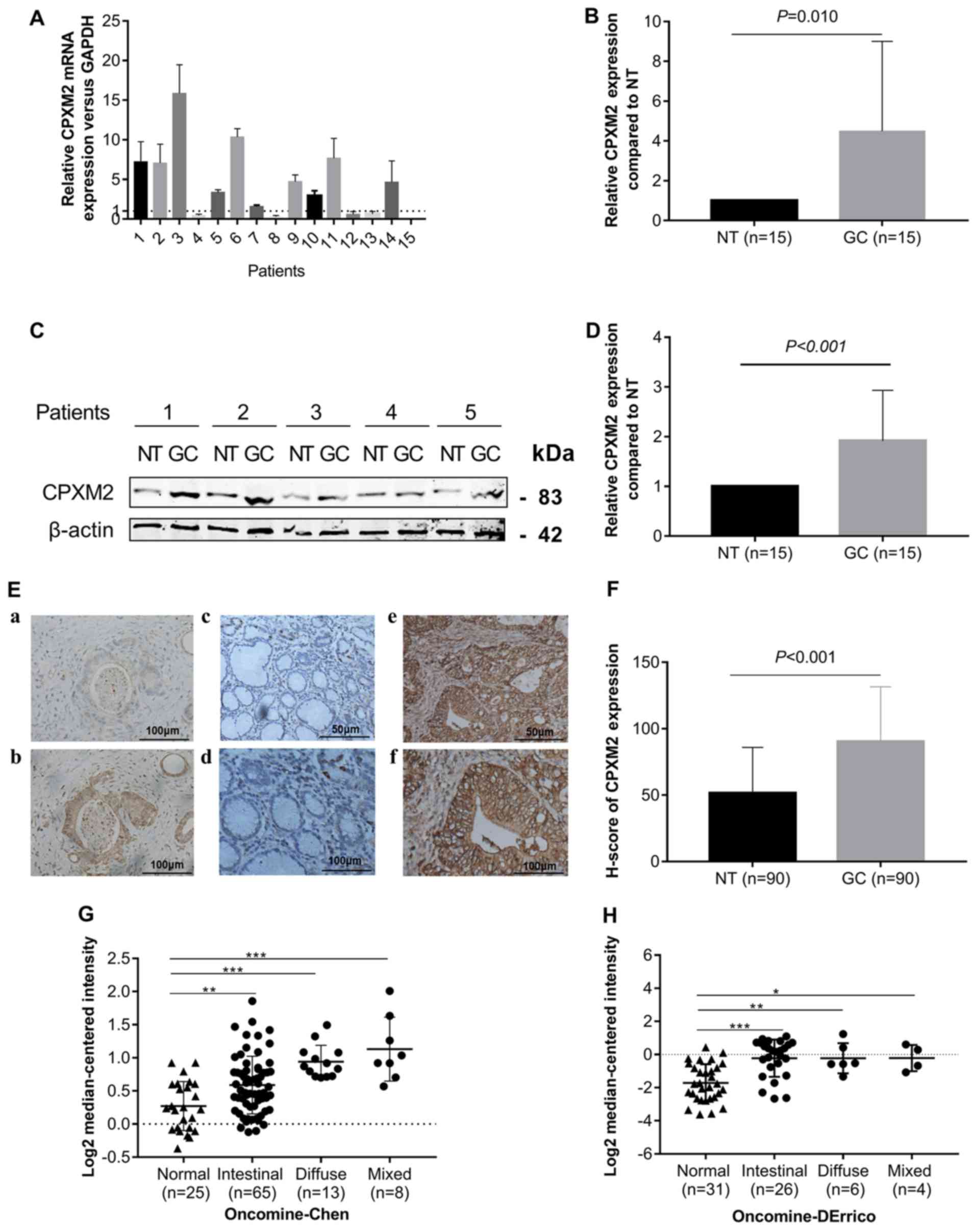
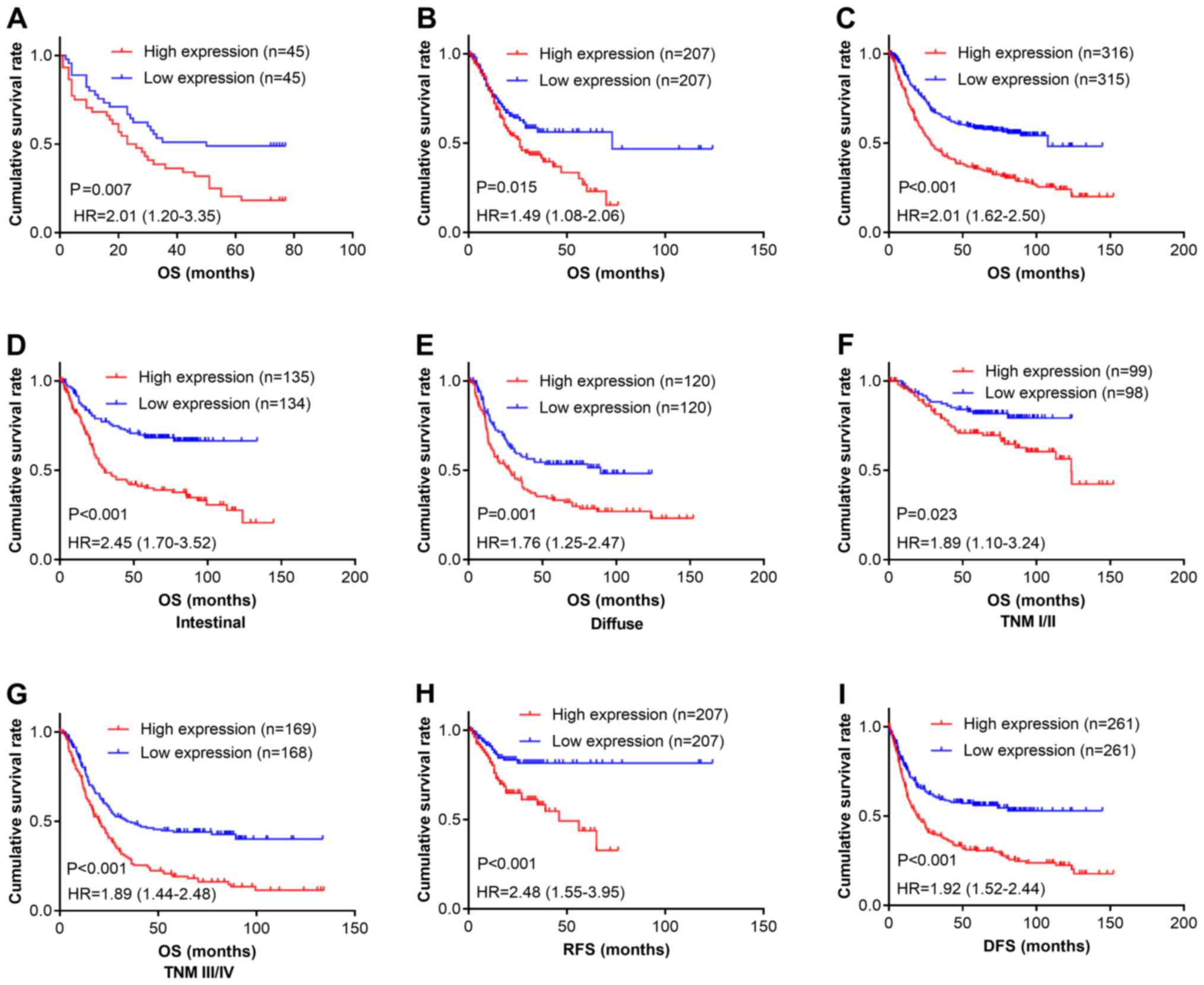
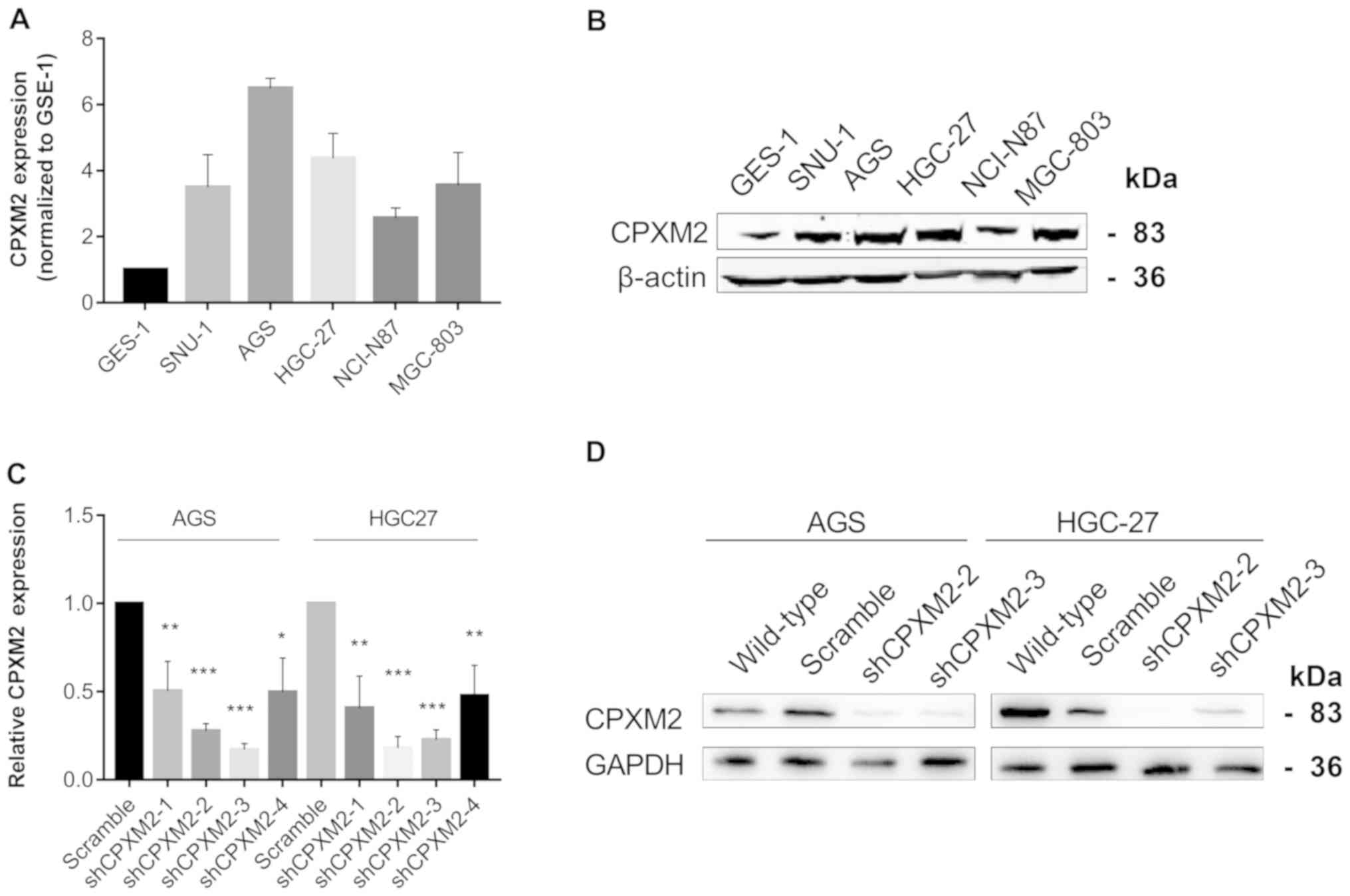
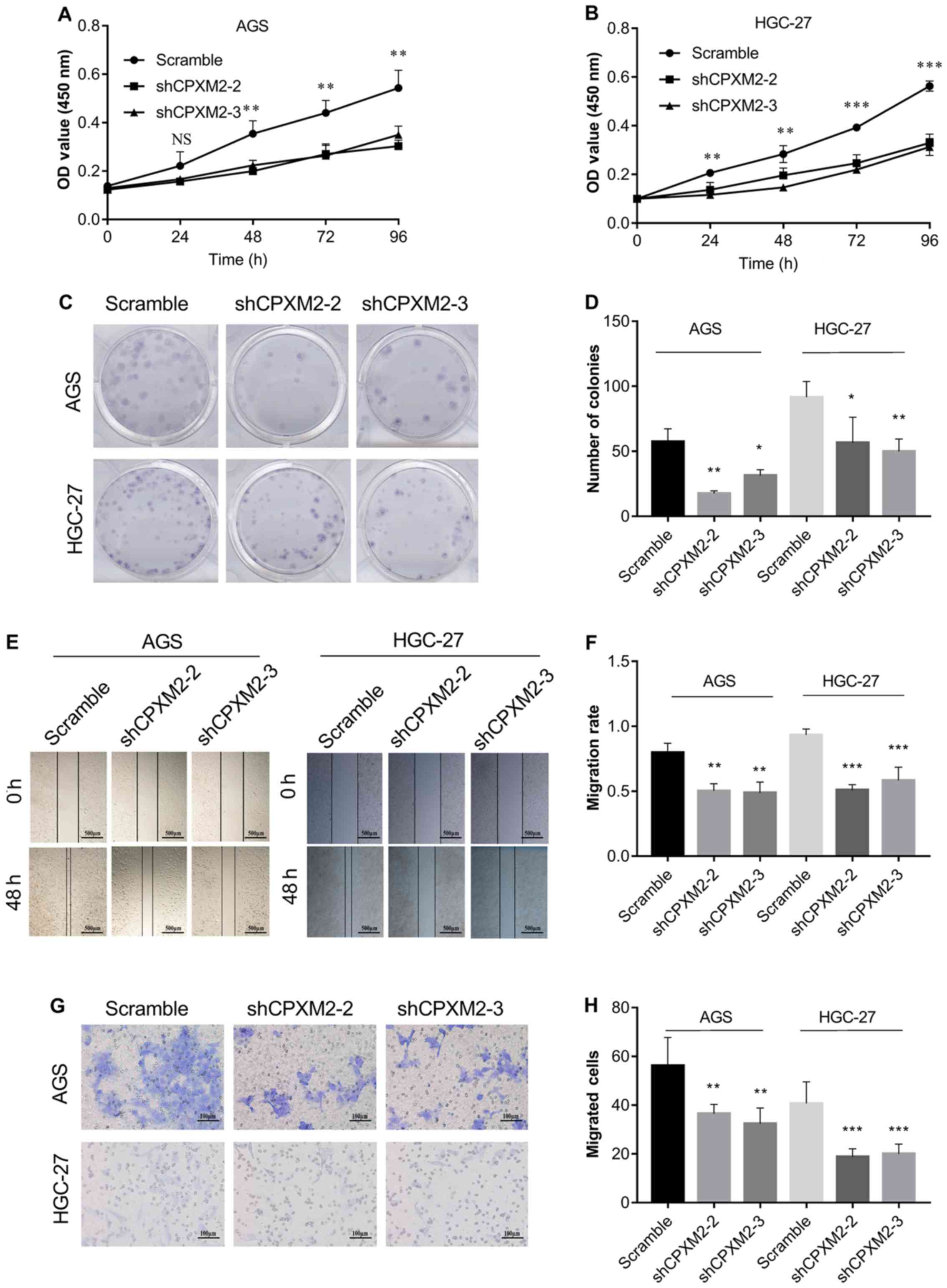
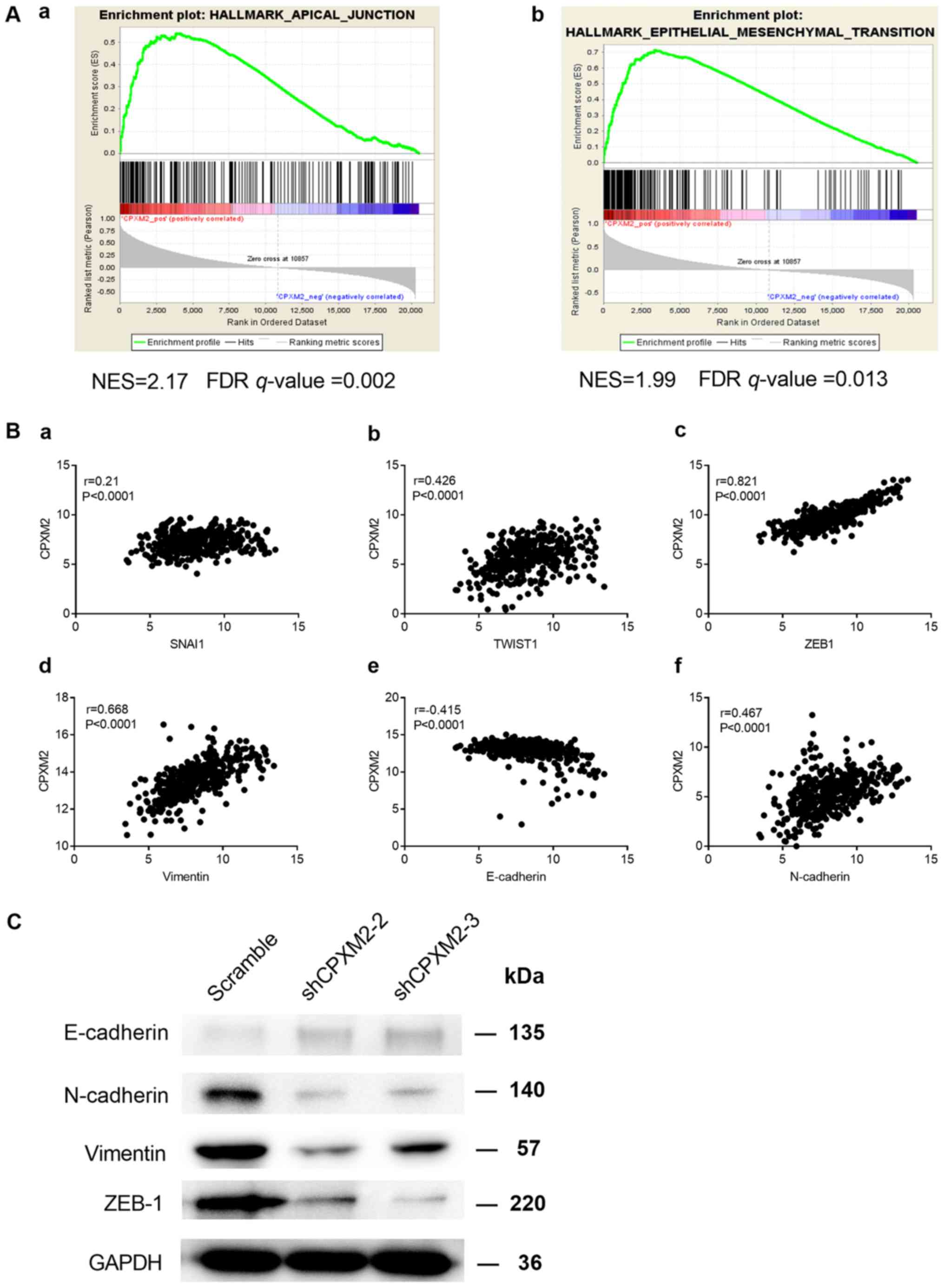
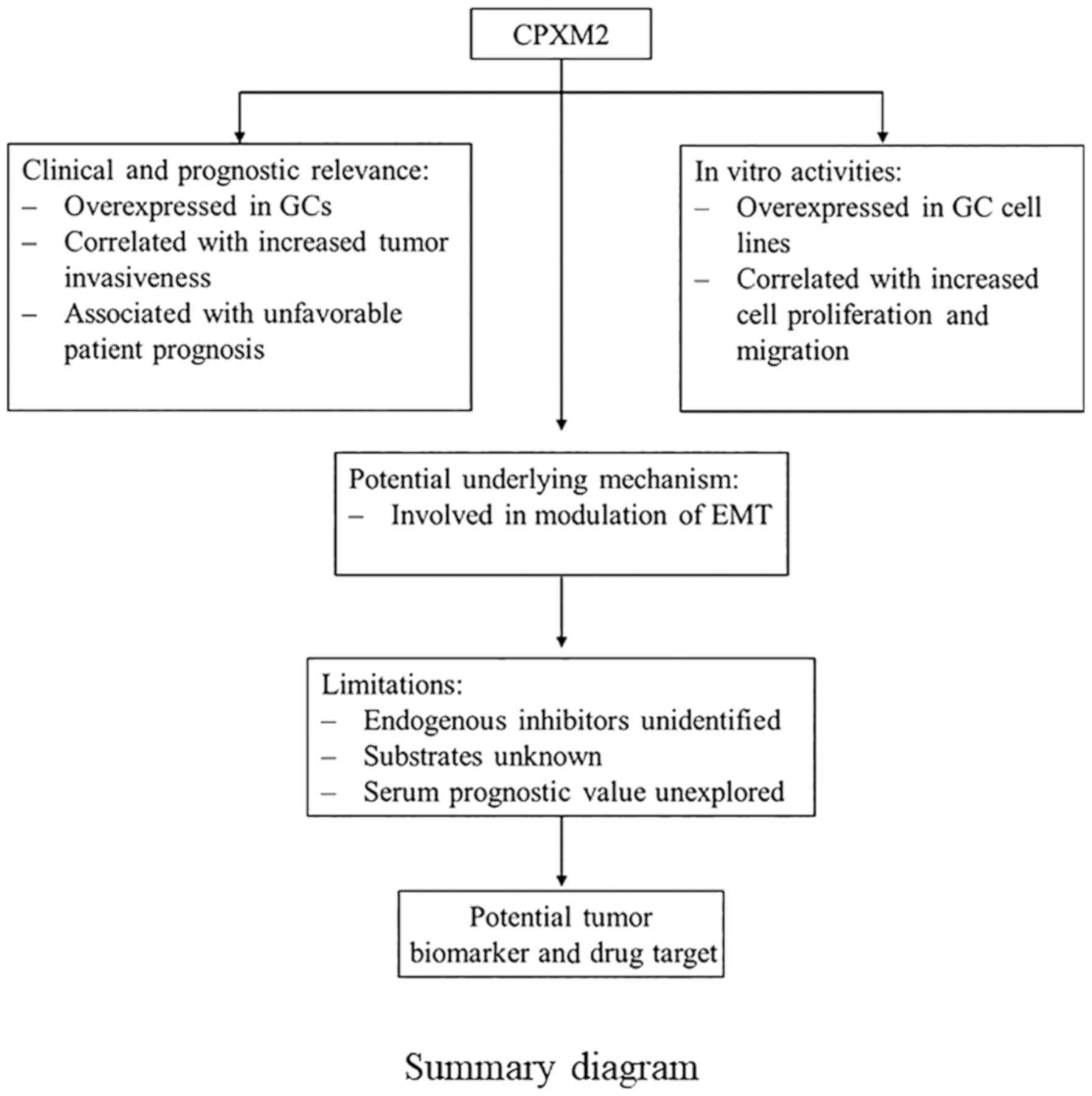
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malvezzi M, Bonifazi M, Bertuccio P, Levi
F, La Vecchia C, Decarli A and Negri E: An age-period-cohort
analysis of gastric cancer mortality from 1950 to 2007 in Europe.
Ann Epidemiol. 20:898–905. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B,
Haustermans K and Prenen H: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 388:2654–2664.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fernandez D, Pallares I, Vendrell J and
Aviles FX: Progress in metallocarboxypeptidases and their small
molecular weight inhibitors. Biochimie. 92:1484–1500. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gomis-Rüth FX: Structure and mechanism of
metallocarboxypeptidases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 43:319–345.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fernandez D, Pallares I, Covaleda G,
Aviles FX and Vendrell J: Metallocarboxypeptidases and their
inhibitors: Recent developments in biomedically relevant protein
and organic ligands. Curr Med Chem. 20:1595–1608. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun L, Guo C, Yuan H, Burnett J, Pan J,
Yang Z, Ran Y, Myers I and Sun D: Overexpression of
carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4) is associated with poor prognosis in
patients with gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res. 8:5071–5075.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cawley NX, Wetsel WC, Murthy SR, Park JJ,
Pacak K and Loh YP: New roles of carboxypeptidase E in endocrine
and neural function and cancer. Endocr Rev. 33:216–253. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Denis CJ and Lambeir AM: The potential of
carboxypeptidase M as a therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 17:265–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Çetinkaya A, Taskiran E, Soyer T,
Şimşek-Kiper PÖ, Utine GE, Tuncbilek G, Boduroğlu K and
Alikaşifoğlu M: Dermal fibroblast transcriptome indicates
contribution of WNT signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of Apert
syndrome. Turk J Pediatr. 59:619–624. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sabri A, Lai D, D'Silva A, Seeho S, Kaur
J, Ng C and Hyett J: Differential placental gene expression in term
pregnancies affected by fetal growth restriction and macrosomia.
Fetal Diagn Ther. 36:173–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen YC, Hsiao CJ, Jung CC, Hu HH, Chen
JH, Lee WC, Chiou JM, Chen TF, Sun Y, Wen LL, et al: Performance
metrics for selecting single nucleotide polymorphisms in Late-onset
Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 6:361552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hashimoto R, Ikeda M, Ohi K, Yasuda Y,
Yamamori H, Fukumoto M, Umeda-Yano S, Dickinson D, Aleksic B, Iwase
M, et al: Genome-wide association study of cognitive decline in
schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 170:683–684. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Howitt BE, Sun HH, Roemer MG, Kelley A,
Chapuy B, Aviki E, Pak C, Connelly C, Gjini E, Shi Y, et al:
Genetic basis for PD-L1 expression in squamous cell carcinomas of
the cervix and vulva. JAMA Oncol. 2:518–522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Chu KM, Ji J,
Li R, Chan AS, Law S, Troyanskaya OG, Wong J, et al: Variation in
gene expression patterns in human gastric cancers. Mol Biol Cell.
14:3208–3215. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
D'Errico M, de Rinaldis E, Blasi MF, Viti
V, Falchetti M, Calcagnile A, Sera F, Saieva C, Ottini L, Palli D,
et al: Genome-wide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers
with microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer. 45:461–469. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Szasz AM, Lanczky A, Nagy A, Forster S,
Hark K, Green JE, Boussioutas A, Busuttil R, Szabó A and Győrffy B:
Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric
cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget.
7:49322–49333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi JY, Ma LJ, Zhang JW, Duan M, Ding ZB,
Yang LX, Cao Y, Zhou J, Fan J, Zhang X, et al: FOXP3 Is a HCC
suppressor gene and Acts through regulating the TGF-β/Smad2/3
signaling pathway. BMC Cancer. 17:6482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao S, Zhou L, Niu G, Li Y, Zhao D and
Zeng H: Differential regulation of orphan nuclear receptor TR3
transcript variants by novel vascular growth factor signaling
pathways. FASEB J. 28:4524–4533. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu HM, Chen Y, Liu L, Zhang CG, Wang W,
Gong K, Huang Z, Guo MX, Li WX and Li W: C1orf61 acts as a tumor
activator in human hepatocellular carcinoma and is associated with
tumorigenesis and metastasis. FASEB J. 27:163–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu G, Ye T, Qin L, Bourbon PM, Chang C,
Zhao S, Li Y, Zhou L, Cui P, Rabinovitz I, et al: Orphan nuclear
receptor TR3/Nur77 improves wound healing by upregulating the
expression of integrin β4. FASEB J. 29:131–140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kos J, Vižin T, Fonović UP and Pišlar A:
Intracellular signaling by cathepsin X: Molecular mechanisms and
diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities in cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 31:76–83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Basang Z, Ding H, Lu Z, Ning T, Wei
H, Cai H and Ke Y: Latexin expression is downregulated in human
gastric carcinomas and exhibits tumor suppressor potential. BMC
Cancer. 11:1212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xue Z, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zheng J, Zhang P,
Zhou L, Wu L, Shan Y, Ye M, He Y and Cai Z: Latexin exhibits
tumor-suppressor potential in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 35:50–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ni QF, Tian Y, Kong LL, Lu YT, Ding WZ and
Kong LB: Latexin exhibits tumor suppressor potential in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:1364–1372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|