Spandidos Publications style
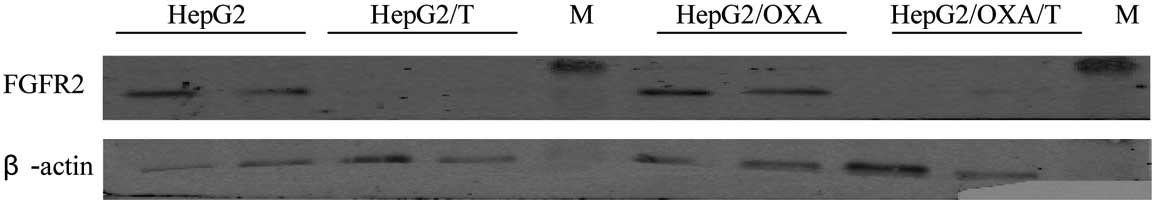
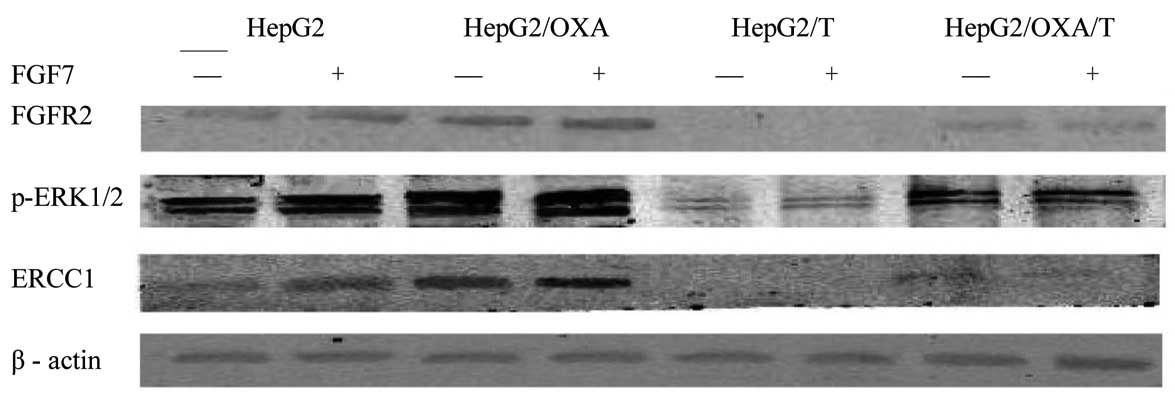
Chen G, Qiu H, Ke S, Hu S, Yu S and Zou S: The fibroblast growth factor receptor 2‑mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway plays is important in regulating excision repair cross‑complementary gene 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Rep 1: 604-608, 2013.
APA
Chen, G., Qiu, H., Ke, S., Hu, S., Yu, S., & Zou, S. (2013). The fibroblast growth factor receptor 2‑mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway plays is important in regulating excision repair cross‑complementary gene 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomedical Reports, 1, 604-608. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2013.96
MLA
Chen, G., Qiu, H., Ke, S., Hu, S., Yu, S., Zou, S."The fibroblast growth factor receptor 2‑mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway plays is important in regulating excision repair cross‑complementary gene 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma". Biomedical Reports 1.4 (2013): 604-608.
Chicago
Chen, G., Qiu, H., Ke, S., Hu, S., Yu, S., Zou, S."The fibroblast growth factor receptor 2‑mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway plays is important in regulating excision repair cross‑complementary gene 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma". Biomedical Reports 1, no. 4 (2013): 604-608. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2013.96