|
1
|
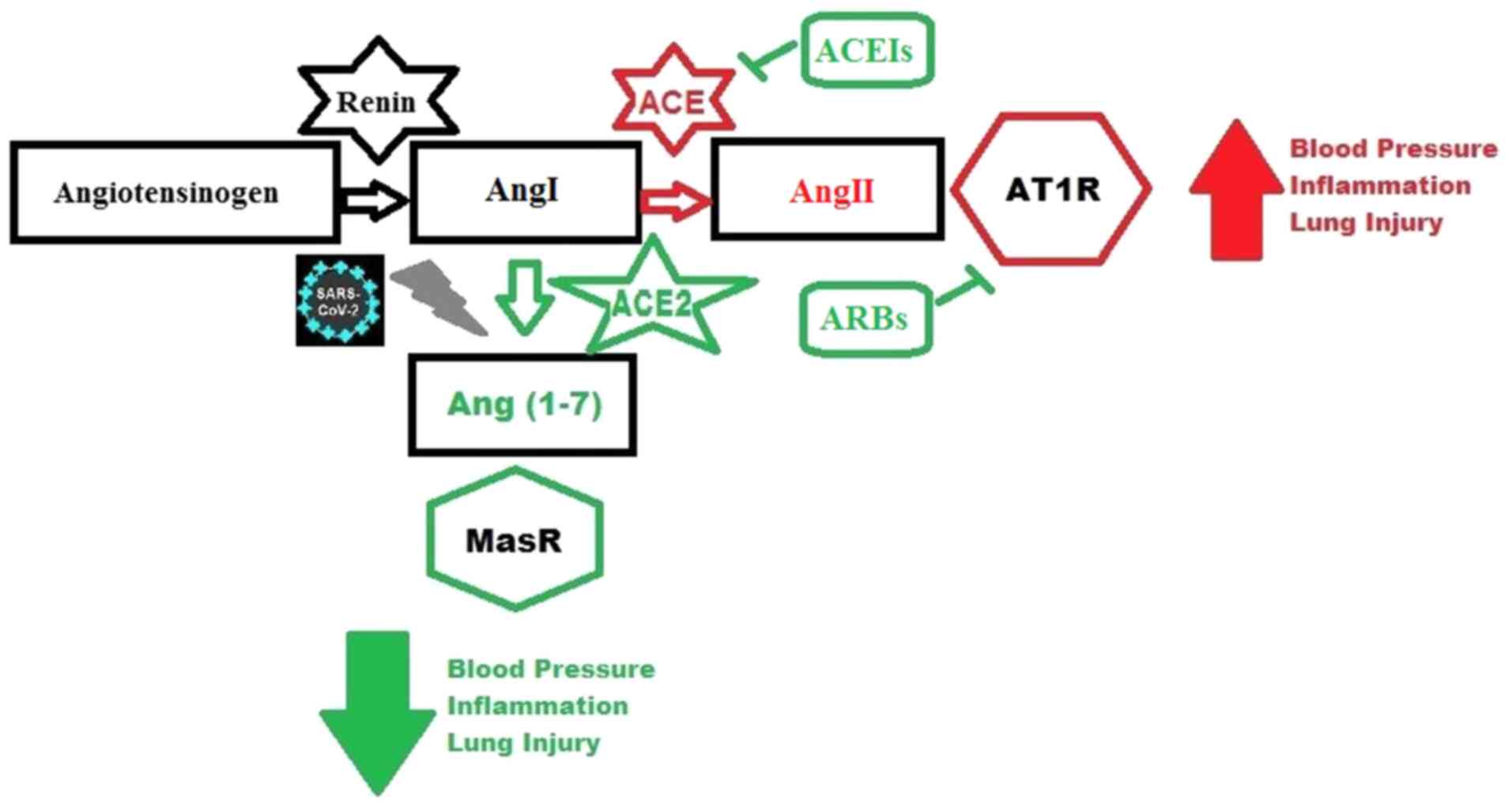
South AM, Brady TM and Flynn JT: ACE2
(angiotensin-converting enzyme 2), COVID-19, and ACE inhibitor and
Ang II (angiotensin II) receptor blocker use during the pandemic:
The pediatric perspective. Hypertension. 76:16–22. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pacurari M, Kafoury R, Tchounwou PB and
Ndebele K: The Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone system in vascular
inflammation and remodeling. Int J Inflamm.
2014(689360)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ferrario CM and Strawn WB: Role of the
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and proinflammatory mediators
in cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 98:121–128.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
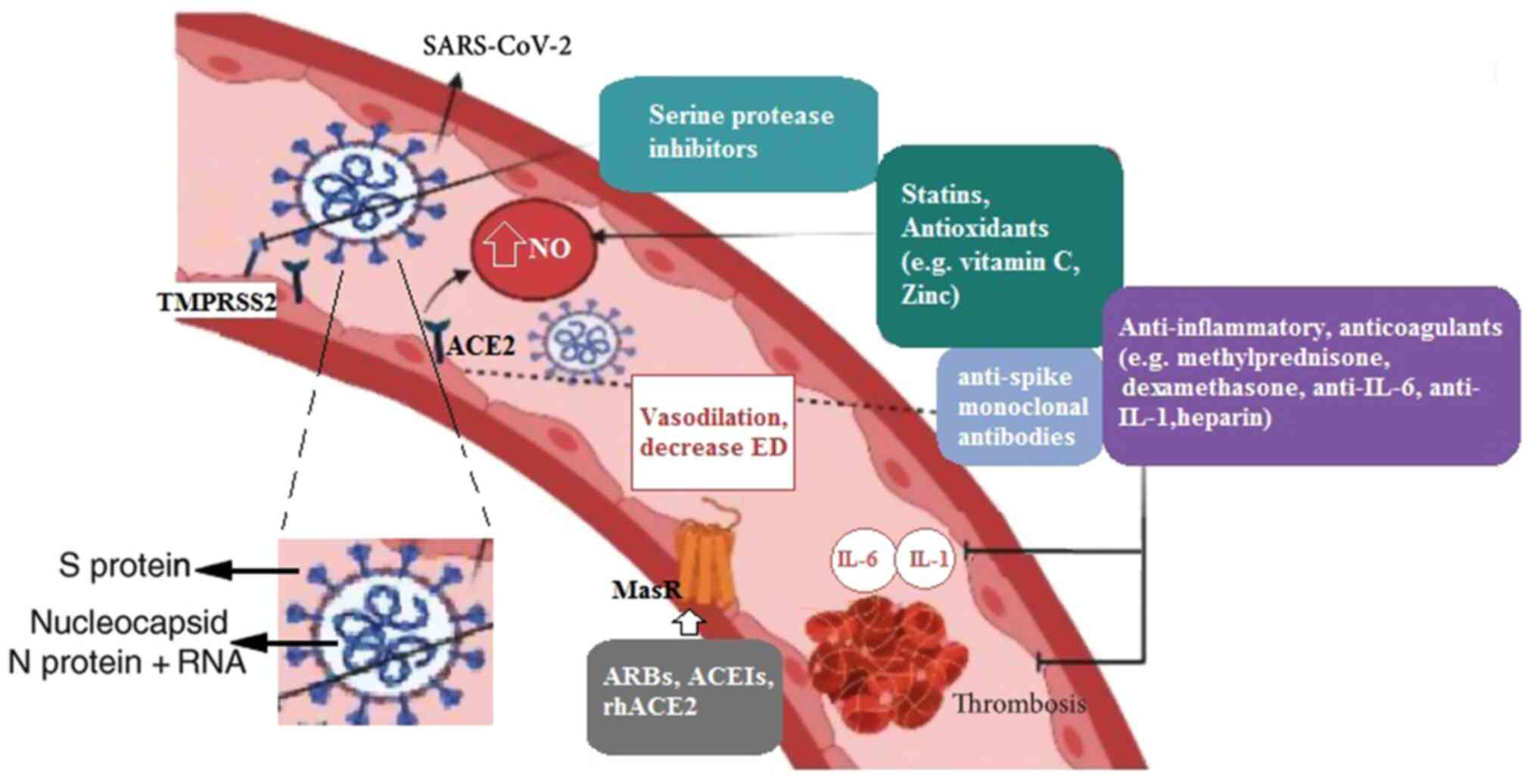
4
|
Daher J: Other forms of oxidized LDL:
Emerging functions. World Acad Sci J. 2:1. 2020.
|
|
5
|
Álvarez A, Cerdá-Nicolás M, Naim Abu Nabah
Y, Mata M, Issekutz AC, Panés J, Lobb RR and Sanz MJ: Direct
evidence of leukocyte adhesion in arterioles by angiotensin II.
Blood. 104:402–408. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kranzhöfer R, Schmidt J, Pfeiffer CA, Hagl
S, Libby P and Kübler W: Angiotensin induces inflammatory
activation of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:1623–1629. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
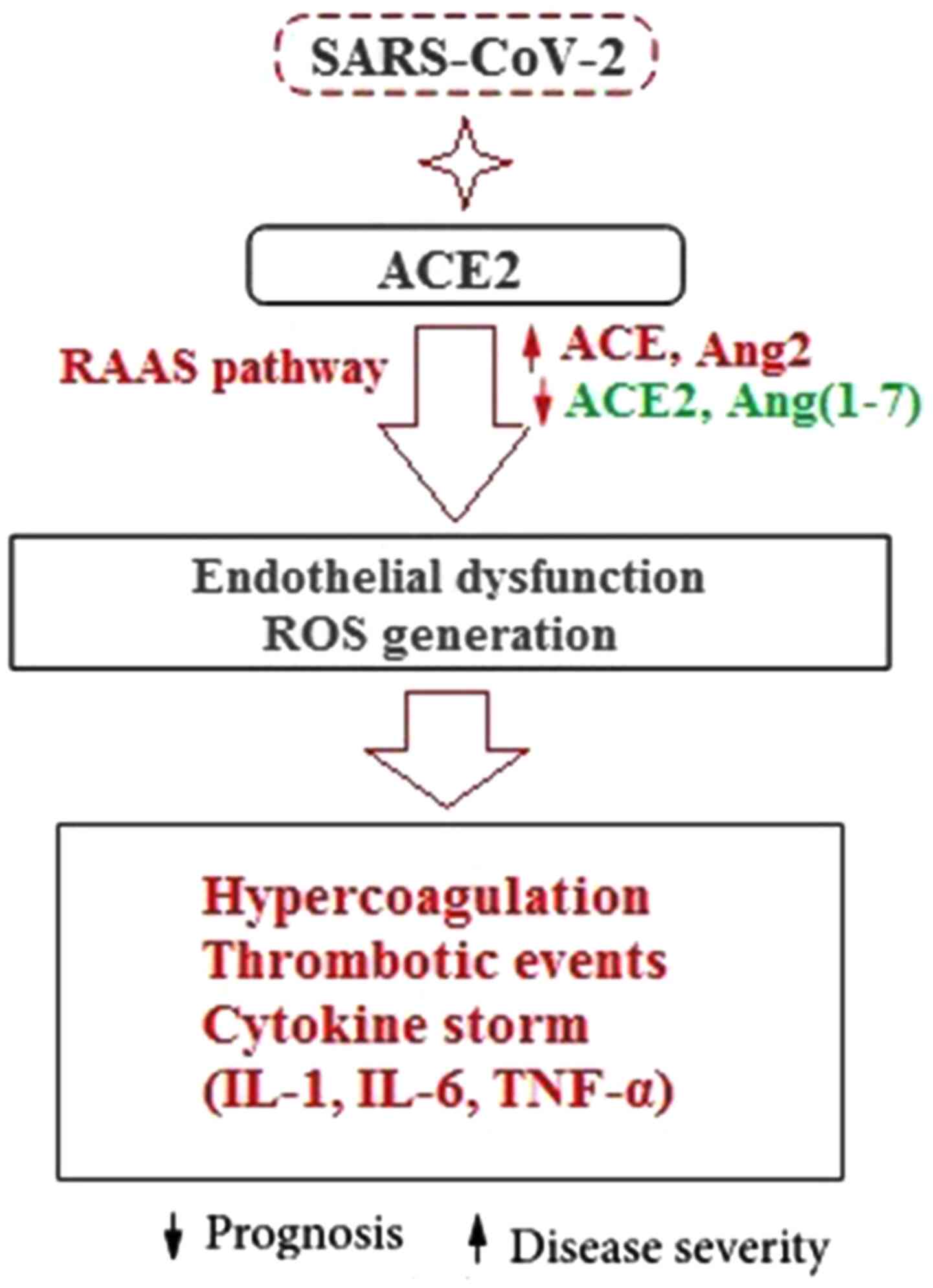
|
|
7
|
Hahn AW, Jonas U, Bühler FR and Resink TJ:
Activation of human peripheral monocytes by angiotensin II. FEBS
Lett. 347:178–180. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tummala PE, Chen X-L, Sundell CL, Laursen
JB, Hammes CP, Alexander RW, Harrison DG and Medford RM:
Angiotensin II induces vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression
in rat vasculature: A potential link between the renin-angiotensin
system and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 100:1223–1229.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rajagopalan S, Kurz S, Münzel T, Tarpey M,
Freeman BA, Griendling KK and Harrison DG: Angiotensin II-mediated
hypertension in the rat increases vascular superoxide production
via membrane NADH/NADPH oxidase activation. Contribution to
alterations of vasomotor tone. J Clin Invest. 97:1916–1923.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wassmann S and Nickenig G:
Pathophysiological regulation of the AT1-receptor and implications
for vascular disease. J Hypertens Suppl. 24 (Suppl 1):S15–S21.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Judkins CP, Diep H, Broughton BRS, Mast
AE, Hooker EU, Miller AA, Selemidis S, Dusting GJ, Sobey CG and
Drummond GR: Direct evidence of a role for Nox2 in superoxide
production, reduced nitric oxide bioavailability, and early
atherosclerotic plaque formation in ApoE-/- mice. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 298:H24–H32. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Förstermann U and Münzel T: Endothelial
nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: From marvel to menace.
Circulation. 113:1708–1714. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ferrari R: RAAS inhibition and mortality
in hypertension. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2013:269–278.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mansur SJ, Hage FG and Oparil S: Have the
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system perturbations in
cardiovascular disease been exhausted? Curr Cardiol Rep.
12:450–463. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
South AM, Tomlinson L, Edmonston D,
Hiremath S and Sparks MA: Controversies of renin-angiotensin system
inhibition during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Rev Nephrol.
16:305–307. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fang L, Karakiulakis G and Roth M: Are
patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk
for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir Med. 8(e21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ferrario CM, Jessup J, Chappell MC,
Averill DB, Brosnihan KB, Tallant EA, Diz DI and Gallagher PE:
Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin
II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
Circulation. 111:2605–2610. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bean D, Kraljevic Z, Searle T, Bendayan R,
Pickles A, Folarin A, Roguski L, Noor K, Shek A, O'Gallagher K, et
al: Treatment with ACE-inhibitors is associated with less severe
disease with SARS-Covid-19 infection in a multi-site UK acute
Hospital Trust. medRxiv: Apr 11, 2020 (Epub ahead of print). doi:
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.07.20056788.
|
|
19
|
Vaduganathan M, Vardeny O, Michel T,
McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA and Solomon SD:
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with
Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 382:1653–1659. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kuster GM, Pfister O, Burkard T, Zhou Q,
Twerenbold R, Haaf P, Widmer AF and Osswald S: SARS-CoV2: Should
inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system be withdrawn in patients
with COVID-19? Eur Heart J. 41:1801–1803. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Simões E, Silva AC and Flynn JT: The
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in 2011: Role in hypertension
and chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 27:1835–1845.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
South AM, Shaltout HA, Washburn LK,
Hendricks AS, Diz DI and Chappell MC: Fetal programming and the
angiotensin-(1-7) axis: A review of the experimental and clinical
data. Clin Sci (Lond). 133:55–74. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Masi S, Uliana M and Virdis A: Angiotensin
II and vascular damage in hypertension: Role of oxidative stress
and sympathetic activation. Vascul Pharmacol. 115:13–17.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wan Y, Shang J, Graham R, Baric RS and Li
F: Receptor recognition by novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An
analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS. J Virol.
94:e00127–e20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gu H, Xie Z, Li T, Zhang S, Lai C, Zhu P,
Wang K, Han L, Duan Y, Zhao Z, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme
2 inhibits lung injury induced by respiratory syncytial virus. Sci
Rep. 6(19840)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li X, Molina-Molina M, Abdul-Hafez A, Uhal
V, Xaubet A and Uhal BD: Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 is
protective but downregulated in human and experimental lung
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 295:L178–L185.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhang C, Huang F, Wang F,
Yuan J, Wang Z, Li J, Li J, Feng C, et al: Clinical and biochemical
indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and
lung injury. Sci China Life Sci. 63:364–374. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Oudit GY, Kassiri Z, Jiang C, Liu PP,
Poutanen SM, Penninger JM and Butany J: SARS-coronavirus modulation
of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with
SARS. Eur J Clin Invest. 39:618–625. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lopes RD, Macedo AVS, de Barros E Silva
PG, Moll-Bernardes RJ, Dos Santos TM, Mazza L, Feldman A, D'Andréa
Saba Arruda G, de Albuquerque DC, Camiletti AS, et al: BRACE CORONA
investigators: Effect of discontinuing vs. continuing
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin ii
receptor blockers on days alive and out of the hospital in patients
admitted with COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA.
325:254–264. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hippisley-Cox J, Young D, Coupland C,
Channon KM, Tan PS, Harrison DA, Rowan K, Aveyard P, Pavord ID and
Watkinson PJ: Risk of severe COVID-19 disease with ACE inhibitors
and angiotensin receptor blockers: Cohort study including 8.3
million people. Heart. 106:1503–1511. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Simko F and Baka T: Angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers: Potential
allies in the COVID-19 pandemic instead of a threat? Clin Sci
(Lond). 135:1009–1014. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Janardhan V, Janardhan V and Kalousek V:
COVID-19 as a blood clotting disorder masquerading as a respiratory
illness: a cerebrovascular perspective and therapeutic implications
for stroke thrombectomy. J Neuroimaging. 30:555–561.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Xiao M, Zhang S, Xia P, Cao W,
Jiang W, Chen H, Ding X, Zhao H, Zhang H, et al: Coagulopathy and
antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with COVID-19. N Engl J
Med. 382(e38)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Oxley TJ, Mocco J, Majidi S, Kellner CP,
Shoirah H, Singh IP, De Leacy RA, Shigematsu T, Ladner TR, Yaeger
KA, et al: Large-vessel stroke as a presenting feature of COVID-19
in the young. N Engl J Med. 382(e60)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, Haberecker
M, Andermatt R, Zinkernagel AS, Mehra MR, Schuepbach RA, Ruschitzka
F and Moch H: Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in
COVID-19. Lancet. 395:1417–1418. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hess DC, Eldahshan W and Rutkowski E:
COVID-19-related stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 11:322–325.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Garrido AM and Griendling KK: NADPH
oxidases and angiotensin II receptor signaling. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 302:148–158. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
El-Assaad F, Krilis SA and Giannakopoulos
B: Posttranslational forms of beta 2-glycoprotein I in the
pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb J. 14 (Suppl
1)(20)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ho YC, Ahuja KDK, Körner H and Adams MJ:
β2GP1, anti-β2GP1 antibodies and platelets: Key players in the
antiphospholipid syndrome. Antibodies (Basel).
5(E12)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Han H, Yang L, Liu R, Liu F, Wu KL, Li J,
Liu XH and Zhu CL: Prominent changes in blood coagulation of
patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Chem Lab Med.
58:1116–1120. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang J, Saguner AM, An J, Ning Y, Yan Y
and Li G: Dysfunctional coagulation in COVID-19: From cell to
bedside. Adv Ther. 37:3033–3039. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gong J, Dong H, Xia SQ, Huang ZY, Wang DK,
Zhao Y, Liu WH, Tu SH, Zhang MM, Wang Q, et al: Correlation
analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related
parameters in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study. BMC
Infect Dis. 20(963)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lipinski S, Bremer L, Lammers T, Thieme F,
Schreiber S and Rosenstiel P: Coagulation and inflammation.
Molecular insights and diagnostic implications. Hamostaseologie.
31:94–102, 104. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lupi L, Adamo M, Inciardi RM and Metra M:
ACE2 down-regulation may contribute to the increased thrombotic
risk in COVID-19. Eur Heart J. 41(3200)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mehrabadi ME, Hemmati R, Tashakor A,
Homaei A, Yousefzadeh M, Hemati K and Hosseinkhani S: Induced
dysregulation of ACE2 by SARS-CoV-2 plays a key role in COVID-19
severity. Biomed Pharmacother. 137(111363)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fraga-Silva RA, Sorg BS, Wankhede M,
Dedeugd C, Jun JY, Baker MB, Li Y, Castellano RK, Katovich MJ,
Raizada MK, et al: ACE2 activation promotes antithrombotic
activity. Mol Med. 16:210–215. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang S, Liu Y, Wang X, Yang L, Li H, Wang
Y, Liu M, Zhao X, Xie Y, Yang Y, et al: SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet
ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19. J Hematol Oncol.
13(120)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Deng H, Tang TX, Chen D, Tang LS, Yang XP
and Tang ZH: Endothelial dysfunction and SARS-CoV-2 infection:
Association and therapeutic strategies. Pathogens.
10(582)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Libby P and Lüscher T: COVID-19 is, in the
end, an endothelial disease. Eur Heart J. 41:3038–3044.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Batlle D, Wysocki J and Satchell K:
Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: A potential approach for
coronavirus infection therapy? Clin Sci (Lond). 134:543–545.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Jahanshahlu L and Rezaei N: Monoclonal
antibody as a potential anti-COVID-19. Biomed Pharmacother.
129(110337)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Fodor A, Tiperciuc B, Login C, Orasan OH,
Lazar AL, Buchman C, Hanghicel P, Sitar-Taut A, Suharoschi R,
Vulturar R, et al: Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and
oxidative stress in COVID-19-mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021(8671713)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Jin Y, Ji W, Yang H, Chen S, Zhang W and
Duan G: Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: From
basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 5(293)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shahin Y, Khan JA, Samuel N and Chetter I:
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors effect on endothelial
dysfunction: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Atherosclerosis. 216:7–16. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Reynolds HR, Adhikari S, Pulgarin C,
Troxel AB, Iturrate E, Johnson SB, Hausvater A, Newman JD, Berger
JS, Bangalore S, et al: Renin-angiotensin-Aldosterone system
inhibitors and risk of covid-19. N Engl J Med. 382:2441–2448.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Fosbøl EL, Butt JH, Østergaard L,
Andersson C, Selmer C, Kragholm K, Schou M, Phelps M, Gislason GH,
Gerds TA, et al: Association of angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker use with COVID-19
diagnosis and mortality. JAMA. 324:168–177. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Flacco ME, Acuti Martellucci C, Bravi F,
Parruti G, Cappadona R, Mascitelli A, Manfredini R, Mantovani LG
and Manzoli L: Treatment with ACE inhibitors or ARBs and risk of
severe/lethal COVID-19: A meta-analysis. Heart. 106:1519–1524.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
De Spiegeleer A, Bronselaer A, Teo JT,
Byttebier G, De Tré G, Belmans L, Dobson R, Wynendaele E, Van De
Wiele C, Vandaele F, et al: The effects of ARBs, ACEis, and statins
on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 infection among nursing home
residents. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 21:909–914.e2. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Reriani MK, Dunlay SM, Gupta B, West CP,
Rihal CS, Lerman LO and Lerman A: Effects of statins on coronary
and peripheral endothelial function in humans: A systematic review
and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Cardiovasc
Prev Rehabil. 18:704–716. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Nägele MP, Haubner B, Tanner FC,
Ruschitzka F and Flammer AJ: Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19:
Current findings and therapeutic implications. Atherosclerosis.
314:58–62. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ayerbe L, Risco C and Ayis S: The
association between treatment with heparin and survival in patients
with Covid-19. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 50:298–301. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S,
Huang H, Zhang L, Zhou X, Du C, et al: Risk factors associated with
acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with
coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern
Med. 180:934–943. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M,
Bell JL, Linsell L, Staplin N, Brightling C, Ustianowski A, Elmahi
E, et al: RECOVERY Collaborative Group: Dexamethasone in
hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 384:693–704.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|