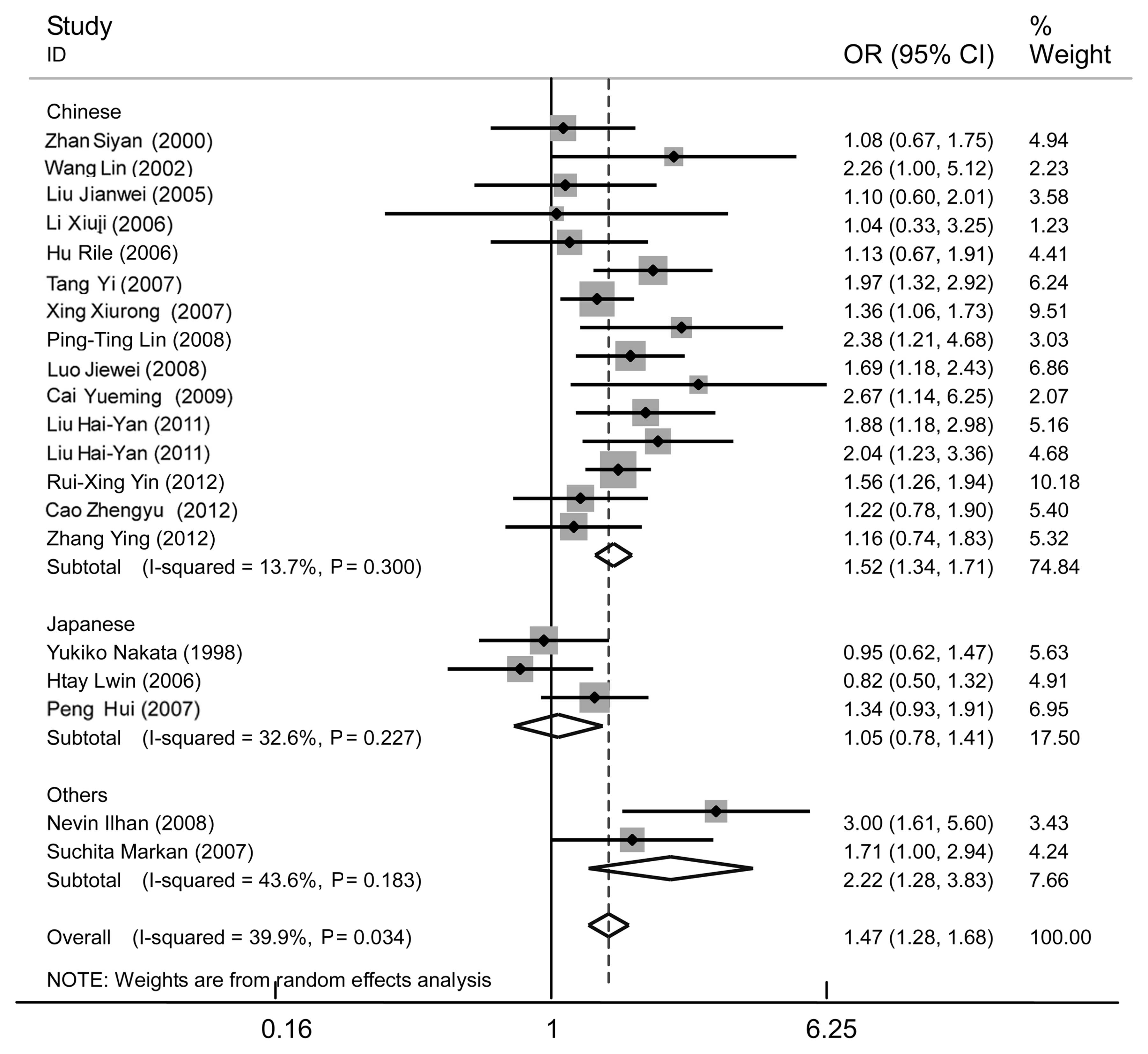
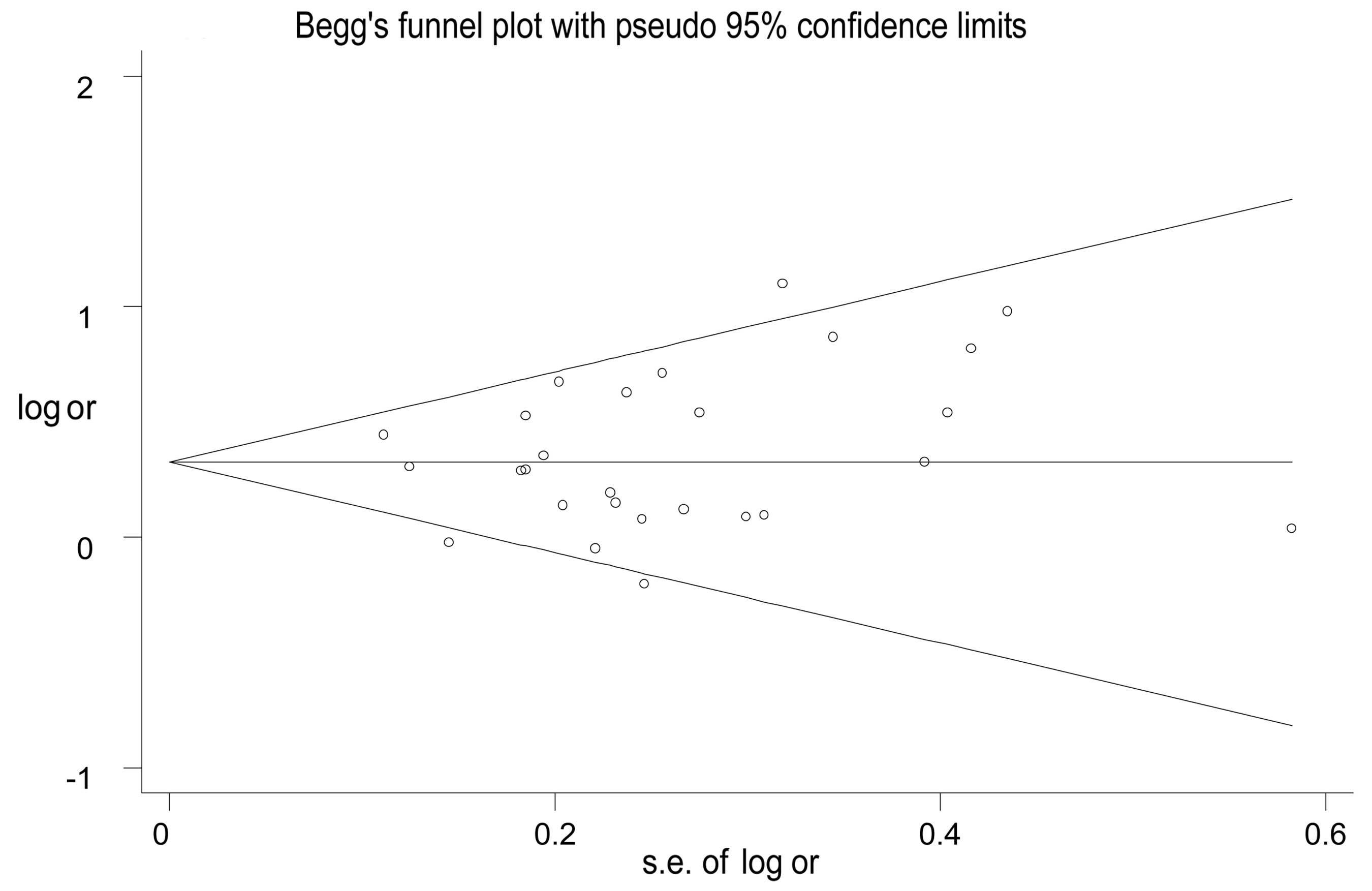
|
1
|
Mein CA, Caulfield MJ, Dobson RJ and
Munroe PB: Genetics of essential hypertension. Hum Mol Genet.
13:R169–R175. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dominiczak AF, Negrin DC, Clark JS,
Brosnan MJ, McBride MW and Alexander MY: Genes and hypertension:
from gene mapping in experimental models to vascular gene transfer
strategies. Hypertension. 35:164–172. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lupton SJ, Chiu CL and Lind JM: A
hypertension gene: are we there yet? Twin Res Hum Genet.
14:295–304. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Men C, Tang K, Lin G, Li J and Zhan Y:
ENOS-G894T polymorphism is a risk factor for essential hypertension
in China. Indian J Biochem Bio. 48:154–157. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goyette P, Pai A, Milos R, et al: Gene
structure of human and mouse methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
(MTHFR). Mamm Genome. 9:652–656. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, et al: A
candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common
mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat Genet.
10:111–113. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tawakol A, Omland T, Gerhard M, Wu JT and
Creager MA: Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia is associated with impaired
endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans. Circulation.
95:1119–1121. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heux S, Morin F, Lea RA, Ovcaric M,
Tajouri L and Griffiths LR: The methylentetrahydrofolate reductase
gene variant (C677T) as a risk factor for essential hypertension in
Caucasians. Hypertens Res. 27:663–667. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li YY: Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
C677T gene polymorphism and coronary artery disease in a Chinese
Han population:a meta-analysis. Metabolism. 61:846–852. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Alam MA, Husain SA, Narang R, Chauhan SS,
Kabra M and Vasisht S: Association of polymorphism in the
thermolabile 5, 10-methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase gene and
hyperhomocysteinemia with coronary artery disease. Mol Cell
Biochem. 310:111–117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Homocysteine Studies Collaboration.
Homocysteine and risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: a
meta-analysis. JAMA. 288:2015–2022. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rodríguez-Esparragón F, Hernández-Perera
O, Rodríguez- Pérez J, et al: The effect of
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T common variant on
hypertensive risk is not solely explained by increased plasma
homocysteine values. Clin Exp Hypertens. 25:209–220.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin PT, Cheng CH, Wei JC and Huang YC: Low
plasma pyridoxal 5′-phosphate concentration and MTHFR 677C-->T
genotypes are associated with increased risk of hypertension. Int J
Vitam Nutr Res. 78:33–40. 2008.
|
|
14
|
Yin RX, Wu JZ, Liu WY, et al: Association
of several lipid-related gene polymorphisms and blood pressure
variation in the Bai Ku Yao population. Am J Hypertens. 25:927–936.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fowdar JY, Lason MV, Szvetko AL, Lea RA
and Griffiths LR: Investigation of homocysteine-pathway-related
variants in essential hypertension. Int J Hypertens.
2012:1909.232012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakata Y, Katsuya T, Takami S, et al:
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism relation to
blood pressure and cerebrovascular disease. Am J Hypertens.
11:1019–1023. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu HY, Ma P and Xu QB: The correlation
between polymorphisms of N5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
and essential hypertension in Han population in Ningxia. Guangdong
Med J. 32:1977–1980. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Chen S, Ma P and Xu Q: The
association between gene polymorphisms of
N5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and essential
hypertension in patients of Ningxia Hui nationality. Tianjin Med J.
39:1095–1098. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Cai YM and Gong WX: Linkage study on
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase single nucleotide polymorphisms
and hypertension in the elderly with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J
Birth Health and Heredity. 17:14–17. 2009.
|
|
20
|
Luo JW, Tang Y, Chen H, Wu XY, Wu YN and
Deng YL: Study on MTHFR C677T polymorphism in hypertensive subjects
with blood stasis syndrome. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med.
31:351–354. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Xing X and Hua Q: Relationships between
the polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677T
and hypertension, cardiac structure and function. Med J Chin PLA.
32:741–744. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Tang Y, Chen H, Wu XY and Luo JW: The
C677T point mutation of N5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
(MTHFR) and essential hypertension. Mol Cardiol China. 7:205–207.
2007.
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Guo H and Li Y: MTHFR gene C 677 T
polymorphisms and variation of plasma homocysteine level in primary
hypertension. Tianjin Med J. 30:579–582. 2002.
|
|
24
|
Ilhan N, Kucuksu M, Kaman D, Ilhan N and
Ozbay Y: The 677 C/T MTHFR polymorphism is associated with
essential hypertension, coronary artery disease, and higher
homocysteine levels. Arch Med Res. 39:125–130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Markan S, Sachdeva M, Sehrawat BS, Kumari
S, Jain S and Khullar M: MTHFR 677 CT/MTHFR 1298 CC genotypes are
associated with increased risk of hypertension in Indians. Mol Cell
Biochem. 302:125–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ng X, Boyd L, Dufficy L, et al: Folate
nutritional genetics and risk for hypertension in an elderly
population sample. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2:1–8. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fridman O, Porcile R, Vanasco V, Junco MN,
Gariglio L, et al: Study on homocysteine levels and
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene variant (C677T) in a
population of Buenos Aires City. Clin Exp Hypertens. 30:574–584.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhan S, Gao YY, Yin X, et al: Elevated
serum homocysteine, MTHFR gene mutataion and essential hypertension
in Chinese. Chin J Hypertens. 8:21–25. 2000.
|
|
29
|
Lwin H, Yokoyama T, Yoshiike N, et al:
Polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene (C677T
MTHFR) is not a confounding factor of the relationship between
serum uric acid level and the prevalence of hypertension in
Japanese men. Circ J. 70:83–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang X, Wang L and Wu G:
Relationship between homocysteine, methylene tetrahydrofolate
reductase C677T polymorphisms and essential hypertension in Kazak
nationality in Xinjiang. J Clin Cardiol (China). 28:570–573.
2012.
|
|
31
|
Cao Z: The Association between
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism and
hypertensive elderly patient with acute myocardial infarction. Chin
J Gerontol. 32:5118–5120. 2012.
|
|
32
|
Li X and Huang W: The analysis of MTHFR
gene polymorphism in patients with renal damage caused by
hypertension and patients with renal parenchymal hypertension. J
Capital Univ Med Sci. 27:497–500. 2006.
|
|
33
|
Hu R, Niu GM, Zhao SG, Zhang CY, Hu RL,
Wang ZG and Jiang MF: The association between gene polymorphisms of
N5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and Mongolian patients
with drimary hypertension. Chin J Hypertension. 14:274–276.
2006.
|
|
34
|
Liu JW, Ye L, Liu J and Li XY: Study on
homocysteine metabolism-related enzymes gene polymorphisms in
elderly essential hypertension patients with peripheral arterial
occlusive disease. Chin J Geriatr. 24:332–335. 2005.
|
|
35
|
Hui P, Nakayama T, Morita A, et al: Common
single nucleotide polymorphisms in Japanese patients with essential
hypertension: aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene as a risk factor
independent of alcohol consumption. Hypertens Res. 30:585–591.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tylicki L, Födinger M, Puttinger H, et al:
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms in essential
hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 18:1442–1448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Benes P, Kanková K, Muzík J, Groch L and
Benedik J: Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism, type
II diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and essential
hypertension in the Czech population. Mol Genet Metab. 73:188–195.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li YY: α-Adducin Gly460Trp gene mutation
and essential hypertension in a Chinese population: a meta-analysis
including 10,960 subjects. PLoS One. 7:e302142012.
|
|
39
|
Li Y: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
4G/5G gene polymorphism and coronary artery disease in the Chinese
Han population: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e335112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ruano-Ravina A, Pérez-Ríos M and
Barros-Dios JM: Population-based versus hospital-based controls:
are they comparable? Gac Sanit. 22:609–613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qian X, Lu Z, Tan M, Liu H and Lu D: A
meta-analysis of association between C677T polymorphism in the
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene and hypertension. Eur J
Hum Genet. 15:1239–1245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Niu WQ, You YG and Qi Y: Strong
association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677T
polymorphism with hypertension and hypertension-in-pregnancy in
Chinese: a meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens. 26:259–267. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Higgins J, Thompson S, Deeks J and Altman
D: Statistical heterogeneity in systematic reviews of clinical
trials: a critical appraisal of guidelines and practice. J Health
Serv Res Policy. 7:51–61. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|