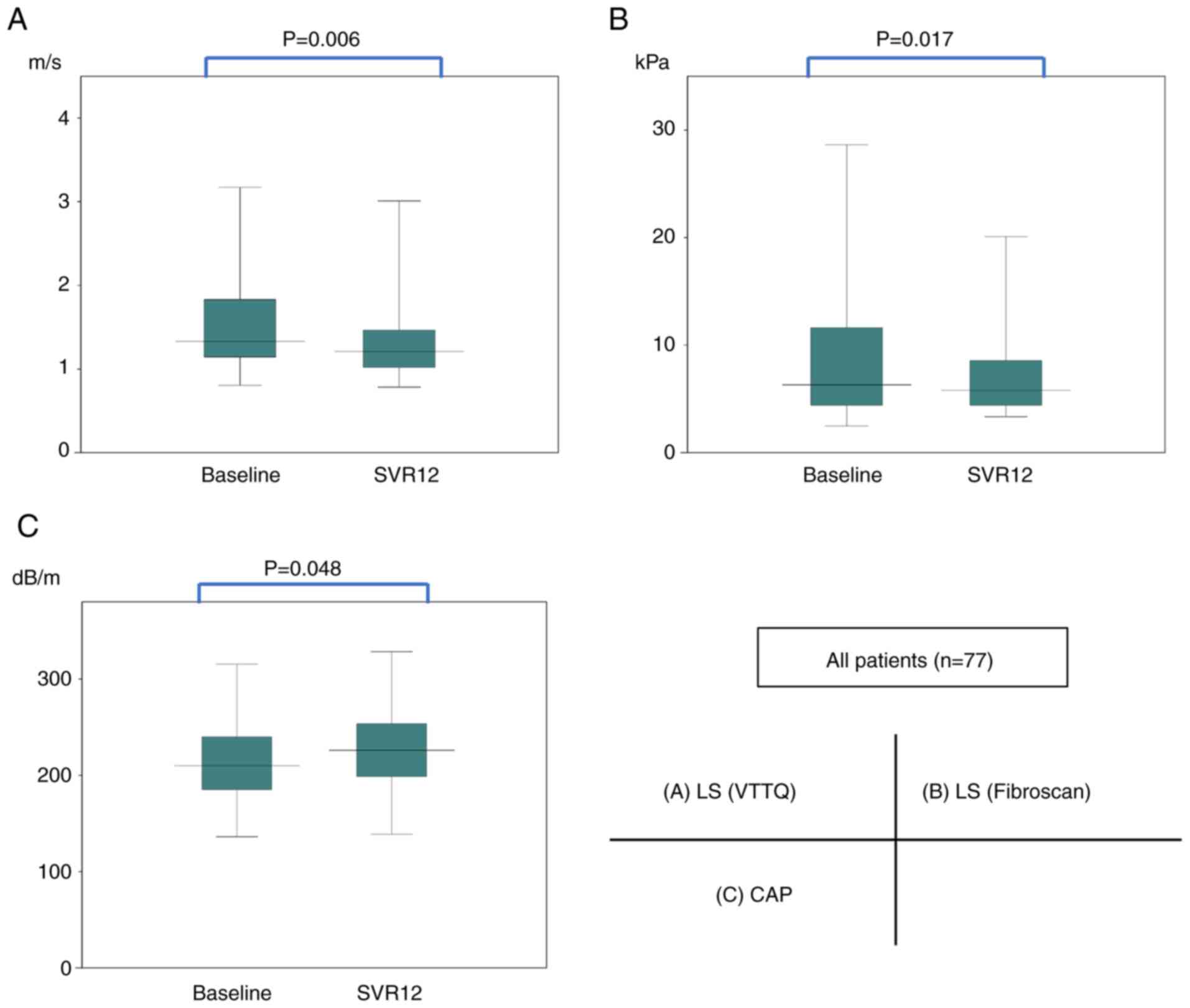
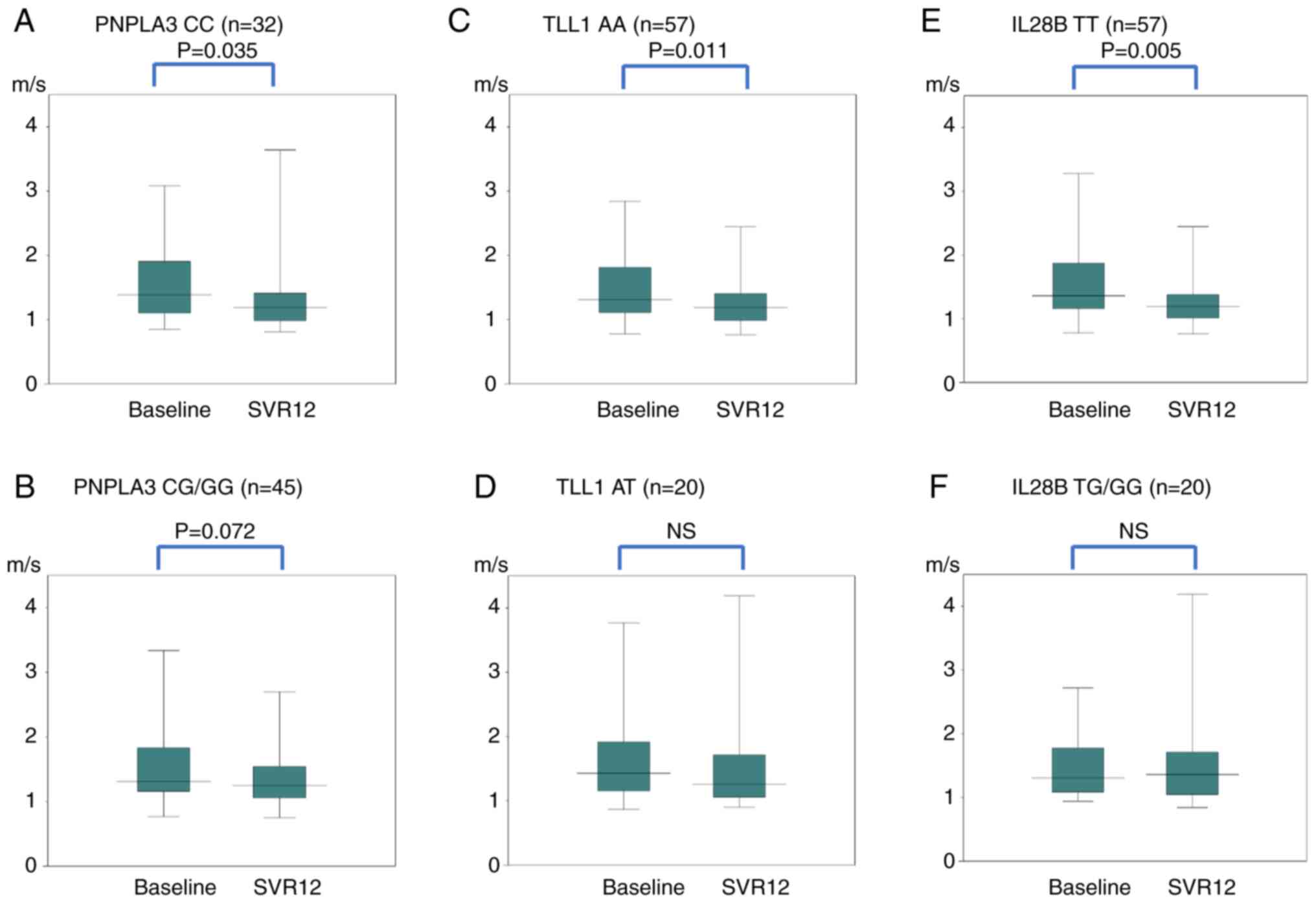
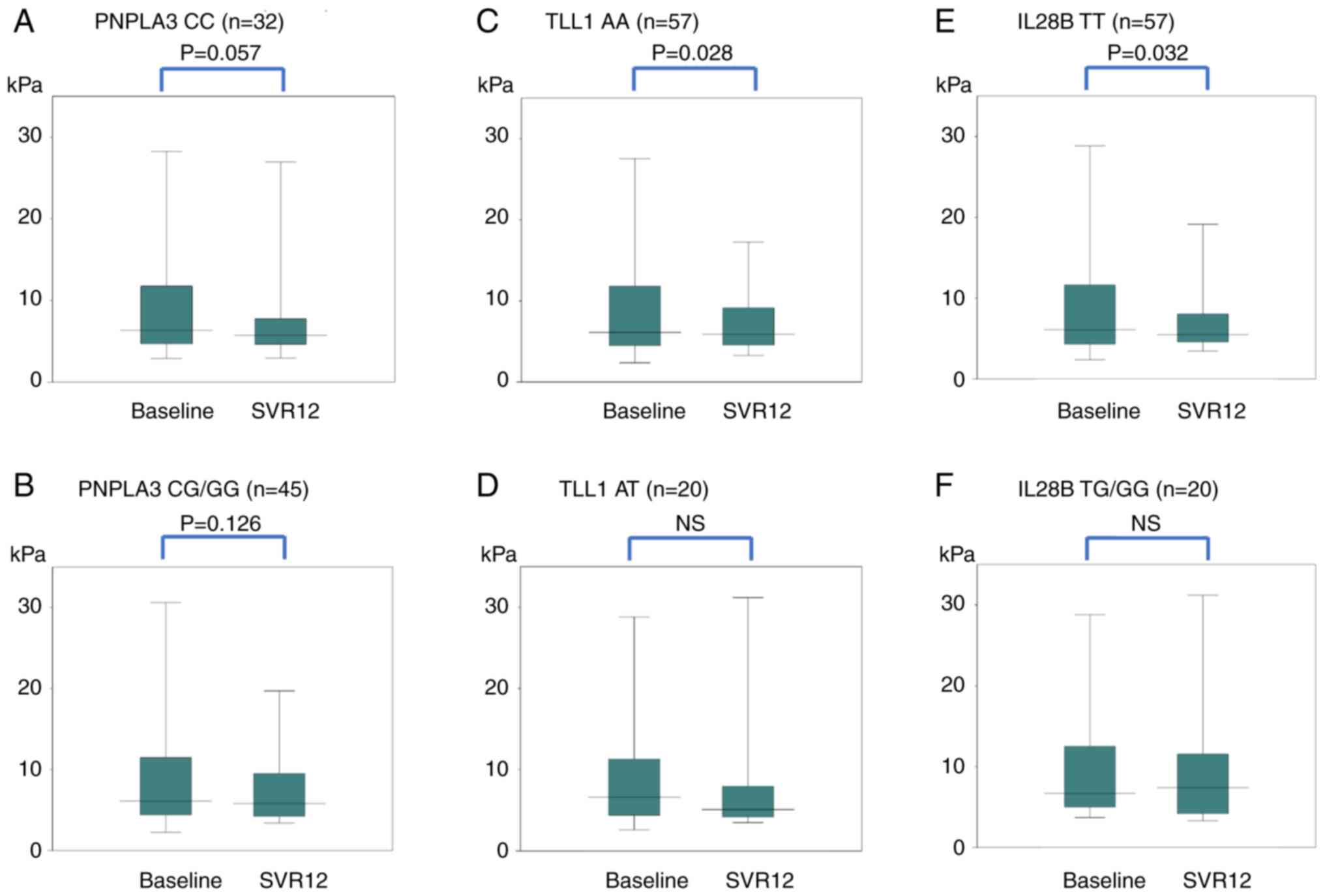
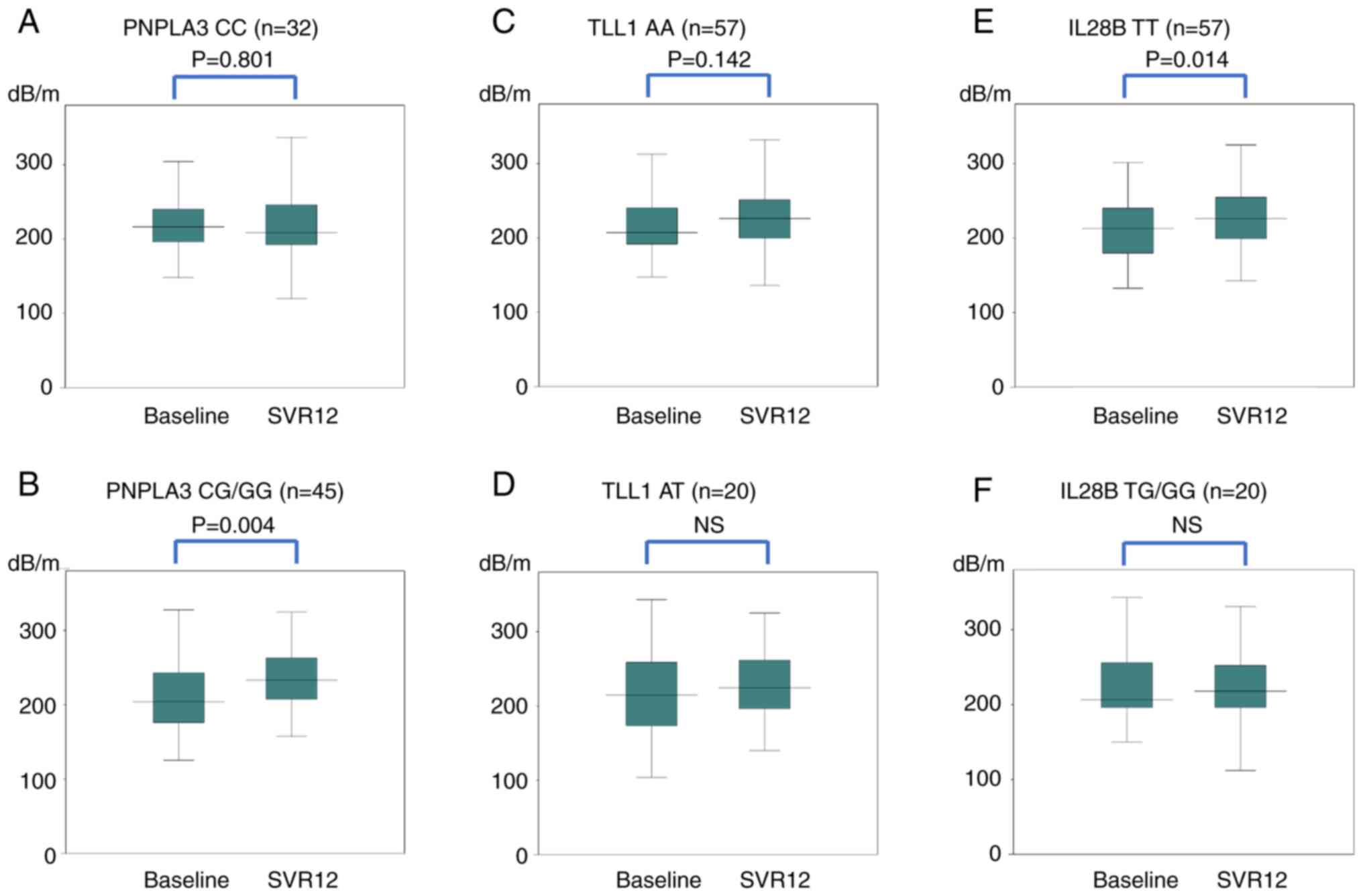
|
1
|
Li R, Li Y, Fang X, Yang H and Wang J,
Kristiansen K and Wang J: SNP detection for massively parallel
whole-genome resequencing. Genome Res. 19:1124–1132.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sato M, Kato N, Tateishi R, Muroyama R,
Kowatari N, Li W, Goto K, Otsuka M, Shiina S, Yoshida H, et al:
Impact of PNPLA3 polymorphisms on the development of hepatocellular
carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
Hepatol Res. 44:E137–E144. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yasui K, Kawaguchi T, Shima T, Mitsuyoshi
H, Seki K, Sendo R, Mizuno M, Itoh Y, Matsuda F and Okanoue T:
Effect of PNPLA3 rs738409 variant (I148 M) on hepatic steatosis,
necroinflammation, and fibrosis in Japanese patients with chronic
hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol. 50:887–893. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Crisan D, Grigorescu M, Crisan N, Craciun
R, Lupsor M, Radu C, Grigorescu MD, Suciu A, Epure F, Avram L and
Leach N: Association between PNPLA3[G]/I148M variant, steatosis and
fibrosis stage in hepatitis C virus-genetic matters. J Physiol
Pharmacol. 70:2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Matsuura K, Sawai H, Ikeo K, Ogawa S, Iio
E, Isogawa M, Shimada N, Komori A, Toyoda H, Kumada T, et al:
Genome-wide association study identifies TLL1 variant associated
with development of hepatocellular carcinoma after eradication of
hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 152:1383–1394.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang CF, Yeh ML, Huang CI, Lin ZY, Chen
SC, Huang JF, Dai CY, Chuang WL, Chen JJ and Yu ML: Tolloid-like 1
genetic variants determine fibrosis regression in chronic hepatitis
C patients with curative antivirals. Sci Rep.
8(15058)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Iio E, Matsuura K, Shimada N, Atsukawa M,
Itokawa N, Abe H, Kato K, Takaguchi K, Senoh T, Eguchi Y, et al:
TLL1 variant associated with development of hepatocellular
carcinoma after eradication of hepatitis C virus by interferon-free
therapy. J Gastroenterol. 54:339–346. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Abe H, Ochi H, Maekawa T, Hayes CN, Tsuge
M, Miki D, Mitsui F, Hiraga N, Imamura M, Takahashi S, et al:
Common variation of IL28 affects gamma-GTP levels and inflammation
of the liver in chronically infected hepatitis C virus patients. J
Hepatol. 53:439–443. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bochud PY, Bibert S, Negro F, Haagmans B,
Soulier A, Ferrari C, Missale G, Zeuzem S, Pawlotsky JM, Schalm S,
et al: IL28B polymorphisms predict reduction of HCV RNA from the
first day of therapy in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 55:980–988.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kurosaki M, Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sakamoto
N, Enomoto N, Honda M, Sugiyama M, Matsuura K, Sugauchi F, Asahina
Y, et al: Pre-treatment prediction of response to
pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C using
genetic polymorphism in IL28B and viral factors. J Hepatol.
54:439–448. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ohnishi M, Tsuge M, Kohno T, Zhang Y, Abe
H, Hyogo H, Kimura Y, Miki D, Hiraga N, Imamura M, et al: IL28B
polymorphism is associated with fatty change in the liver of
chronic hepatitis C patients. J Gastroenterol. 47:834–844.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Nishimura T,
Muraoka M, Suzuki Y, Tamaki N, Yasui Y, Hosokawa T, Ueda K,
Nakanishi H, et al: Genetic variation near interleukin 28B and the
risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis
C. J Gastroenterol. 49:1152–1162. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sato M, Kondo M, Tateishi R, Fujiwara N,
Kato N, Yoshida H, Taguri M and Koike K: Impact of IL28B genetic
variation on HCV-induced liver fibrosis, inflammation, and
steatosis: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9(e91822)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tamaki N, Kurosaki M, Higuchi M, Takada H,
Nakakuki N, Yasui Y, Suzuki S, Tsuchiya K, Nakanishi H, Itakura J,
et al: Genetic polymorphisms of IL28B and PNPLA3 are predictive for
HCV related rapid fibrosis progression and identify patients who
require urgent antiviral treatment with new regimens. PLoS One.
10(e0137351)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Myers RP, Fong A and Shaheen AA:
Utilization rates, complications and costs of percutaneous liver
biopsy: A population-based study including 4275 biopsies. Liver
Int. 28:705–712. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sasso M, Beaugrand M, de Ledinghen V,
Douvin C, Marcellin P, Poupon R, Sandrin L and Miette V: Controlled
attenuation parameter (CAP): A novel VCTE™ guided
ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic
steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients
with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med
Biol. 36:1825–1835. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Petruzziello A, Marigliano S, Loquercio G,
Cozzolino A and Cacciapuoti C: Global epidemiology of hepatitis C
virus infection: An up-date of the distribution and circulation of
hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J Gastroenterol. 22:7824–7840.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Attar BM and Van Thiel DH: Hepatitis C
virus: A time for decisions. Who should be treated and when? World
J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 7:33–40. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Leroy V, Angus P, Bronowicki JP, Dore GJ,
Hezode C, Pianko S, Pol S, Stuart K, Tse E, McPhee F, et al:
Daclatasvir, sofosbuvir, and ribavirin for hepatitis C virus
genotype 3 and advanced liver disease: A randomized phase III study
(ALLY-3+). Hepatology. 63:1430–1441. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ogasawara N, Kobayashi M, Akuta N,
Kominami Y, Fujiyama S, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, Hosaka T, Suzuki F,
Saitoh S, et al: Serial changes in liver stiffness and controlled
attenuation parameter following direct-acting antiviral therapy
against hepatitis C virus genotype 1b. J Med Virol. 90:313–319.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
World Medical Association: World medical
association declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF,
Fromageau J, Bojunga J, Calliada F, Cantisani V, Correas JM,
D'Onofrio M, Drakonaki EE, et al: EFSUMB guidelines and
recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography.
Part 1: Basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med.
34:169–184. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Boursier J, Zarski JP, de Ledinghen V,
Rousselet MC, Sturm N, Lebail B, Fouchard-Hubert I, Gallois Y,
Oberti F, Bertrais S, et al: Determination of reliability criteria
for liver stiffness evaluation by transient elastography.
Hepatology. 57:1182–1191. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kumagai E, Korenaga K, Korenaga M, Imamura
M, Ueyama M, Aoki Y, Sugiyama M, Murata K, Masaki N, Kanto T, et
al: Appropriate use of virtual touch quantification and FibroScan M
and XL probes according to the skin capsular distance. J
Gastroenterol. 51:496–505. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
De la Vega FM, Lazaruk KD, Rhodes MD and
Wenz MH: Assessment of two flexible and compatible SNP genotyping
platforms: TaqMan SNP genotyping assays and the SNPlex genotyping
system. Mutat Res. 573:111–135. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Romeo S, Kozlitina J, Xing C, Pertsemlidis
A, Cox D, Pennacchio LA, Boerwinkle E, Cohen JC and Hobbs HH:
Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 40:1461–1465. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Seko Y, Sumida Y, Tanaka S, Mori K,
Taketani H, Ishiba H, Hara T, Okajima A, Umemura A, Nishikawa T, et
al: Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japanese patients
with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Association
between PNPLA3 genotype and hepatocarcinogenesis/fibrosis
progression. Hepatol Res. 47:1083–1092. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Kurosaki
M, Matsuura K, Sakamoto N, Nakagawa M, Korenaga M, Hino K, Hige S,
et al: Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated
interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat
Genet. 41:1105–1109. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Morgan TR, Ghany MG, Kim HY, Snow KK,
Shiffman ML, De Santo JL, Lee WM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bonkovsky HL,
Dienstag JL, et al: Outcome of sustained virological responders
with histologically advanced chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology.
52:833–844. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kanwal F, Kramer J, Asch SM, Chayanupatkul
M, Cao Y and El-Serag HB: Risk of hepatocellular cancer in HCV
patients treated with direct-acting antiviral agents.
Gastroenterology. 153:996–1005.e1. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ogata F, Kobayashi M, Akuta N, Osawa M,
Fujiyama S, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S,
et al: Outcome of all-oral direct-acting antiviral regimens on the
rate of development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with
hepatitis C virus genotype 1-related chronic liver disease.
Oncology. 93:92–98. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Makiyama A, Itoh Y, Kasahara A, Imai Y,
Kawata S, Yoshioka K, Tsubouchi H, Kiyosawa K, Kakumu S, Okita K,
et al: Characteristics of patients with chronic hepatitis C who
develop hepatocellular carcinoma after a sustained response to
interferon therapy. Cancer. 101:1616–1622. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Nishimura T,
Muraoka M, Suzuki Y, Tamaki N, Yasui Y, Hosokawa T, Ueda K,
Nakanishi H, et al: α-Fetoprotein levels after interferon therapy
and risk of hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 58:1253–1262. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
El-Serag HB, Kanwal F, Richardson P and
Kramer J: Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after sustained
virological response in Veterans with hepatitis C virus infection.
Hepatology. 64:130–137. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ioannou GN, Green PK, Beste LA, Mun EJ,
Kerr KF and Berry K: Development of models estimating the risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma after antiviral treatment for hepatitis C.
J Hepatol. 69:1088–1098. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Motoyama H, Tamori A, Kubo S,
Uchida-Kobayashi S, Takemura S, Tanaka S, Ohfuji S, Teranishi Y,
Kozuka R, Kawamura E, et al: Stagnation of histopathological
improvement is a predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma development
after hepatitis C virus eradication. PLoS One.
13(e0194163)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tanaka A, Uegaki S, Kurihara H, Aida K,
Mikami M, Nagashima I, Shiga J and Takikawa H: Hepatic steatosis as
a possible risk factor for the development of hepatocellular
carcinoma after eradication of hepatitis C virus with antiviral
therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:5180–5187. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R,
Pollett A, Duarte-Rojo A, Wong D, Beaton M, Levstik M, Crotty P and
Elkashab M: Feasibility and diagnostic performance of the FibroScan
XL probe for liver stiffness measurement in overweight and obese
patients. Hepatology. 55:199–208. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|