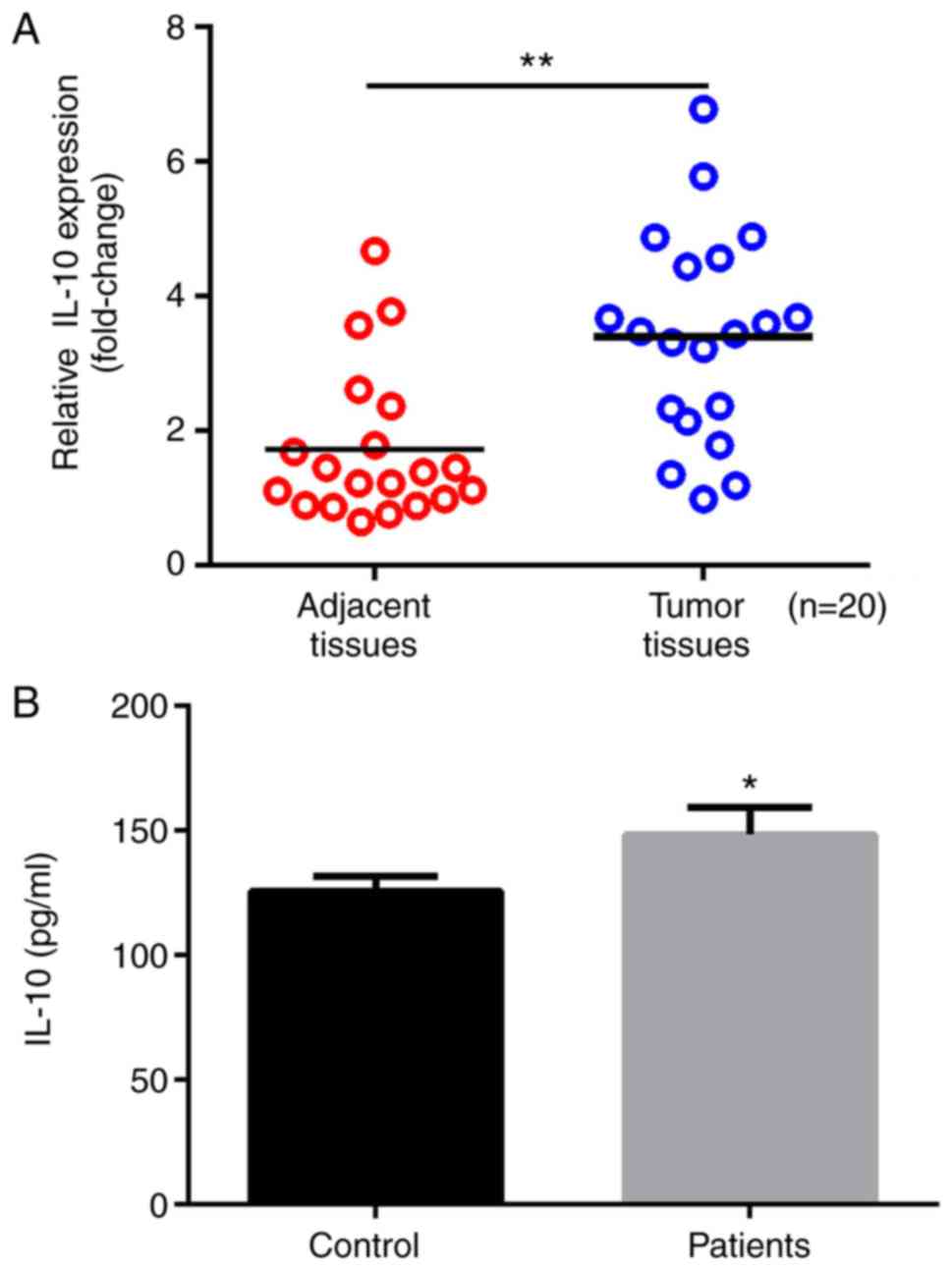
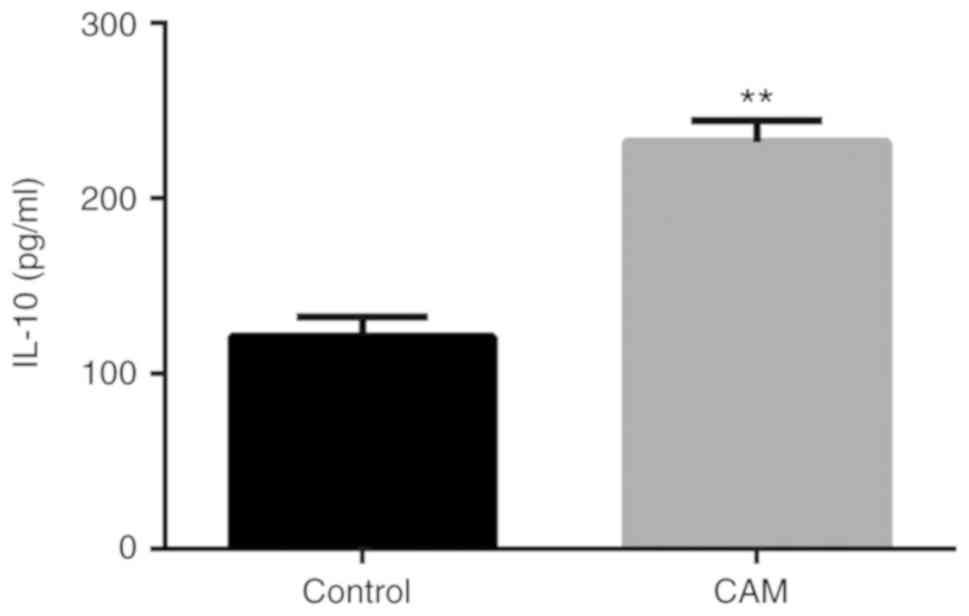
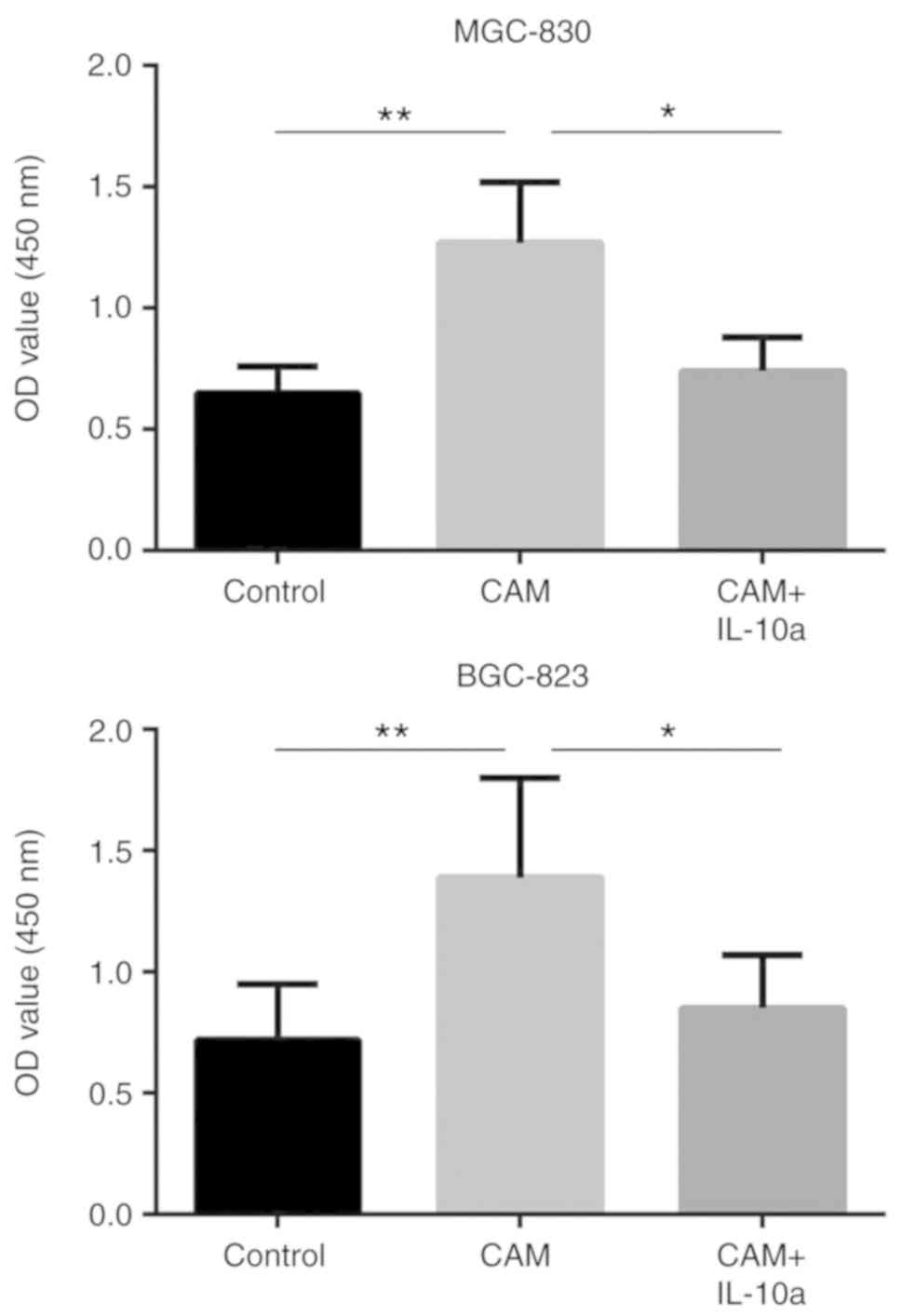
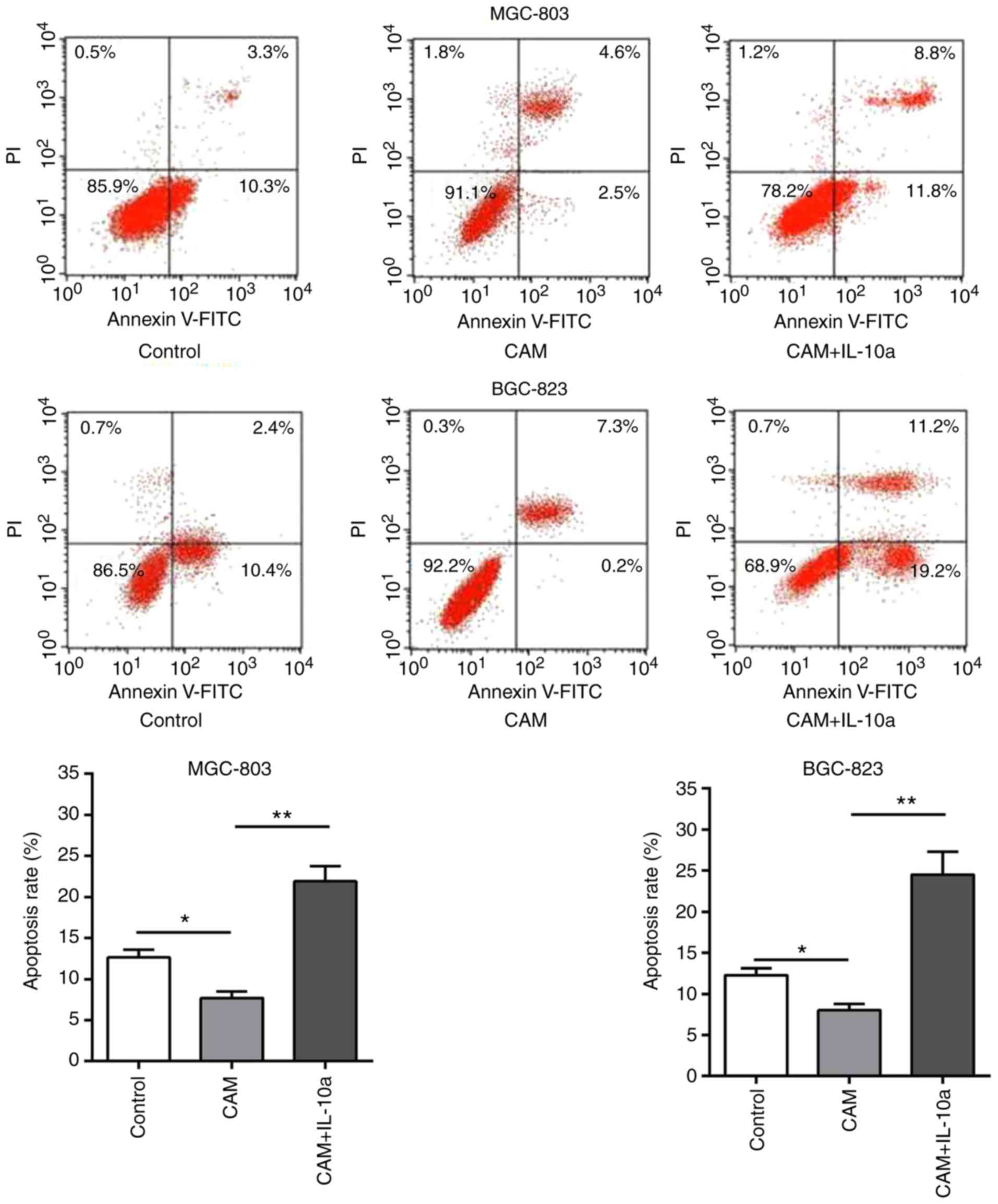
|
1
|
Yao Q, Tu C, Lu D, Zou Y, Liu H and Zhang
S: Clinicopathological significance of the
microRNA-146a/WASP-family verprolin-homologous protein-2 axis in
gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 108:1285–1292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang DY, Wang J, Zhang GQ, Chu XQ, Zhang
JL and Zhou Y: Correlations of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 gene polymorphisms
with the risk and prognosis of gastric cancer. Int J Exp Med.
8:20391–20401. 2015.
|
|
3
|
Zhu X, Tian X, Yu C, Shen C, Yan T, Hong
J, Wang Z, Fang JY and Chen H: A long non-coding RNA signature to
improve prognosis prediction of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer.
15:602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakamoto N, Tsujimoto H, Takahata R, Cao
B, Zhao P, Ito N, Shimazaki H, Ichikura T, Hase K, Vande Woude GF
and Shinomiya N: MET4 expression predicts poor prognosis of gastric
cancers with Helicobacter pylori infection. Cancer Sci.
108:322–330. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Higuchi K, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y, Ishikawa
T, Otsuki S, Uetake H, Kojima K and Kawano T: Cadherin 5 expression
correlates with poor survival in human gastric cancer. J Clin
Pathol. 70:217–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mosser DM and Zhang X: Interleukin-10: New
perspectives on an old cytokine. Immunol Rev. 226:205–218. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pereira L, Font-Nieves M, Van den Haute C,
Baekelandt V, Planas AM and Pozas E: IL-10 regulates adult
neurogenesis by modulating ERK and STAT3 activity. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu BS, Cao Y, Huizinga TW, Hafler DA and
Toes RE: TLR-mediated STAT3 and ERK activation controls IL-10
secretion by human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 44:2121–2129. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen D, Xie J, Fiskesund R, Dong W, Liang
X, Lv J, Jin X, Liu J, Mo S, Zhang T, et al: Chloroquine modulates
antitumor immune response by resetting tumor-associated macrophages
toward M1 phenotype. Nat Commun. 9:8732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ohno Y, Toyoshima Y, Yurino H, Monma N,
Xiang H, Sumida K, Kaneumi S, Terada S, Hashimoto S, Ikeo K, et al:
Lack of interleukin-6 in the tumor microenvironment augments type-1
immunity and increases the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer
Sci. 108:1959–1966. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lan C, Huang X, Lin S, Huang H, Cai Q, Wan
T, Lu J and Liu J: Expression of M2-polarized macrophages is
associated with poor prognosis for advanced epithelial ovarian
cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 12:259–267. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herrera M, Herrera A, Domínguez G, Silva
J, García V, García JM, Gómez I, Soldevilla B, Muñoz C, Provencio
M, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblast and M2 macrophage markers
together predict outcome in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Sci.
104:437–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu JY, Peng CW, Yang GF, Hu WQ, Yang XJ,
Huang CQ, Xiong B and Li Y: Distribution pattern of tumor
associated macrophages predicts the prognosis of gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:92757–92769. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin S, Huang J, Li Z, Zhang J, Luo J, Lu C
and Xu H and Xu H: The prognostic and clinicopathological
significance of tumor-associated macrophages in patients with
gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 12:e01700422017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salvi A, Abeni E, Portolani N, Barlati S
and De Petro G: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell-specific miRNAs
reveal the differential expression of miR-24 and miR-27a in
cirrhotic/non-cirrhotic HCC. Int J Oncol. 42:391–402. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Statist Soc Ser B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
18
|
He F, Ai B and Tian L: Identification of
genes and pathways in esophageal adenocarcinoma using
bioinformatics analysis. Biomed Rep. 9:305–312. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu JC, Wang CT, Hung HC, Wu WJ, Wu DC,
Chang MC, Sung PJ, Chou YW, Wen ZH and Tai MH: Heteronemin is a
novel c-Met/STAT3 inhibitor against advanced prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 76:1469–1483. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Syed ZA, Yin W, Hughes K, Gill JN, Shi R
and Clifford JL: HGF/c-met/Stat3 signaling during skin tumor cell
invasion: Indications for a positive feedback loop. BMC Cancer.
11:1802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding H, Zhao L, Dai S, Li L, Wang F and
Shan B: CCL5 secreted by tumor associated macrophages may be a new
target in treatment of gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
77:142–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamaguchi T, Fushida S, Yamamoto Y,
Tsukada T, Kinoshita J, Oyama K, Miyashita T, Tajima H, Ninomiya I,
Munesue S, et al: Tumor-associated macrophages of the M2 phenotype
contribute to progression in gastric cancer with peritoneal
dissemination. Gastric Cancer. 19:1052–1065. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gholamin S, Fiuji H, Maftouh M, Mirhafez
R, Shandiz FH and Avan A: Targeting c-MET/HGF signaling pathway in
upper gastrointestinal cancers: Rationale and progress. Curr Drug
Targets. 15:1302–1311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marano L, Chiari R, Fabozzi A, De Vita F,
Boccardi V, Roviello G, Petrioli R, Marrelli D, Roviello F and
Patriti A: C-Met targeting in advanced gastric cancer: An open
challenge. Cancer Lett. 365:30–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ding X, Ji J, Jiang J, Cai Q, Wang C, Shi
M, Yu Y, Zhu Z and Zhang J: HGF-mediated crosstalk between
cancer-associated fibroblasts and MET-unamplified gastric cancer
cells activates coordinated tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cell
Death Dis. 9:8672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Okamoto W, Okamoto I, Arao T, Yanagihara
K, Nishio K and Nakagawa K: Differential roles of STAT3 depending
on the mechanism of STAT3 activation in gastric cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 105:407–412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wei X, Juan ZX, Min FX, Nan C, Hua ZX,
Qing FZ and Zheng L: Recombinant immunotoxin anti-c-Met/PE38KDEL
inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:672011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ries CH, Cannarile MA, Hoves S, Benz J,
Wartha K, Runza V, Rey-Giraud F, Pradel LP, Feuerhake F, Klaman I,
et al: Targeting tumor-associated macrophages with anti-CSF-1R
antibody reveals a strategy for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell.
25:846–859. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|