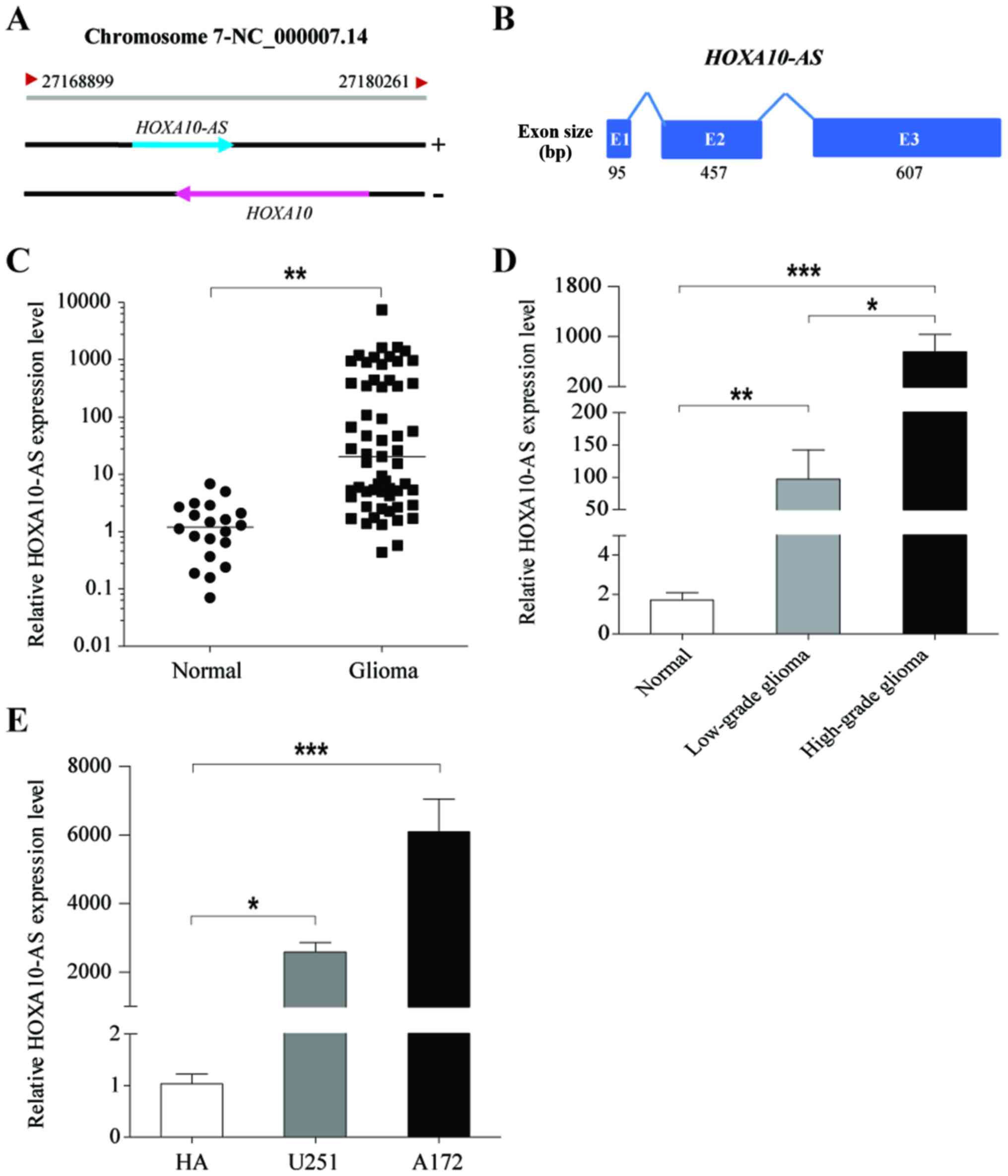
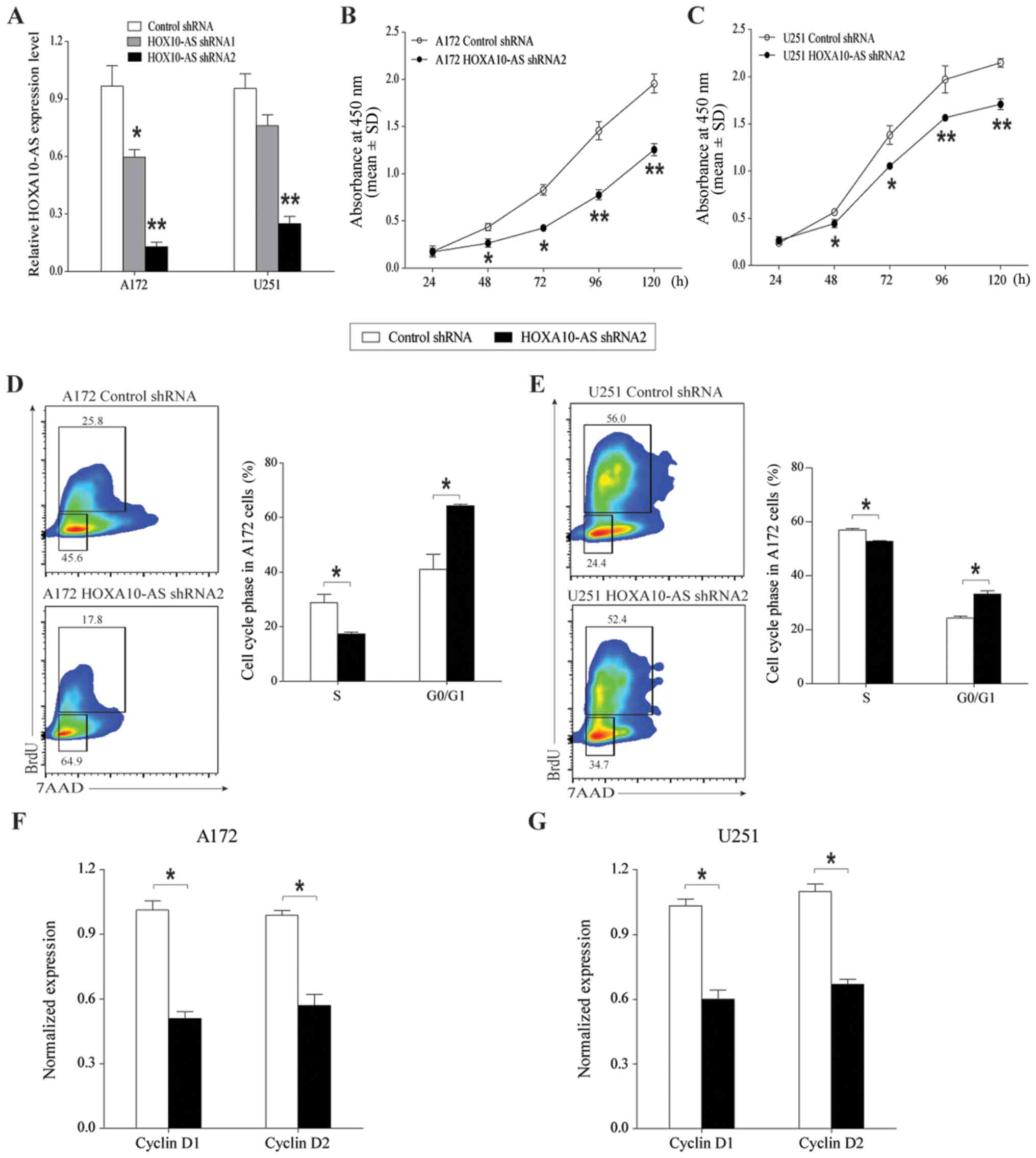
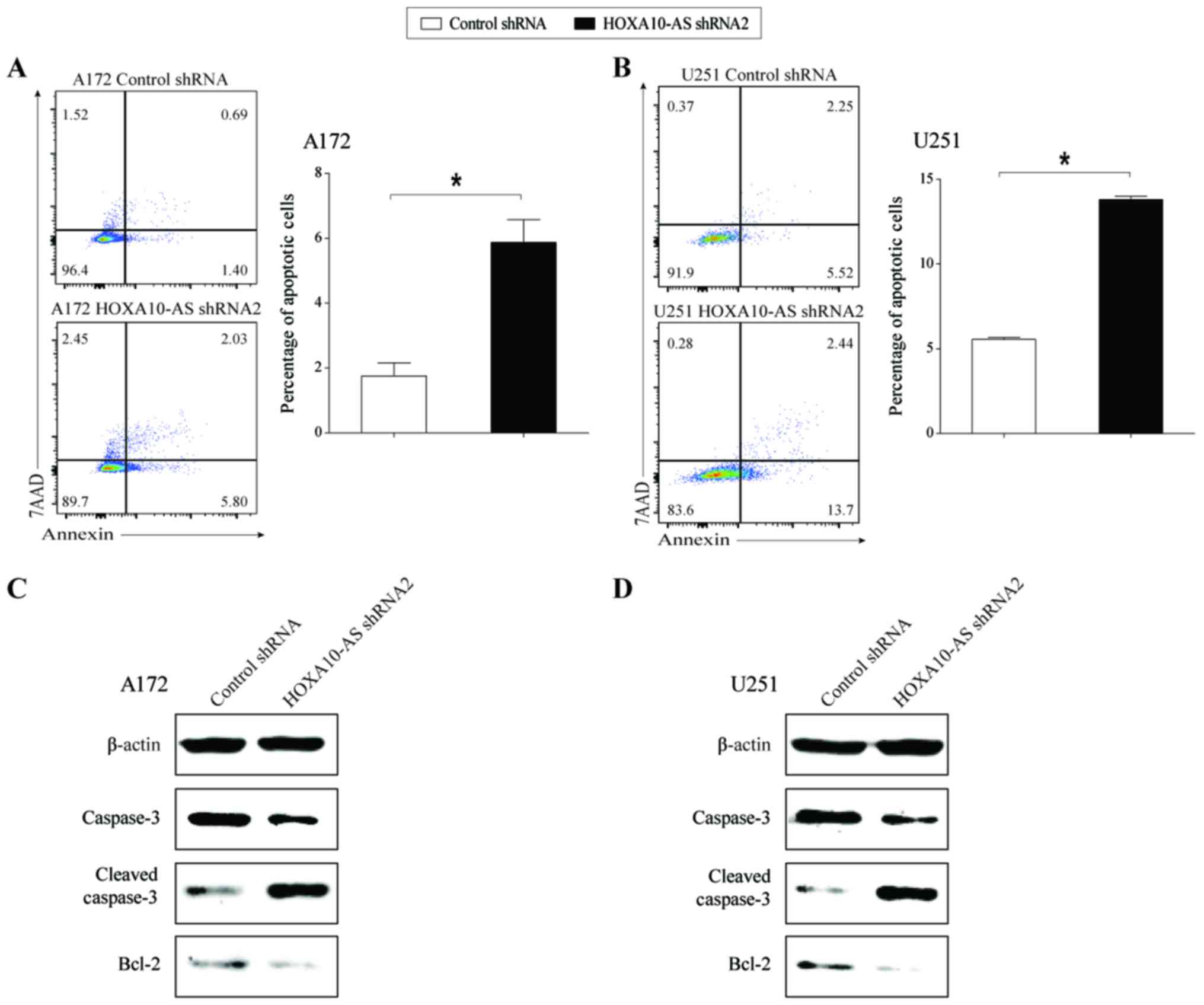
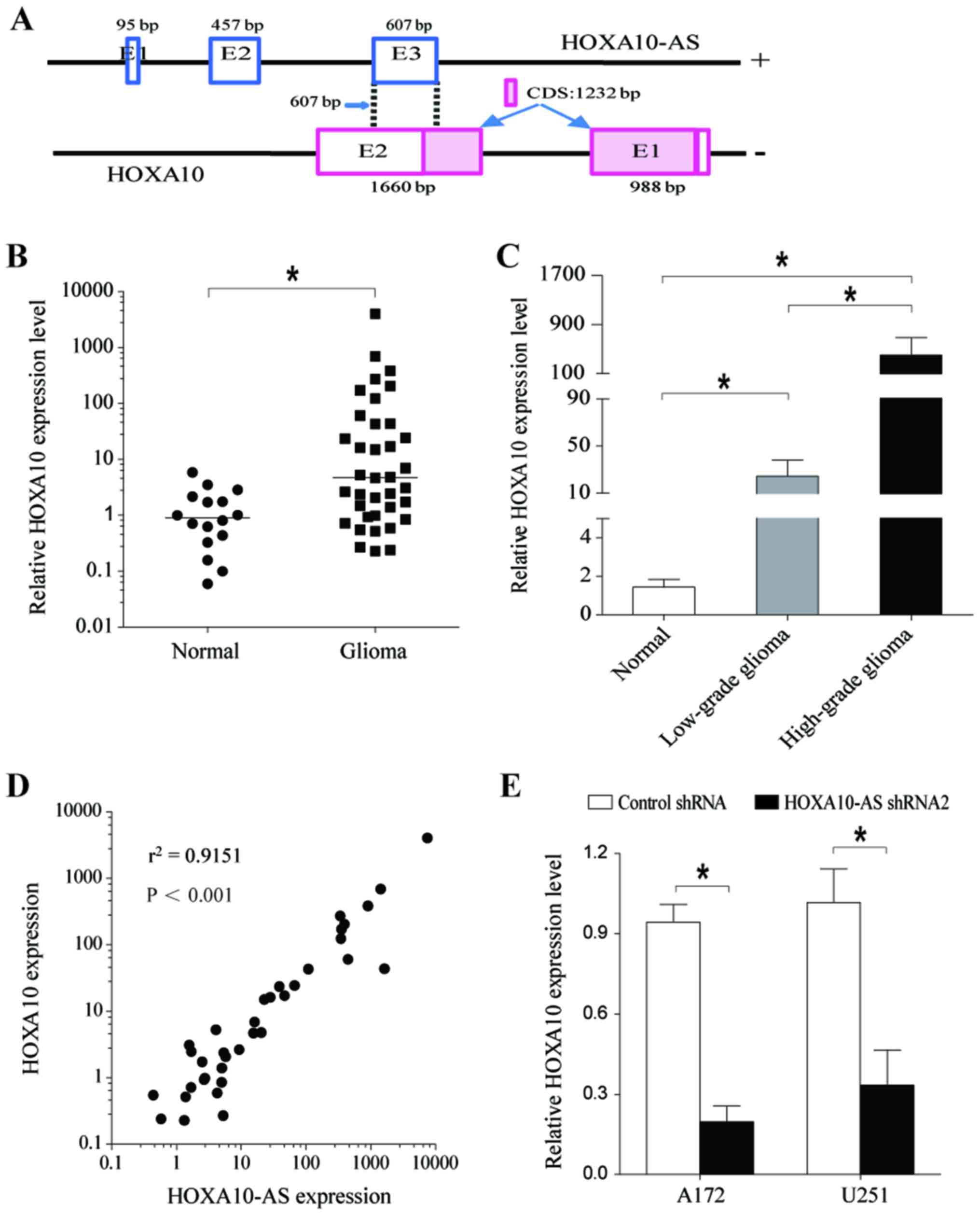
|
1
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 world health organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Omuro A and Deangelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Taylor LP: Diagnosis, treatment, and
prognosis of glioma: Five new things. Neurology. 75 18 Suppl
1:S28–S32. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF,
de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani
L, et al: MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide
in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I,
Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Lu KV, Yoshimoto K, Huang JH, Chute
DJ, et al: Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas
to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 353:2012–2024. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Claverie JM: Fewer genes, more noncoding
RNA. Science. 309:1529–1930. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nature Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer
A, Djebali S, Tilgner H, Guernec G, Martin D, Merkel A, Knowles DG,
et al: The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs:
Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome
Res. 22:1775–1789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weidle UH, Birzele F, Kollmorgen G and
Rüger R: Long noncoding RNAs and their role in metastasis. Cancer
Genomics Proteomics. 14:143–160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alvarez-Dominguez JR and Lodish HF:
Emerging mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function during normal
and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood. 130:1965–1975. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klingenberg M, Matsuda A, Diederichs S and
Patel T: Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms,
biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Hepatol. 67:603–618. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Ye C, Xiong H, Shen Y, Lu Y, Zhou
J and Wang L: Dysregulation of long non-coding RNA in breast
cancer: An overview of mechanism and clinical implication.
Oncotarget. 8:5508–5522. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie W, Yuan S, Sun Z and Li Y: Long
noncoding and circular RNAs in lung cancer: Advances and
perspectives. Epigenomics. 8:1275–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun W, Yang Y, Xu C, Xie Y and Guo J:
Roles of long noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer and their clinical
applications. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:2231–2237. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hosseini ES, Meryet-Figuiere M,
Sabzalipoor H, Kashani HH, Nikzad H and Asemi Z: Dysregulated
expression of long noncoding RNAs in gynecologic cancers. Mol
Cancer. 16:1072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Richtig G, Ehall B, Richtig E,
Aigelsreiter A, Gutschner T and Pichler M: Function and clinical
implications of long non-coding RNAs in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci.
18:pii: E715. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brunner AL, Beck AH, Edris B, Sweeney RT,
Zhu SX, Li R, Montgomery K, Varma S, Gilks T, Guo X, et al:
Transcriptional profiling of long non-coding RNAs and novel
transcribed regions across a diverse panel of archived human
cancers. Genome Biol. 13:R752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bartonicek N, Maag JL and Dinger ME: Long
noncoding RNAs in cancer: Mechanisms of action and technological
advancements. Mol Cancer. 15:432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi T, Gao G and Cao Y: Long noncoding
RNAs as novel biomarkers have a promising future in cancer
diagnostics. Dis Markers. 2016:90851952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang JX, Han L, Bao ZS, Wang YY, Chen LY,
Yan W, Yu SZ, Pu PY, Liu N, You YP, et al: HOTAIR, a cell
cycle-associated long noncoding RNA and a strong predictor of
survival, is preferentially expressed in classical and mesenchymal
glioma. Neuro Oncol. 15:1595–1603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang B, Wei ZY, Wang BQ, Yang HC, Wang JY
and Bu XY: Down-regulation of the long noncoding RNA-HOX transcript
antisense intergenic RNA inhibits the occurrence and progression of
glioma. J Cell Biochem. 119:2278–2287. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Yin H and
Han B: CRNDE, a long-noncoding RNA, promotes glioma cell growth and
invasion through mTOR signaling. Cancer Lett. 367:122–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang X, Yan Y, Hu M, Chen X, Wang Y, Dai
Y, Wu D, Wang Y, Zhuang Z and Xia H: Increased level of H19 long
noncoding RNA promotes invasion, angiogenesis, and stemness of
glioblastoma cells. J Neurosurg. 124:129–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matouk IJ, Mezan S, Mizrahi A, Ohana P,
Abu-Lail R, Fellig Y, Degroot N, Galun E and Hochberg A: The
oncofetal H19 RNA connection: Hypoxia, p53 and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1803:443–451. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Liu J,
Chen L, Xi Z, Teng H, Wang Z, et al: Knockdown of long non-coding
RNA XIST exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma
stem cells by up-regulating miR-152. Cancer Lett. 359:75–86. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao J, Zhou B, Zhang J, Geng P, Liu K, Zhu
Y and Zhu W: A new tumor suppressor LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 is regulated
by DNMT1 and inhibits migration of glioma cells. Tumour Biol.
35:7935–7944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang P, Liu YH, Yao YL, Li Z, Li ZQ, Ma J
and Xue YX: Long non-coding RNA CASC2 suppresses malignancy in
human gliomas by miR-21. Cell Signal. 27:275–282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang P, Ren Z and Sun P: Overexpression of
the long non-coding RNA MEG3 impairs in vitro glioma cell
proliferation. J Cell Biochem. 113:1868–1874. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han Y, Wu Z, Wu T, Huang Y, Cheng Z, Li X,
Sun T, Xie X, Zhou Y and Du Z: Tumor-suppressive function of long
noncoding RNA MALAT1 in glioma cells by downregulation of MMP2 and
inactivation of ERK/MAPK signaling. Cell Death Dis. 7:e21232016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Katayama S, Tomaru Y, Kasukawa T, Waki K,
Nakanishi M, Nakamura M, Nishida H, Yap CC, Suzuki M, Kawai J, et
al: Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome.
Science. 309:1564–1566. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Werner A, Carlile M and Swan D: What do
natural antisense transcripts regulate? RNA Biol. 6:43–48. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sanfilippo PG and Hewitt AW: Translating
the ENCyclopedia of DNA elements project findings to the clinic:
ENCODE's implications for eye disease. Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
42:78–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tragante V, Moore JH and Asselberg FW: The
ENCODE project and perspectives on pathways. Genet Epidemiol.
38:275–280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen ZH, Zhao KM and Du T: HOXA10 promotes
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via
inducing the expression of ZIC2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:945–952. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eoh KJ, Kim HJ, Lee JY, Nam EJ, Kim S, Kim
SW and Kim YT: Dysregulated expression of homeobox family genes may
influence survival outcomes of patients with epithelial ovarian
cancer: Analysis of data from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Oncotarget.
8:70579–70585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lim JY, Yoon SO, Seol SY, Hong SW, Kim JW,
Choi SH, Lee JS and Cho JY: Overexpression of miR-196b and HOXA10
characterize a poor-prognosis gastric cancer subtype. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:7078–7088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bonfim-Silva R, Melo Ferreira FU, Thomé
CH, Abraham KJ, De Souza FAL, Ramalho FS, Machado HR, De Oliveira
RS, Cardoso AA, Covas DT, et al: Functional analysis of
HOXA10 and HOXB4 in human medulloblastoma cell lines.
Int J Oncol. 51:1929–1940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Carrera M, Bitu CC, de Oliveira CE,
Cervigne NK, Graner E, Manninen A, Salo T and Coletta RD: HOXA10
controls proliferation, migration and invasion in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3613–3623. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kurscheid S, Bady P, Sciuscio D, Samarzija
I, Shay T, Vassallo I, Criekinge WV, Daniel RT, van den Bent MJ,
Marosi C, et al: Chromosome 7 gain and DNA hypermethylation at the
HOXA10 locus are associated with expression of a stem cell related
HOX-signature in glioblastoma. Genome Biol. 16:162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mahmoudi S, Henriksson S, Corcoran M,
Méndez-Vidal C, Wiman KG and Farnebo M: Wrap53, a natural p53
antisense transcript required for p53 induction upon DNA damage.
Mol Cell. 33:462–471. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tufarelli C, Stanley JA, Garrick D, Sharpe
JA, Ayyub H, Wood WG and Higgs DR: Transcription of antisense RNA
leading to gene silencing and methylation as a novel cause of human
genetic disease. Nat Genet. 34:157–165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun BK, Deaton AM and Lee JT: A transient
heterochromatic state in Xist preempts X inactivation choice
without RNA stabilization. Mol Cell. 21:617–628. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun S, Su C, Zhu Y, Li H, Liu N, Xu T, Sun
C and Lv Y: MicroRNA-544a regulates migration and invasion in
colorectal cancer cells via regulation of homeobox A10. Dig Dis
Sci. 61:2535–2544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Libório-Kimura TN, Jung HM and Chan EK:
miR-494 represses HOXA10 expression and inhibits cell proliferation
in oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 51:151–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xiao ZD, Jiao CY, Huang HT, He LJ, Zhao
JJ, Lu ZY and Liu LX: miR-218 modulate hepatocellular carcinoma
cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT/PI3K pathway and HoxA10. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4039–4044. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhao J, Xu C, Du
Y, Luo X, Zheng F, Liu R, Zhang H, et al: miRNA-135a promotes
breast cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting
HOXA10. BMC Cancer. 12:1112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|