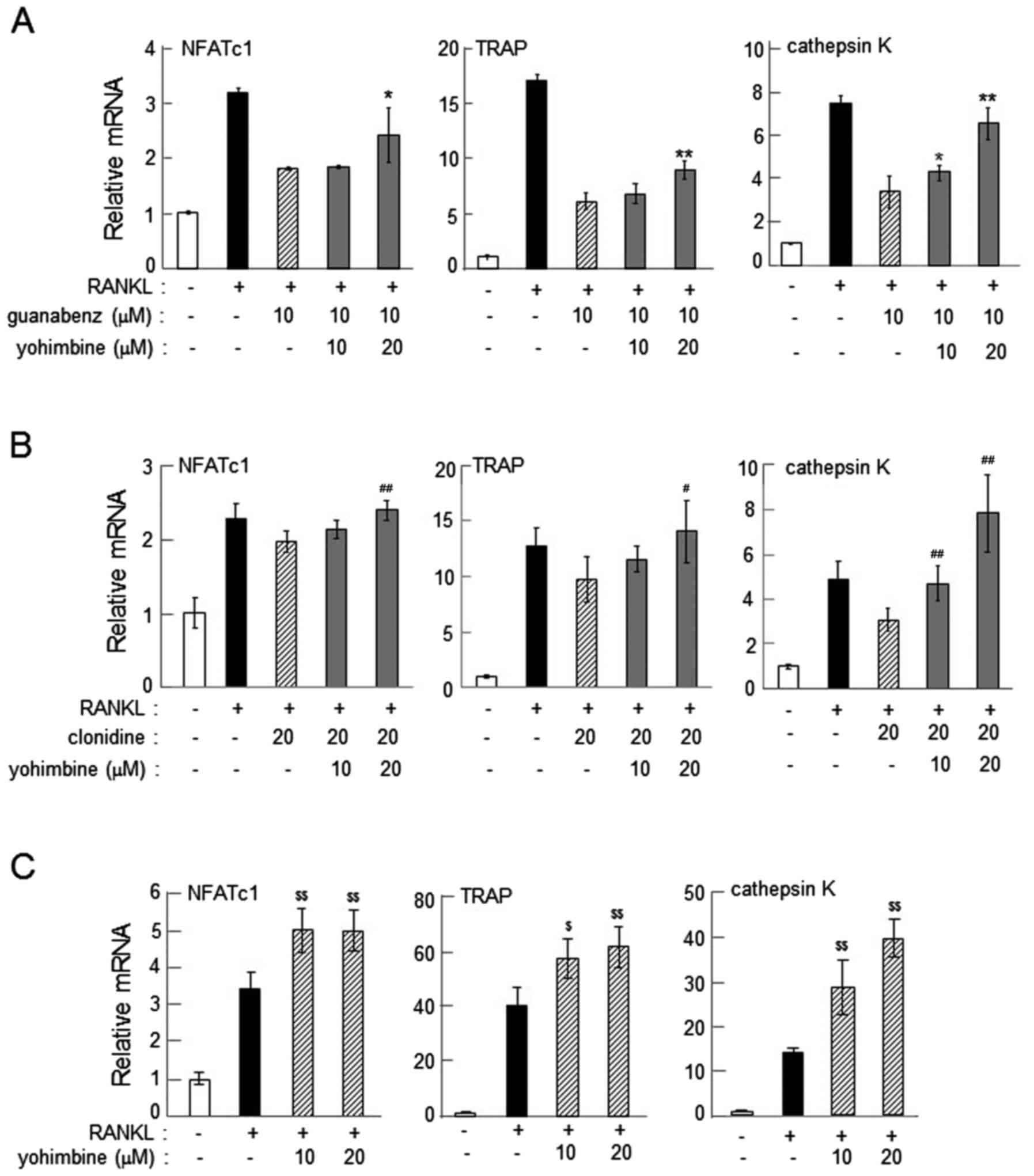
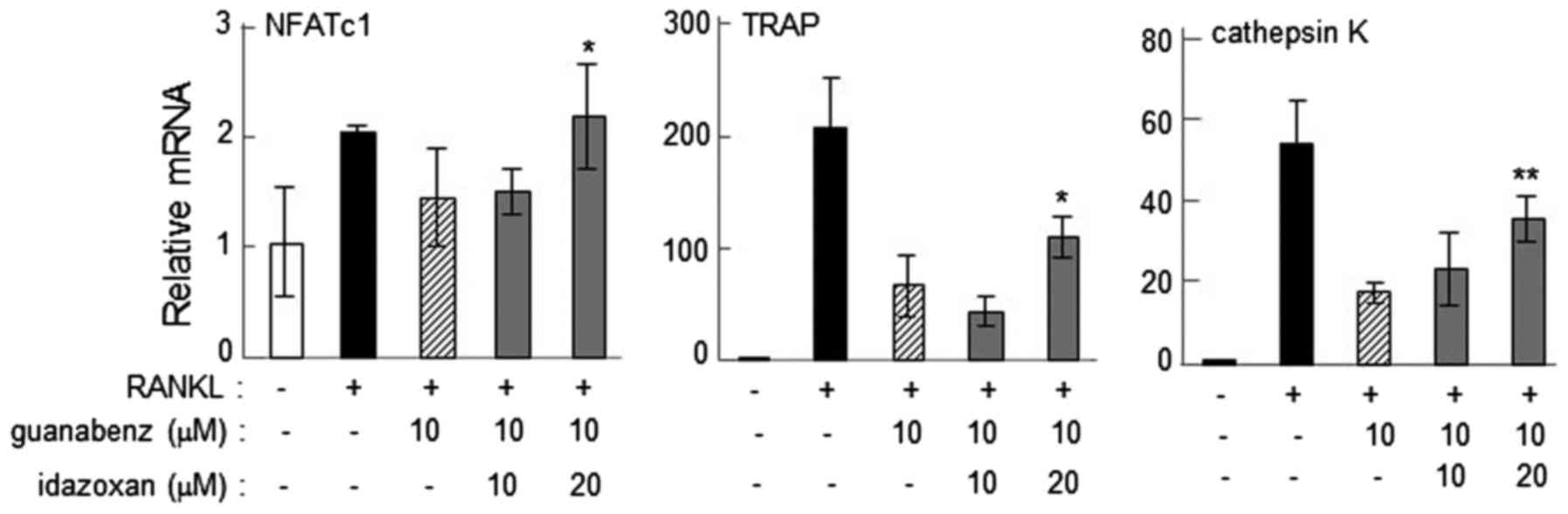
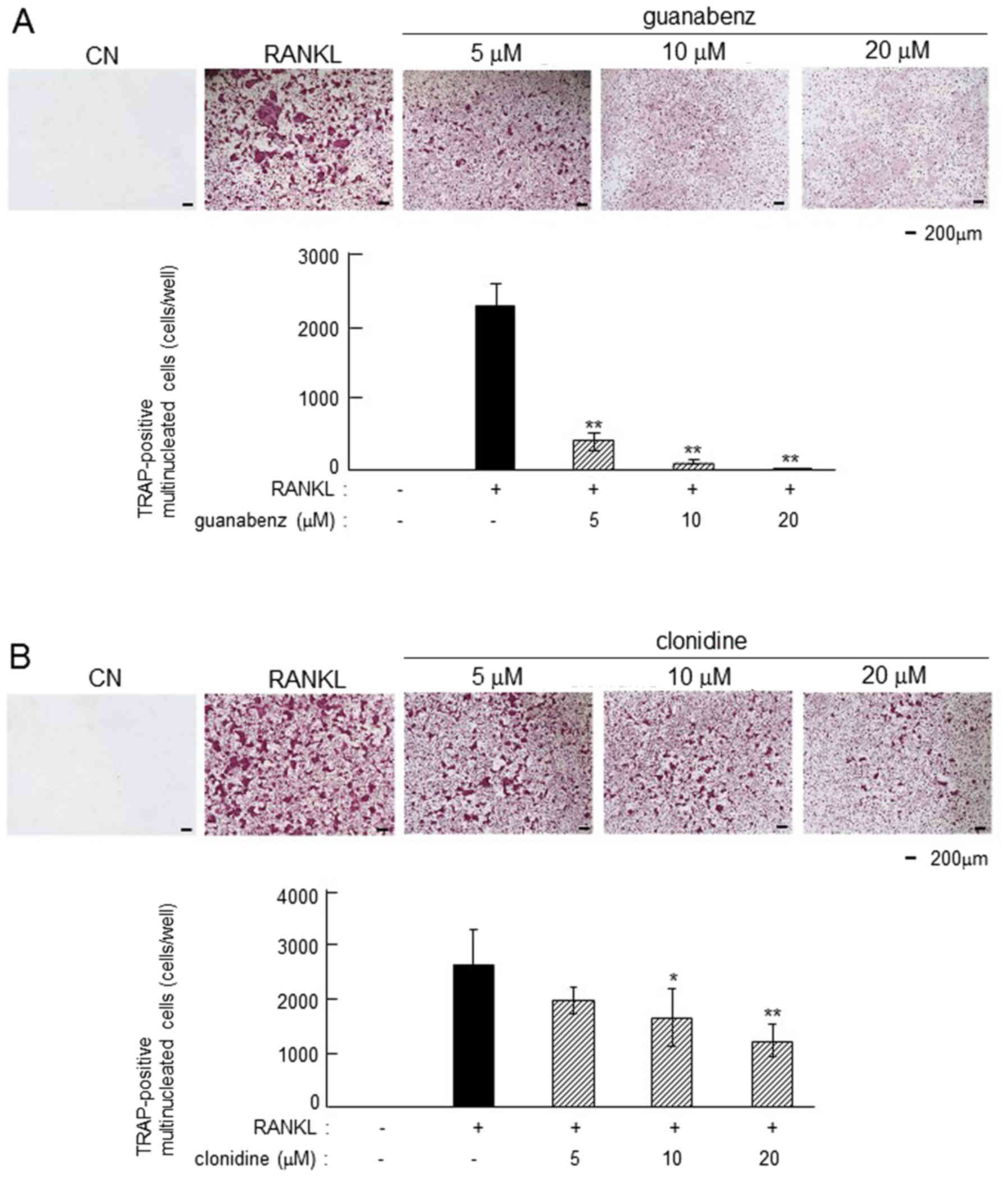
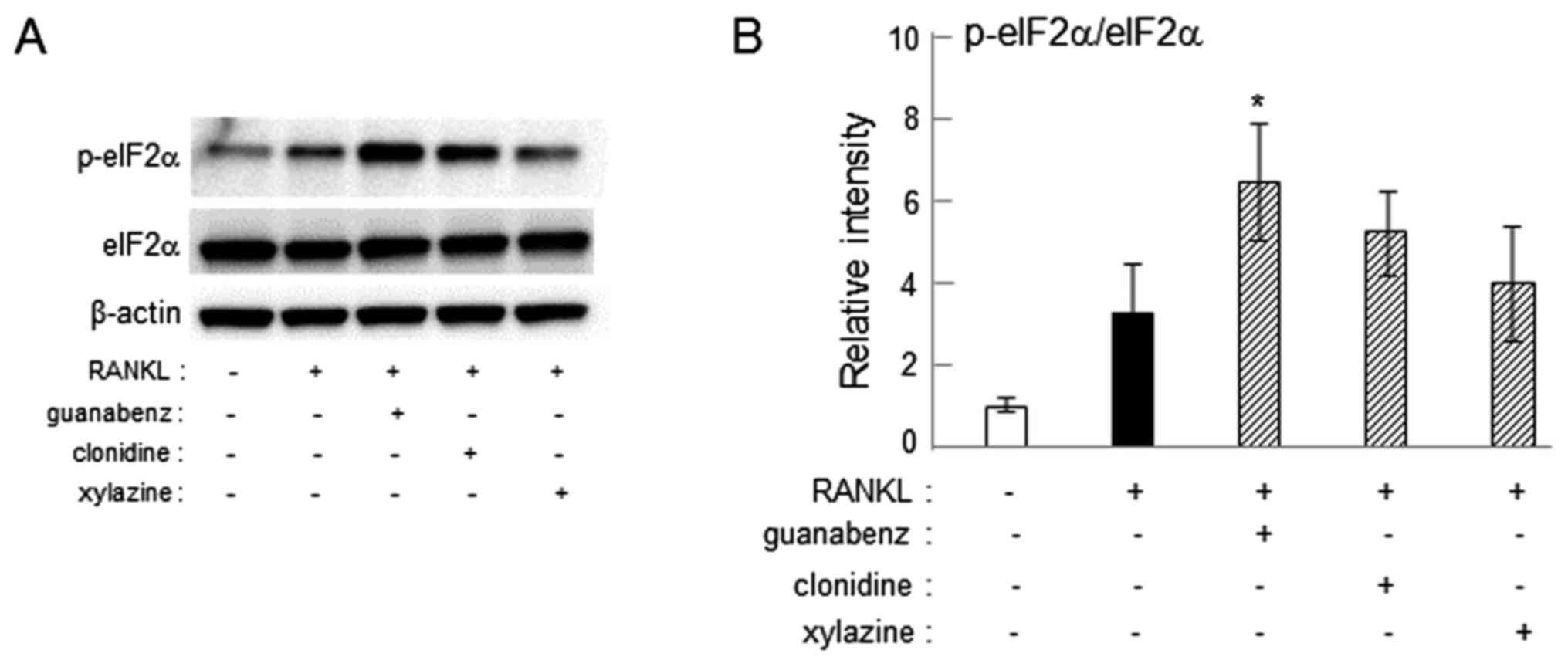
|
1
|
Karsenty G: Convergence between bone and
energy homeostases: Leptin regulation of bone mass. Cell Metab.
4:341–348. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Togari A, Arai M and Kondo A: The role of
the sympathetic nervous system in controlling bone metabolism.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 9:931–940. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Elefteriou F, Campbell P and Ma Y: Control
of bone remodeling by the peripheral sympathetic nervous system.
Calcif Tissue Int. 94:140–151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Niedermair T, Kuhn V, Doranehgard F,
Stange R, Wieskötter B, Beckmann J, Salmen P, Springorum H-R,
Straub RH, Zimmer A, et al: Absence of substance P and the
sympathetic nervous system impact on bone structure and chondrocyte
differentiation in an adult model of endochondral ossification.
Matrix Biol. 38:22–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Togari A: Adrenergic regulation of bone
metabolism: Possible involvement of sympathetic innervation of
osteoblastic and osteoclastic cells. Microsc Res Tech. 58:77–84.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arai M, Nagasawa T, Koshihara Y, Yamamoto
S and Togari A: Effects of beta-adrenergic agonists on
bone-resorbing activity in human osteoclast-like cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1640:137–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fonseca TL, Jorgetti V, Costa CC, Capelo
LP, Covarrubias AE, Moulatlet AC, Teixeira MB, Hesse E, Morethson
P, Beber EH, et al: Double disruption of α2A- and α2C-adrenoceptors
results in sympathetic hyperactivity and high-bone-mass phenotype.
J Bone Miner Res. 26:591–603. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kodama D and Togari A: Noradrenaline
stimulates cell proliferation by suppressing potassium channels via
G(i/o) -protein-coupled α(1B) -adrenoceptors in human osteoblasts.
Br J Pharmacol. 168:1230–1239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanaka K, Hirai T, Kodama D, Kondo H,
Hamamura K and Togari A: α1B-Adrenoceptor signalling regulates bone
formation through the up-regulation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein δ expression in osteoblasts. Br J Pharmacol. 173:1058–1069.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kajimura D, Hinoi E, Ferron M, Kode A,
Riley KJ, Zhou B, Guo XE and Karsenty G: Genetic determination of
the cellular basis of the sympathetic regulation of bone mass
accrual. J Exp Med. 208:841–851. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McDonald SJ, Dooley PC, McDonald AC,
Djouma E, Schuijers JA, Ward AR and Grills BL: α(1) adrenergic
receptor agonist, phenylephrine, actively contracts early rat rib
fracture callus ex vivo. J Orthop Res. 29:740–745. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kondo H, Takeuchi S and Togari A:
β-Adrenergic signaling stimulates osteoclastogenesis via reactive
oxygen species. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 304:E507–E515. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takeuchi T, Tsuboi T, Arai M and Togari A:
Adrenergic stimulation of osteoclastogenesis mediated by expression
of osteoclast differentiation factor in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 61:579–586. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nishiura T and Abe K: α1-adrenergic
receptor stimulation induces the expression of receptor activator
of nuclear factor kappaB ligand gene via protein kinase C and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways in MC3T3-E1
osteoblast-like cells. Arch Oral Biol. 52:778–785. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aitken SJ, Landao-Bassonga E, Ralston SH
and Idris AI: Beta2-adrenoreceptor ligands regulate osteoclast
differentiation in vitro by direct and indirect mechanisms. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 482:96–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hein L, Altman JD and Kobilka BK: Two
functionally distinct α2-adrenergic receptors regulate sympathetic
neurotransmission. Nature. 402:181–184. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
MacMillan LB, Hein L, Smith MS, Piascik MT
and Limbird LE: Central hypotensive effects of the
alpha2a-adrenergic receptor subtype. Science. 273:801–803. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lakhlani PP, MacMillan LB, Guo TZ, McCool
BA, Lovinger DM, Maze M and Limbird LE: Substitution of a mutant
α2a-adrenergic receptor via ‘hit and run’ gene targeting reveals
the role of this subtype in sedative, analgesic, and
anesthetic-sparing responses in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:9950–9955. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fagerholm V, Haaparanta M and Scheinin M:
α2-adrenoceptor regulation of blood glucose homeostasis. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 108:365–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Albarrán-Juárez J, Gilsbach R, Piekorz RP,
Pexa K, Beetz N, Schneider J, Nürnberg B, Birnbaumer L and Hein L:
Modulation of α2-adrenoceptor functions by heterotrimeric Galphai
protein isoforms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 331:35–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Storch U, Straub J, Erdogmus S, Gudermann
T, Mederos Y and Schnitzler M: Dynamic monitoring of
Gi/o-protein-mediated decreases of intracellular cAMP by FRET-based
Epac sensors. Pflugers Arch. 469:725–737. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamamura K, Chen A, Nishimura A, Tanjung
N, Sudo A and Yokota H: Predicting and validating the pathway of
Wnt3a-driven suppression of osteoclastogenesis. Cell Signal.
26:2358–2369. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hamamura K, Tanjung N and Yokota H:
Suppression of osteoclastogenesis through phosphorylation of
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha. J Bone Miner
Metab. 31:618–628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hamamura K, Chen A, Tanjung N, Takigawa S,
Sudo A and Yokota H: In vitro and in silico analysis of an
inhibitory mechanism of osteoclastogenesis by salubrinal and
guanabenz. Cell Signal. 27:353–362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamamura K, Tanjung N, Chen A, Yokota H
and Togari A: Suppression of osteoclastogenesis via upregulation of
Zfyve21 and Ddit4 by salubrinal and guanabenz. Oral Therap
Pharmacol. 35:127–135. 2016.
|
|
27
|
Wade SM, Lan K, Moore DJ and Neubig RR:
Inverse agonist activity at the alpha(2A)-adrenergic receptor. Mol
Pharmacol. 59:532–542. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Strange PG: Mechanisms of inverse agonism
at G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 23:89–95.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Milligan G: Constitutive activity and
inverse agonists of G protein-coupled receptors: A current
perspective. Mol Pharmacol. 64:1271–1276. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Soudijn W, van Wijngaarden I and Ijzerman
AP: Structure-activity relationships of inverse agonists for
G-protein-coupled receptors. Med Res Rev. 25:398–426. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cotecchia S: Constitutive activity and
inverse agonism at the α1adrenoceptors. Biochem Pharmacol.
73:1076–1083. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He W, Wilder T and Cronstein BN:
Rolofylline, an adenosine A1 receptor antagonist, inhibits
osteoclast differentiation as an inverse agonist. Br J Pharmacol.
170:1167–1176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mediero A, Perez-Aso and Cronstein BN:
Activation of EPAC1/2 is essential for osteoclast formation by
modulating NFκB nuclear translocation and actin cytoskeleton
rearrangements. FASEB J. 28:4901–4913. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Rooij J, Zwartkruis FJ, Verheijen MH,
Cool RH, Nijman SM, Wittinghofer A and Bos JL: Epac is a Rap1
guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor directly activated by cyclic
AMP. Nature. 396:474–477. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ferrero JJ, Alvarez AM, Ramírez-Franco J,
Godino MC, Bartolomé-Martín D, Aguado C, Torres M, Luján R, Ciruela
F and Sánchez-Prieto J: β-Adrenergic receptors activate exchange
protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac), translocate Munc13-1,
and enhance the Rab3A-RIM1α interaction to potentiate glutamate
release at cerebrocortical nerve terminals. J Biol Chem.
288:31370–31385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aerts I, Grobben B, Van Ostade X and
Slegers H: Cyclic AMP-dependent down regulation of ecto-nucleotide
pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (NPP1) in rat C6 glioma. Eur J
Pharmacol. 654:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Inda C, Bonfiglio JJ, Dos Santos Claro PA,
Senin SA, Armando NG, Deussing JM and Silberstein S: cAMP-dependent
cell differentiation triggered by activated CRHR1 in hippocampal
neuronal cells. Sci Rep. 7:19442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
El-Mas MM and Abdel-Rahman AA: Clonidine
diminishes c-jun gene expression in the cardiovascular sensitive
areas of the rat brainstem. Brain Res. 856:245–249. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Limonard EJ, Schoenmaker T, de Vries TJ,
Tanck MW, Heijboer AC, Endert E, Fliers E, Everts V and Bisschop
PH: Clonidine increases bone resorption in humans. Osteoporos Int.
27:1063–1071. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|