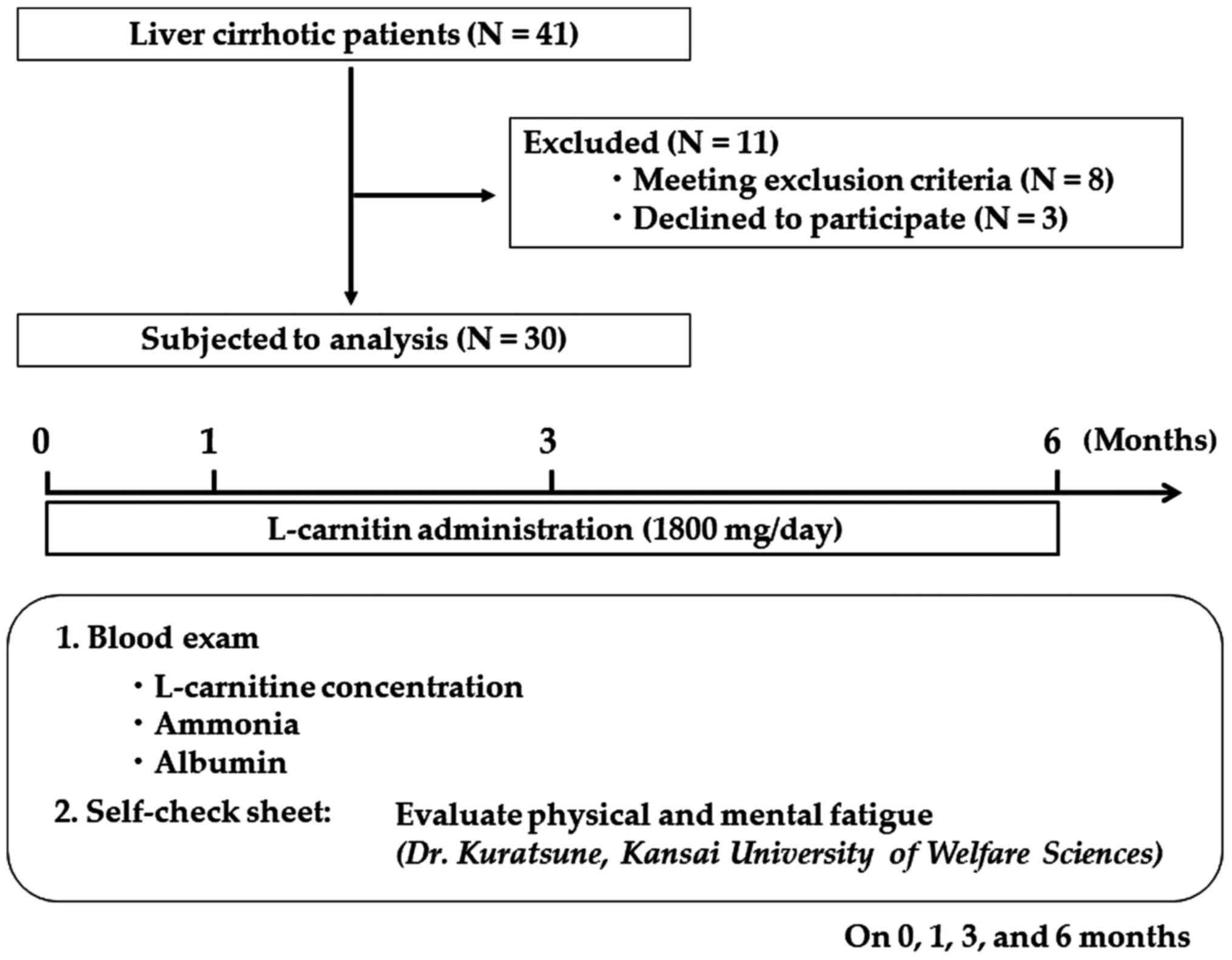
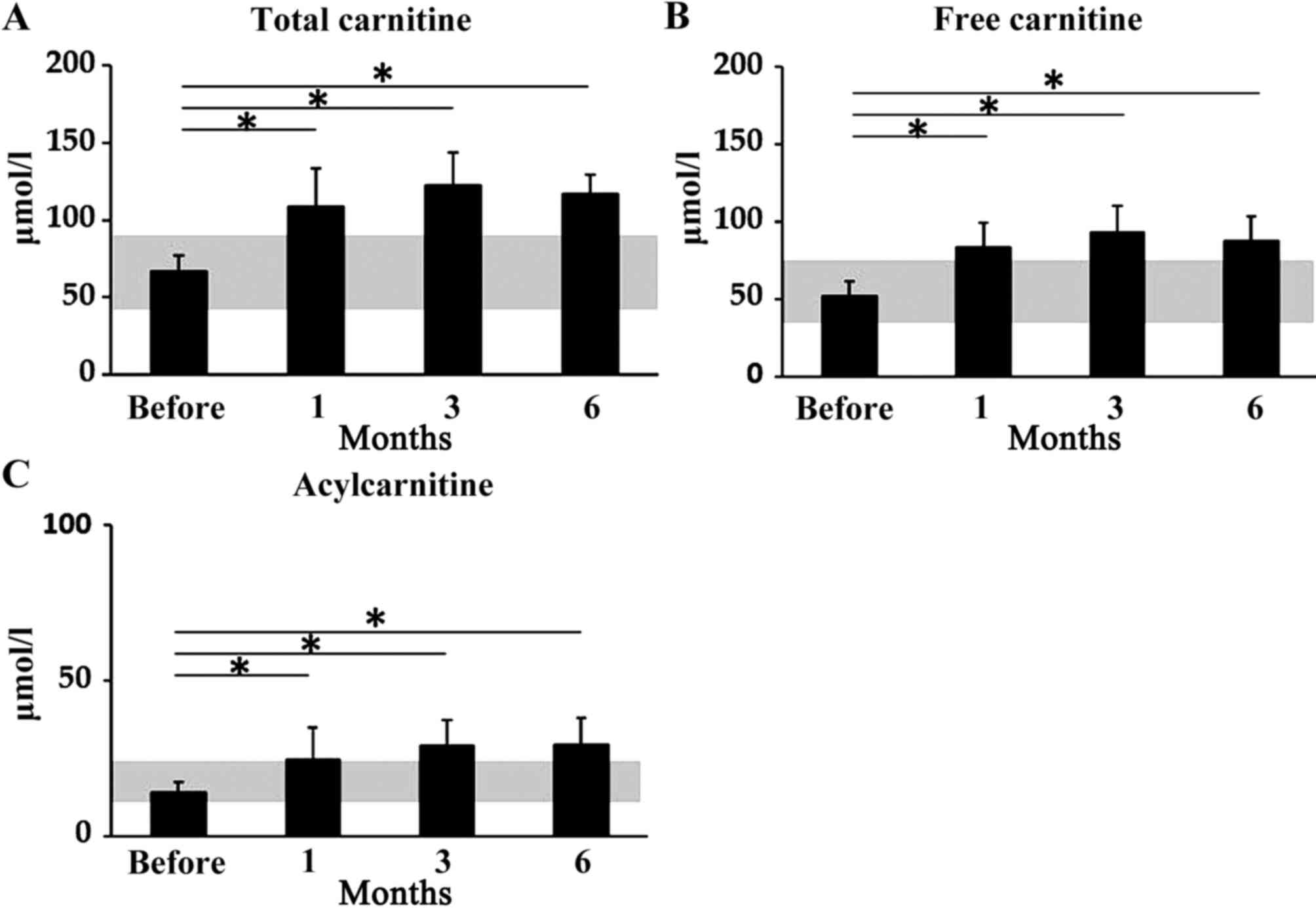
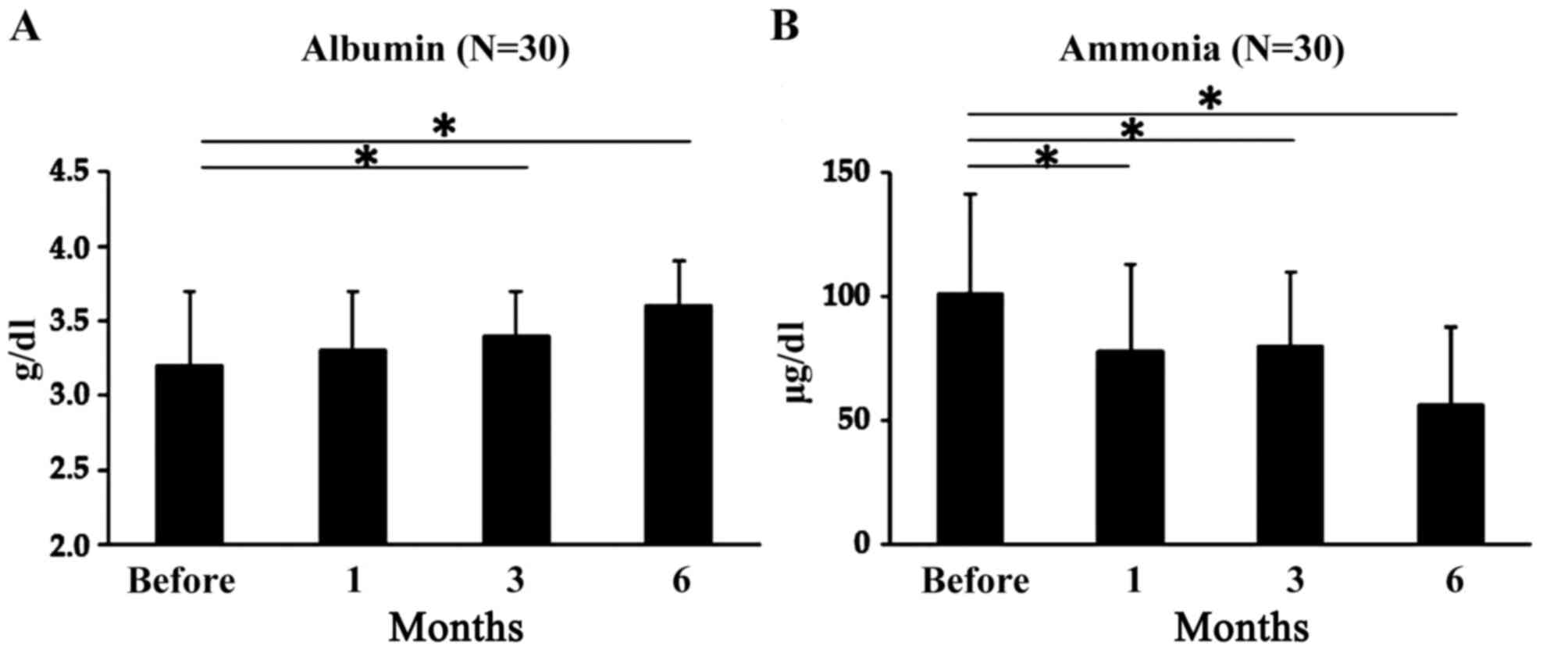
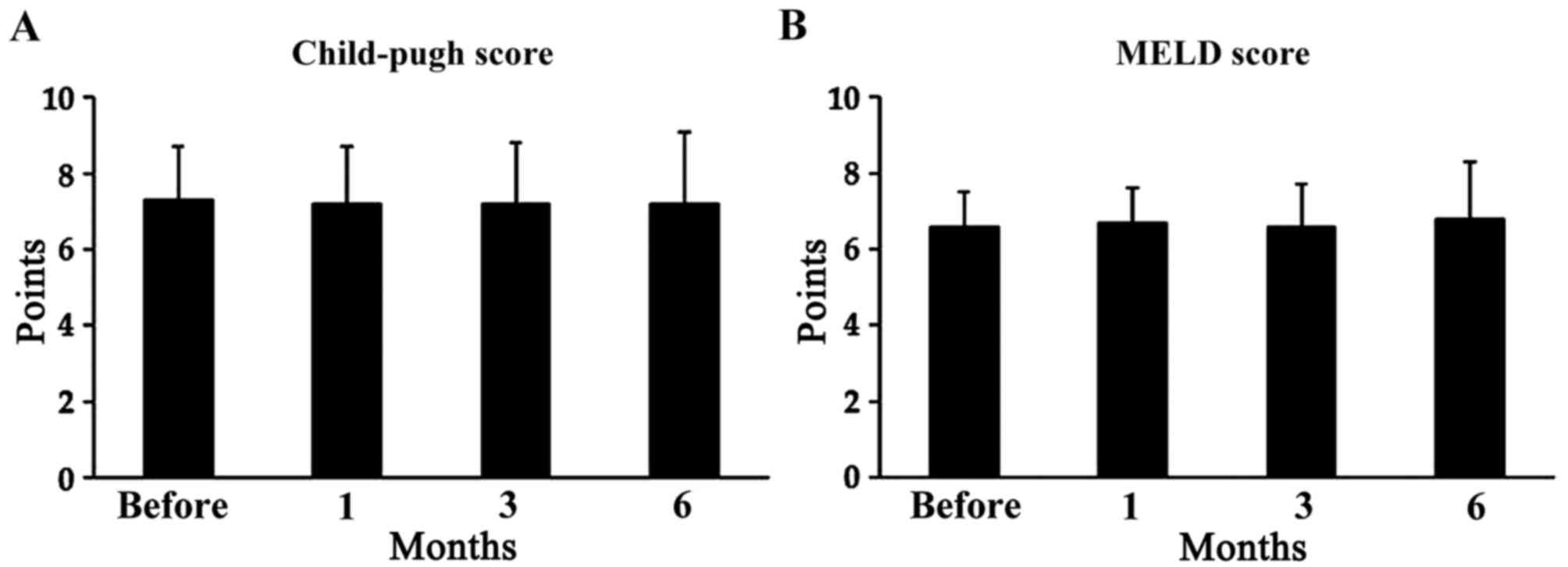
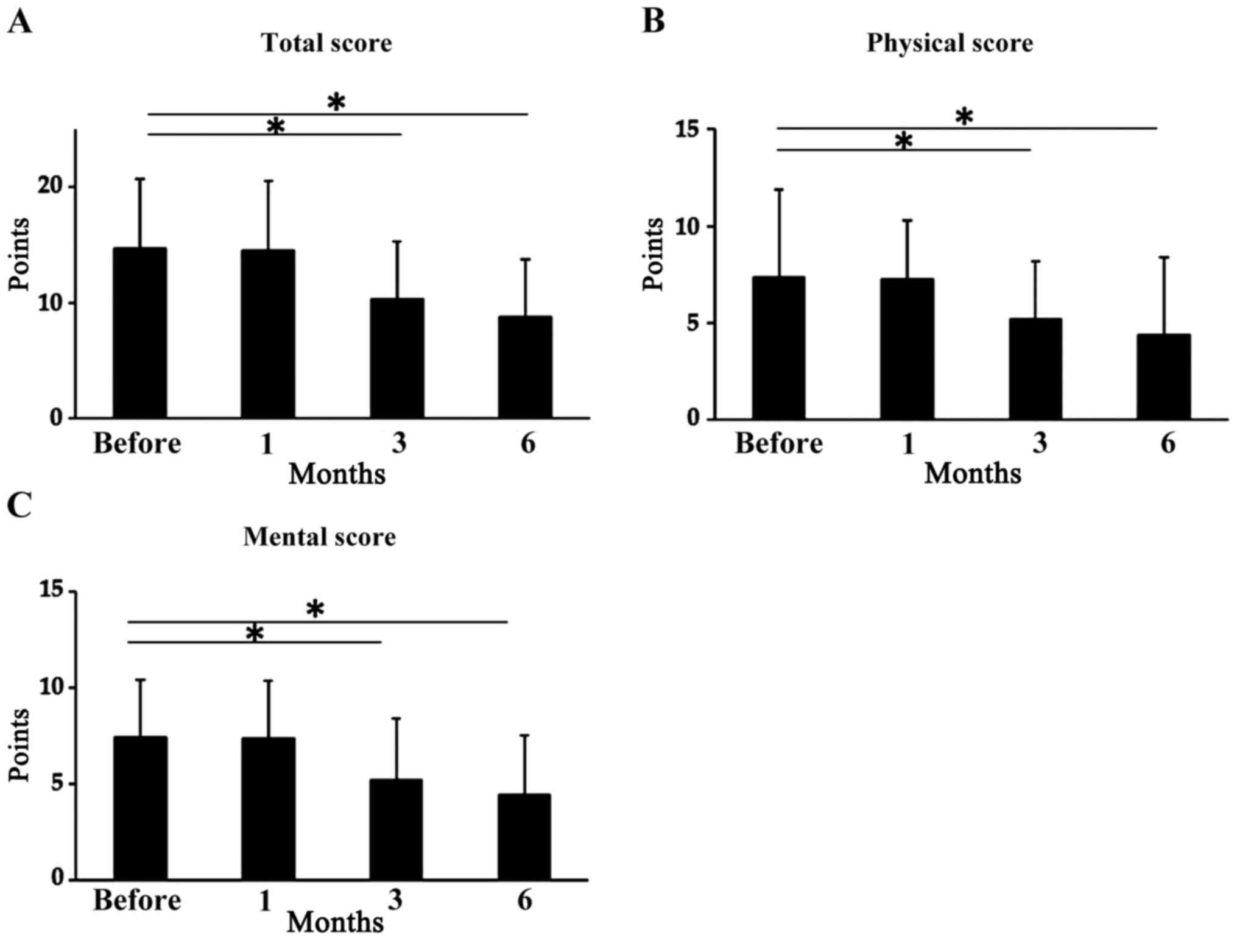
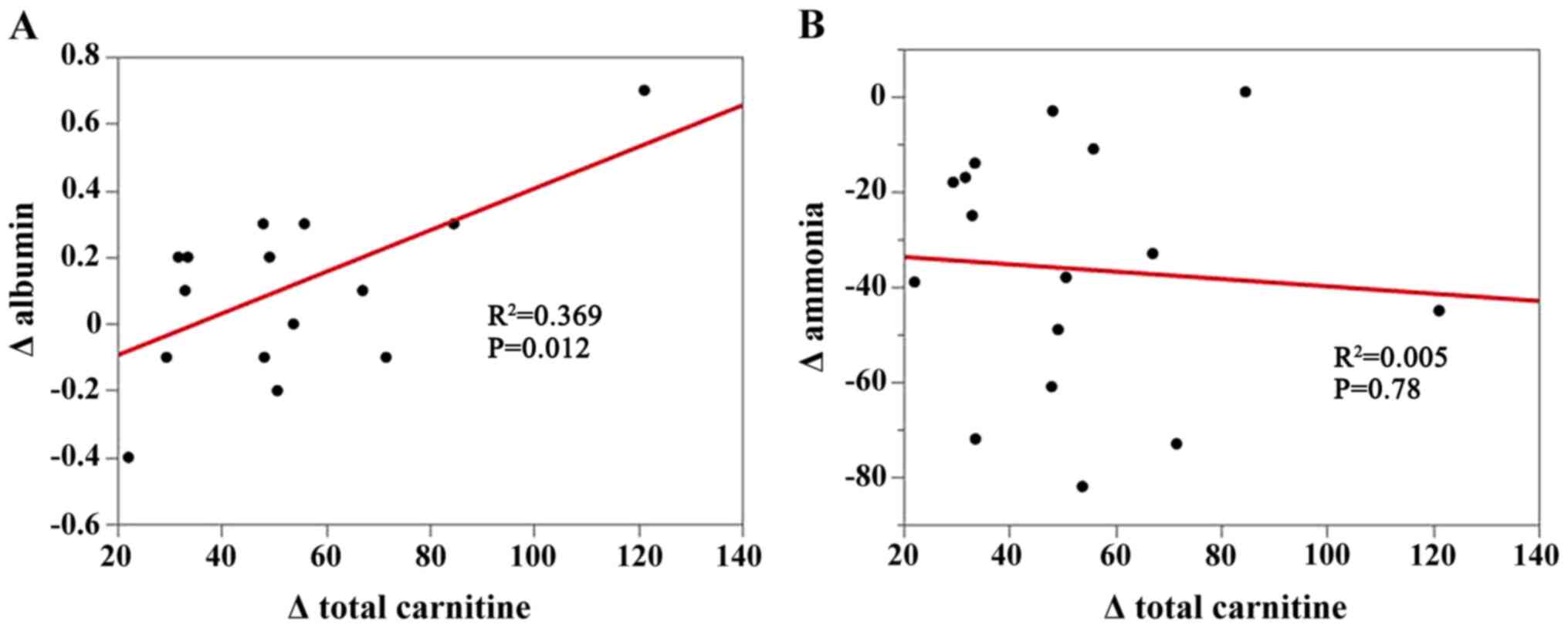
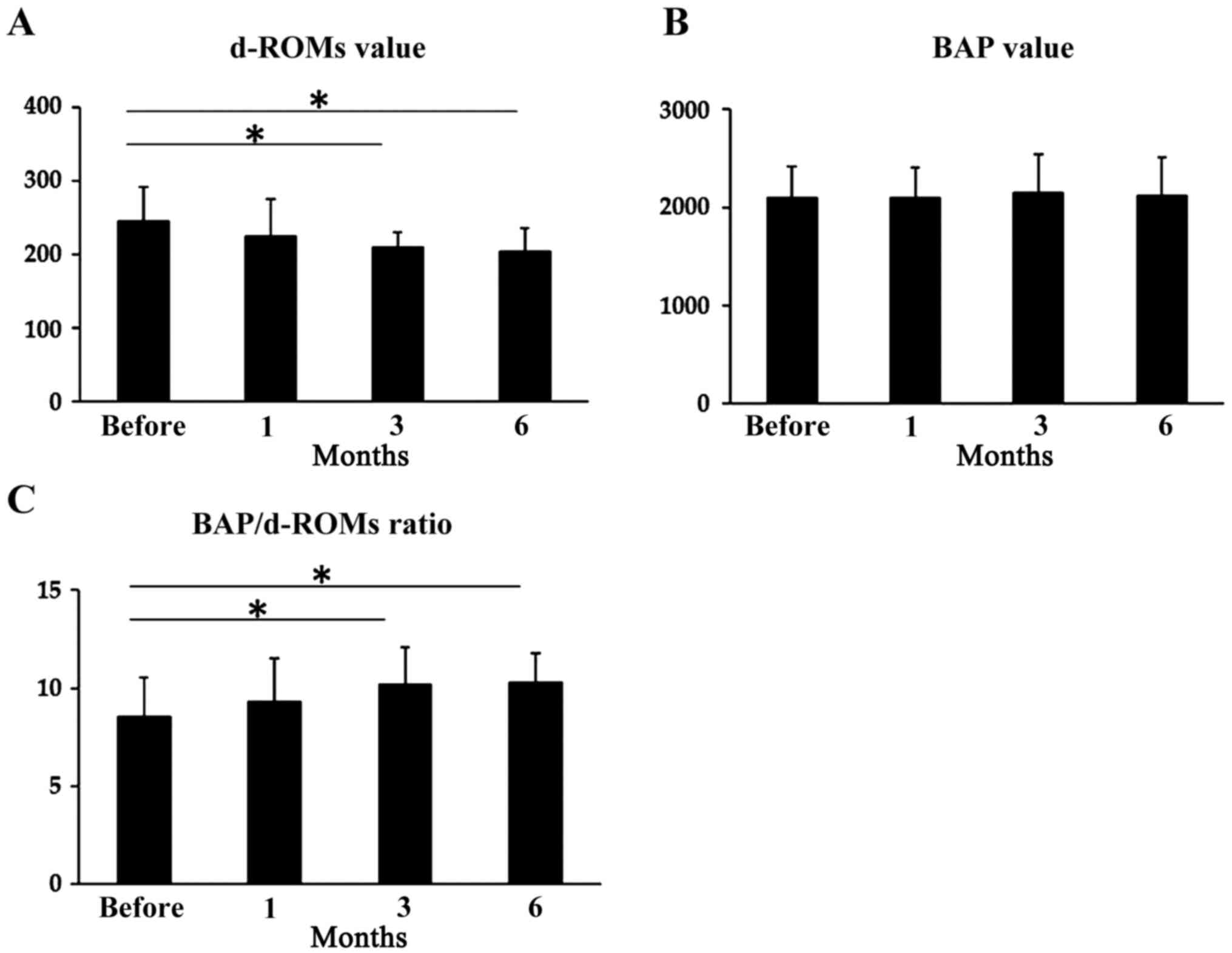
|
1
|
Oney-Birol S: Exogenous L-carnitine
promotes plant growth and cell division by mitigating genotoxic
damage of salt stress. Sci Rep. 9(17229)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rinaudo MT, Curto M, Bruno R, Piccinini M
and Marino C: Acid soluble, short chain esterified and free
carnitine in the liver, heart, muscle and brain of pre and post
hatched chicks. Int J Biochem. 23:59–65. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Khan L and Bamji MS: Tissue carnitine
deficiency due to dietary lysine dificiency: Triglyceride
accumulation and concomitant impairment in fatty acid oxidation. J
Nutr. 109:24–31. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rebouche CJ: Carnitine function and
requirements during the life cycle. FASEB J. 6:3379–3386.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cimmino A, Andolfi A, Zonno MC, Troise C,
Santini A, Tuzi A, Vurro M, Ash G and Evidente A: Phomentrioloxin:
A phytotoxic pentasubstituted geranylcyclohexentriol produced by
Phomopsis sp., a potential mycoherbicide for Carthamus lanatus
Biocontrol. J Nat Prod. 75:1130–1137. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Longo N, Frigeni M and Pasquali M:
Carnitine transport and fatty acid oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2422–2435. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ringseis R, Keller J and Eder K: Role of
carnitine in the regulation of glucose homeostasis and insulin
sensitivity: Evidence from in vivo and in vitro studies with
carnitine supplementation and carnitine deficiency. Eur J Nutr.
51:1–18. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Irvine KM, Ratnasekera I, Powell EE and
Hume DA: Causes and consequences of innate immune dysfunction in
cirrhosis. Front Immunol. 10(293)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Motta M,
Giordano M, Malaguarnera G, Bella R, Nunnari G, Rampello L and
Pennisi G: Acetyl-L-carnitine improves cognitive functions in
severe hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized and controlled clinical
trial. Metab Brain Dis. 26:281–289. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cecere A, Ciaramella F, Tancredi L, Romano
C and Gattoni A: Efficacy of L-carnitine in reducing
hyperammonaemia and improving neuropsychological test performance
in patients with hepatic cirrhosis: Results of a randomised trial.
Clin Drug Investig. 22 (Suppl 1):S7–S14. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hiramatsu A, Aikata H, Uchikawa S, Ohya K,
Kodama K, Nishida Y, Daijo K, Osawa M, Teraoka Y, Honda F, et al:
Levocarnitine use is associated with improvement in sarcopenia in
patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol Commun. 3:348–355.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nakanishi H, Kurosaki M, Tsuchiya K,
Nakakuki N, Takada H, Matsuda S, Gondo K, Asano Y, Hattori N,
Tamaki N, et al: L-carnitine reduces muscle cramps in patients with
cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:1540–1543.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tajiri K, Futsukaichi Y, Kobayashi S,
Yasumura S, Takahara T, Minemura M and Sugiyama T: L-carnitine for
the treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with
advanced liver cirrhosis. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 64:321–328.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Abbasnezhad A, Choghakhori R, Kashkooli S,
Alipour M, Asbaghi O and Mohammadi R: Effect of L-carnitine on
liver enzymes and biochemical factors in hepatic encephalopathy: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
34:2062–2070. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shang R, Sun Z and Li H: Effective dosing
of L-carnitine in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular
disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc
Disord. 14(88)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Howanitz JH, Howanitz PJ, Skrodzki CA and
Iwanski JA: Influences of specimen processing and storage
conditions on results for plasma ammonia. Clin Chem. 30:906–908.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P,
Shawcross DL, Butterworth RF and Morgan MY: International Society
for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN). Review
article: The design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy-an
International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen
Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
33:739–747. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Michalak A, Rose C, Butterworth J and
Butterworth RF: Neuroactive amino acids and glutamate (NMDA)
receptors in frontal cortex of rats with experimental acute liver
failure. Hepatology. 24:908–913. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Peng Y, Qi X and Guo X: Child-pugh versus
MELD score for the assessment of prognosis in liver cirrhosis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95(e2877)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tanaka S, Kuratsune H, Hidaka Y, Hakariya
Y, Tatsumi KI, Takano T, Kanakura Y and Amino N: Autoantibodies
against muscarinic cholinergic receptor in chronic fatigue
syndrome. Int J Mol Med. 12:225–230. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okada T, Tanaka M, Kuratsune H, Watanabe Y
and Sadato N: Mechanisms underlying fatigue: A voxel-based
morphometric study of chronic fatigue syndrome. BMC Neurol.
4(14)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Matsuda Y, Matsui T, Kataoka K, Fukada R,
Fukuda S, Kuratsune H, Tajima S, Yamaguti K, Kato YH and Kiriike N:
A two-year follow-up study of chronic fatigue syndrome comorbid
with psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 63:365–373.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
General Assembly of the World Medical
Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki:
Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J
Am Coll Dent. 81:14–18. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morimoto M, Hashimoto T, Tsuda Y, Kitaoka
T and Kyotani S: Evaluation of oxidative stress and antioxidant
capacity in healthy children. J Chin Med Assoc. 82:651–654.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Celi P, Sullivan M and Evans D: The
stability of the reactive oxygen metabolites (d-ROMs) and
biological antioxidant potential (BAP) tests on stored horse blood.
Vet J. 183:217–218. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bergami R, Maranesi M, Marchetti M,
Sangiorgi Z and Tolomelli B: Influence of dietary n-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipemic effect of vitamin B6
deficiency. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 69:315–321. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kuratsune H, Yamaguti K, Lindh G, Evengård
B, Hagberg G, Matsumura K, Iwase M, Onoe H, Takahashi M, Machii T,
Kanakura Y, et al: Brain regions involved in fatigue sensation:
Reduced acetylcarnitine uptake into the brain. Neuroimage.
17:1256–1265. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Nozaki S, Mizuma H,
Ataka S, Tahara T, Sugino T, Shirai T, Kajimoto Y, Kuratsune H,
Kajimoto O and Watanabe Y: Antifatigue effects of coenzyme Q10
during physical fatigue. Nutrition. 24:293–299. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Malaguarnera M: Carnitine derivatives:
Clinical usefulness. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 28:166–176.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kendler BS: Carnitine: An overview of its
role in preventive medicine. Prev Med. 15:373–390. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Malaguarnera M: Acetyl-L-carnitine in
hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 28:193–199.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gonwa TA and Wadei HM: Kidney disease in
the setting of liver failure: Core curriculum. Am J Kidney Dis
2013. 62:1198–1212. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Flanagan JL, Simmons PA, Vehige J, Willcox
MD and Garrett Q: Role of carnitine in disease. Nutr Metab (Lond).
7(30)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shiraki M, Shimizu M, Moriwaki H, Okita K
and Koike K: Carnitine dynamics and their effects on hyperammonemia
in cirrhotic Japanese patients. Hepatol Res. 47:321–327.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hassan A, Tsuda Y, Asai A, Yokohama K,
Nakamura K, Sujishi T, Ohama H, Tsuchimoto Y, Fukunishi S, Abdelaal
UM, Arafa UA, et al: Effects of oral L-carnitine on liver functions
after transarterial chemoembolization in intermediate-stage HCC
patients. Mediators Inflamm. 2015(608216)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Malaguarnera M, Gargante MP, Russo C,
Antic T, Vacante M, Malaguarnera M, Avitabile T, Li Volti G and
Galvano F: L-carnitine supplementation to diet: A new tool in
treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-a randomized and
controlled clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 105:1338–1345.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Soeters PB, Wolfe RR and Shenkin A:
Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and clinical significance. JPEN J
Parenter Enteral Nutr. 43:181–193. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
DaVanzo WJ and Ullian ME: L-carnitine
administration reverses acute mental status changes in a chronic
hemodialysis patient with hepatitis C infection. Clin Nephrol.
57:402–405. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stephens FB, Constantin-Teodosiu D and
Greenhaff PL: New insights concerning the role of carnitine in the
regulation of fuel metabolism in skeletal muscle. J Physiol.
581:431–444. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Malaguarnera M, Gargante MP, Cristaldi E,
Vacante M, Risino C, Cammalleri L, Pennisi G and Rampello L:
Acetyl-L-carnitine treatment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Dig
Dis Sci. 53:3018–3025. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Giordano M,
Pennisi G, Bella R, Rampello L, Malaguarnera M, Li Volti G and
Galvano F: Oral acetyl-L-carnitine therapy reduces fatigue in overt
hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:799–808.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Malaguarnera M, Bella R, Vacante M,
Giordano M, Malaguarnera G, Gargante MP, Motta M, Mistretta A,
Rampello L and Pennisi G: Acetyl-L-carnitine reduces depression and
improves quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic
encephalopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 46:750–759. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Amodio P, Angeli P, Merkel C, Menon F and
Gatta A: Plasma carnitine levels in liver cirrhosis: Relationship
with nutritional status and liver damage. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem.
28:619–626. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
D'Arienzo A, Mattera D, Ambrogio G,
Duranti L, Zeuli L and Mazzacca G: Hypercarnitinemia in cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 5(343)1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gimenes AC, Bravo DM, Napolis LM, Mello
MT, Oliveira AS, Neder JA and Nery LE: Effect of L-carnitine on
exercise performance in patients with mitochondrial myopathy. Braz
J Med Biol Res. 48:354–362. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lee JS, Kim HG, Lee DS and Son CG:
Oxidative stress is a convincing contributor to idiopathic chronic
fatigue. Sci Rep. 8(12890)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sitar ME, Aydin S and Cakatay U: Human
serum albumin and its relation with oxidative stress. Clin Lab.
59:945–952. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kinoshita H, Watanabe K, Azma T, Feng GG,
Akahori T, Hayashi H, Sato M, Fujiwara Y and Wakatsuki A: Human
serum albumin and oxidative stress in preeclamptic women and the
mechanism of albumin for stress reduction. Heliyon.
3(e00369)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Malaguarnera M, Pistone G, Astuto M,
Vecchio I, Raffaele R, Lo Giudice E and Rampello L: Effects of
L-acetylcarnitine on cirrhotic patients with hepatic coma:
Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Dig Dis Sci.
51:2242–2247. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|