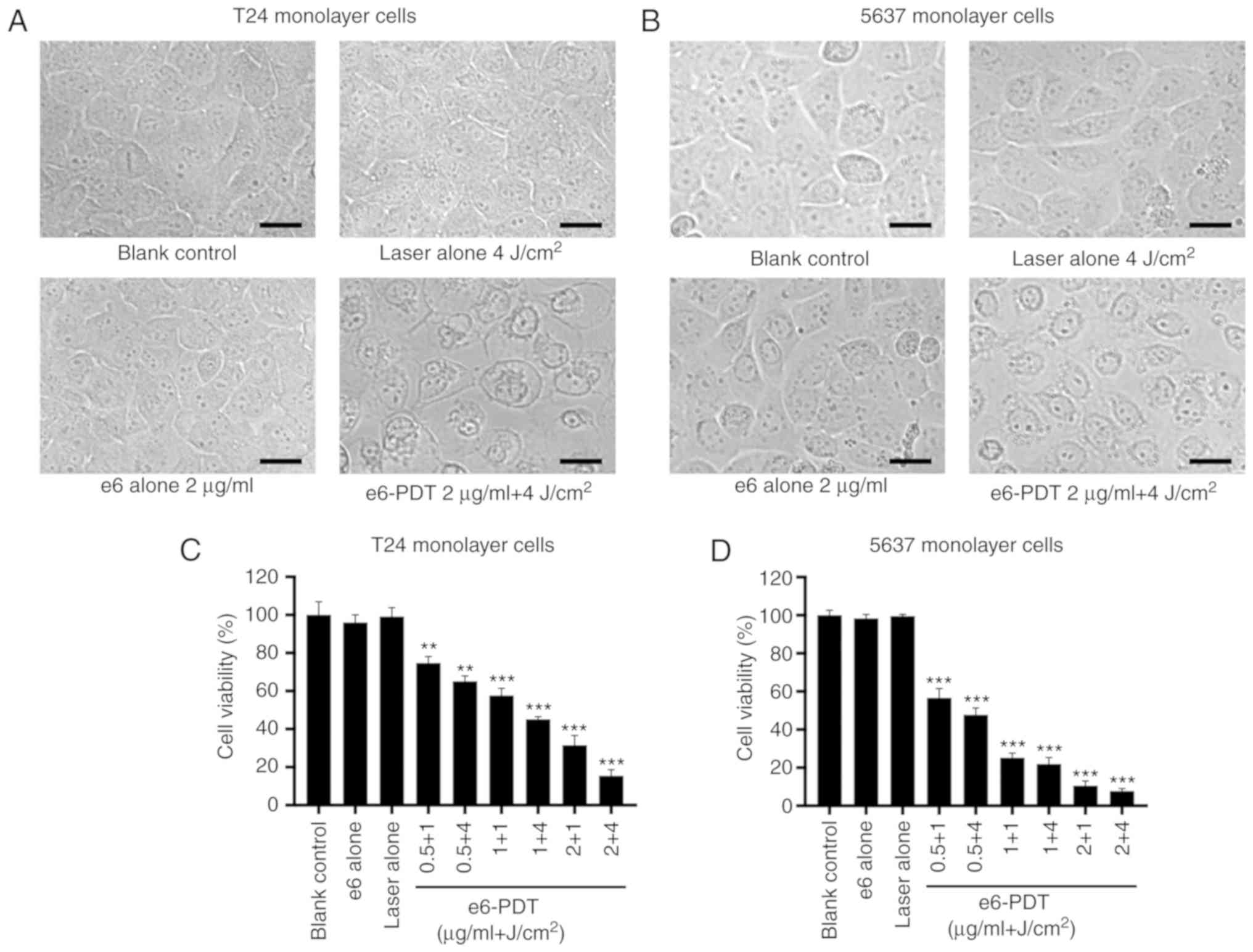
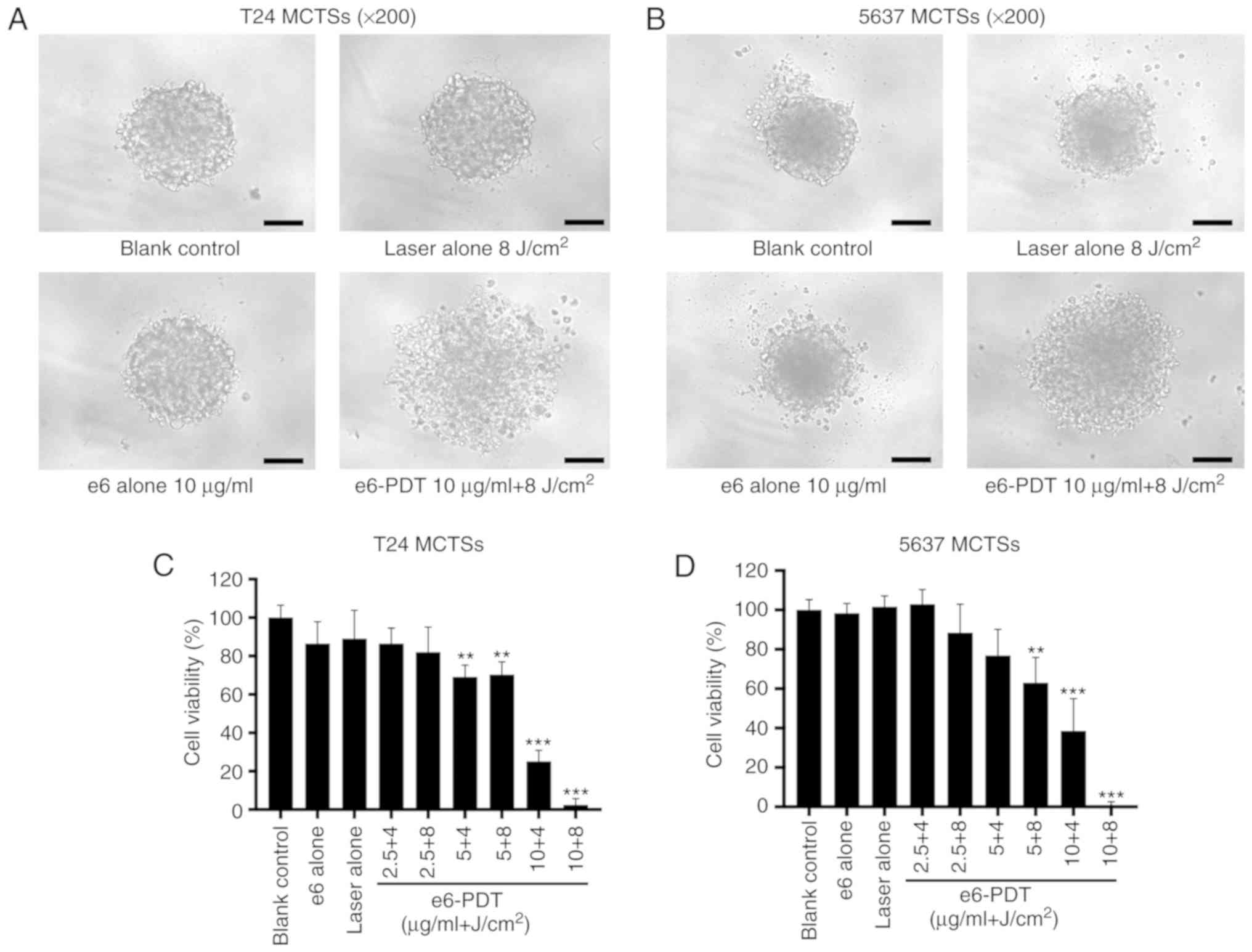
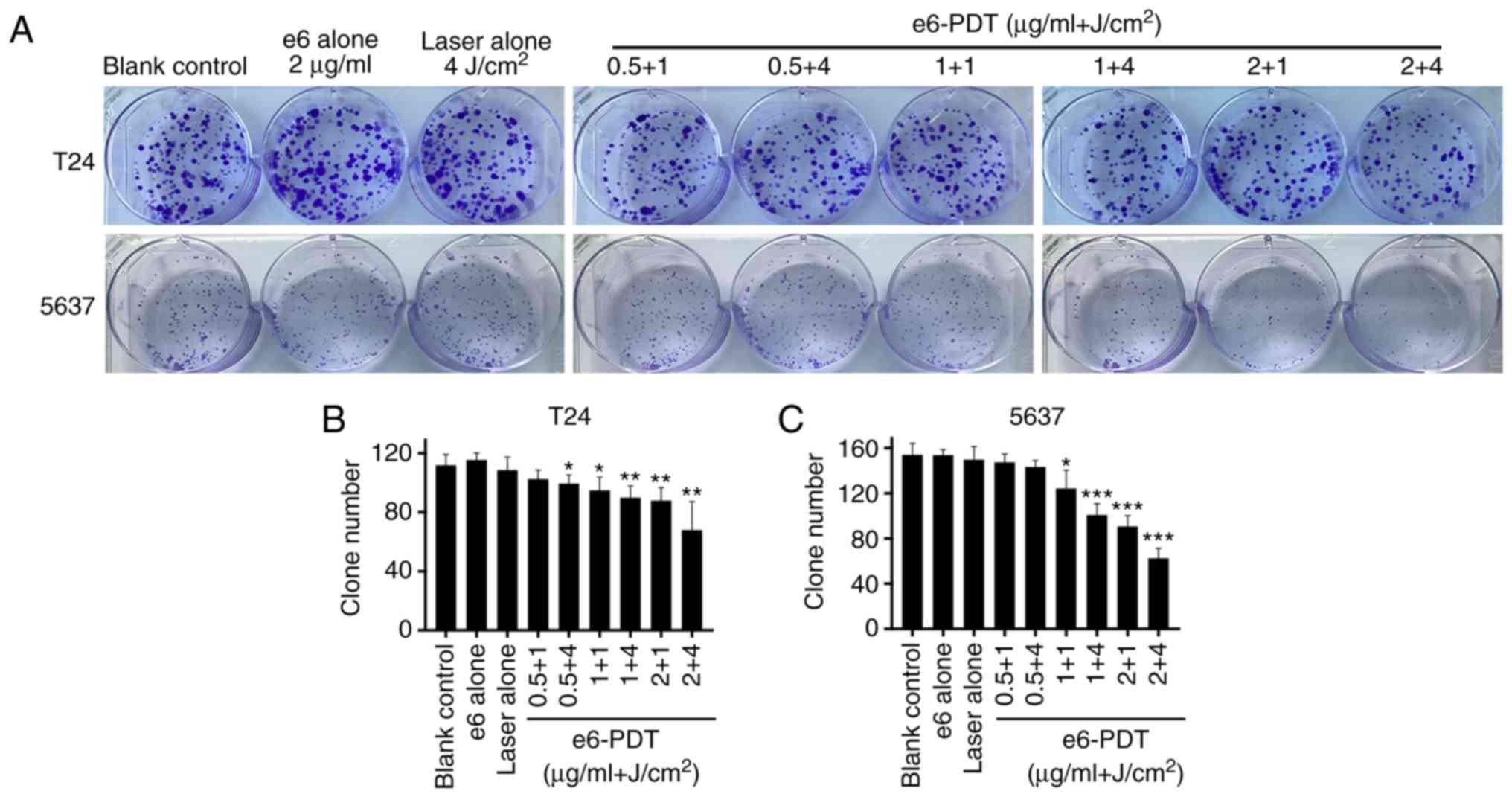
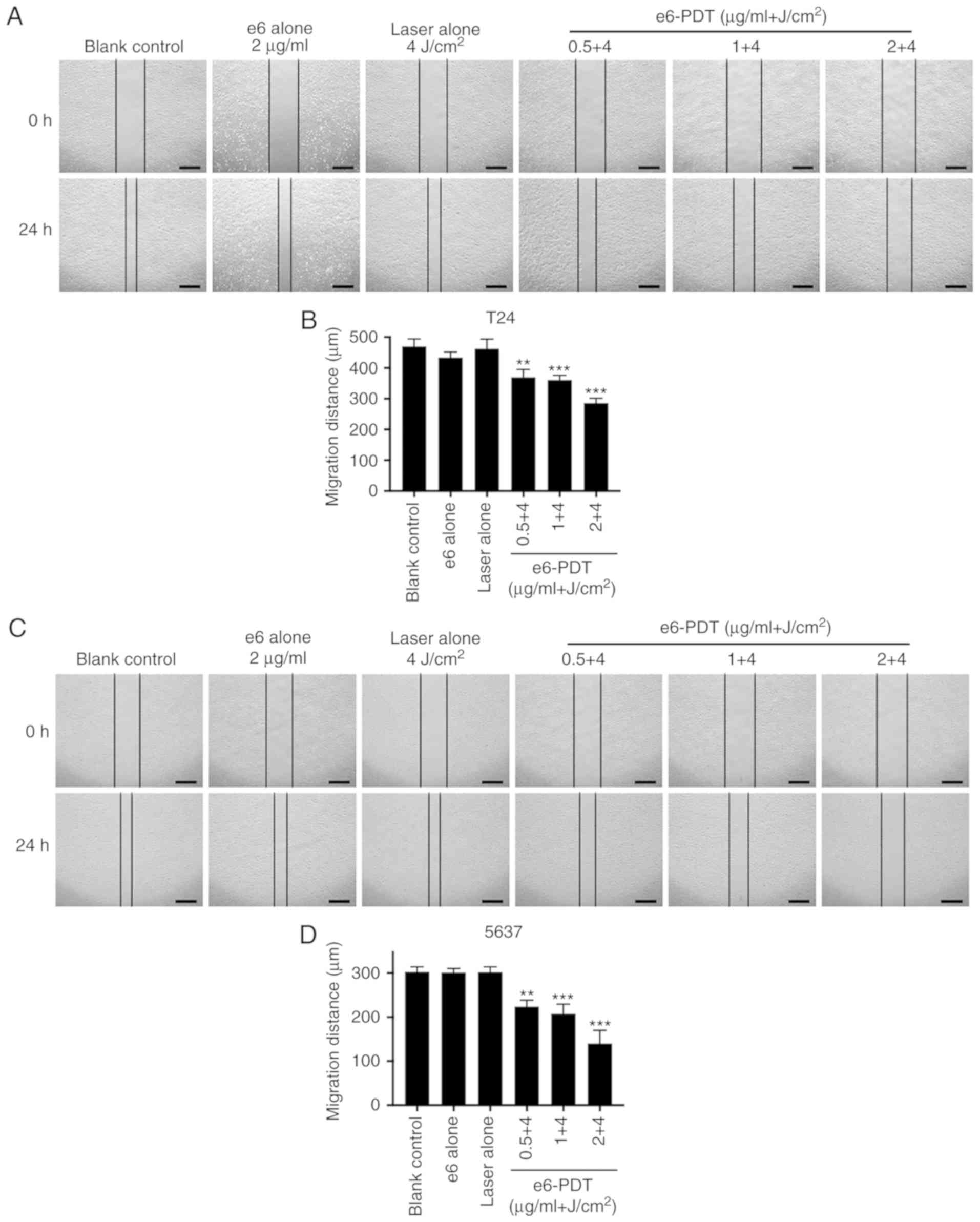
|
1
|
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor
A, Jemal A and Bray F: Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: A
global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 71:96–108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Spiess PE, Agarwal N, Bangs R, Boorjian
SA, Buyyounouski MK, Clark PE, Downs TM, Efstathiou JA, Flaig TW,
Friedlander T, et al: Bladder cancer, version 5.2017, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
15:1240–1267. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner
SP, Malmstrom PU, Choi W, Guo CC, Lotan Y and Kassouf W: Bladder
cancer. Lancet. 388:2796–2810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bohle A, Jocham D and Bock PR:
Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C for
superficial bladder cancer: A formal meta-analysis of comparative
studies on recurrence and toxicity. J Urol. 169:90–95. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Rhijn BW, Burger M, Lotan Y, Solsona
E, Stief CG, Sylvester RJ, Witjes JA and Zlotta AR: Recurrence and
progression of disease in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: From
epidemiology to treatment strategy. Eur Urol. 56:430–442. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Botteman MF, Pashos CL, Redaelli A, Laskin
B and Hauser R: The health economics of bladder cancer-A
comprehensive review of the published literature.
Pharmacoeconomics. 21:1315–1330. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sievert KD, Amend B, Nagele U, Schilling
D, Bedke J, Horstmann M, Hennenlotter J, Kruck S and Stenzl A:
Economic aspects of bladder cancer: What are the benefits and
costs? World J Urol. 27:295–300. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gontero P, Bohle A, Malmstrom PU,
O'Donnell MA, Oderda M, Sylvester R and Witjes F: The role of
bacillus Calmette-Guérin in the treatment of non-muscle-invasive
bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 57:410–429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Triesscheijn M, Baas P, Schellens JH and
Stewart FA: Photodynamic therapy in oncology. Oncologist.
11:1034–1044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Agostinis P, Berg K, Cengel KA, Foster TH,
Girotti AW, Gollnick SO, Hahn SM, Hamblin MR, Juzeniene A, Kessel
D, et al: Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:250–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Robertson CA, Evans DH and Abrahamse H:
Photodynamic therapy (PDT): A short review on cellular mechanisms
and cancer research applications for PDT. J Photochem Photobiol B.
96:1–8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kapinova A, Stefanicka P, Kubatka P, Zubor
P, Uramova S, Kello M, Mojzis J, Blahutova D, Qaradakhi T, Zulli A,
et al: Are plant-based functional foods better choice against
cancer than single phytochemicals? A critical review of current
breast cancer research. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:1465–1477. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eghbaliferiz S and Iranshahi M: Prooxidant
activity of polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins and carotenoids:
Updated review of mechanisms and catalyzing metals. Phytother Res.
30:1379–1391. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abrahamse H and Hamblin MR: New
photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochem J. 473:347–364.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benov L: Photodynamic therapy: Current
status and future directions. Med Princ Pract. 1 (Suppl
24):S14–S28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang Q, Li ZH, Li YY, Shi SJ, Zhou SW, Fu
YY, Zhang Q, Yang X, Fu RQ and Lu LC: Hypericin-photodynamic
therapy induces human umbilical vein endothelial cell apoptosis.
Sci Rep. 5:183982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bown SG, Rogowska AZ, Whitelaw DE, Lees
WR, Lovat LB, Ripley P, Jones L, Wyld P, Gillams A and Hatfield AW:
Photodynamic therapy for cancer of the pancreas. Gut. 50:549–557.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lou PJ, Jager HR, Jones L, Theodossy T,
Bown SG and Hopper C: Interstitial photodynamic therapy as salvage
treatment for recurrent head and neck cancer. Br J Cancer.
91:441–446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Filonenko EV, Kaprin AD, Alekseev BY,
Apolikhin OI, Slovokhodov EK, Ivanova-Radkevich VI and Urlova AN:
5-Aminolevulinic acid in intraoperative photodynamic therapy of
bladder cancer (results of multicenter trial). Photodiagnosis
Photodyn Ther. 16:106–109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Azzouzi AR, Vincendeau S, Barret E, Cicco
A, Kleinclauss F, van der Poel HG, Stief CG, Rassweiler J, Salomon
G, Solsona E, et al: Padeliporfin vascular-targeted photodynamic
therapy versus active surveillance in men with low-risk prostate
cancer (CLIN1001 PCM301): An open-label, phase 3, randomised
controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:181–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Walther MM, Delaney TF, Smith PD, Friauf
WS, Thomas GF, Shawker TH, Vargas MP, Choyke PL, Linehan WM,
Abraham EH, et al: Phase I trial of photodynamic therapy in the
treatment of recurrent superficial transitional cell carcinoma of
the bladder. Urology. 50:199–206. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Skyrme RJ, French AJ, Datta SN, Allman R,
Mason MD and Matthews PN: A phase-1 study of sequential mitomycin C
and 5-aminolaevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy in
recurrent superficial bladder carcinoma. BJU Int. 95:1206–1210.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bader MJ, Stepp H, Beyer W, Pongratz T,
Sroka R, Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Welschof M, Tilki D, Stief CG, et al:
Photodynamic therapy of bladder cancer-a phase I study using
hexaminolevulinate (HAL). Urol Oncol. 31:1178–1183. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li B, Wu Z, Li W, Jia G, Lu J, Fang J and
Chen G: Chlorophyllin e4 is a novel photosensitizer against human
bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1455–1460. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nath S and Devi GR: Three-dimensional
culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model.
Pharmacol Ther. 163:94–108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF and
Yang L: Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their
applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay
Drug Dev Technol. 12:207–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Costa EC, Moreira AF, de Melo-Diogo D,
Gaspar VM, Carvalho MP and Correia IJ: 3D tumor spheroids: An
overview on the tools and techniques used for their analysis.
Biotechnol Adv. 34:1427–1441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kapuscinski J and Szer W: Interactions of
4′,6-diamidine-2- phenylindole with synthetic polynucleotides.
Nucleic Acids Res. 6:3519–3534. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xodo LE, Rapozzi V, Zacchigna M, Drioli S
and Zorzet S: The chlorophyll catabolite pheophorbide a as a
photosensitizer for the photodynamic therapy. Curr Med Chem.
19:799–807. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dai R, Shoemaker R, Farrens D, Han MJ, Kim
CS and Song PS: Characterization of silkworm chlorophyll
metabolites as an active photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy.
J Nat Prod. 55:1241–1251. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirschhaeuser F, Menne H, Dittfeld C, West
J, Mueller-Klieser W and Kunz-Schughart LA: Multicellular tumor
spheroids: An underestimated tool is catching up again. J
Biotechnol. 148:3–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Friedrich J, Seidel C, Ebner R and
Kunz-Schughart LA: Spheroid-based drug screen: Considerations and
practical approach. Nat Protoc. 4:309–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Manoto SL, Houreld NN and Abrahamse H:
Resistance of lung cancer cells grown as multicellular tumour
spheroids to zinc sulfophthalocyanine photosensitization. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:10185–10200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huygens A, Huyghe D, Bormans G, Verbruggen
A, Kamuhabwa AR, Roskams T and de Witte PA: Accumulation and
photocytotoxicity of hypericin and analogs in two- and
three-dimensional cultures of transitional cell carcinoma cells.
Photochem Photobiol. 78:607–614. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A Perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kluck RM, BossyWetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria:
A primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V,
Stoica BA, Wang GP, Iyer S and Smulson M: Role of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP
mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol
Chem. 274:22932–22940. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou Z, Song J, Nie L and Chen X: Reactive
oxygen species generating systems meeting challenges of
photodynamic cancer therapy. Chem Soc Rev. 45:6597–6626. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lam M, Oleinick NL and Nieminen AL:
Photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis in epidermoid carcinoma
cells. Reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial inner membrane
permeabilization. J Biol Chem. 276:47379–47386. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim CH, Chung CW, Choi KH, Yoo JJ, Kim DH,
Jeong YI and Kang DH: Effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-based
photodynamic therapy via reactive oxygen species in human
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:1357–1363.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Abreu IA and Cabelli DE: Superoxide
dismutases-a review of the metal-associated mechanistic variations.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:263–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun WH, Liu F, Chen Y and Zhu YC: Hydrogen
sulfide decreases the levels of ROS by inhibiting mitochondrial
complex IV and increasing SOD activities in cardiomyocytes under
ischemia/reperfusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:164–169.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Su L, Zhao B, Lv X, Wang N, Zhao J, Zhang
S and Miao J: Safrole oxide induces neuronal apoptosis through
inhibition of integrin beta 4/SOD activity and elevation of
ROS/NADPH oxidase activity. Life Sci. 80:999–1006. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Golab J, Nowis D, Skrzycki M, Czeczot H,
Baranczyk-Kuzma A, Wilczynski GM, Makowski M, Mroz P, Kozar K,
Kaminski R, et al: Antitumor effects of photodynamic therapy are
potentiated by 2-methoxyestradiol. A superoxide dismutase
inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 278:407–414. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kimani SG, Phillips JB, Bruce JI,
MacRobert AJ and Golding JP: Antioxidant inhibitors potentiate the
cytotoxicity of photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol.
88:175–187. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fleury C, Mignotte B and Vayssiere JL:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling.
Biochimie. 84:131–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Redza-Dutordoir M and Averill-Bates DA:
Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen
species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:2977–2992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado
AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X: Prevention of apoptosis by
Bcl-2: Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked.
Science. 275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ruemmele FM, Dionne S, Qureshi I, Sarma
DS, Levy E and Seidman EG: Butyrate mediates Caco-2 cell apoptosis
via up-regulation of pro-apoptotic BAK and inducing caspase-3
mediated cleavage of poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Cell
Death Differ. 6:729–735. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tyagi A, Agarwal C, Harrison G, Glode LM
and Agarwal R: Silibinin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
human bladder transitional cell carcinoma cells by regulating
CDKI-CDK-cyclin cascade, and caspase 3 and PARP cleavages.
Carcinogenesis. 25:1711–1720. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|