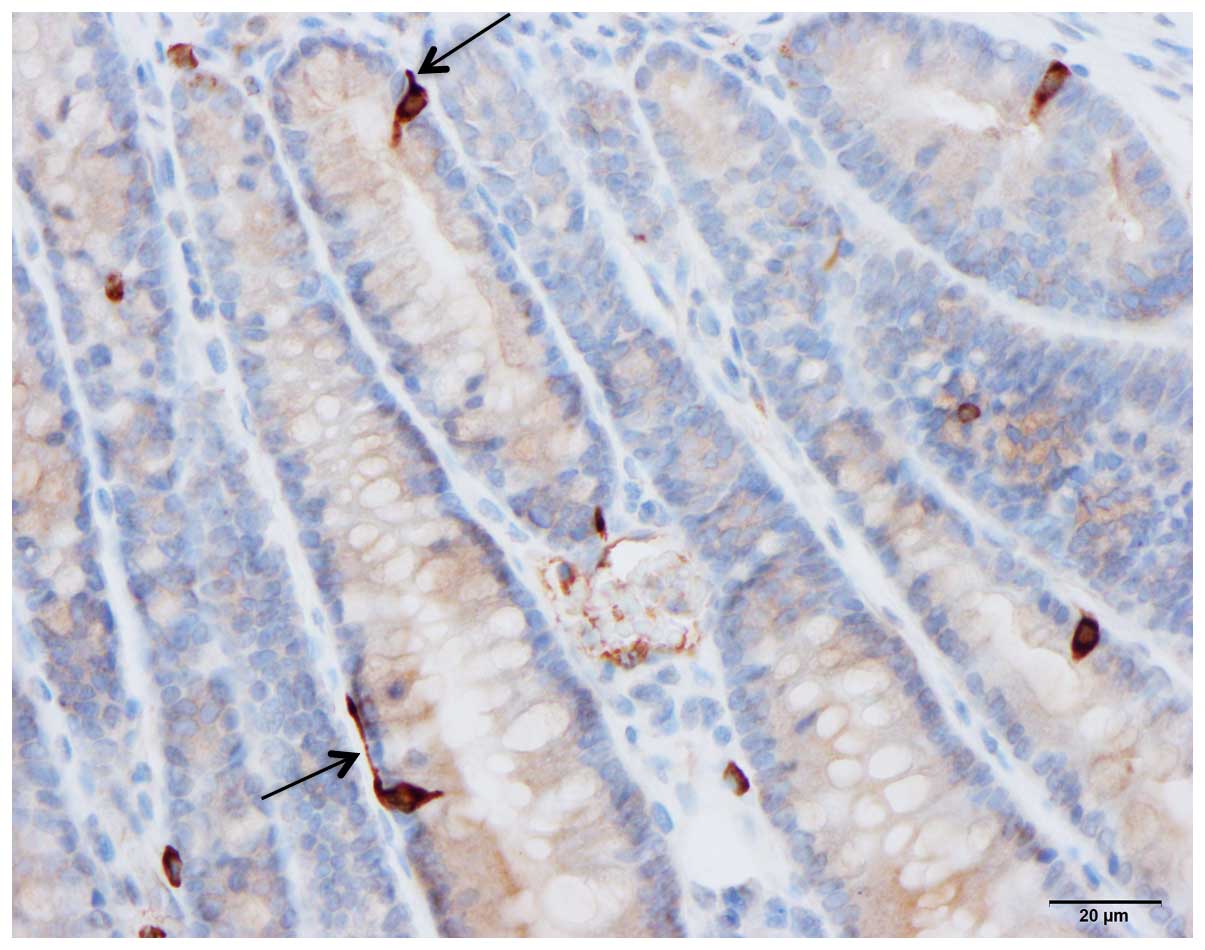
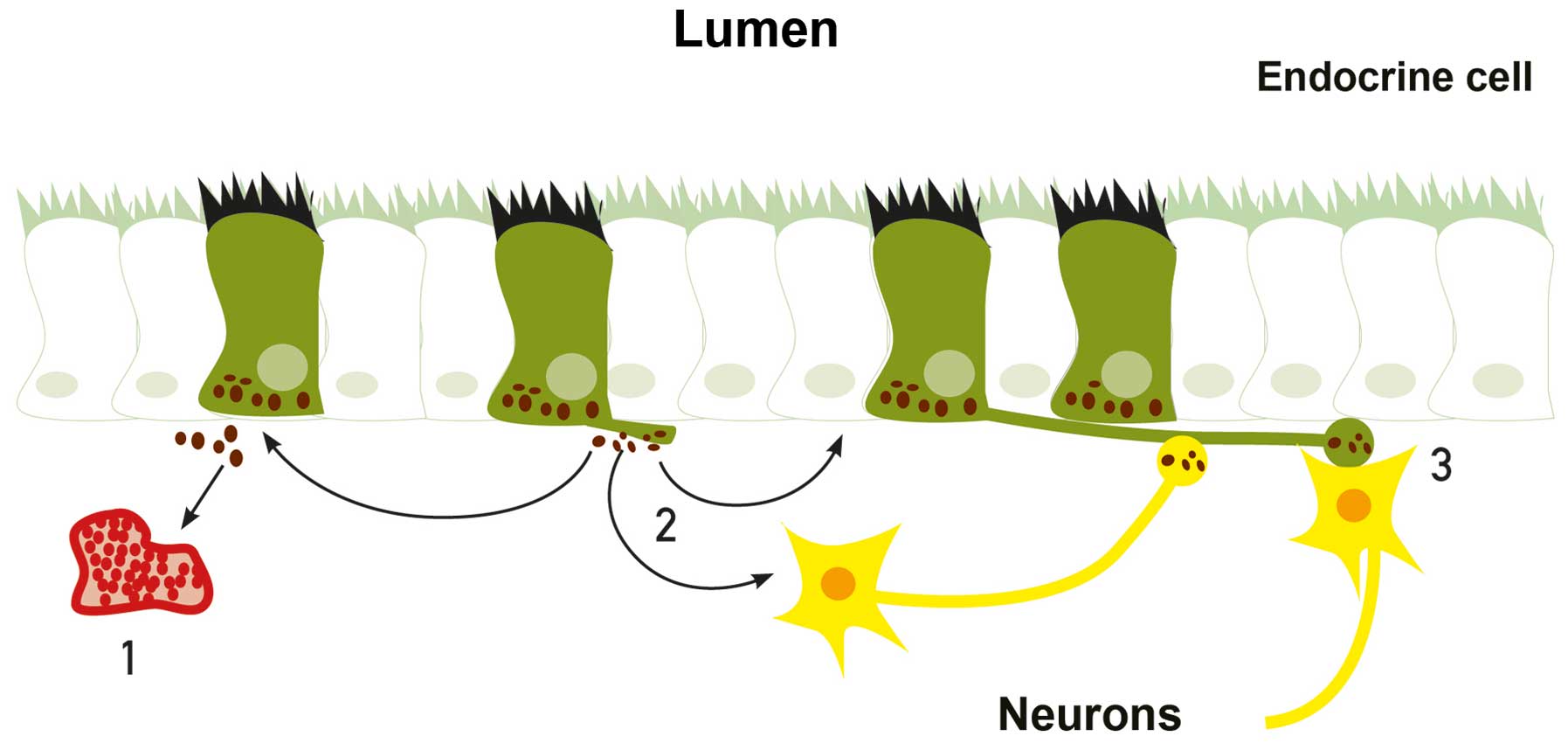
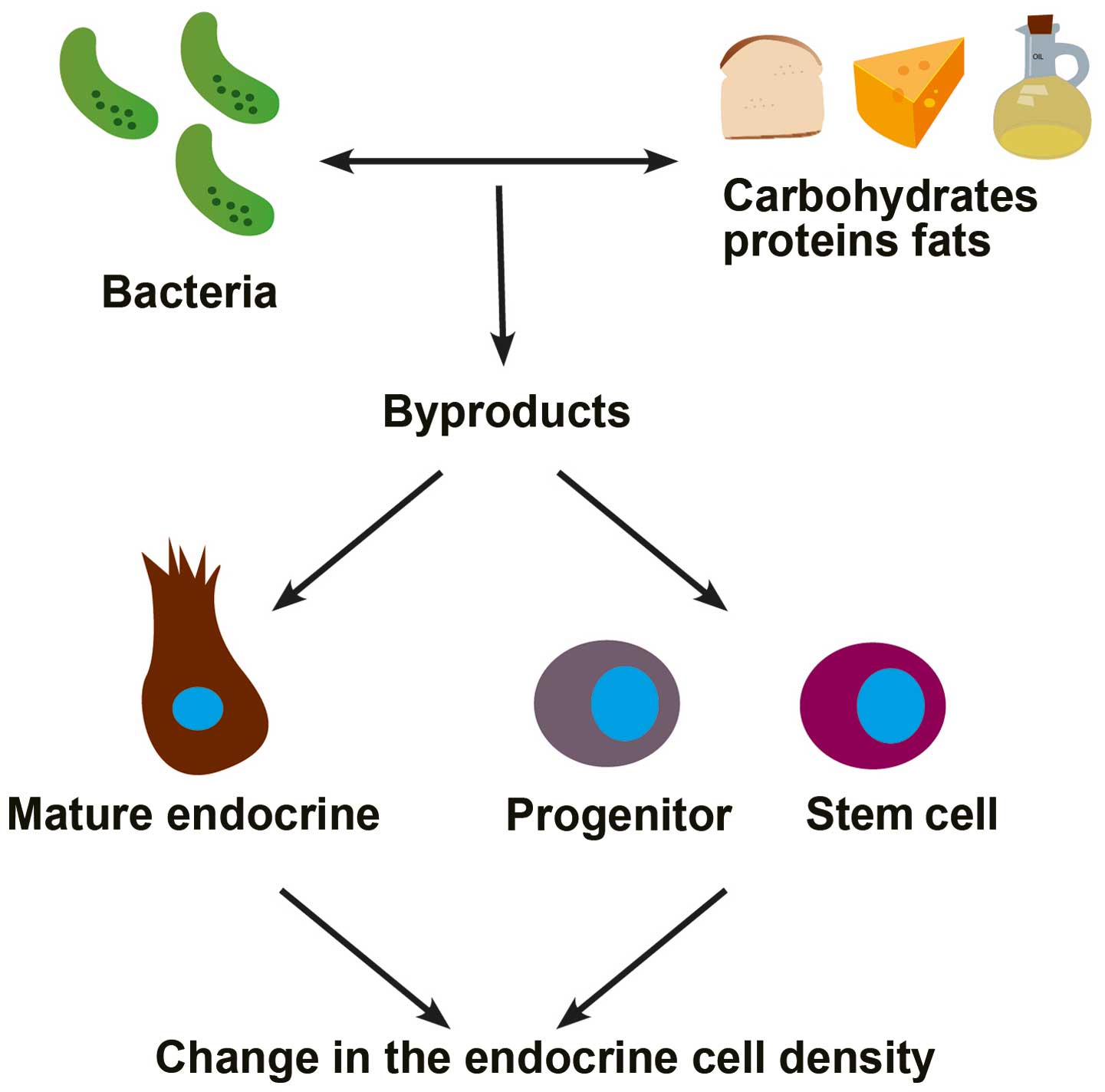
|
1
|
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: Interaction between ingested nutrients
and gut endocrine cells in patients with irritable bowel syndrome
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 34:363–371. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mittermaier C, Dejaco C, Waldhoer T,
Oefferlbauer-Ernst A, Miehsler W, Beier M, Tillinger W, Gangl A and
Moser G: Impact of depressive mood on relapse in patients with
inflammatory bowel disease: A prospective 18-month follow-up study.
Psychosom Med. 66:79–84. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mazzawi T, Gundersen D, Hausken T and
El-Salhy M: Increased gastric chromogranin A cell density following
changes to diets of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med
Rep. 10:2322–2326. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mazzawi T, Gundersen D, Hausken T and
El-Salhy M: Increased chromogranin A cell density in the large
intestine of patients with irritable bowel syndrome after receiving
dietary guidance. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015:8238972015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mazzawi T, Hausken T, Gundersen D and
El-Salhy M: Effect of dietary management on the gastric endocrine
cells in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Clin Nutr.
69:519–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mazzawi T, Hausken T, Gundersen D and
El-Salhy M: Normalization of large intestinal endocrine cells
following dietary management in patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Eur J Clin Nutr. 70:175–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
El-Salhy M, Seim I, Chopin L, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: Irritable bowel syndrome: The role of
gut neuroendocrine peptides. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:2783–2800.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Irritable bowel syndrome: diagnosis, pathogenesis and
treatment options. Nova Science Publishers, Inc. New York, NY:
2012.
|
|
9
|
May CL and Kaestner KH: Gut endocrine cell
development. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 323:70–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gunawardene AR, Corfe BM and Staton CA:
Classification and functions of enteroendocrine cells of the lower
gastrointestinal tract. Int J Exp Pathol. 92:219–231. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Salhy M, Grimelius L, Wilander E,
Ryberg B, Terenius L, Lundberg JM and Tatemoto K:
Immunocytochemical identification of polypeptide YY (PYY) cells in
the human gastrointestinal tract. Histochemistry. 77:15–23. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: Duodenal chromogranin a cell density as
a biomarker for the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014:4628562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH and Hausken T:
Chromogranin A cells in the stomachs of patients with sporadic
irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 10:1753–1757.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
El-Salhy M, Mazzawi T, Gundersen D and
Hausken T: Chromogranin A cell density in the rectum of patients
with irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 6:1223–1225.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
El-Salhy M, Lomholt-Beck B and Hausken T:
Chromogranin A as a possible tool in the diagnosis of irritable
bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 45:1435–1439. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
El-Salhy M, Wendelbo IH and Gundersen D:
Reduced chromogranin A cell density in the ileum of patients with
irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 7:1241–1244. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
El-Salhy M, Ostgaard H, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: The role of diet in the pathogenesis
and management of irritable bowel syndrome (Review). Int J Mol Med.
29:723–731. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
El-Salhy M: Irritable bowel syndrome:
Diagnosis and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5151–5163.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mawe GM, Coates MD and Moses PL: Review
article: Intestinal serotonin signalling in irritable bowel
syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:1067–1076. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wade PR, Chen J, Jaffe B, Kassem IS,
Blakely RD and Gershon MD: Localization and function of a 5-HT
transporter in crypt epithelia of the gastrointestinal tract. J
Neurosci. 16:2352–2364. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gershon MD and Tack J: The serotonin
signaling system: From basic understanding to drug development for
functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology. 132:397–414. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gershon MD: 5-Hydroxytryptamine
(serotonin) in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Opin Endocrinol
Diabetes Obes. 20:14–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gershon MD: Serotonin is a sword and a
shield of the bowel: Serotonin plays offense and defense. Trans Am
Clin Climatol Assoc. 123:268–280; discussion 280. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
El-Salhy M, Mazzawi T, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: The role of peptide YY in
gastrointestinal diseases and disorders (Review). Int J Mol Med.
31:275–282. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dubrasquet M, Bataille D and Gespach C:
Oxyntomodulin (glucagon-37 or bioactive enteroglucagon): A potent
inhibitor of pentagastrin-stimulated acid secretion in rats. Biosci
Rep. 2:391–395. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schjoldager BT, Baldissera FG, Mortensen
PE, Holst JJ and Christiansen J: Oxyntomodulin: A potential hormone
from the distal gut. Pharmacokinetics and effects on gastric acid
and insulin secretion in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 18:499–503. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schjoldager B, Mortensen PE, Myhre J,
Christiansen J and Holst JJ: Oxyntomodulin from distal gut. Role in
regulation of gastric and pancreatic functions. Dig Dis Sci.
34:1411–1419. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dakin CL, Small CJ, Batterham RL, Neary
NM, Cohen MA, Patterson M, Ghatei MA and Bloom SR: Peripheral
oxyntomodulin reduces food intake and body weight gain in rats.
Endocrinology. 145:2687–2695. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wynne K, Park AJ, Small CJ, Patterson M,
Ellis SM, Murphy KG, Wren AM, Frost GS, Meeran K, Ghatei MA, et al:
Subcutaneous oxyntomodulin reduces body weight in overweight and
obese subjects: A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.
Diabetes. 54:2390–2395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Camilleri M: Peripheral mechanisms in
irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. 367:1626–1635. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jianu CS, Fossmark R, Syversen U, Hauso Ø
and Waldum HL: A meal test improves the specificity of chromogranin
A as a marker of neuroendocrine neoplasia. Tumour Biol. 31:373–380.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seim I, El-Salhy M, Hausken T, Gundersen D
and Chopin L: Ghrelin and the brain-gut axis as a pharmacological
target for appetite control. Curr Pharm Des. 18:768–775. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Cortina G, Wu SV, Tran R, Cho JH,
Tsai MJ, Bailey TJ, Jamrich M, Ament ME, Treem WR, et al: Mutant
neurogenin-3 in congenital malabsorptive diarrhea. N Engl J Med.
355:270–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ghia JE, Blennerhassett P, Deng Y, Verdu
EF, Khan WI and Collins SM: Reactivation of inflammatory bowel
disease in a mouse model of depression. Gastroenterology.
136:2280–2288, e1–4. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Spångéus A, Forsgren S and el-Salhy M:
Does diabetic state affect co-localization of peptide YY and
enteroglucagon in colonic endocrine cells? Histol Histopathol.
15:37–41. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pyarokhil AH, Ishihara M, Sasaki M and
Kitamura N: The developmental plasticity of colocalization pattern
of peptide YY and glucagon-like peptide-1 in the endocrine cells of
bovine rectum. Biomed Res. 33:35–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haroon E, Raison CL and Miller AH:
Psychoneuroimmunology meets neuropsychopharmacology: Translational
implications of the impact of inflammation on behavior.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 37:137–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
El-Salhy M, Wilander E and Grimelius L:
Immunocytochemical localization of gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
in the human foetal pancreas. Ups J Med Sci. 87:81–85. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ghia JE, Li N, Wang H, Collins M, Deng Y,
El-Sharkawy RT, Côté F, Mallet J and Khan WI: Serotonin has a key
role in pathogenesis of experimental colitis. Gastroenterology.
137:1649–1660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dryden S, Wang Q, Frankish HM, Pickavance
L and Williams G: The serotonin (5-HT) antagonist methysergide
increases neuropeptide Y (NPY) synthesis and secretion in the
hypothalamus of the rat. Brain Res. 699:12–18. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sandström O and El-Salhy M: Ageing and
endocrine cells of human duodenum. Mech Ageing Dev. 108:39–48.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
El-Salhy M: Ghrelin in gastrointestinal
diseases and disorders: A possible role in the pathophysiology and
clinical implications (Review). Int J Mol Med. 24:727–732. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tolhurst G, Reimann F and Gribble FM:
Intestinal sensing of nutrients. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 209:309–335.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee J, Cummings BP, Martin E, Sharp JW,
Graham JL, Stanhope KL, Havel PJ and Raybould HE: Glucose sensing
by gut endocrine cells and activation of the vagal afferent pathway
is impaired in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 302:R657–R666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Parker HE, Reimann F and Gribble FM:
Molecular mechanisms underlying nutrient-stimulated incretin
secretion. Expert Rev Mol Med. 12:e12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Raybould HE: Nutrient sensing in the
gastrointestinal tract: Possible role for nutrient transporters. J
Physiol Biochem. 64:349–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
San Gabriel A, Nakamura E, Uneyama H and
Torii K: Taste, visceral information and exocrine reflexes with
glutamate through umami receptors. J Med Invest. 56:209–217. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rudholm T, Wallin B, Theodorsson E,
Näslund E and Hellström PM: Release of regulatory gut peptides
somatostatin, neurotensin and vasoactive intestinal peptide by acid
and hyperosmolal solutions in the intestine in conscious rats.
Regul Pept. 152:8–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sternini C, Anselmi L and Rozengurt E:
Enteroendocrine cells: A site of ‘taste’ in gastrointestinal
chemosensing. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 15:73–78. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sternini C: Taste receptors in the
gastrointestinal tract. IV. Functional implications of bitter taste
receptors in gastrointestinal chemosensing. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 292:G457–G461. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Buchan AM: Nutrient Tasting and signaling
mechanisms in the gut III. Endocrine cell recognition of luminal
nutrients. Am J Physiol. 277:G1103–G1107. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Montero-Hadjadje M, Elias S, Chevalier L,
Benard M, Tanguy Y, Turquier V, Galas L, Yon L, Malagon MM,
Driouich A, et al: Chromogranin A promotes peptide hormone sorting
to mobile granules in constitutively and regulated secreting cells:
Role of conserved N- and C-terminal peptides. J Biol Chem.
284:12420–12431. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shooshtarizadeh P, Zhang D, Chich JF,
Gasnier C, Schneider F, Haïkel Y, Aunis D and Metz-Boutigue MH: The
antimicrobial peptides derived from chromogranin/secretogranin
family, new actors of innate immunity. Regul Pept. 165:102–110.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Reber SO, Obermeier F, Straub RH, Falk W
and Neumann ID: Chronic intermittent psychosocial stress (social
defeat/overcrowding) in mice increases the severity of an acute
DSS-induced colitis and impairs regeneration. Endocrinology.
147:4968–4976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Milde AM and Murison R: A study of the
effects of restraint stress on colitis induced by dextran sulphate
sodium in singly housed rats. Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 37:140–150.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Furness JB, Kunze WA and Clerc N: Nutrient
tasting and signaling mechanisms in the gut. II. The intestine as a
sensory organ: Neural, endocrine, and immune responses. Am J
Physiol. 277:G922–G928. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hassani H, Lucas G, Rozell B and Ernfors
P: Attenuation of acute experimental colitis by preventing NPY Y1
receptor signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
288:G550–G556. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cani PD, Everard A and Duparc T: Gut
microbiota, enteroendocrine functions and metabolism. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 13:935–940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cani PD, Hoste S, Guiot Y and Delzenne NM:
Dietary non-digestible carbohydrates promote L-cell differentiation
in the proximal colon of rats. Br J Nutr. 98:32–37. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Petitto JM, Huang Z and McCarthy DB:
Molecular cloning of NPY-Y1 receptor cDNA from rat splenic
lymphocytes: Evidence of low levels of mRNA expression and
[125I]NPY binding sites. J Neuroimmunol. 54:81–86. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
De la Fuente M, Bernaez I, Del Rio M and
Hernanz A: Stimulation of murine peritoneal macrophage functions by
neuropeptide Y and peptide YY. Involvement of protein kinase C.
Immunology. 80:259–265. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shibata M, Hisajima T, Nakano M, Goris RC
and Funakoshi K: Morphological relationships between peptidergic
nerve fibers and immunoglobulin A-producing lymphocytes in the
mouse intestine. Brain Behav Immun. 22:158–166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Painsipp E, Herzog H, Sperk G and Holzer
P: Sex-dependent control of murine emotional-affective behaviour in
health and colitis by peptide YY and neuropeptide Y. Br J
Pharmacol. 163:1302–1314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rindi G, Inzani F and Solcia E: Pathology
of gastrointestinal disorders. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
39:713–727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cummings DE and Overduin J:
Gastrointestinal regulation of food intake. J Clin Invest.
117:13–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bertrand PP: The cornucopia of intestinal
chemosensory transduction. Front Neurosci. 3:482009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bertrand PP and Bertrand RL: Serotonin
release and uptake in the gastrointestinal tract. Auton Neurosci.
153:47–57. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
El-Salhy M, Grimelius L, Wilander E,
Abu-Sinna G and Lundqvist G: Histological and immunohistochemical
studies of the endocrine cells of the gastrointestinal mucosa of
the toad (Bufo regularis). Histochemistry. 71:53–65. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sandstrom O: Age-related changes in the
neuroendocrine system of the gut. Umea Univ Med Diss. 617:1–46.
1999.
|
|
70
|
Bohórquez DV, Chandra R, Samsa LA, Vigna
SR and Liddle RA: Characterization of basal pseudopod-like
processes in ileal and colonic PYY cells. J Mol Histol. 42:3–13.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Gustafsson BI, Bakke I, Hauso Ø, Kidd M,
Modlin IM, Fossmark R, Brenna E and Waldum HL: Parietal cell
activation by arborization of ECL cell cytoplasmic projections is
likely the mechanism for histamine induced secretion of
hydrochloric acid. Scand J Gastroenterol. 46:531–537. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gustafsson BI, Bakke I, Tømmerås K and
Waldum HL: A new method for visualization of gut mucosal cells,
describing the enterochromaffin cell in the rat gastrointestinal
tract. Scand J Gastroenterol. 41:390–395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pang XH, Li TK, Xie Q, He FQ, Cui J, Chen
YQ, Huang XL and Gan HT: Amelioration of dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis by neuropeptide Y antisense
oligodeoxynucleotide. Int J Colorectal Dis. 25:1047–1053. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bohórquez DV, Samsa LA, Roholt A,
Medicetty S, Chandra R and Liddle RA: An enteroendocrine
cell-enteric glia connection revealed by 3D electron microscopy.
PLoS One. 9:e898812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bohórquez DV, Shahid RA, Erdmann A, Kreger
AM, Wang Y, Calakos N, Wang F and Liddle RA: Neuroepithelial
circuit formed by innervation of sensory enteroendocrine cells. J
Clin Invest. 125:782–786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
El-Salhy M: On the phylogeny of the
gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) neuroendocrine system. Acta Uni
Uppsal. 385:1–39. 1981.
|
|
77
|
El-Salhy M, Abou-el-Ela R, Falkmer S,
Grimelius L and Wilander E: Immunohistochemical evidence of
gastro-entero-pancreatic neurohormonal peptides of vertebrate type
in the nervous system of the larva of a dipteran insect, the
hoverfly, Eristalis aeneus. Regul Pept. 1:187–204. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
El-Salhy M, Falkmer S, Kramer KJ and
Speirs RD: Immunohistochemical investigations of neuropeptides in
the brain, corpora cardiaca, and corpora allata of an adult
lepidopteran insect, Manduca sexta (L). Cell Tissue Res.
232:295–317. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
El-Salhy M, Falkmer S, Kramer KJ and
Speirs RD: Immunocytochemical evidence for the occurrence of
insulin in the frontal ganglion of a Lepidopteran insect, the
tobacco hornworm moth, Manduca sexta L. Gen Comp Endocrinol.
54:85–88. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Mazzawi T, Hausken T, Gundersen D and
El-Salhy M: Effects of dietary guidance on the symptoms, quality of
life and habitual dietary intake of patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 8:845–852. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ostgaard H, Hausken T, Gundersen D and
El-Salhy M: Diet and effects of diet management on quality of life
and symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med
Rep. 5:1382–1390. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
García-Martínez JM, Chocarro-Calvo A, De
la Vieja A and García-Jiménez C: Insulin drives glucose-dependent
insulinotropic peptide expression via glucose-dependent regulation
of FoxO1 and LEF1/β-catenin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:1141–1150.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
García-Martínez JM, Chocarro-Calvo A, Moya
CM and García-Jiménez C: WNT/beta-catenin increases the production
of incretins by entero-endocrine cells. Diabetologia. 52:1913–1924.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Freeland KR, Wilson C and Wolever TM:
Adaptation of colonic fermentation and glucagon-like peptide-1
secretion with increased wheat fibre intake for 1 year in
hyperinsulinaemic human subjects. Br J Nutr. 103:82–90. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Korner J, Bessler M, Inabnet W, Taveras C
and Holst JJ: Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide-1 and blunted
glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide secretion are associated
with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not adjustable gastric banding.
Surg Obes Relat Dis. 3:597–601. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|