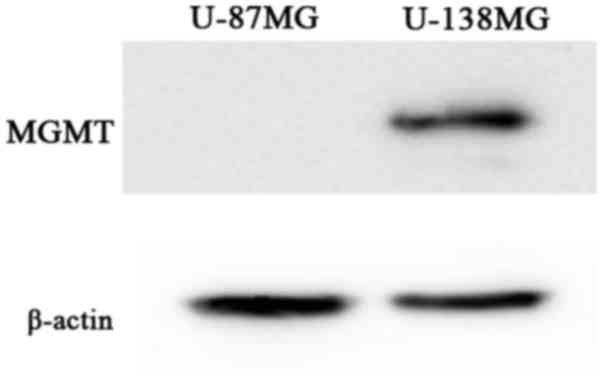
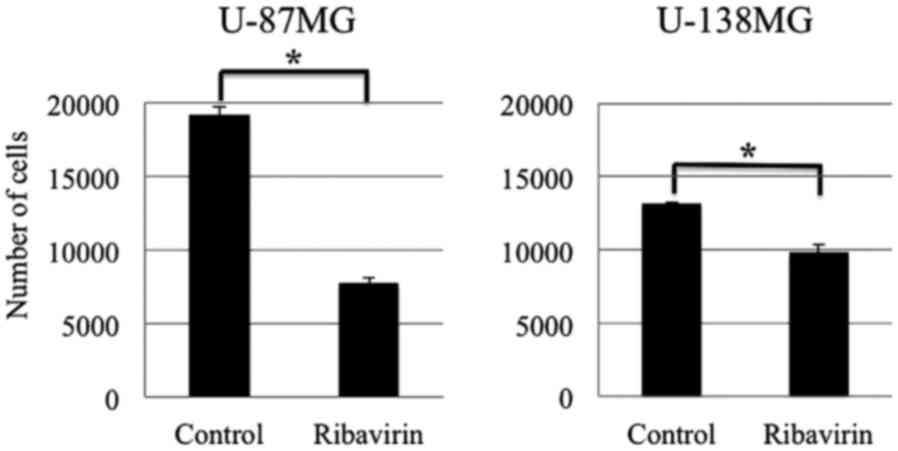
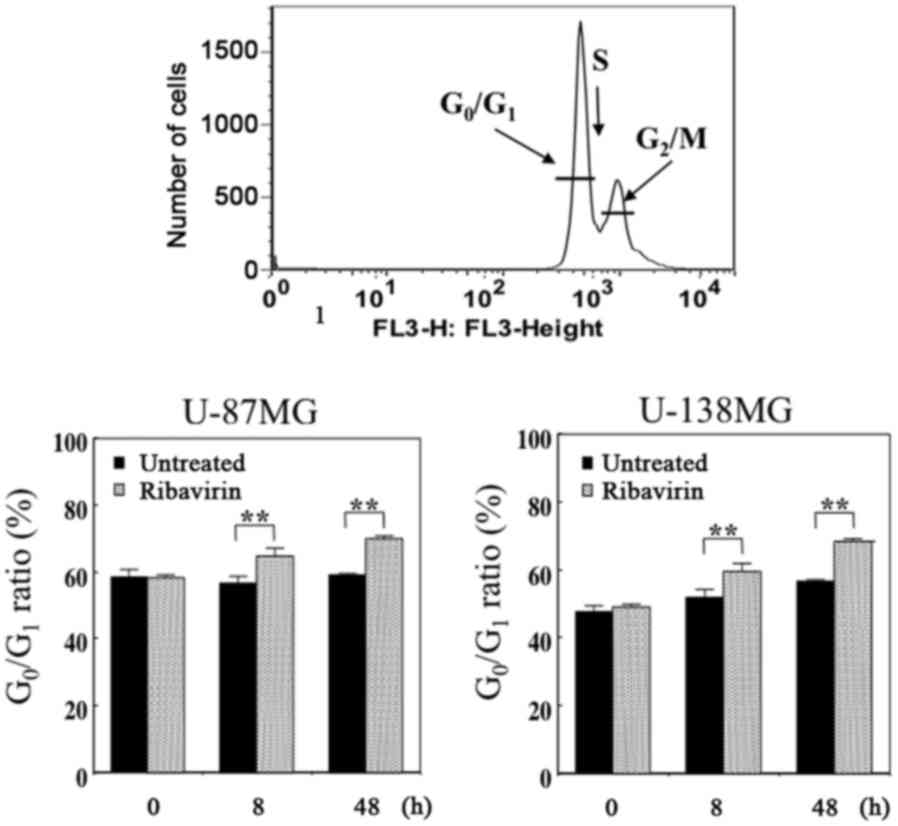
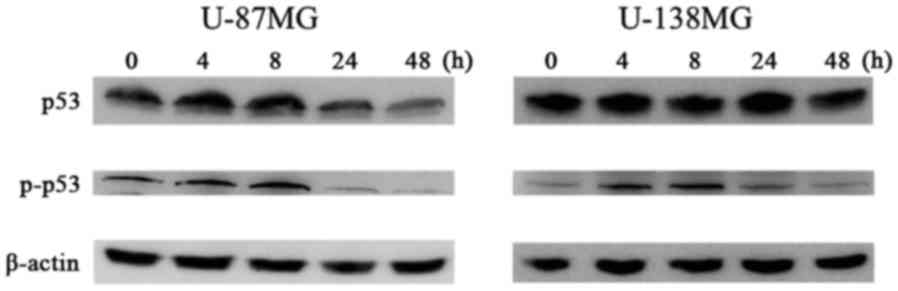
|
1
|
Committee of Brain Tumor Registry of
Japan, . Report of Brain Tumor Registry of Japan (2001–2004). Vol.
13. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 54:1–102. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups, ; National Cancer Institute of
Canada Clinical Trials Group, : Radiotherapy plus concomitant and
adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, Van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al European Organisation for Research and Treatment
of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups, ; National
Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group, : Effects of
radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus
radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised
phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet
Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF,
de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani
L, et al: MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukushima T, Takeshima H and Kataoka H:
Anti-glioma therapy with temozolomide and status of the DNA-repair
gene MGMT. Anticancer Res. 29:4845–4854. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bello MJ, Alonso ME, Amiñoso C, Anselmo
NP, Arjona D, Gonzalez-Gomez P, Lopez-Marin I, de Campos JM,
Gutierrez M, Isla A, et al: Hypermethylation of the DNA repair gene
MGMT: association with TP53 G:C to A:T transitions in a series of
469 nervous system tumors. Mutat Res. 554:23–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamiryo T, Tada K, Shiraishi S, Shinojima
N, Kochi M and Ushio Y: Correlation between promoter
hypermethylation of the O6-methylguanine-deoxyribonucleic acid
methyltransferase gene and prognosis in patients with high-grade
astrocytic tumors treated with surgery, radiotherapy, and
1-(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl-3-(2-chloroethyl)-3-nitrosourea-based
chemotherapy. Neurosurgery. 54:349–357, discussion 357. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakamura M, Watanabe T, Yonekawa Y,
Kleihues P and Ohgaki H: Promoter methylation of the DNA repair
gene MGMT in astrocytomas is frequently associated with G:C ->
A:T mutations of the TP53 tumor suppressor gene. Carcinogenesis.
22:1715–1719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sidwell RW, Huffman JH, Khare GP, Allen
LB, Witkowski JT and Robins RK: Broad-spectrum antiviral activity
of Virazole: 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide.
Science. 177:705–706. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kohli A, Shaffer A, Sherman A and Kottilil
S: Treatment of hepatitis C: A systematic review. JAMA.
312:631–640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kentsis A, Topisirovic I, Culjkovic B,
Shao L and Borden KL: Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic
transformation by physical mimicry of the 7-methyl guanosine mRNA
cap. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:pp. 18105–18110. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Borden KL and Culjkovic-Kraljacic B:
Ribavirin as an anti-cancer therapy: Acute myeloid leukemia and
beyond? Leuk Lymphoma. 51:1805–1815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Assouline S, Culjkovic B, Cocolakis E,
Rousseau C, Beslu N, Amri A, Caplan S, Leber B, Roy DC, Miller WH
Jr, et al: Molecular targeting of the oncogene eIF4E in acute
myeloid leukemia (AML): A proof-of-principle clinical trial with
ribavirin. Blood. 114:257–260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
De la Cruz-Hernandez E, Medina-Franco JL,
Trujillo J, Chavez-Blanco A, Dominguez-Gomez G, Perez-Cardenas E,
Gonzalez-Fierro A, Taja-Chayeb L and Dueñas-Gonzalez A: Ribavirin
as a tri-targeted antitumor repositioned drug. Oncol Rep.
33:2384–2392. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Volpin F, Casaos J, Sesen J, Mangraviti A,
Choi J, Gorelick N, Frikeche J, Lott T, Felder R, Scotland SJ, et
al: Use of an anti-viral drug, Ribavirin, as an anti-glioblastoma
therapeutic. Oncogene. 36:3037–3047. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ogino A, Sano E, Ochiai Y, Yamamuro S,
Tashiro S, Yachi K, Ohta T, Fukushima T, Okamoto Y, Tsumoto K, et
al: Efficacy of ribavirin against malignant glioma cell lines.
Oncol Lett. 8:2469–2474. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Naik GS and Tyagi MG: A pharmacological
profile of ribavirin and monitoring of its plasma concentration in
chronic hepatitis C infection. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2:42–54. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Durocher D and Jackson SP: DNA-PK, ATM and
ATR as sensors of DNA damage: Variations on a theme? Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 13:225–231. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kurz EU and Lees-Miller SP: DNA
damage-induced activation of ATM and ATM-dependent signaling
pathways. DNA Repair (Amst). 3:889–900. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoshino A, Ogino A, Yachi K, Ohta T,
Fukushima T, Watanabe T, Katayama Y, Okamoto Y, Naruse N and Sano
E: Effect of IFN-beta on human glioma cell lines with temozolomide
resistance. Int J Oncol. 35:139–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Löbrich M, Shibata A, Beucher A, Fisher A,
Ensminger M, Goodarzi AA, Barton O and Jeggo PA: gammaH2AX foci
analysis for monitoring DNA double-strand break repair: Strengths,
limitations and optimization. Cell Cycle. 9:662–669. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y,
Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB and Siliciano JD:
Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and
phosphorylation of p53. Science. 281:1677–1679. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tu WZ, Li B, Huang B, Wang Y, Liu XD, Guan
H, Zhang SM, Tang Y, Rang WQ and Zhou PK: γH2AX foci formation in
the absence of DNA damage: Mitotic H2AX phosphorylation is mediated
by the DNA-PKcs/CHK2 pathway. FEBS Lett. 587:3437–3443. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goodarzi AA and Jeggo PA: The repair and
signaling responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Adv Genet.
82:1–45. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pegg AE: Mammalian O6-alkylguanine-DNA
alkyltransferase: Regulation and importance in response to
alkylating carcinogenic and therapeutic agents. Cancer Res.
50:6119–6129. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoshino A, Tashiro S, Ogino A, Yachi K,
Ohta T, Fukushima T, Watanabe T, Katayama Y, Okamoto Y, Sano E, et
al: Gene expression profiles predicting the response to IFN-β and a
combination of temozolomide and IFN-β in malignant gliomas. Int J
Oncol. 39:529–542. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|