|
1
|
Liu L, Wang S, Cao X and Liu J: Diagnostic
value of circulating microRNAs for gastric cancer in Asian
populations: A meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 35:11995–2004. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
World Health Organization. Cancer Fact
Sheets. http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.aspx
|
|
3
|
Duguan FU: Epigenetic alterations in
gastric cancer (Review). Mol Med Rep. 12:3223–3230. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
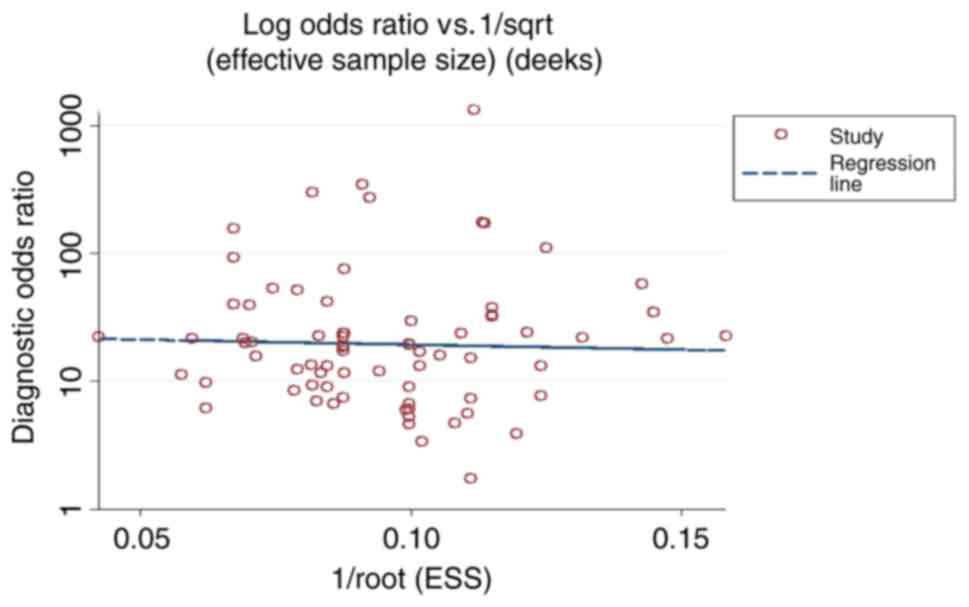
|
4
|
Wang QX, Zhu YQ, Zhang H and Xiao J:
Altered MiRNA expression in gastric cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:933–944. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Charalampakis N, Economopoulou P,
Kotsantis I, Tolia M, Schizas D, Liakakos T, Elimova E, Ajani JA
and Psyrri A: Medical management of gastric cancer: A 2017 update.
Cancer Med. 7:123–133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu N, Yin JF, Ji Z, Hong Y, Wu P, Bian B,
Song Z, Li R, Liu Q and Wu F: Strengthening gastric cancer therapy
by trastuzumab-conjugated nanoparticles with simultaneous
encapsulation of anti-MiR-21 and 5-Fluorouridine. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 44:2158–2173. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang S, Wang J, Li J, Luo Q, Zhao M,
Zheng L, Dong X, Chen C, Che Y, Liu P, et al: Serum microRNA
expression profile as a diagnostic panel for gastric cancer. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 46:8112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kitano S, Shiraishi N, Uyama I, Sugihara K
and Tanigawa N: Japanese Laparoscopic Surgery Study Group: A
multicenter study on oncologic outcome of laparoscopic gastrectomy
for early cancer in Japan. Ann Surg. 245:68–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Uedo N, Takeuchi Y and Ishihara R:
Endoscopic management of early gastric cancer: Endoscopic mucosal
resection or endoscopic submucosal dissection: Data from a Japanese
high-volume center and literature review. Ann Gastroenterol.
25:281–290. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaneko S and Yoshimura T: Time trend
analysis of gastric cancer incidence in Japan by histological
types. 1975–1989. Br J Cancer. 84:400–405. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bonenkamp JJ, Hermans J, Sasako M, van de
Velde CJ, Welvaart K, Songun I, Meyer S, Plukker JT, Van Elk P,
Obertop H, et al: Extended lymph-node dissection for gastric
cancer. N Engl J Med. 340:908–914. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garrido M, Bustos M, Orellana E, Madrid J,
Galindo H, Sánchez C, Pimentel F, Guzmán S, Ibáñez L, Butte JM, et
al: Postoperative radio chemotherapy in locally advanced gastric
cancer. Rev Med Chil. 136:844–850. 2008.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Madhavan D, Cuk K, Burwinkel B and Yang R:
Cancer diagnosis and prognosis decoded by blood-based circulating
microRNA signatures. Front Genet. 4:1162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Tsujiura M, Konishi
H, Takeshita H, Nagata H, Kawaguchi T, Hirajima S, Arita T,
Shiozaki A, et al: Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 in the
plasma of patients with gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
33:271–276. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gorur A, Balci Fidanci S, Dogruer Unal N,
Ayaz L, Akbayir S, Yildirim Yaroglu H, Dirlik M, Serin MS and Tamer
L: Determination of plasma microRNA for early detection of gastric
cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 40:2091–2096. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM: QUADAS-2 Group: QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Deeks JJ and Morris JM: 6 Evaluating
diagnostic tests. Baillière's Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 10:613–630.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Deeks JJ: Systematic reviews in health
care: Systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening
tests. BMJ. 323:157–162. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH and Sackett DL:
Users' guides to the medical literature. III. How to use an article
about a diagnostic test. B. What are the results and will they help
me in caring for my patients? The Evidence-Based Medicine Working
Group. JAMA. 271:703–707. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P and Irwig L: The
performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size
effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was
assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:882–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jackson D, White IR and Thompson SG:
Extending DerSimonian and Laird's methodology to perform
multivariate random effects meta-analyses. Stat Med. 29:1282–1297.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peng WZ, Ma R, Wang F, Yu J and Liu ZB:
Role of miR-191/425 cluster in tumorigenesis and diagnosis of
gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 15:4031–4048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiu X, Zhang J, Shi W, Liu S, Kang M, Chu
H, Wu D, Tong N, Gong W, Tao G, et al: Circulating microRNA-26a in
plasma and its potential diagnostic value in gastric cancer. PLoS
One. 11:e01513452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsujiura M, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D,
Shiozaki A, Konishi H, Takeshita H, Moriumura R, Nagata H,
Kawaguchi T, Hirajima S, et al: Circulating miR-18a in plasma
contributes to cancer detection and monitoring in patients with
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 18:271–279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Song Y, Zhang C, Zhi X, Fu H, Ma
Y, Chen Y, Pan F, Wang K, Ni J, et al: Circulating MiR-16-5p and
MiR-19b-3p as two novel potential biomarkers to indicate
progression of gastric cancer. Theranostics. 5:733–745. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsai MM, Wang CS, Tsai CY, Huang CG, Lee
KF, Huang HW, Lin YH, Chi HC, Kuo LM, Lu PH and Lin KH: Circulating
microRNA-196a/b are novel biomarkers associated with metastatic
gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer. 64:137–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Su ZX, Zhao J, Rong ZH, Wu YG, Geng WM and
Qin CK: Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-18a in
the plasma of patients with gastric cancer. Tumor Biol.
35:12119–12125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Reboredo M,
Medina-Villaamil V, Iglesias-Díaz P, Lorenzo-Patiño MJ, Haz M,
Santamarina I, Blanco M, Fernández-Tajes J, Quindós M, et al:
Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for
gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 10:1862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu X, Yang Z, Zhang J and Liu H:
Investigation of microRNA-145 as a serum diagnostic and prognostic
biomarker for gastric cancer: A Chinese cohort-based study. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 10:9440–9447. 2017.
|
|
35
|
Zhuang K, Han K, Tang H, Yin X, Zhang J,
Zhang X and Zhang L: Up-regulation of plasma miR-23b is associated
with poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit. 22:356–361.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hung PS, Chen CY, Chen WT, Kuo CY, Fang
WL, Huang KH, Chiu PC and Lo SS: MiR-376c promotes carcinogenesis
and serves as a plasma marker for gastric carcinoma. PLoS One.
12:e01773462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Le Q, Jianhua N, Mulati, Yu X and Jiageng
H: Increased miR-25 expression in serum of gastric cancer patients
is correlated with CA19-9 and acts as a potential diagnostic
biomarker. Open Medicine. 12:266–270. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li BS, Zhao YL, Guo G, Li W, Zhu ED, Luo
X, Mao XH, Zou QM, Yu PW, Zuo QF, et al: Plasma microRNAs, miR-223,
miR-21 and miR-218, as novel potential biomarkers for gastric
cancer detection. PLoS One. 7:e416292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li F, Guo Y, Liu J and Zhang R: The
significance of elevated plasma expression of microRNA 106b~25
clusters in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 12:e01784272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li M, Gu K, Liu W, Xie X and Huang X:
MicroRNA-200c as a prognostic and sensitivity marker for platinum
chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 8:51190–51199.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hou X, Zhang M and Qiao H: Diagnostic
significance of miR-106a in gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:13096–13101. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou CG, Luo XY and Li G: Diagnostic and
prognostic value of serum MicroRNA-206 in patients with gastric
cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:1512–1520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang WH, Gui JH, Wang CZ, Chang Q, Xu SP,
Cai CH, Li YN, Tian YP, Yan L and Wu B: The identification of
miR-375 as a potential biomarker in distal gastric adenocarcinoma.
Oncol Res. 20:139–147. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Song MY, Pan KF, Su HJ, Zhang L, Ma JL, Li
JY, Yuasa Y, Kang D, Kim YS and You WC: Identification of serum
microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of
gastric cancer. PLoS One. 7:e336082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S,
Shiozaki A, Takeshita H, Kosuga T, Konishi H, Morimura R, Deguchi
K, Fujiwara H, et al: Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients
with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer. 102:1174–1179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang B and Zhang Q: The expression and
clinical significance of circulating microRNA-21 in serum of five
solid tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1659–1666. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu C, Ren C, Han J, Ding Y, Du J, Dai N,
Dai J, Ma H, Hu Z, Shen H, et al: A five-microRNA panel in plasma
was identified as potential biomarker for early detection of
gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:2291–2299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu R, Zhang C, Hu Z, Li G, Wang C, Yang
C, Huang D, Chen X, Zhang H, Zhuang R, et al: A five-microRNA
signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression
profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis. Eur
J Cancer. 47:784–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Konishi H, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, Shiozaki
A, Tsujiura M, Takeshita H, Morimura R, Nagata H, Arita T,
Kawaguchi T, et al: Detection of gastric cancer-associated
microRNAs on microRNA microarray comparing pre- and post-operative
plasma. Br J Cancer. 106:740–747. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu H, Zhu L, Liu B, Yang L, Meng X, Zhang
W, Ma Y and Xiao H: Genome-wide microRNA profiles identify miR-378
as a serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Cancer
Lett. 316:196–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu X, Kwong A, Sihoe A and Chu KM: Plasma
miR-940 may serve as a novel biomarker for gastric cancer. Tumor
Biol. 37:3589–3597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hu Y, Wang J, Han Y, Liu Q and Niu Q:
Serum miR-133a is down-regulated and associated with the diagnosis
of patients with gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
9:2015–2020. 2016.
|
|
53
|
Sun Y, Ma J, Hu M, Zheng X, Li J and Gu
Wei: Level of miR-183 in peripheral blood of the patients with
gastric cancer. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 37:75–79. 2017.
|
|
54
|
Li B and Zhang H: Plasma microRNA-320 is a
potential diagnostic and prognostic bio-marker in gastric cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:7356–7361. 2017.
|
|
55
|
Wu J, Li G, Yao Y, Wang Z, Sun W and Wang
J: MicroRNA-421 is a new potential diagnosis biomarker with higher
sensitivity and specificity than carcinoembryonic antigen and
cancer antigen 125 in gastric cancer. Biomarkers. 20:58–63. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zeng Q, Jin C, Chen W, Xia F, Wang Q, Fan
F, Du J, Guo Y, Lin C, Yang K, et al: Downregulation of serum
miR-17 and miR-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric
diseases. Chin J Cancer Res. 26:711–716. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou H, Xiao B, Zhou F, Deng H, Zhang X,
Lou Y, Gong Z, Du C and Guo J: MiR-421 is a functional marker of
circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Biomarkers.
17:104–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhou X, Zhu W, Li H, Wen W, Cheng W, Wang
F, Wu Y, Qi L, Fan Y, Chen Y, et al: Diagnostic value of a plasma
microRNA signature in gastric cancer: A microRNA expression
analysis. Sci Rep. 5:112512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu J, Li G, Wang Z, Yao Y, Chen R, Pu X
and Wang J: Circulating MicroRNA-21 is a potential diagnostic
biomarker in gastric cancer. Dis Markers. 2015:4356562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wu D, Cao G, Huang Z, Jin K, Hu H, Yu J
and Zeng Y: Decreased miR-503 expression in gastric cancer is
inversely correlated with serum carcinoembryonic antigen and acts
as a potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarker. OncoTargets
Ther. 10:129–135. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wang H, Wang L, Wu Z, Sun R, Jin H, Ma J,
Liu L, Ling R, Yi J, Wang L, et al: Three dysregulated microRNAs in
serum as novel biomarkers for gastric cancer screening. Med Oncol.
31:2982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shin VY, Ng EK, Chan VW, Kwong A and Chu
KM: A three-miRNA signature as promising non-invasive diagnostic
marker for gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 14:2022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cui YJ, Xie XH, Xing YF, Yuan ZH, Wu QY
and Wei YM: Feasibility study on plasmatic microRNA-27b-3p as a
potential biomarker for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Tumor.
35:183–189. 2015.
|
|
64
|
Fu Z, Qian F, Yang X, Jiang H, Chen Y and
Liu S: Circulating miR-222 in plasma and its potential diagnostic
and prognostic value in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 31:1642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu H, Yang Z, Zhang J and Zhu X:
MicroRNA-217 in plasma: A potential biomarker in gastric cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 10:3313–3320. 2017.
|
|
66
|
Zhou H, Guo JM, Lou YR, Zhang XJ, Zhong
FD, Jiang Z, Cheng J and Xiao BX: Detection of circulating tumor
cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using
microRNA as a marker. J Mol Med (Berl). 88:709–717. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhou X and Zhang G: Exosome-mediated
transfer of miR-223 increases tumor malignancy in gastric cancer. J
Gastroen Hepatol (Australia). 31:45–46. 2016.
|
|
68
|
Zheng Y, Cui L, Sun W, Zhou H, Yuan X, Huo
M, Chen J, Lou Y and Guo J: MicroRNA-21 is a new marker of
circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark.
10:71–77. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li H, Wu Q, Li T, Liu C, Xue L, Ding J,
Shi Y and Fan D: The miR-17-92 cluster as a potential biomarker for
the early diagnosis of gastric cancer: Evidence and literature
review. Oncotarget. 8:45060–45071. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Park JL, Kim M, Song KS, Kim SY and Kim
YS: Cell-Free miR-27a, a potential diagnostic and prognostic
biomarker for gastric cancer. Genomics Inform. 13:70–75. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li C, Li JF, Cai Q, Qiu QQ, Yan M, Liu BY
and Zhu ZG: MiRNA-199a-3p: A potential circulating diagnostic
biomarker for early gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 108:89–92. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li C, Li JF, Cai Q, Qiu QQ, Yan M, Liu BY
and Zhu ZG: MiRNA-199a-3p in plasma as a potential diagnostic
biomarker for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 20((Suppl 3)):
S397–S405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu S, Suo J, Wang C, Sun X, Wang D, He L,
Zhang Y and Li W: Prognostic significance of low miR-144 expression
in gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 20:547–552. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lurje G, Schiesser M, Claudius A and
Schneider PM: Circulating tumor cells in gastrointestinal
malignancies: Current techniques and clinical implications. J
Oncol. 2010:3926522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, Kim JJ, Yeoh
KG, Goh KL, Wu KC, Wu DC, Sollano J, Kachintorn U, et al: Screening
for gastric cancer in Asia: Current evidence and practice. Lancet
Oncol. 9:279–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Redova M, Sana J and Slaby O: Circulating
miRNAs as new blood-based biomarkers for solid cancers. Future
Oncol. 9:387–402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shen J, Stass SA and Jiang F: MicroRNAs as
potential biomarkers in human solid tumors. Cancer Lett.
329:125–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY,
Yu J, Poon TC, Ng SS and Sung JJ: Differential expression of
microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential
marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut. 58:1375–1381. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zanutto S, Pizzamiglio S, Ghilotti M,
Bertan C, Ravagnani F, Perrone F, Leo E, Pilotti S, Verderio P,
Gariboldi M and Pierotti MA: Circulating miR-378 in plasma: A
reliable haemolysis independent biomarker for colorectal cancer. Br
J Cancer. 110:1001–1007. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Inoue N, Nakayama
T, Hayashi T, Nakayama M, Nakao K, Hirayama T and Kohno S: MicroRNA
signatures in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Int J
Cancer. 128:361–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|