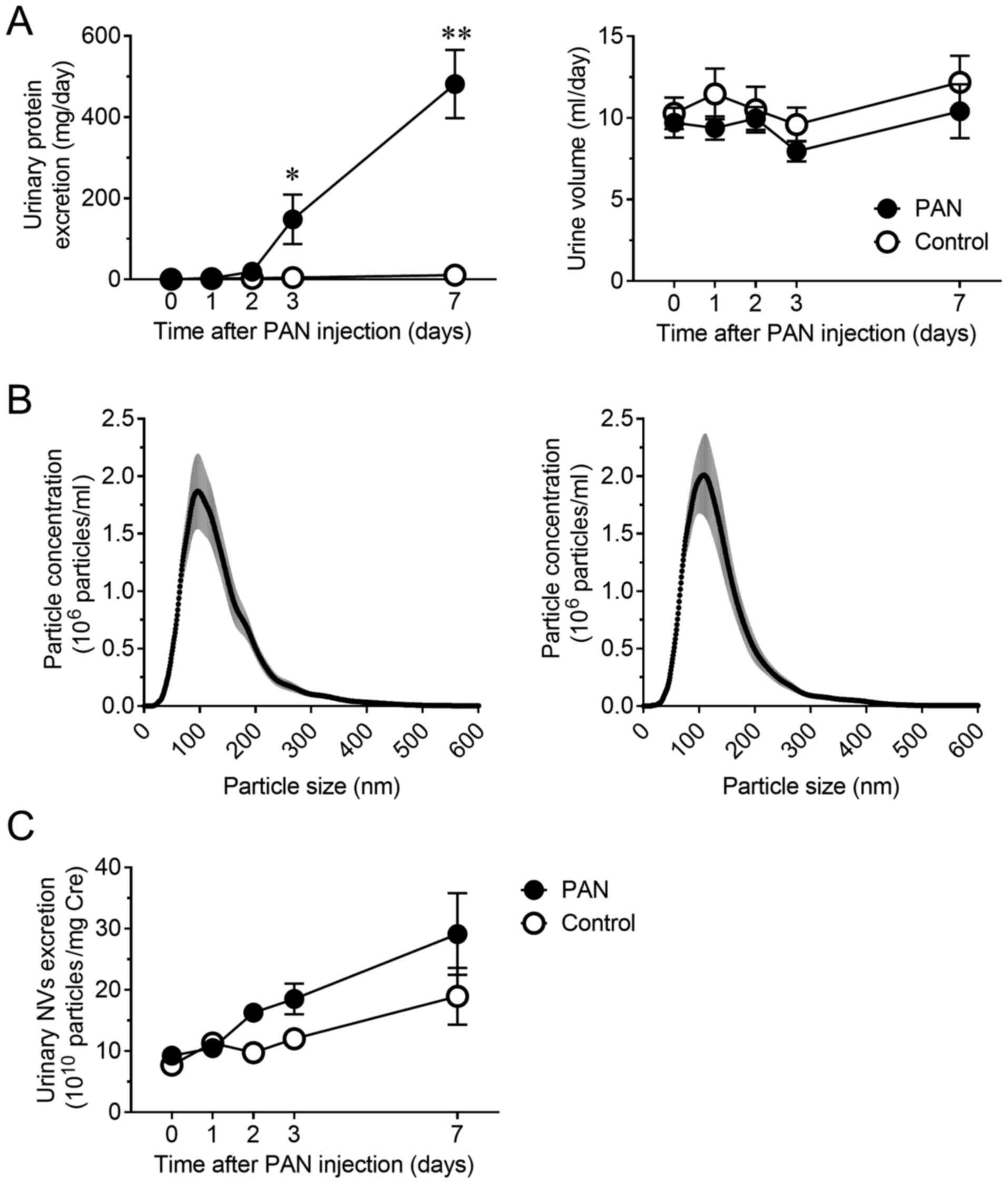
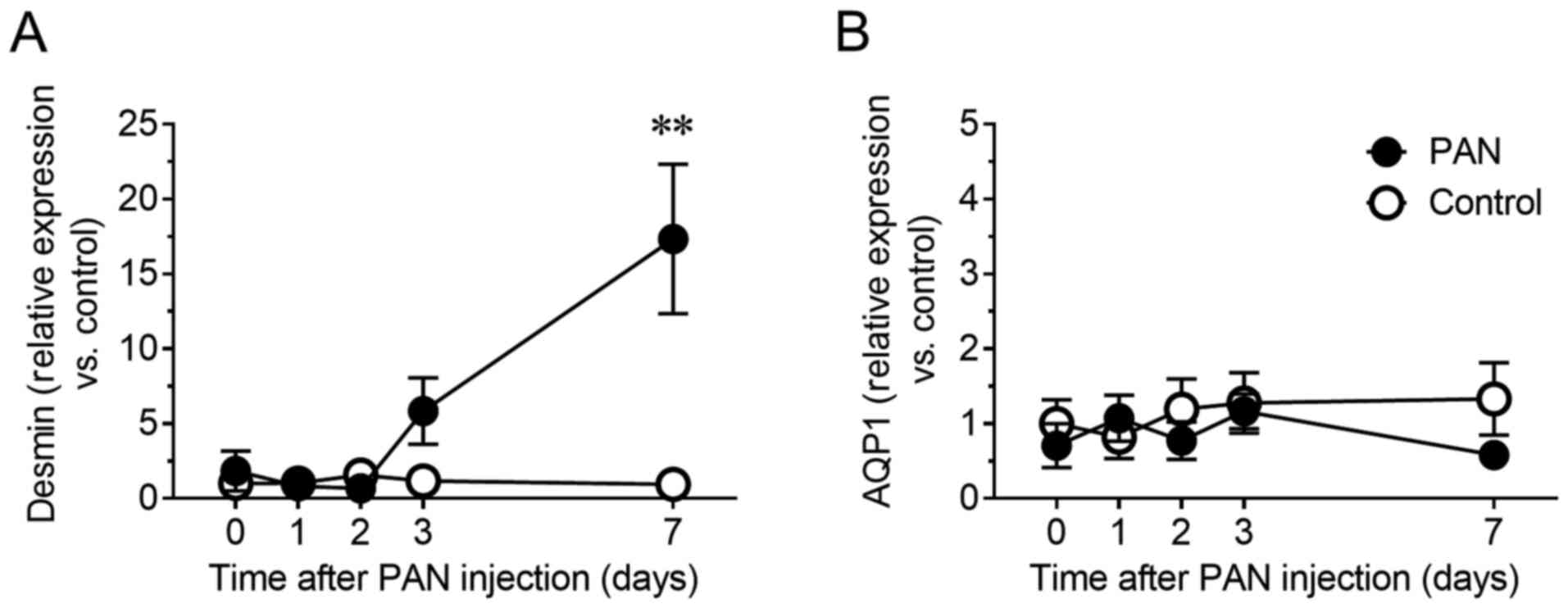
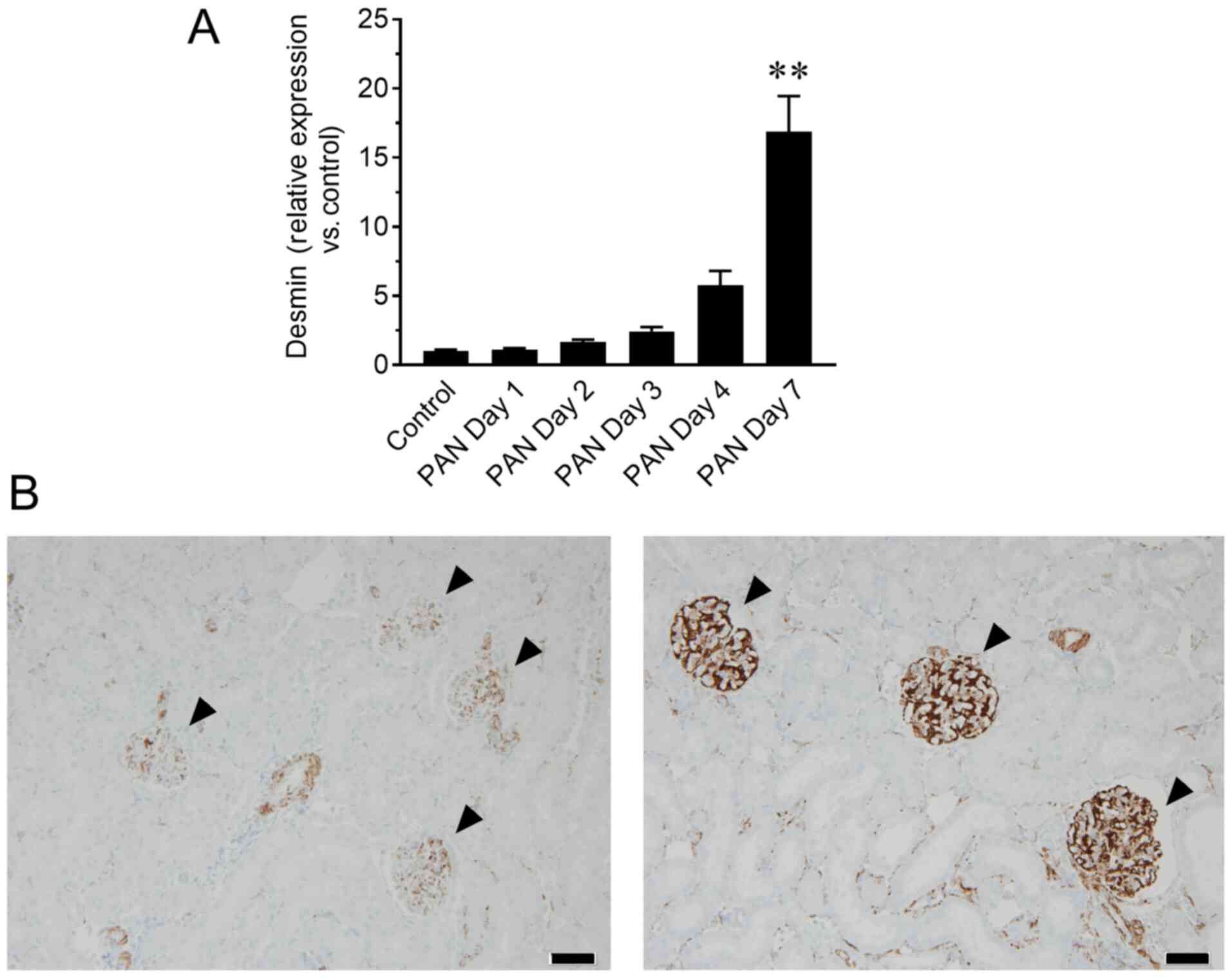
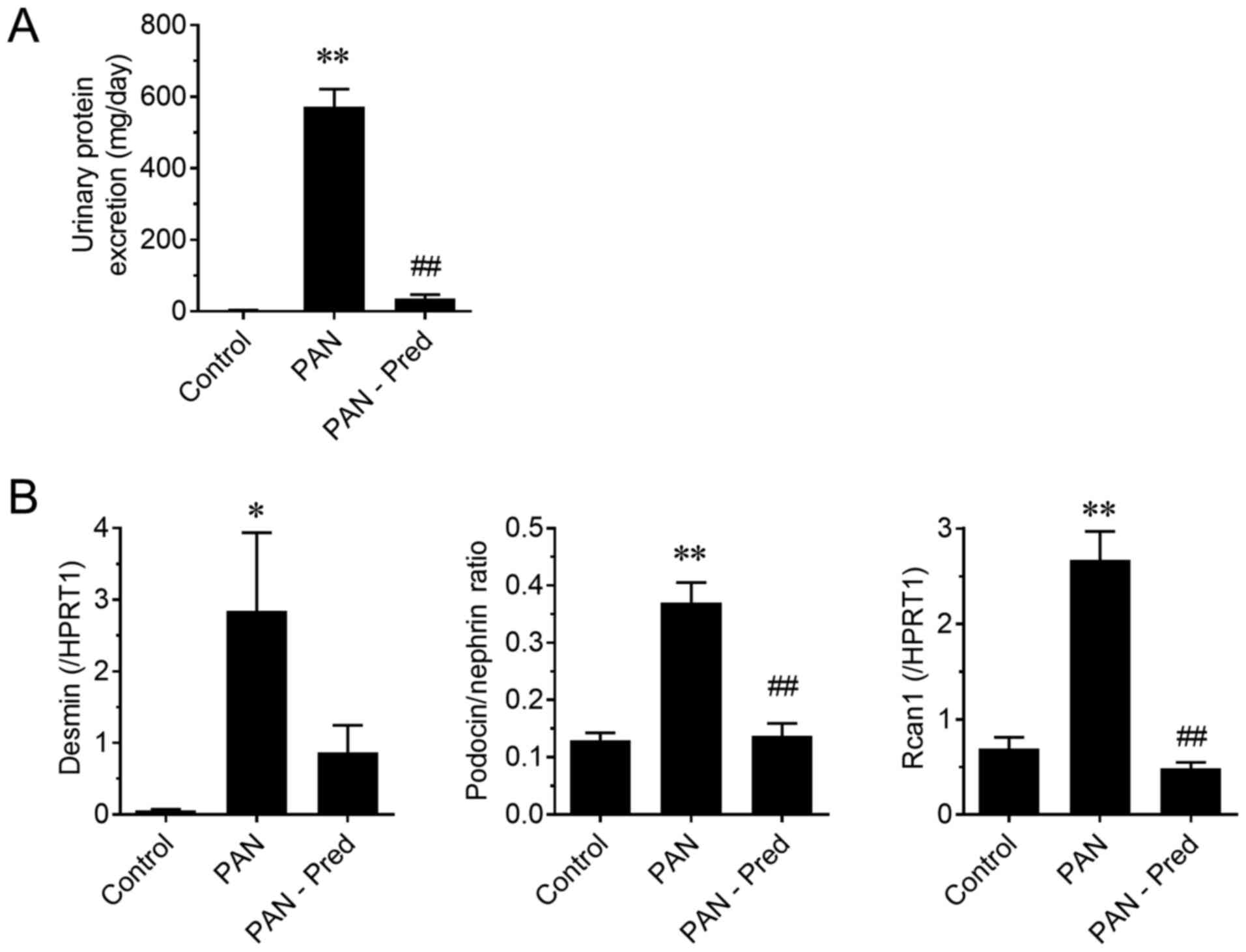
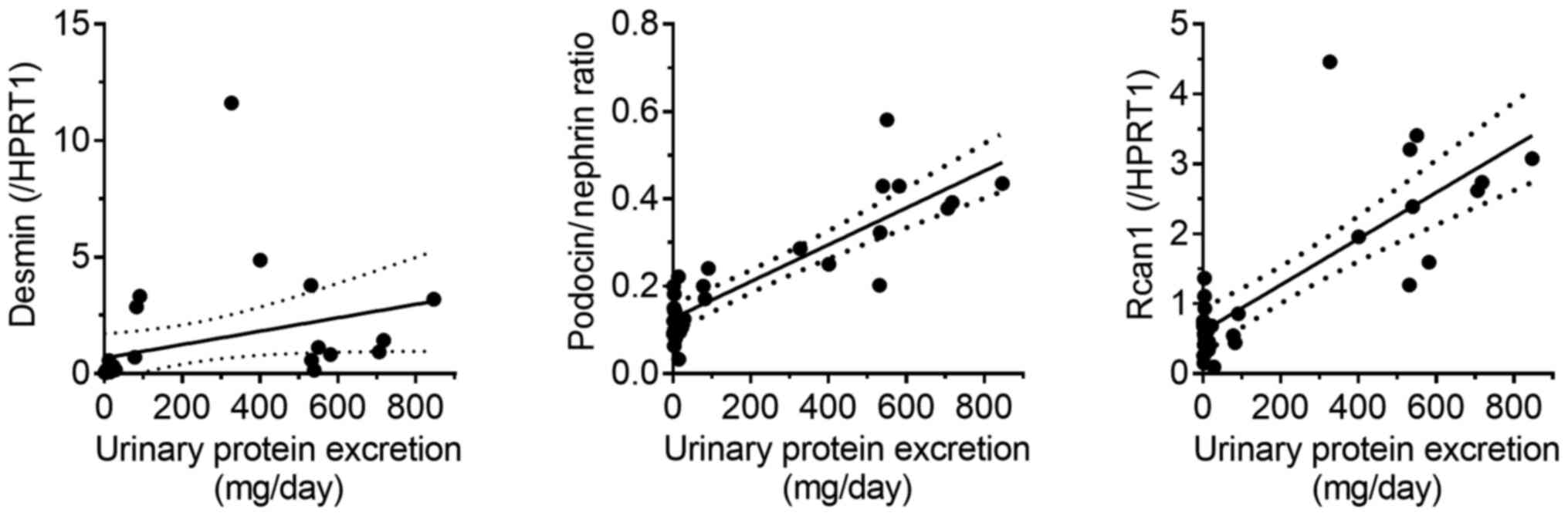
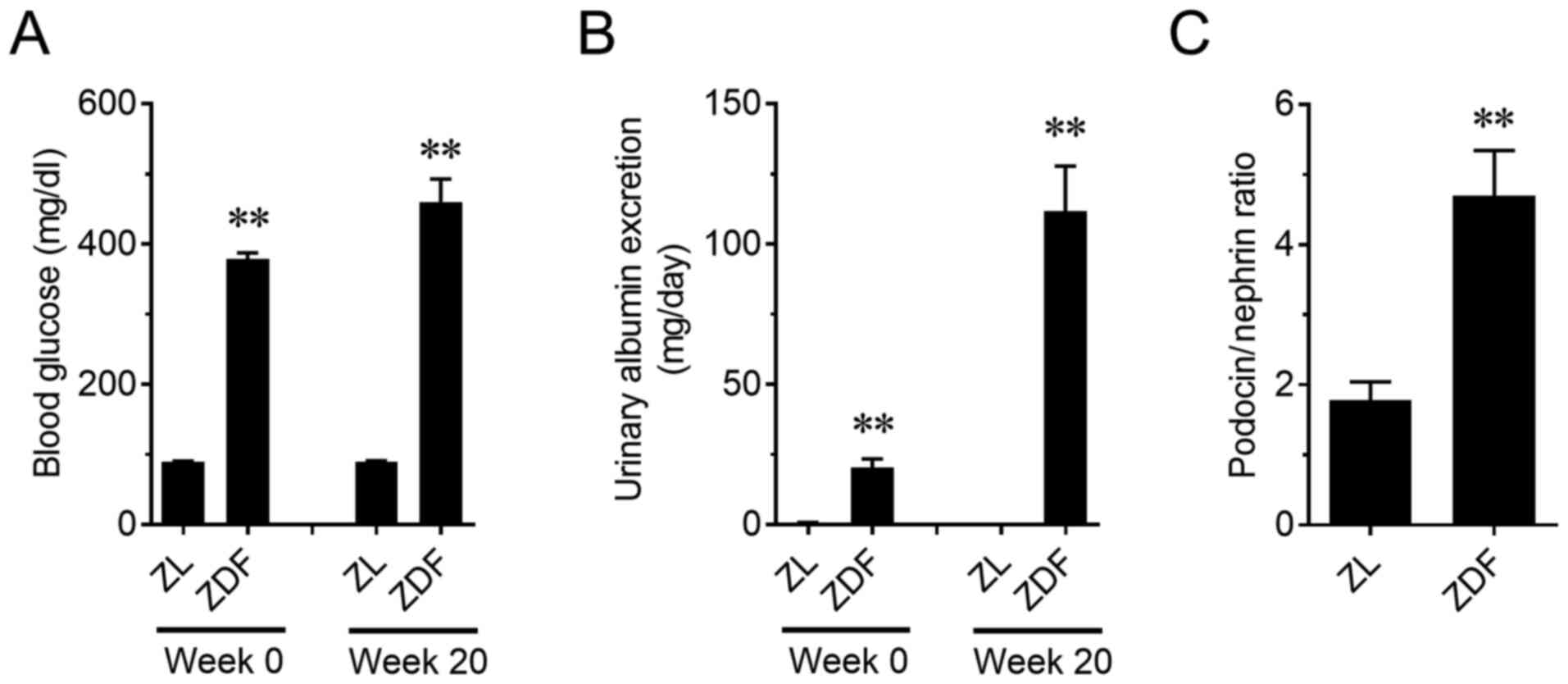
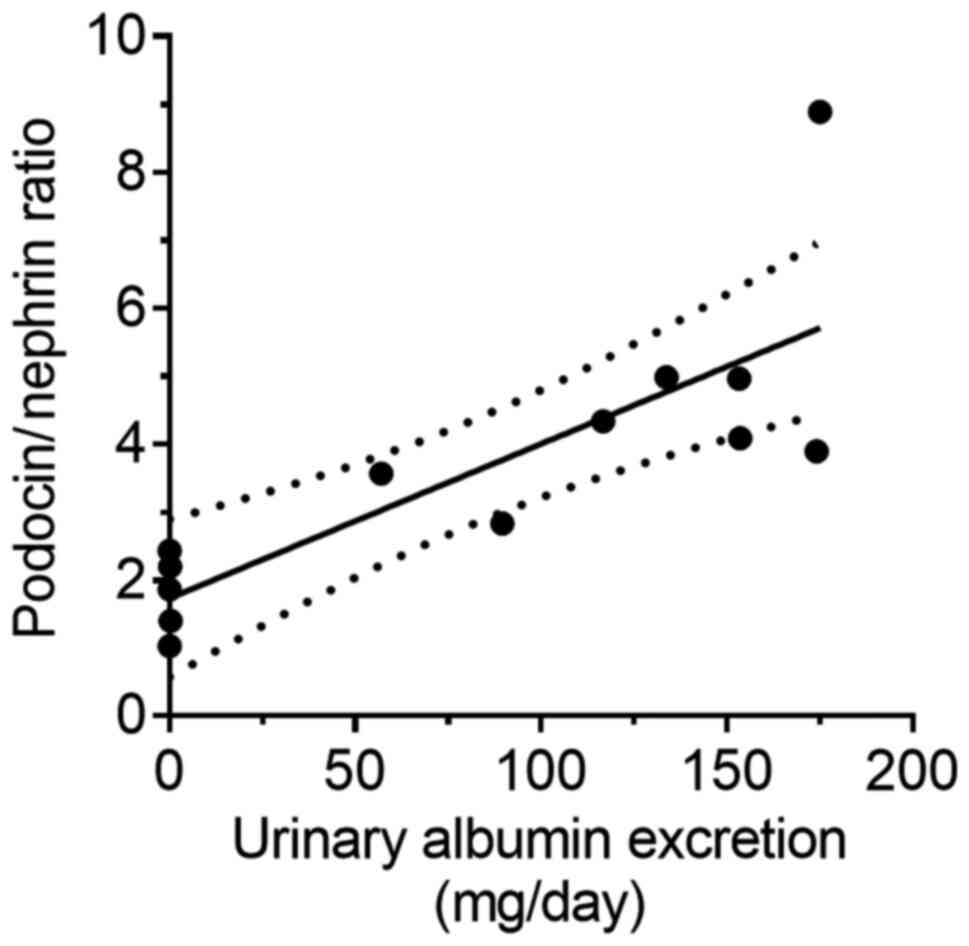
|
1
|
Wang V, Vilme H, Maciejewski ML and
Boulware LE: The economic burden of chronic kidney disease and
end-stage renal disease. Semin Nephrol. 36:319–330. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Takemoto Y and Naganuma T: Economic issues
of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Contrib
Nephrol. 198:87–93. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Glassock RJ, Warnock DG and Delanaye P:
The global burden of chronic kidney disease: Estimates, variability
and pitfalls. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:104–114. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Levin A and Stevens PE: Early detection of
CKD: The benefits, limitations and effects on prognosis. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 7:446–457. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rysz J, Gluba-Brzózka A, Franczyk B,
Jabłonowski Z and Ciałkowska-Rysz A: Novel biomarkers in the
diagnosis of chronic kidney disease and the prediction of its
outcome. Int J Mol Sci. 18(1702)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hessvik NP and Llorente A: Current
knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci.
75:193–208. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Raposo G and Stoorvogel W: Extracellular
vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol.
200:373–383. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Braun F and Muller RU: Urinary
extracellular vesicles as a source of biomarkers reflecting renal
cellular biology in human disease. Methods Cell Biol. 154:43–65.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
De Palma G, Di Lorenzo VF, Krol S and
Paradiso AV: Urinary exosomal shuttle RNA: Promising cancer
diagnosis biomarkers of lower urinary tract. Int J Biol Markers.
34:101–107. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gardiner C, Ferreira YJ, Dragovic RA,
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Extracellular vesicle sizing and
enumeration by nanoparticle tracking analysis. J Extracell Vesicles
2: 2013.
|
|
11
|
Murakami T, Oakes M, Ogura M, Tovar V,
Yamamoto C and Mitsuhashi M: Development of glomerulus-, tubule-,
and collecting duct-specific mRNA assay in human urinary exosomes
and microvesicles. PLoS One. 9(e109074)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li B, Yao J, Morioka T and Oite T: Nitric
oxide increases albumin permeability of isolated rat glomeruli via
a phosphorylation-dependent mechanism. J Am Soc Nephrol.
12:2616–2624. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kakimoto T, Okada K, Hirohashi Y, Relator
R, Kawai M, Iguchi T, Fujitaka K, Nishio M, Kato T, Fukunari A and
Utsumi H: Automated image analysis of a glomerular injury marker
desmin in spontaneously diabetic Torii rats treated with losartan.
J Endocrinol. 222:43–51. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Baranyai T, Herczeg K, Onodi Z, Voszka I,
Modos K, Marton N, Nagy G, Mager I, Wood MJ, El Andaloussi S, et
al: Isolation of exosomes from blood plasma: Qualitative and
quantitative comparison of ultracentrifugation and size exclusion
chromatography methods. PLoS One. 10(e0145686)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu M, Ouyang Y, Wang Z, Zhang R, Huang PH,
Chen C, Li H, Li P, Quinn D, Dao M, et al: Isolation of exosomes
from whole blood by integrating acoustics and microfluidics. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:10584–10589. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pippin JW, Brinkkoetter PT, Cormack-Aboud
FC, Durvasula RV, Hauser PV, Kowalewska J, Krofft RD, Logar CM,
Marshall CB, Ohse T and Shankland SJ: Inducible rodent models of
acquired podocyte diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
296:F213–F229. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Floege J, Alpers CE, Sage EH, Pritzl P,
Gordon K, Johnson RJ and Couser WG: Markers of complement-dependent
and complement-independent glomerular visceral epithelial cell
injury in vivo. Expression of antiadhesive proteins and
cytoskeletal changes. Lab Invest. 67:486–497. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoshi S, Shu Y, Yoshida F, Inagaki T,
Sonoda J, Watanabe T, Nomoto K and Nagata M: Podocyte injury
promotes progressive nephropathy in zucker diabetic fatty rats. Lab
Invest. 82:25–35. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yatsu T, Aoki M and Tanaka A: Effect of
zelandopam, a dopamine D1-like receptor agonist, in puromycin
aminonucleoside nephrosis rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 510:121–126.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fukuda A, Wickman LT, Venkatareddy MP,
Sato Y, Chowdhury MA, Wang SQ, Shedden KA, Dysko RC, Wiggins JE and
Wiggins RC: Angiotensin II-dependent persistent podocyte loss from
destabilized glomeruli causes progression of end stage kidney
disease. Kidney Int. 81:40–55. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Spurney RF: Non-immunologic actions of
calcineurin inhibitors in proteinuric kidney diseases. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 5(181)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Alimirzaie S, Bagherzadeh M and Akbari MR:
Liquid biopsy in breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Clin Genet.
95:643–660. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cui S, Cheng Z, Qin W and Jiang L:
Exosomes as a liquid biopsy for lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
116:46–54. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nuzhat Z, Kinhal V, Sharma S, Rice GE,
Joshi V and Salomon C: Tumour-derived exosomes as a signature of
pancreatic cancer-liquid biopsies as indicators of tumour
progression. Oncotarget. 8:17279–17291. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Perez-Hernandez J, Forner MJ, Pinto C,
Chaves FJ, Cortes R and Redon J: Increased urinary exosomal
MicroRNAs in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One.
10(e0138618)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lv LL, Cao YH, Ni HF, Xu M, Liu D, Liu H,
Chen PS and Liu BC: MicroRNA-29c in urinary exosome/microvesicle as
a biomarker of renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
305:F1220–F1227. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chun-Yan L, Zi-Yi Z, Tian-Lin Y, Yi-Li W,
Bao L, Jiao L and Wei-Jun D: Liquid biopsy biomarkers of renal
interstitial fibrosis based on urinary exosome. Exp Mol Pathol.
105:223–228. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Perez-Hernandez J, Olivares D, Forner MJ,
Ortega A, Solaz E, Martinez F, Chaves FJ, Redon J and Cortes R:
Urinary exosome miR-146a is a potential marker of albuminuria in
essential hypertension. J Transl Med. 16(228)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Abe H, Sakurai A, Ono H, Hayashi S,
Yoshimoto S, Ochi A, Ueda S, Nishimura K, Shibata E, Tamaki M, et
al: Urinary exosomal mRNA of WT1 as diagnostic and prognostic
biomarker for diabetic nephropathy. J Med Invest. 65:208–215.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Feng Y, Lv LL, Wu WJ, Li ZL, Chen J, Ni
HF, Zhou LT, Tang TT, Wang FM, Wang B, et al: Urinary exosomes and
exosomal CCL2 mRNA as biomarkers of active histologic injury in IgA
nephropathy. Am J Pathol. 188:2542–2552. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
He L, Zhu D, Wang J and Wu X: A highly
efficient method for isolating urinary exosomes. Int J Mol Med.
43:83–90. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sonoda H, Yokota-Ikeda N, Oshikawa S,
Kanno Y, Yoshinaga K, Uchida K, Ueda Y, Kimiya K, Uezono S, Ueda A,
et al: Decreased abundance of urinary exosomal aquaporin-1 in renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
297:F1006–F1016. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xia L, Zhou M, Kalhorn TF, Ho HT and Wang
J: Podocyte-specific expression of organic cation transporter PMAT:
Implication in puromycin aminonucleoside nephrotoxicity. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 296:F1307–F1313. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Spanu S, van Roeyen CR, Denecke B, Floege
J and Muhlfeld AS: Urinary exosomes: A novel means to
non-invasively assess changes in renal gene and protein expression.
PLoS One. 9(e109631)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fukuda A, Wickman LT, Venkatareddy MP,
Wang SQ, Chowdhury MA, Wiggins JE, Shedden KA and Wiggins RC: Urine
podocin: Nephrin mRNA ratio (PNR) as a podocyte stress biomarker.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 27:4079–4087. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang K, Sun W, Zhang L, Xu X, Wang J and
Hong Y: miR-499 ameliorates podocyte injury by targeting
calcineurin in minimal change disease. Am J Nephrol. 47:94–102.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Jarad G, Tripathi P, Pan M,
Cunningham J, Martin DR, Liapis H, Miner JH and Chen F: Activation
of NFAT signaling in podocytes causes glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:1657–1666. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ding F, Li X, Li B, Guo J, Zhang Y and
Ding J: Calpain-mediated cleavage of calcineurin in puromycin
aminonucleoside-induced podocyte injury. PLoS One.
11(e0155504)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shen X, Jiang H, Ying M, Xie Z, Li X, Wang
H, Zhao J, Lin C, Wang Y, Feng S, et al: Calcineurin inhibitors
cyclosporin A and tacrolimus protect against podocyte injury
induced by puromycin aminonucleoside in rodent models. Sci Rep.
6(32087)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sipka S, Szücs K, Szántó S, Kovács I,
Lakos G, Antal-Szalmás P, Szegedi G and Gergely P: Inhibition of
calcineurin activity and protection against cyclosporine A induced
cytotoxicity by prednisolone sodium succinate in human peripheral
mononuclear cells. Immunopharmacology. 48:87–92. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sipka S, Szucs K, Szántó S, Kovács I,
Lakos G, Kiss E, Antal-Szalmás P, Szegedi G and Gergely P:
Glucocorticosteroid dependent decrease in the activity of
calcineurin in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients
with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 60:380–384.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Funk J, Ott V, Herrmann A, Rapp W, Raab S,
Riboulet W, Vandjour A, Hainaut E, Benardeau A, Singer T and
Jacobsen B: Semiautomated quantitative image analysis of glomerular
immunohistochemistry markers desmin, vimentin, podocin,
synaptopodin and WT-1 in acute and chronic rat kidney disease
models. Histochem Cell Biol. 145:315–326. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|