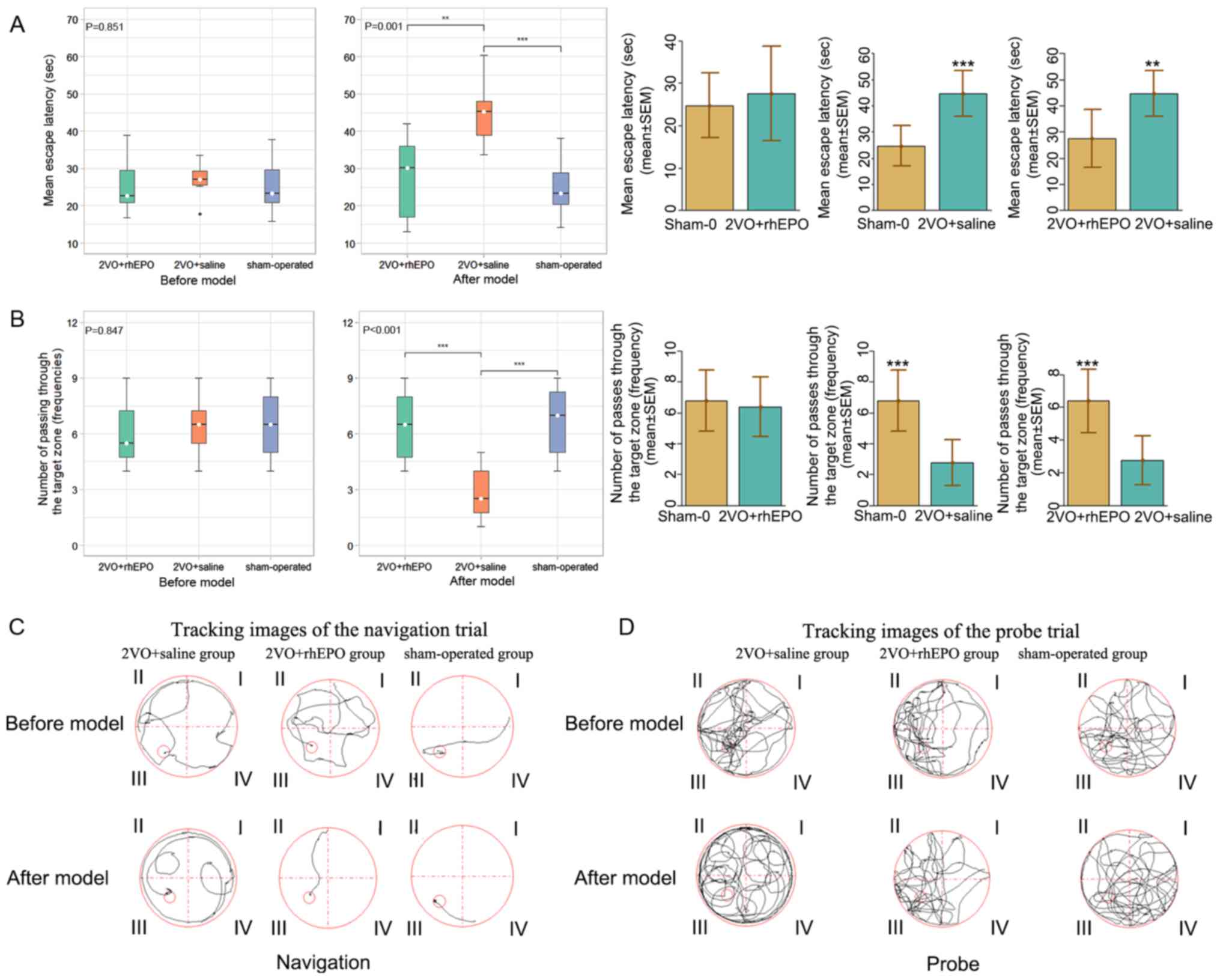
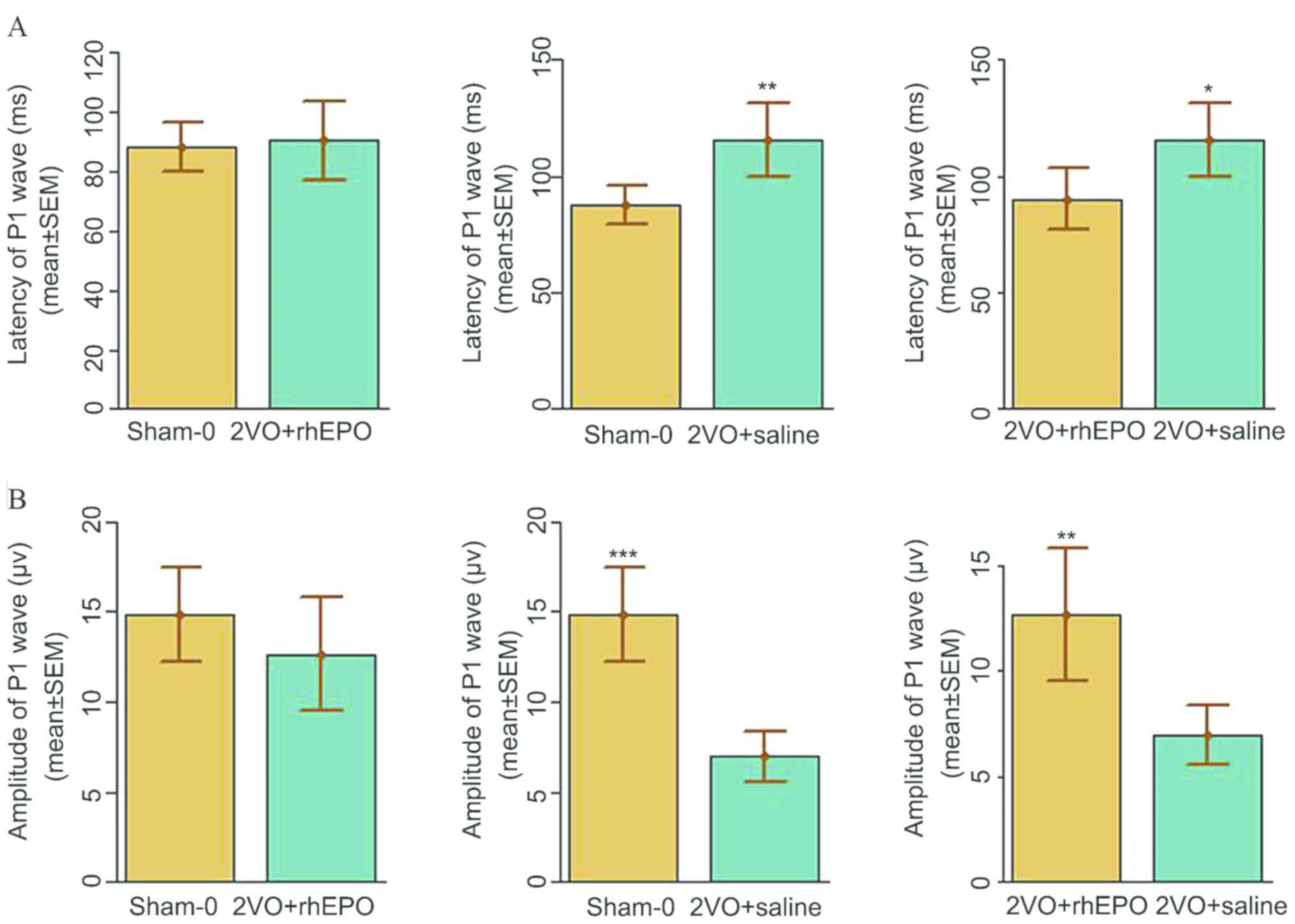
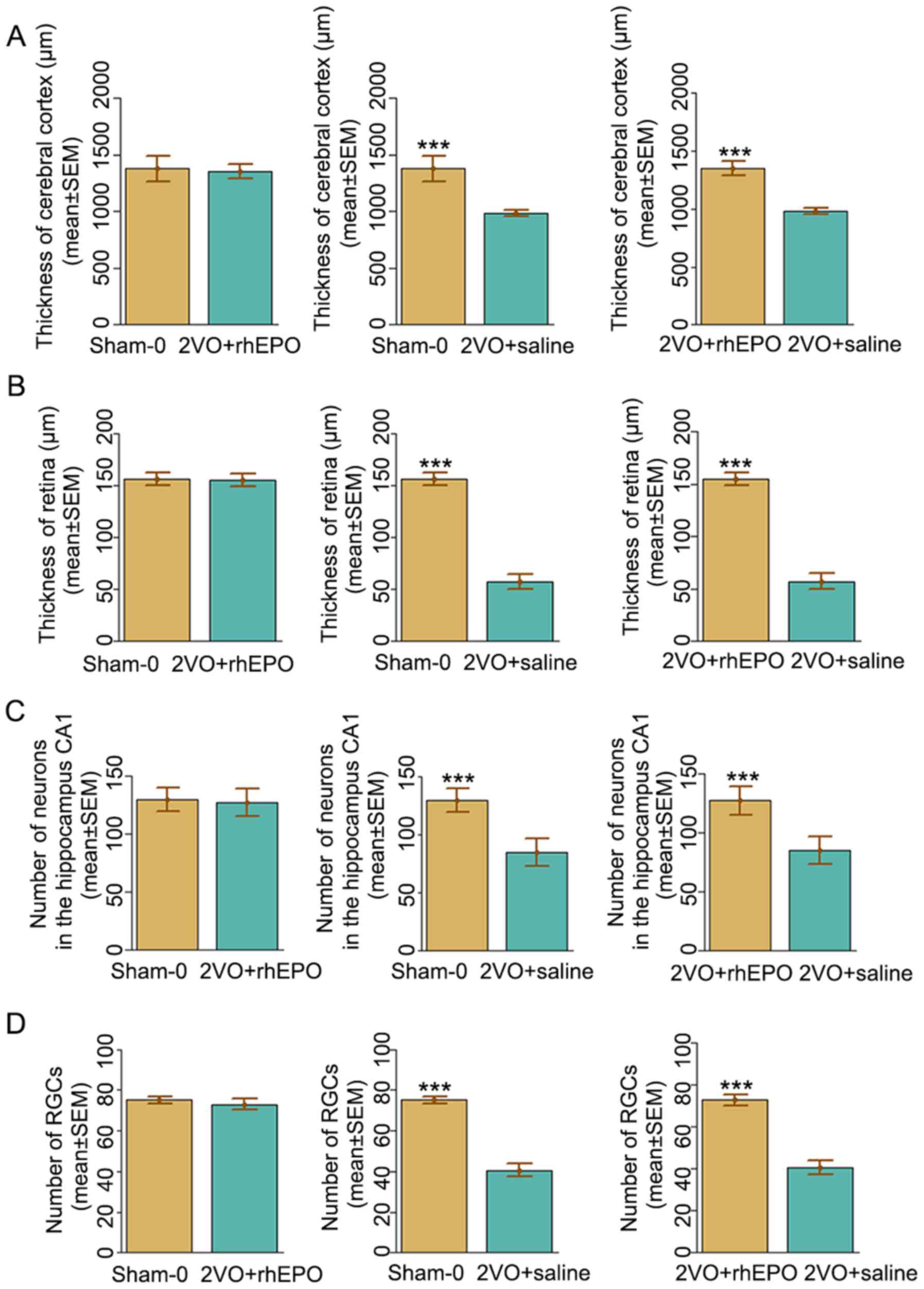
|
1
|
Miller JL, Church TJ, Leonoudakis D,
Lariosa-Willingham K, Frigon NL, Tettenborn CS, Spencer JR and
Punnonen J: Discovery and characterization of nonpeptidyl agonists
of the tissue-protective erythropoietin receptor. Mol Pharmacol.
88:357–367. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rainville N, Jachimowicz E and Wojchowski
DM: Targeting EPO and EPO receptor pathways in anemia and
dysregulated erythropoiesis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 20:287–301.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Miller JL, Rai M, Frigon NL, Pandolfo M,
Punnonen J and Spencer JR: Erythropoietin and small molecule
agonists of the tissue-protective erythropoietin receptor increase
FXN expression in neuronal cells in vitro and in Fxn-deficient KIKO
mice in vivo. Neuropharmacology. 123:34–45. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Wang X, Su H, Han Z, Yu H, Wang D,
Jiang R, Liu Z and Zhang J: Recombinant human erythropoietin
improves the neurofunctional recovery of rats following traumatic
brain injury via an increase in circulating endothelial progenitor
cells. Transl Stroke Res. 6:50–59. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ren Q, Zhang XF and Yang JY:
Erythropoietin reduces white matter damage in two-day-old rats
exposed to hypoxic/ischemia injury. Neurol Res. 38:1020–1026.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang F, Xing J, Liou AK, Wang S, Gan Y,
Luo Y, Ji X, Stetler RA, Chen J and Cao G: Enhanced delivery of
erythropoietin across the blood-brain barrier for neuroprotection
against ischemic neuronal injury. Transl Stroke Res. 1:113–121.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Brines M and Cerami A: Emerging biological
roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci.
6:484–494. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wolf RF, Peng J, Friese P, Gilmore LS,
Burstein SA and Dale GL: Erythropoietin administration increases
production and reactivity of platelets in dogs. Thromb Haemost.
78:1505–1509. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wiessner C, Allegrini PR, Ekatodramis D,
Jewell UR, Stallmach T and Gassmann M: Increased cerebral infarct
volumes in polyglobulic mice overexpressing erythropoietin. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 21:857–864. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Leyland-Jones B, Investigators B and Study
G: Breast cancer trial with erythropoietin terminated unexpectedly.
Lancet Oncol. 4:459–460. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wun T, Law L, Harvey D, Sieracki B,
Scudder SA and Ryu JK: Increased incidence of symptomatic venous
thrombosis in patients with cervical carcinoma treated with
concurrent chemotherapy, radiation, and erythropoietin. Cancer.
98:1514–1520. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sadamoto Y, Igase K, Sakanaka M, Sato K,
Otsuka H, Sakaki S, Masuda S and Sasaki R: Erythropoietin prevents
place navigation disability and cortical infarction in rats with
permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 253:26–32. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sakanaka M, Wen TC, Matsuda S, Masuda S,
Morishita E, Nagao M and Sasaki R: In vivo evidence that
erythropoietin protects neurons from ischemic damage. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:4635–4640. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bernaudin M, Marti HH, Roussel S, Divoux
D, Nouvelot A, MacKenzie ET and Petit E: A potential role for
erythropoietin in focal permanent cerebral ischemia in mice. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 19:643–651. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Alcalá-Barraza SR, Lee MS, Hanson LR,
McDonald AA, Frey WH II and McLoon LK: Intranasal delivery of
neurotrophic factors BDNF, CNTF, EPO, and NT-4 to the CNS. J Drug
Target. 18:179–190. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chauhan MB and Chauhan NB: Brain Uptake of
neurotherapeutics after intranasal versus intraperitoneal delivery
in Mice. J Neurol Neurosurg. 2(009)2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang T, Gu J, Wu L, Li N, Sun Y, Yu P,
Wang Y, Zhang G and Zhang Z: Neuroprotective and axonal
outgrowth-promoting effects of tetramethylpyrazine nitrone in
chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats and primary hippocampal neurons
exposed to hypoxia. Neuropharmacology. 118:137–147. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Merelli A, Caltana L, Girimonti P, Ramos
AJ, Lazarowski A and Brusco A: Recovery of motor spontaneous
activity after intranasal delivery of human recombinant
erythropoietin in a focal brain hypoxia model induced by CoCl2 in
rats. Neurotox Res. 20:182–192. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Patil SS, Sunyer B, Höger H and Lubec G:
Evaluation of spatial memory of C57BL/6J and CD1 mice in the Barnes
maze, the Multiple T-maze and in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain
Res. 198:58–68. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Miskowiak KW, Vinberg M, Macoveanu J,
Ehrenreich H, Køster N, Inkster B, Paulson OB, Kessing LV,
Skimminge A and Siebner HR: Effects of erythropoietin on
hippocampal volume and memory in mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry.
78:270–277. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Holmes MD and Sires BS: Flash visual
evoked potentials predict visual outcome in traumatic optic
neuropathy. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 20:342–346.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
R Core Team. R: A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing,
Vienna, Austria, 2012. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org/.
|
|
23
|
R-Studio Team. R-Studio: Integrated
Development for R. RStudio, Inc., Boston MA, 2015. URL http://www.rstudio.com/.
|
|
24
|
Brown RE and Wong AA: The influence of
visual ability on learning and memory performance in 13 strains of
mice. Learn Mem. 14:134–144. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kaur C, Foulds WS and Ling EA:
Hypoxia-ischemia and retinal ganglion cell damage. Clin Ophthalmol.
2:879–889. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bartsch T, Döhring J, Rohr A, Jansen O and
Deuschl G: CA1 neurons in the human hippocampus are critical for
autobiographical memory, mental time travel, and autonoetic
consciousness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:17562–17567.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu MC, Shi M, Cho HJ, Zhang J, Pavlenco A,
Liu S, Sidhu S, Huang LJ and Moe OW: The erythropoietin receptor is
a downstream effector of Klotho-induced cytoprotection. Kidney Int.
84:468–481. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lourhmati A, Buniatian GH, Paul C,
Verleysdonk S, Buecheler R, Buadze M, Proksch B, Schwab M, Gleiter
CH and Danielyan L: Age-dependent astroglial vulnerability to
hypoxia and glutamate: The role for erythropoietin. PLoS One.
8(e77182)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Alnaeeli M, Raaka BM, Gavrilova O, Teng R,
Chanturiya T and Noguchi CT: Erythropoietin signaling: A novel
regulator of white adipose tissue inflammation during diet-induced
obesity. Diabetes. 63:2415–2431. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vinberg M, Weikop P, Olsen NV, Kessing LV
and Miskowiak K: Effect of recombinant erythropoietin on
inflammatory markers in patients with affective disorders: A
randomised controlled study. Brain Behav Immun. 57:53–57.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ardalan MR, Estakhri R, Hajipour B,
Ansarin K, Asl NA, Nasirizade MR, Azar AN, Ghorbanihaghjou A,
Vatankhah AM and Esmaili HA: Erythropoietin ameliorates oxidative
stress and tissue injury following renal ischemia/reperfusion in
rat kidney and lung. Med Princ Pract. 22:70–74. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yu YP, Xu QQ, Zhang Q, Zhang WP, Zhang LH
and Wei EQ: Intranasal recombinant human erythropoietin protects
rats against focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 387:5–10.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fletcher L, Kohli S, Sprague SM, Scranton
RA, Lipton SA, Parra A, Jimenez DF and Digicaylioglu M: Intranasal
delivery of erythropoietin plus insulin-like growth factor-I for
acute neuroprotection in stroke. Laboratory investigation. J
Neurosurg. 111:164–170. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhu S, Min D, Zeng J, Ju Y, Liu Y and Chen
X: Transplantation of Stem Cells from human exfoliated deciduous
teeth decreases cognitive impairment from chronic cerebral ischemia
by reducing neuronal apoptosis in rats. J Stem Cells Int.
2020(6393075)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Masuda T, Shimazawa M, Ishizuka F,
Nakamura S, Tsuruma K and Hara H: Tissue kallikrein
(kallidinogenase) protects against retinal ischemic damage in mice.
Eur J Pharmacol. 738:74–82. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bird B and Stawicki SP: Anatomy, head and
neck, ophthalmic arteries. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL),
2019.
|