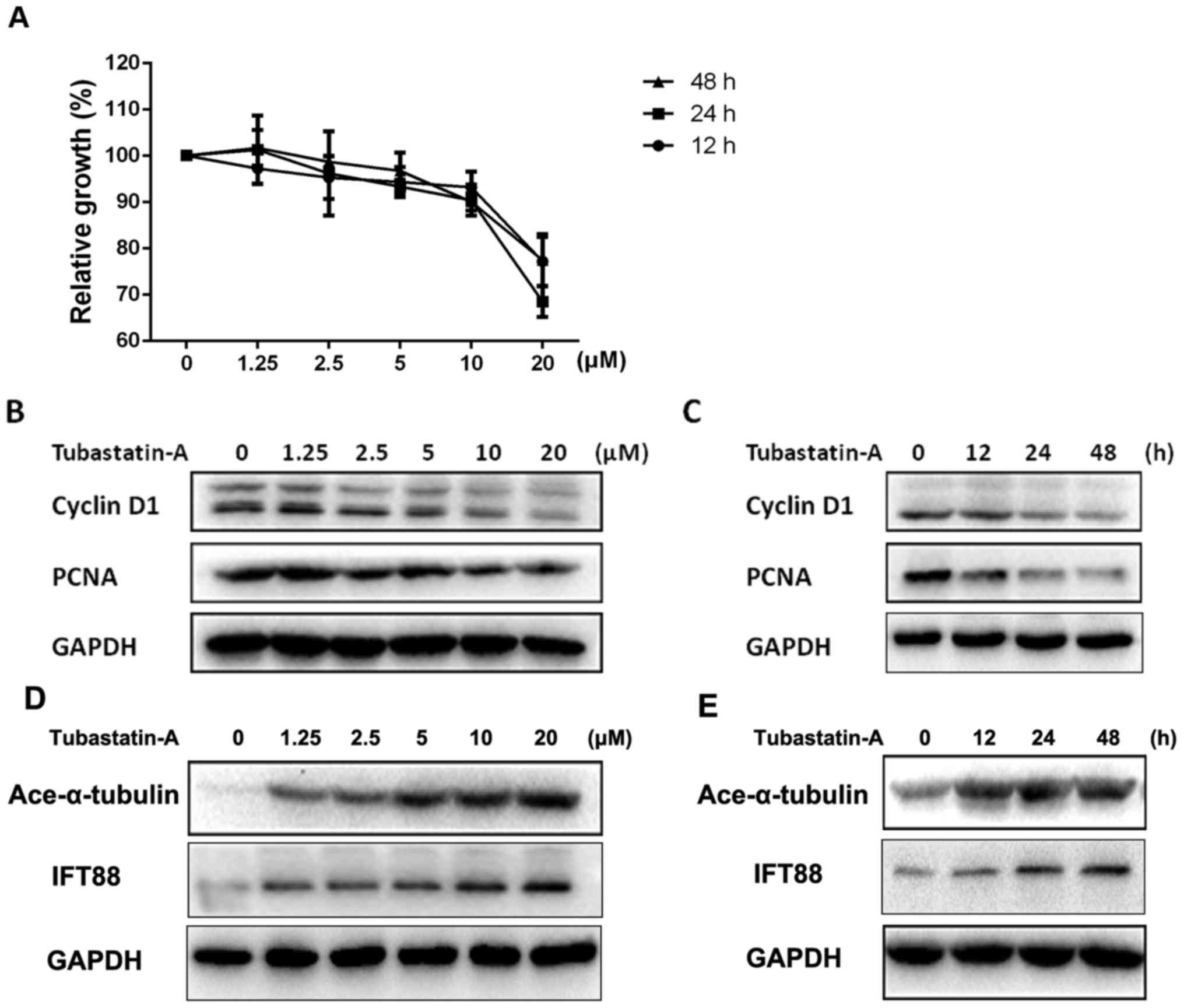
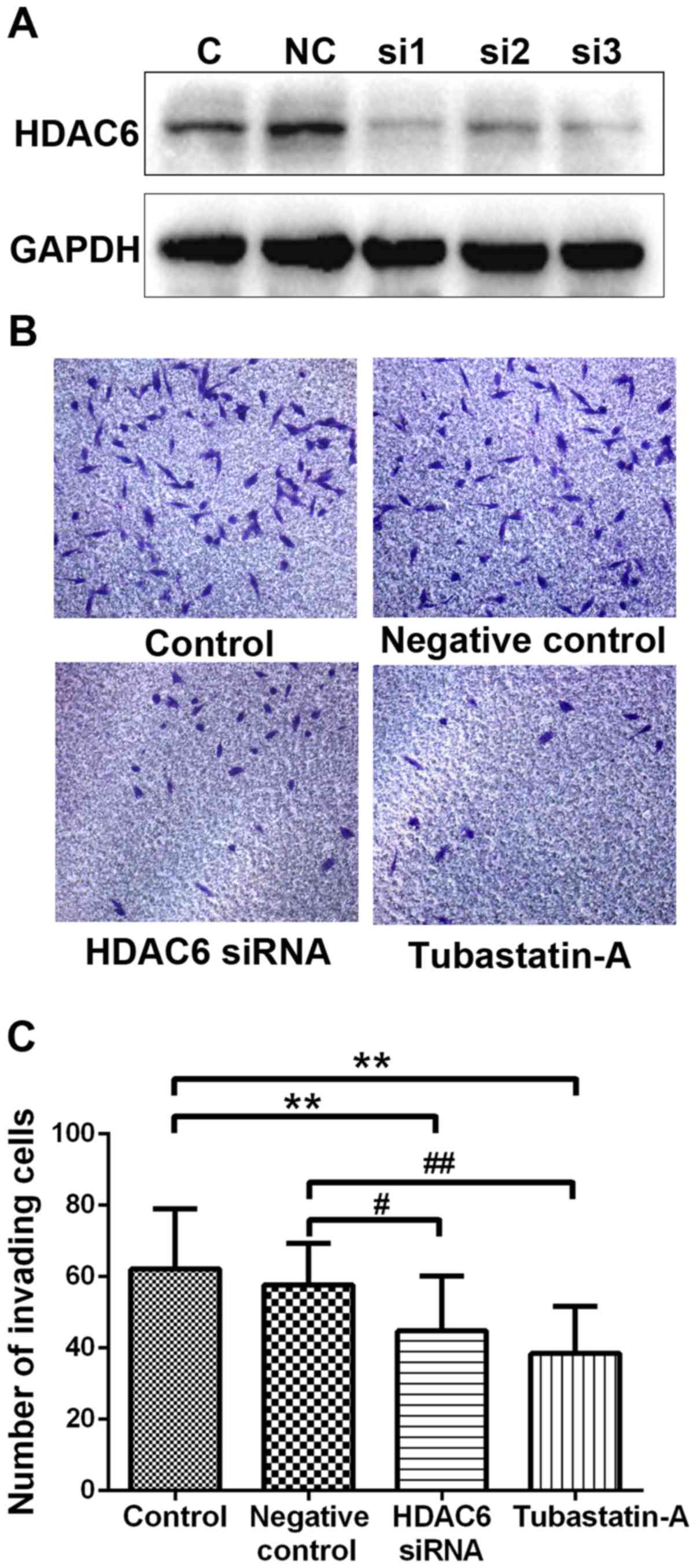
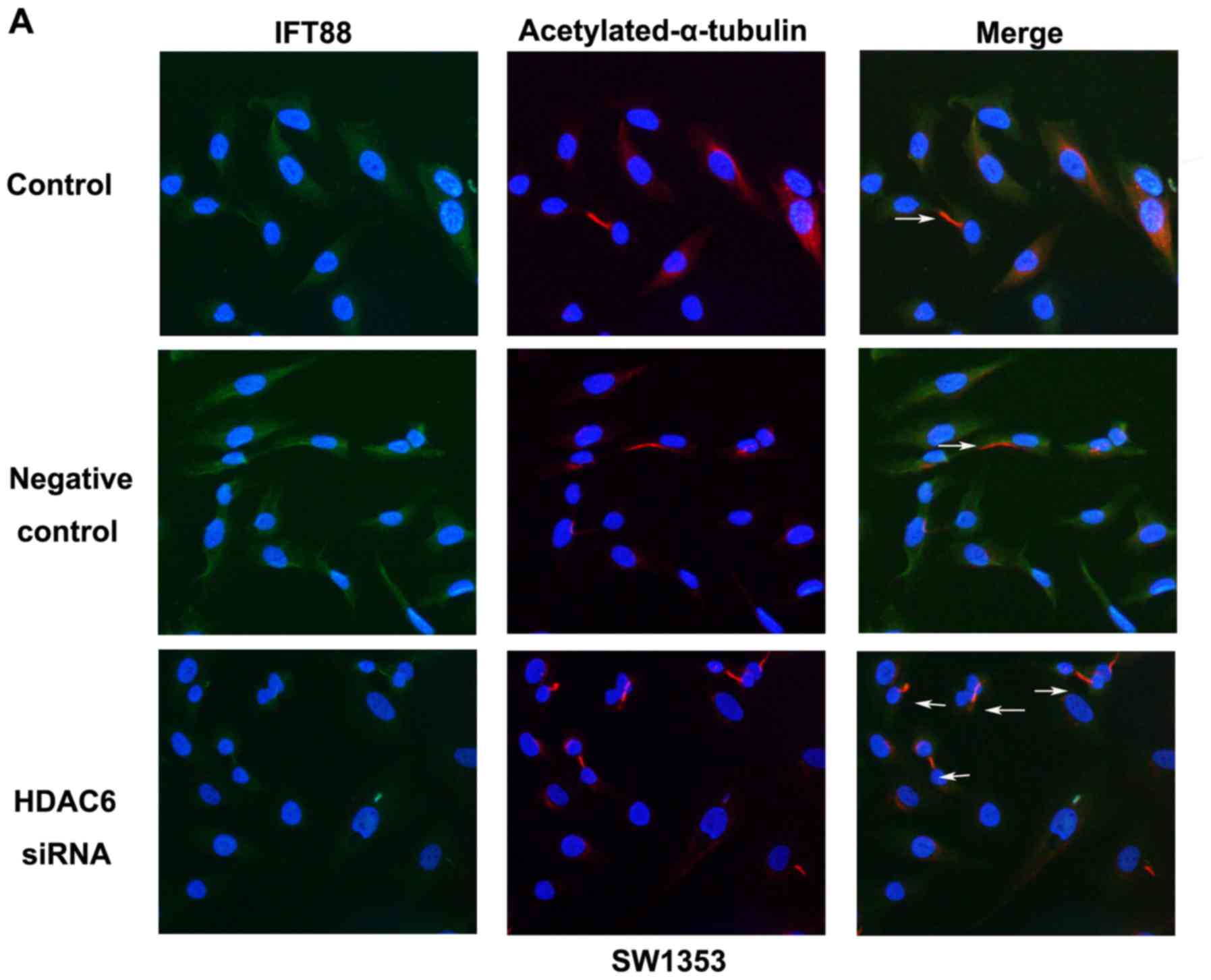
|
1
|
Leddy LR and Holmes RE: Chondrosarcoma of
bone. Cancer Treat Res. 162:117–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leucht P, Monica SD, Temiyasathit S,
Lenton K, Manu A, Longaker MT, Jacobs CR, Spilker RL, Guo H,
Brunski JB, et al: Primary cilia act as mechanosensors during bone
healing around an implant. Med Eng Phys. 35:392–402. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muhammad H, Rais Y, Miosge N and Ornan EM:
The primary cilium as a dual sensor of mechanochemical signals in
chondrocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:2101–2107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zimmerman K and Yoder BK: SnapShot:
Sensing and signaling by cilia. Cell. 161:692–2.e1. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seeger-Nukpezah T, Little JL, Serzhanova V
and Golemis EA: Cilia and cilia-associated proteins in cancer. Drug
Discov Today Dis Mech. 10:e135–e142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hassounah NB, Bunch TA and McDermott KM:
Molecular pathways: The role of primary cilia in cancer progression
and therapeutics with a focus on Hedgehog signaling. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2429–2435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de Andrea CE, Zhu JF, Jin H, Bovée JV and
Jones KB: Cell cycle deregulation and mosaic loss of Ext1 drive
peripheral chondrosarcomagenesis in the mouse and reveal an
intrinsic cilia deficiency. J Pathol. 236:210–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Izawa I, Goto H, Kasahara K and Inagaki M:
Current topics of functional links between primary cilia and cell
cycle. Cilia. 4:122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ke YN and Yang WX: Primary cilium: An
elaborate structure that blocks cell division? Gene. 547:175–185.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu F, Ran J and Zhou J: Ciliopathies: Does
HDAC6 represent a new therapeutic target? Trends Pharmacol Sci.
37:114–119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ran J, Yang Y, Li D, Liu M and Zhou J:
Deacetylation of α-tubulin and cortactin is required for HDAC6 to
trigger ciliary disassembly. Sci Rep. 5:129172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valenzuela-Fernández A, Cabrero JR,
Serrador JM and Sánchez-Madrid F: HDAC6: A key regulator of
cytoskeleton, cell migration and cell-cell interactions. Trends
Cell Biol. 18:291–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Sugiura H,
Omoto Y, Ando Y, Mita K, Hamaguchi M, Hayashi S and Iwase H: HDAC6
expression is correlated with better survival in breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:6962–6968. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gradilone SA, Radtke BN, Bogert PS, Huang
BQ, Gajdos GB and LaRusso NF: HDAC6 inhibition restores ciliary
expression and decreases tumor growth. Cancer Res. 73:2259–2270.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dhanyamraju PK, Holz PS, Finkernagel F,
Fendrich V and Lauth M: Histone deacetylase 6 represents a novel
drug target in the oncogenic Hedgehog signaling pathway. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:727–739. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Butler KV, Kalin J, Brochier C, Vistoli G,
Langley B and Kozikowski AP: Rational design and simple chemistry
yield a superior, neuroprotective HDAC6 inhibitor, Tubastatin A. J
Am Chem Soc. 132:10842–10846. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ho L, Ali SA, Al-Jazrawe M, Kandel R,
Wunder JS and Alman BA: Primary cilia attenuate hedgehog signalling
in neoplastic chondrocytes. Oncogene. 32:5388–5396. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kawasaki M, Ezura Y, Hayata T, Notomi T,
Izu Y and Noda M: TGF-β suppresses Ift88 expression in chondrocytic
ATDC5 Cells. J Cell Physiol. 230:2788–2795. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pugacheva EN, Jablonski SA, Hartman TR,
Henske EP and Golemis EA: HEF1-dependent Aurora A activation
induces disassembly of the primary cilium. Cell. 129:1351–1363.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deren ME, Yang X, Guan Y and Chen Q:
Biological and chemical removal of primary cilia affects mechanical
activation of chondrogenesis markers in chondroprogenitors and
hypertrophic chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 17:1882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poole CA, Jensen CG, Snyder JA, Gray CG,
Hermanutz VL and Wheatley DN: Confocal analysis of primary cilia
structure and colocalization with the Golgi apparatus in
chondrocytes and aortic smooth muscle cells. Cell Biol Int.
21:483–494. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song B, Haycraft CJ, Seo HS, Yoder BK and
Serra R: Development of the post-natal growth plate requires
intraflagellar transport proteins. Dev Biol. 305:202–216. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuan X and Yang S: Primary cilia and
intraflagellar transport proteins in bone and cartilage. J Dent
Res. 95:1341–1349. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiang W, Jiang T, Guo F, Xu T, Gong C,
Cheng P, Zhao L, Cheng W and Xu K: Evaluating the role of PTH in
promotion of chondrosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by
inhibiting primary cilia expression. Int J Mol Sci. 15:19816–19831.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mahankali M, Henkels KM, Speranza F and
Gomez-Cambronero J: A non-mitotic role for Aurora kinase A as a
direct activator of cell migration upon interaction with PLD, FAK
and Src. J Cell Sci. 128:516–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Al-Bataineh MM, Alzamora R, Ohmi K, Ho PY,
Marciszyn AL, Gong F, Li H, Hallows KR and Pastor-Soler NM: Aurora
kinase A activates the vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) in kidney
carcinoma cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 310:F1216–F1228. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kozyreva VK, McLaughlin SL, Livengood RH,
Calkins RA, Kelley LC, Rajulapati A, Ice RJ, Smolkin MB, Weed SA
and Pugacheva EN: NEDD9 regulates actin dynamics through cortactin
deacetylation in an AURKA/HDAC6-dependent manner. Mol Cancer Res.
12:681–693. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|