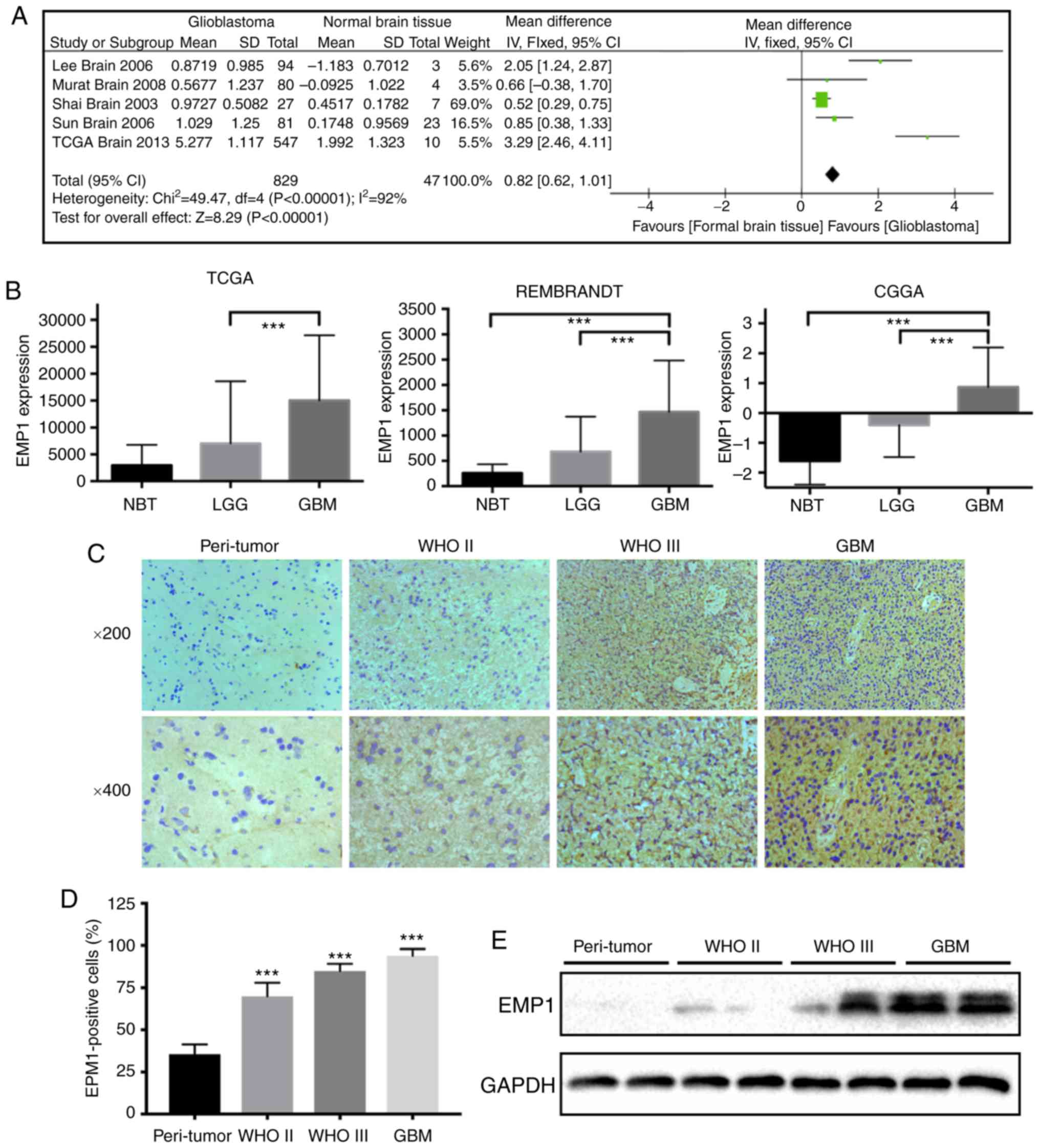
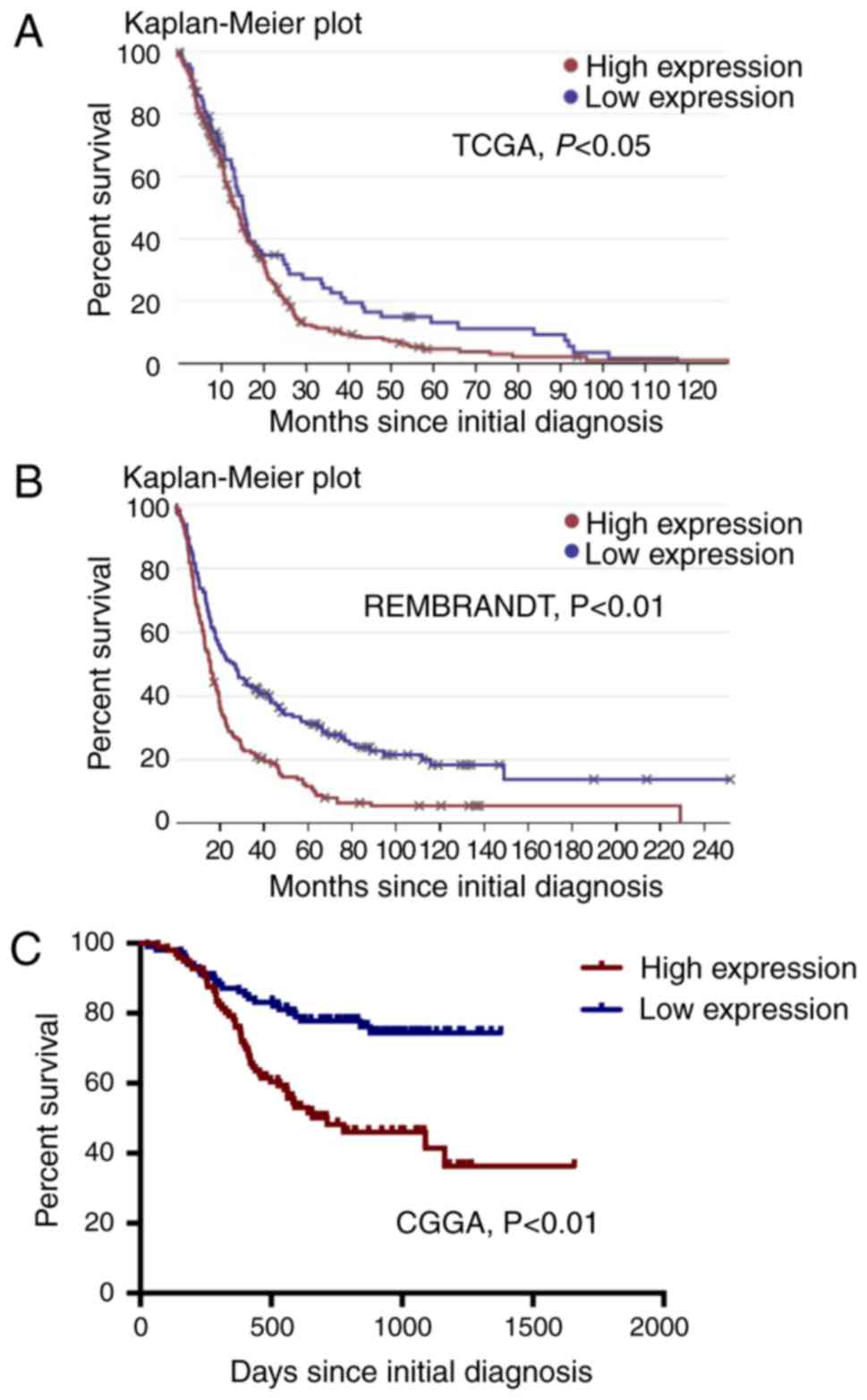
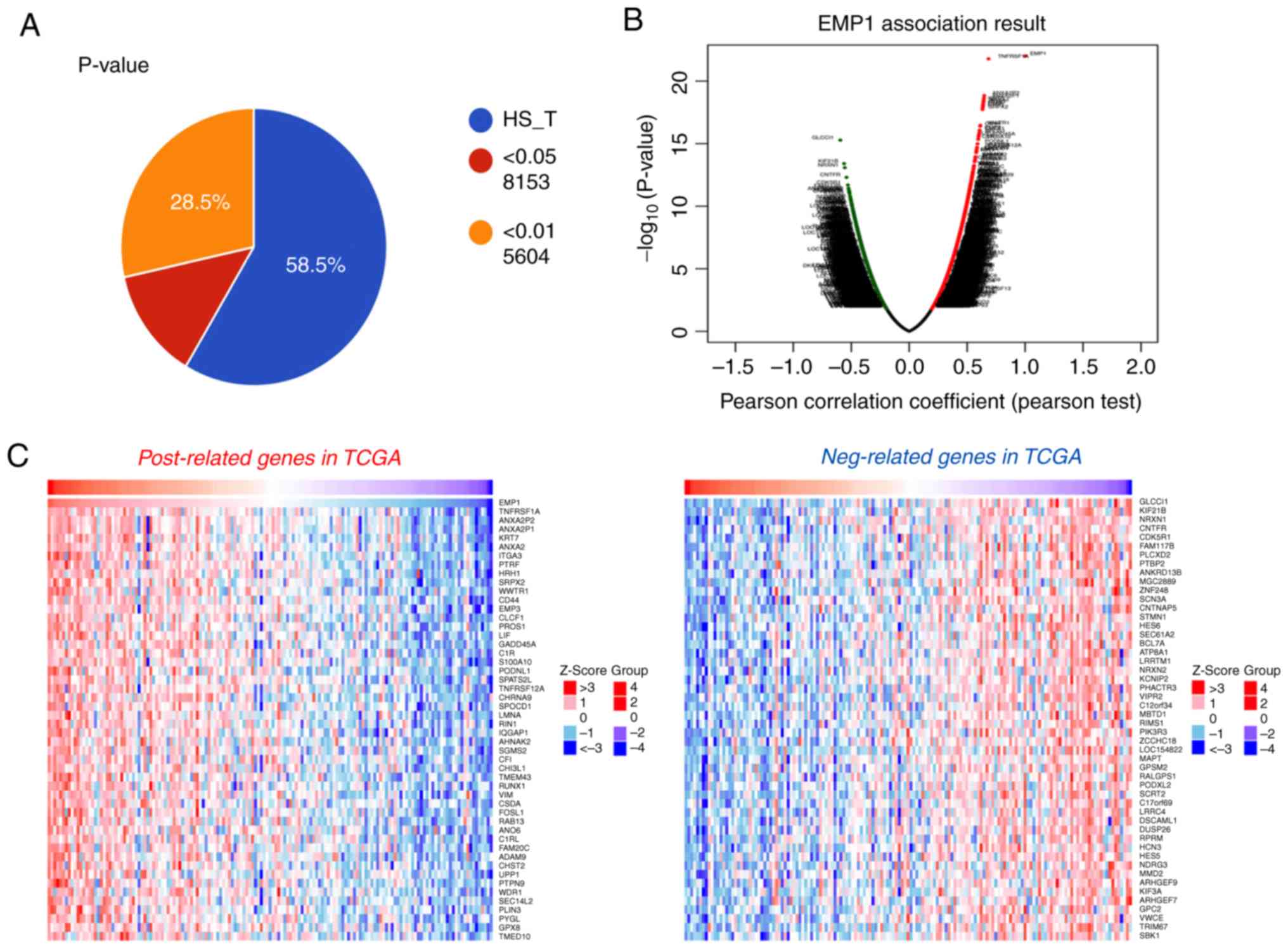
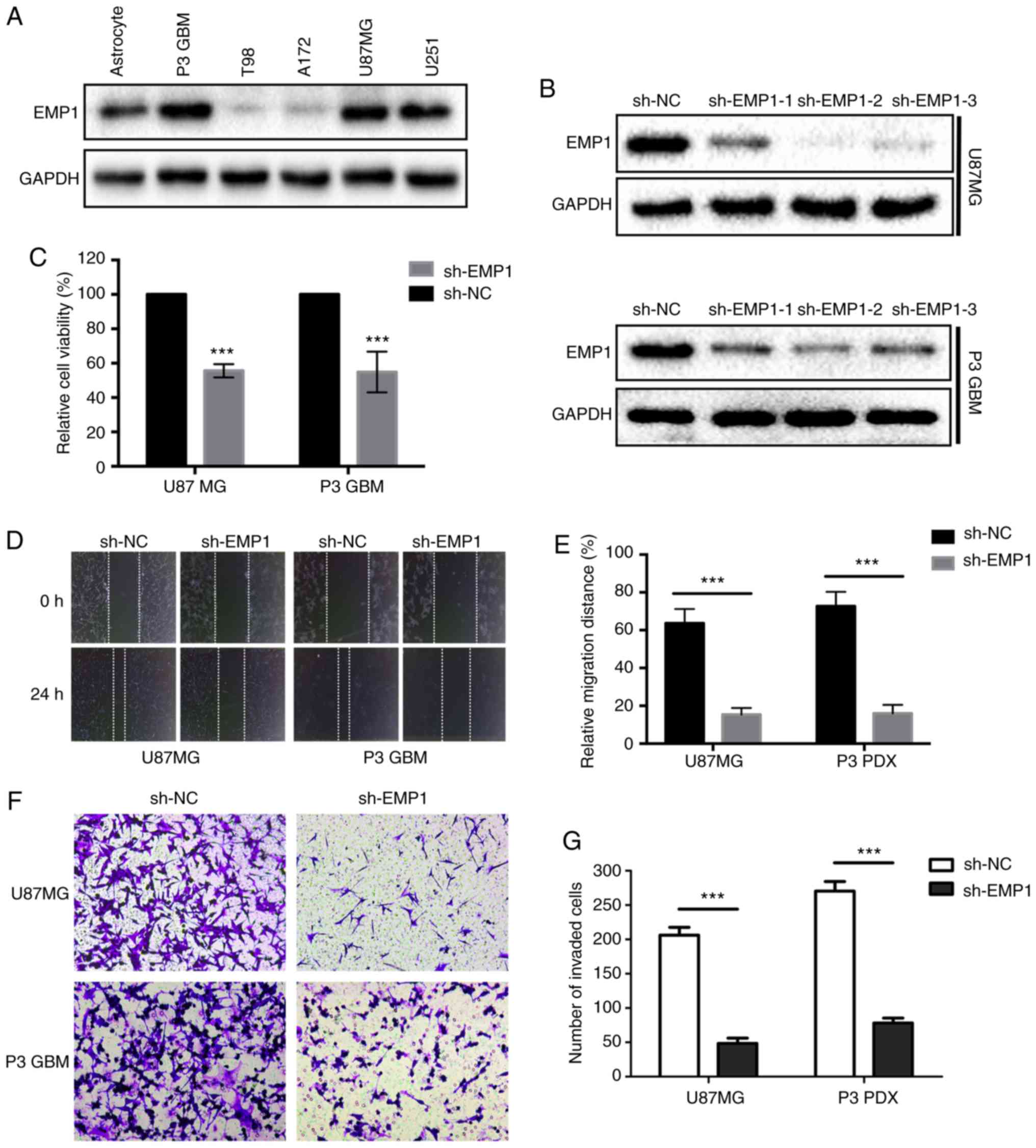
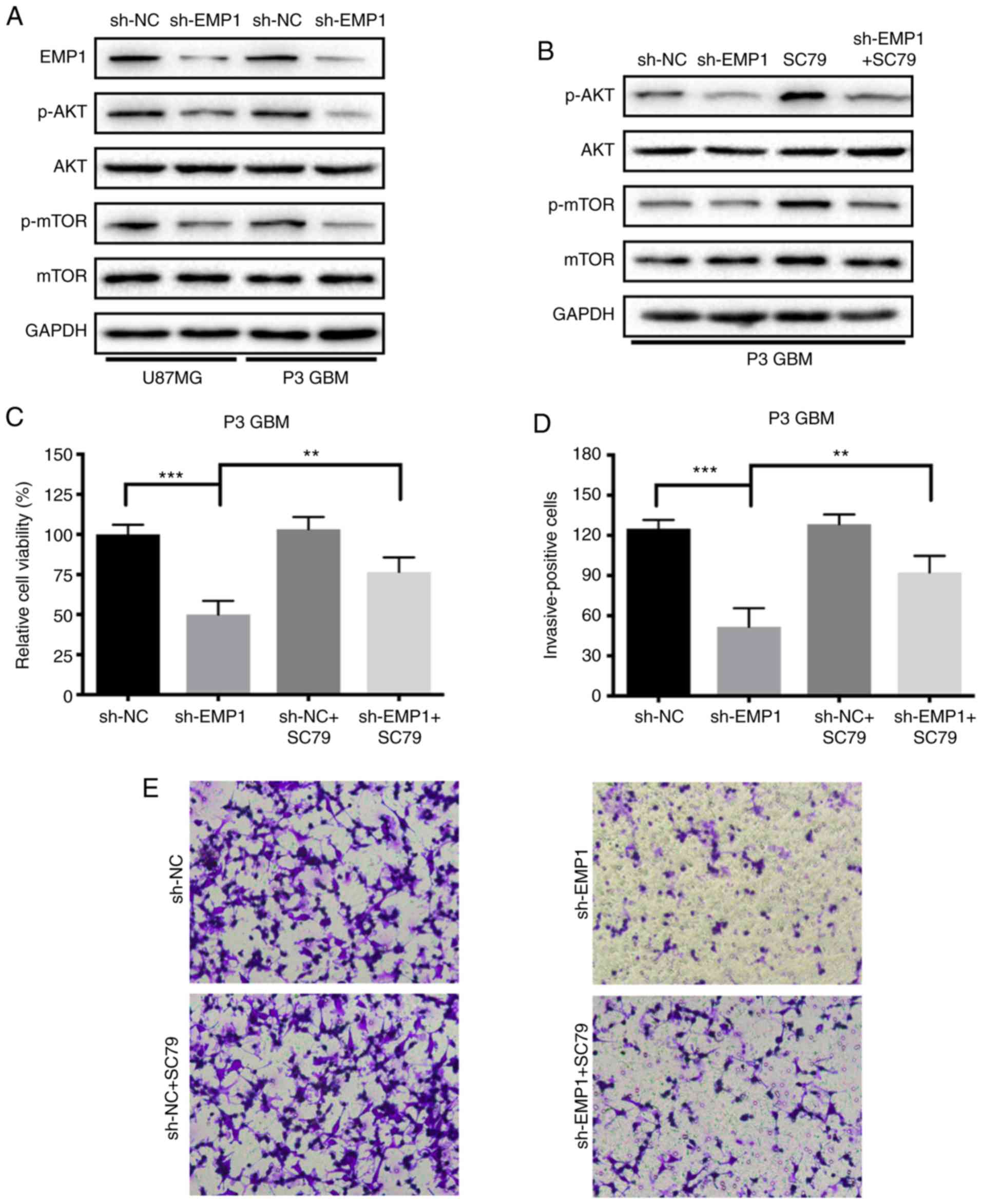
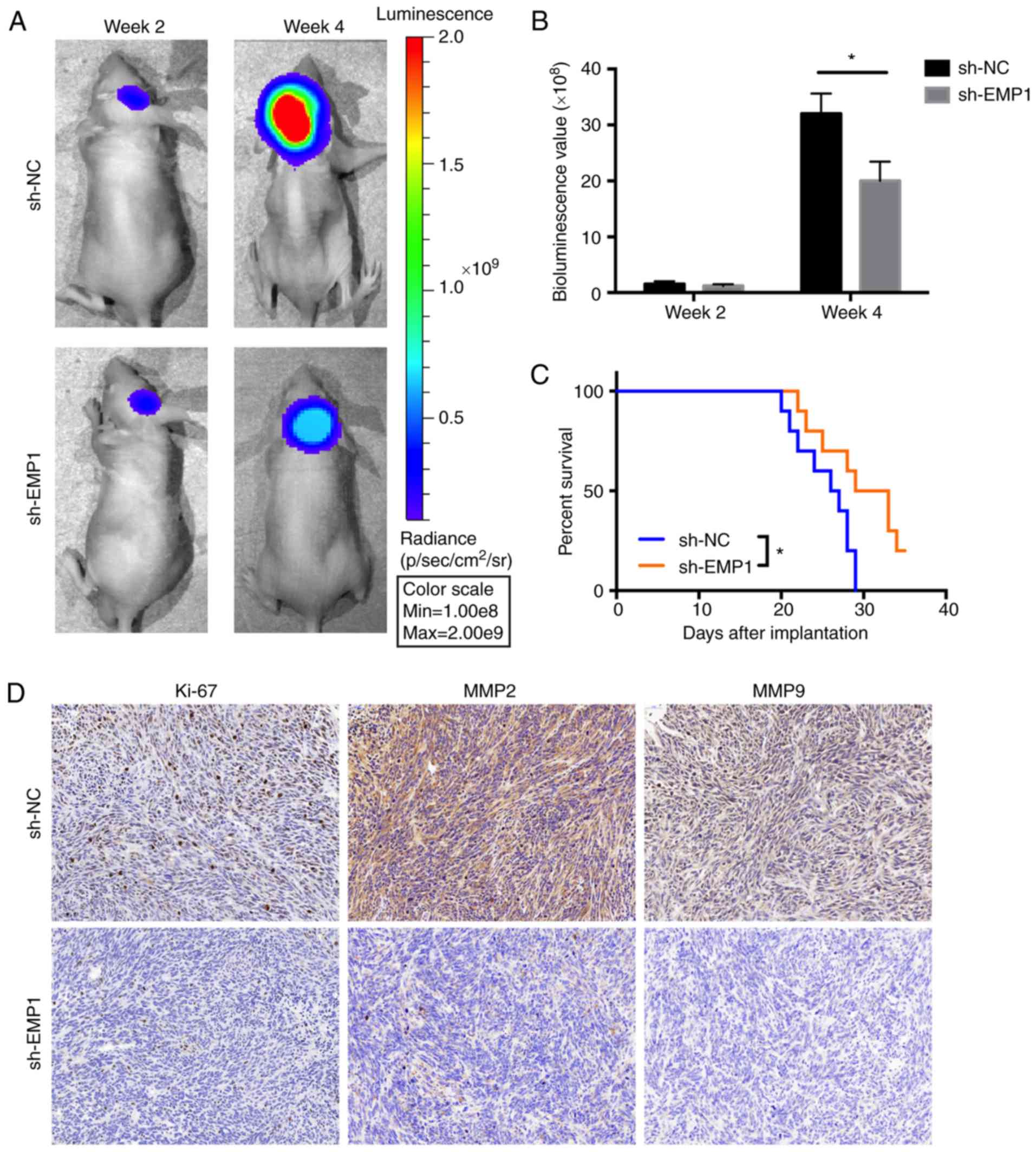
|
1
|
Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, Lahutte M,
Hoang-Xuan K and Delattre JY: Primary brain tumours in adults.
Lancet. 379:1984–1996. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kalpathy-Cramer J, Gerstner ER, Emblem KE,
Andronesi OC and Rosen B: Advanced magnetic resonance imaging of
the physical processes in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
74:4622–4637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van den Bent M, Chinot OL and Cairncross
JG: Recent developments in the molecular characterization and
treatment of oligodendroglial tumors. Neuro Oncol. 5:128–138. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garrido W, Rocha JD, Jaramillo C,
Fernandez K, Oyarzun C, San Martin R and Quezada C: Chemoresistance
in high-grade gliomas: Relevance of adenosine signalling in
stem-like cells of glioblastoma multiforme. Curr Drug Targets.
15:931–942. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee CY: Strategies of temozolomide in
future glioblastoma treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 10:265–270. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uribe D, Torres A, Rocha JD, Niechi I,
Oyarzún C, Sobrevia L, San Martín R and Quezada C: Multidrug
resistance in glioblastoma stem-like cells: Role of the hypoxic
microenvironment and adenosine signaling. Mol Aspects Med.
55:140–151. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bangsow T, Baumann E, Bangsow C, Jaeger
MH, Pelzer B, Gruhn P, Wolf S, von Melchner H and Stanimirovic DB:
The epithelial membrane protein 1 is a novel tight junction protein
of the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:1249–1260.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aries IM, Jerchel IS, van den Dungen RE,
van den Berk LC, Boer JM, Horstmann MA, Escherich G, Pieters R and
den Boer ML: EMP1, a novel poor prognostic factor in pediatric
leukemia regulates prednisolone resistance, cell proliferation,
migration and adhesion. Leukemia. 28:1828–1837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun G, Zhao G, Lu Y, Wang Y and Yang C:
Association of EMP1 with gastric carcinoma invasion, survival and
prognosis. Int J Oncol. 45:1091–1098. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Harsh GR,
Vogel H, Recht LD and Sikic BI: Functional network analysis reveals
extended gliomagenesis pathway maps and three novel MYC-interacting
genes in human gliomas. Cancer Res. 65:8679–8689. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Qi Q, Feng Z, Zhang X, Huang B,
Chen A, Prestegarden L, Li X and Wang J: Berberine induces
autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:66944–66958. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fack F, Espedal H, Keunen O, Golebiewska
A, Obad N, Harter PN, Mittelbronn M, Bähr O, Weyerbrock A, Stuhr L,
et al: Bevacizumab treatment induces metabolic adaptation toward
anaerobic metabolism in glioblastomas. Acta Neuropathol.
129:115–131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fack F, Tardito S, Hochart G, Oudin A,
Zheng L, Fritah S, Golebiewska A, Nazarov PV, Bernard A, Hau AC, et
al: Altered metabolic landscape in IDH-mutant gliomas affects
phospholipid, energy, and oxidative stress pathways. EMBO Mol Med.
9:1681–1695. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tardito S, Oudin A, Ahmed SU, Fack F,
Keunen O, Zheng L, Miletic H, Sakariassen PØ, Weinstock A, Wagner
A, et al: Glutamine synthetase activity fuels nucleotide
biosynthesis and supports growth of glutamine-restricted
glioblastoma. Nat Cell Biol. 17:1556–1568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rajesh Y, Pal I, Banik P, Chakraborty S,
Borkar SA, Dey G, Mukherjee A and Mandal M: Insights into molecular
therapy of glioma: Current challenges and next generation
blueprint. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:591–613. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsieh YH, Hsieh SC, Lee CH, Yang SF, Cheng
CW, Tang MJ, Lin CL, Lin CL and Chou RH: Targeting EMP3 suppresses
proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through inactivation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncotarget.
6:34859–34874. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai S, Wang G, Cao X, Li Z, Hu J and Wang
J: EMP-1 promotes tumorigenesis of NSCLC through PI3K/AKT pathway.
J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 32:834–838. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang HT, Kong JP, Ding F, Wang XQ, Wang
MR, Liu LX, Wu M and Liu ZH: Analysis of gene expression profile
induced by EMP-1 in esophageal cancer cells using cDNA Microarray.
World J Gastroenterol. 9:392–398. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang YW, Cheng HL, Ding YR, Chou LH and
Chow NH: EMP1, EMP 2, and EMP3 as novel therapeutic targets in
human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1868:199–211. 2017.
|
|
20
|
Ramnarain DB, Park S, Lee DY, Hatanpaa KJ,
Scoggin SO, Otu H, Libermann TA, Raisanen JM, Ashfaq R, Wong ET, et
al: Differential gene expression analysis reveals generation of an
autocrine loop by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in
glioma cells. Cancer Res. 66:867–874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun GG, Lu YF, Fu ZZ, Cheng YJ and Hu WN:
EMP1 inhibits nasopharyngeal cancer cell growth and metastasis
through induction apoptosis and angiogenesis. Tumour Biol.
35:3185–3193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Manning BD and Toker A: AKT/PKB signaling:
Navigating the network. Cell. 169:381–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|