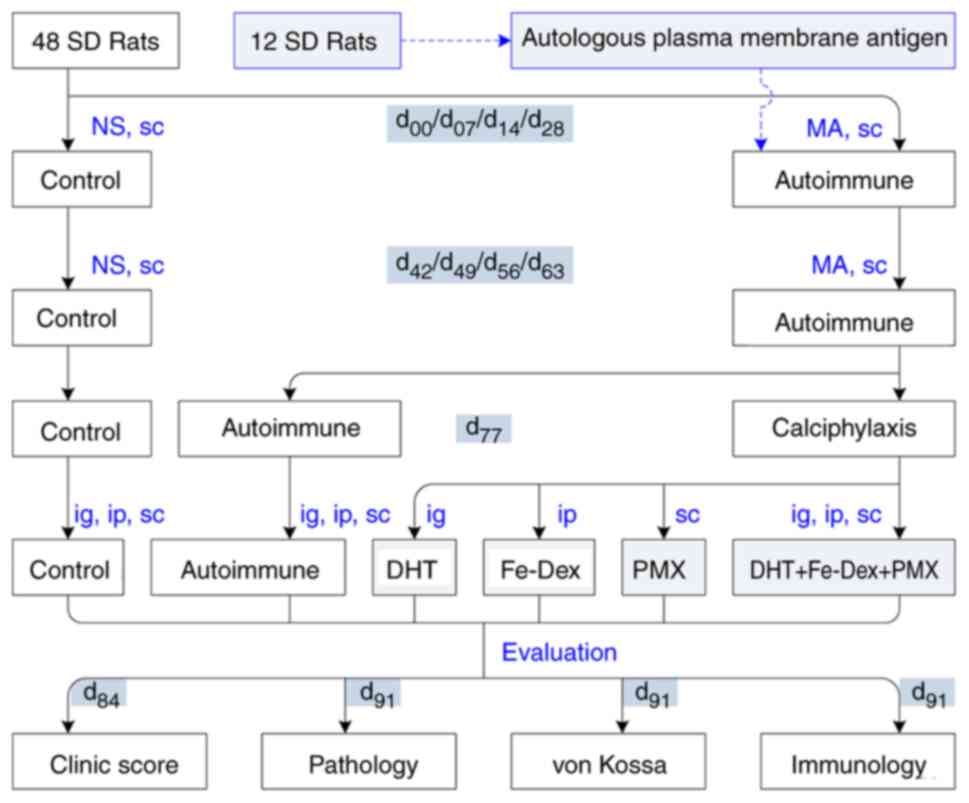
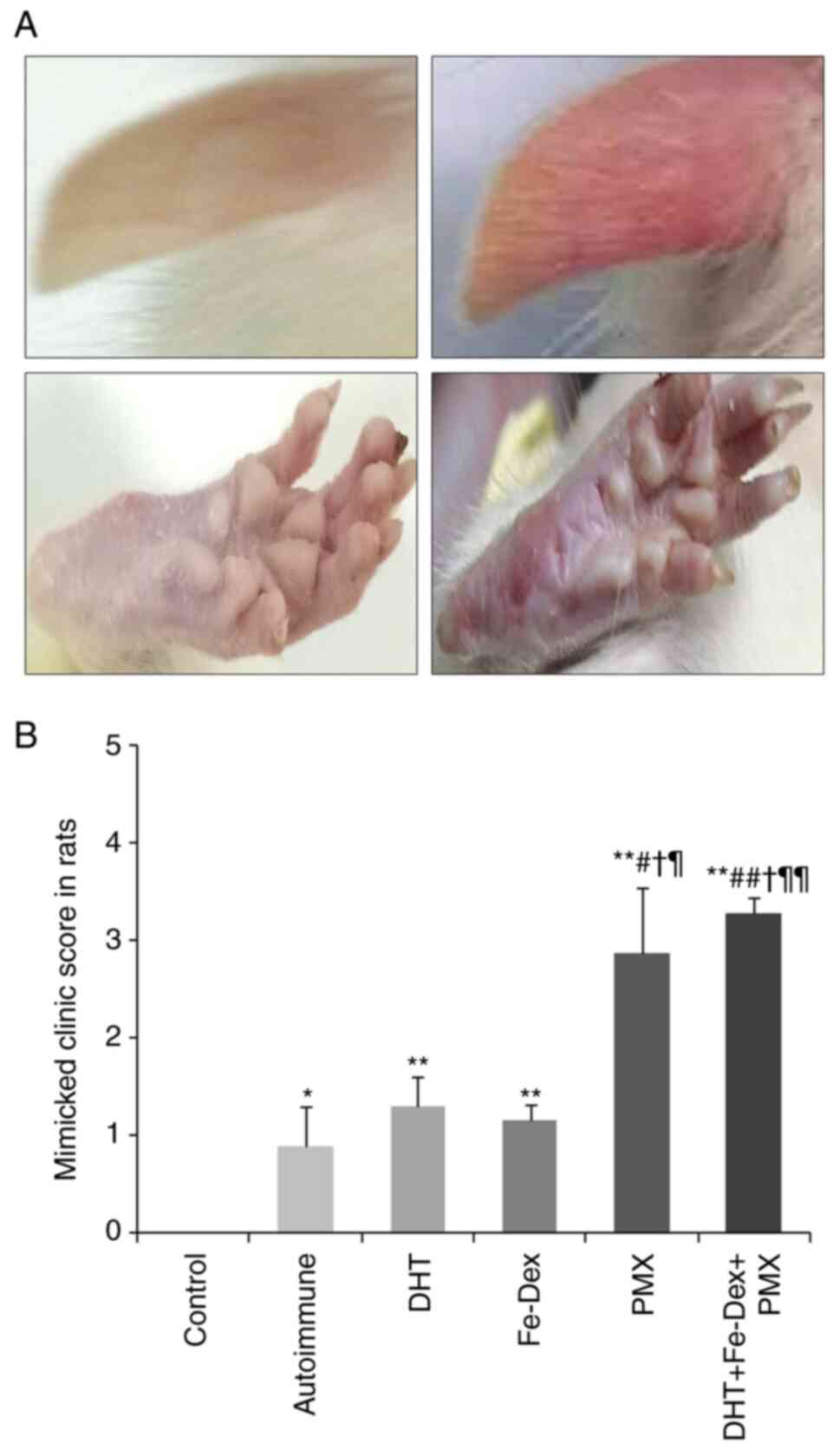
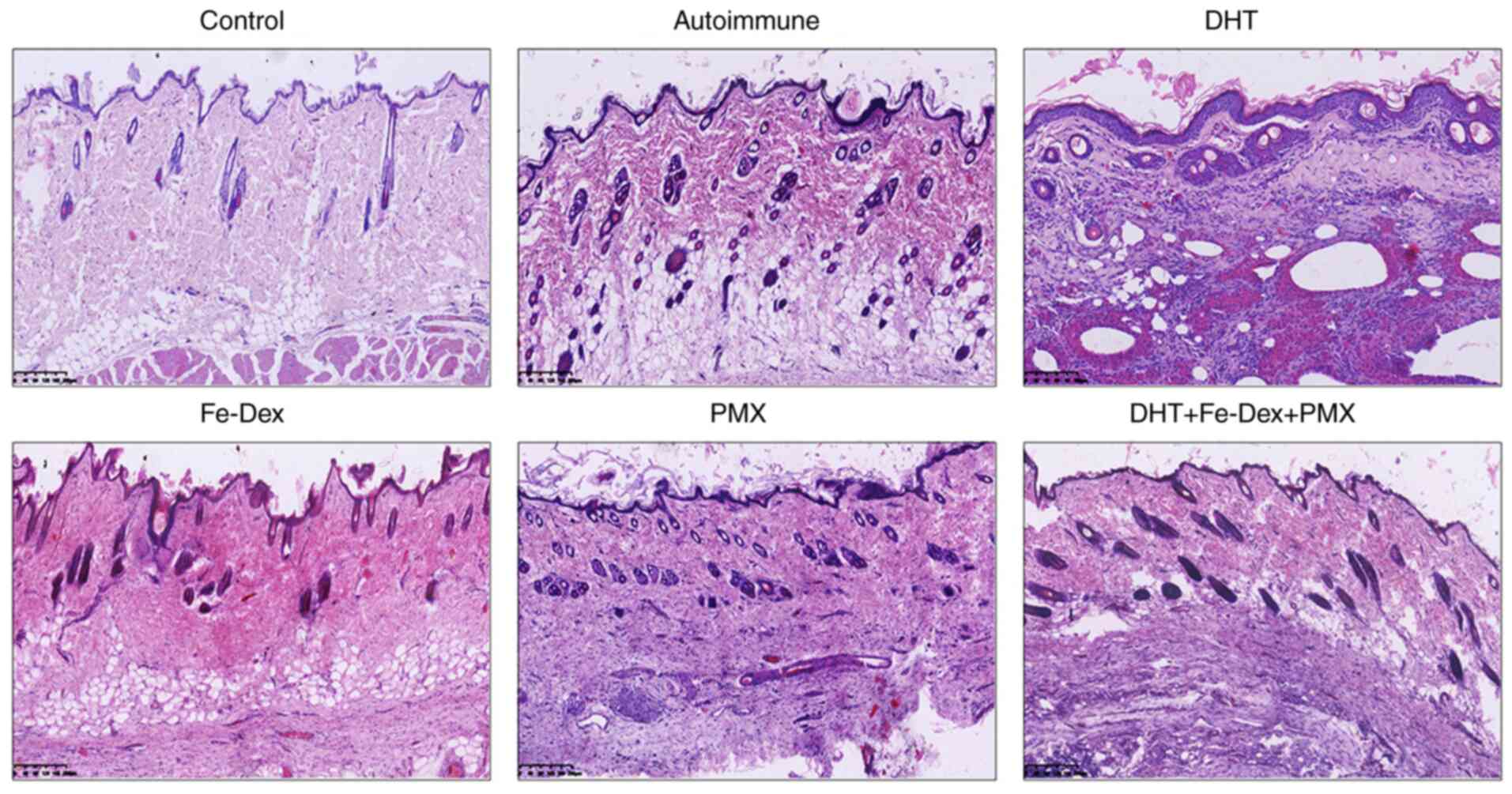
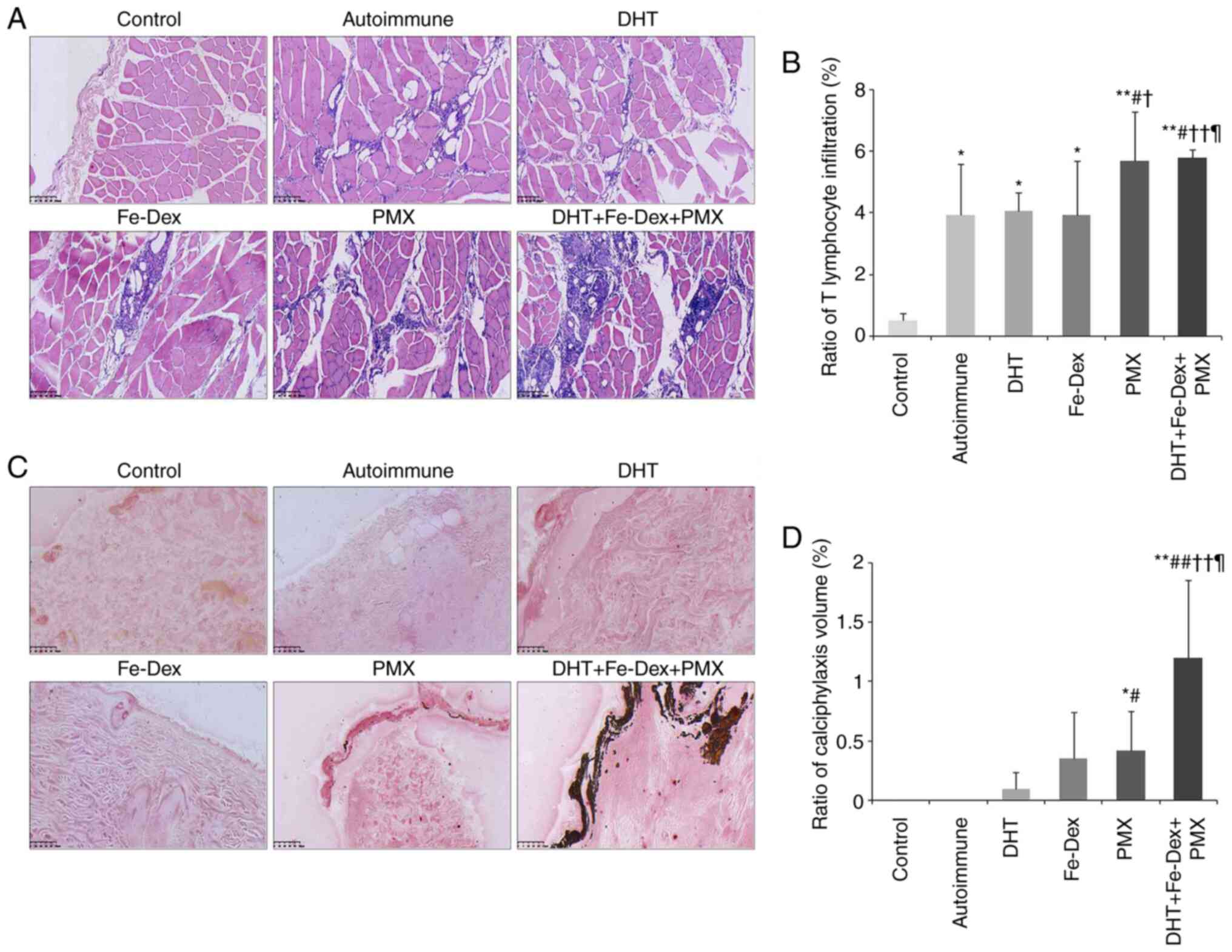
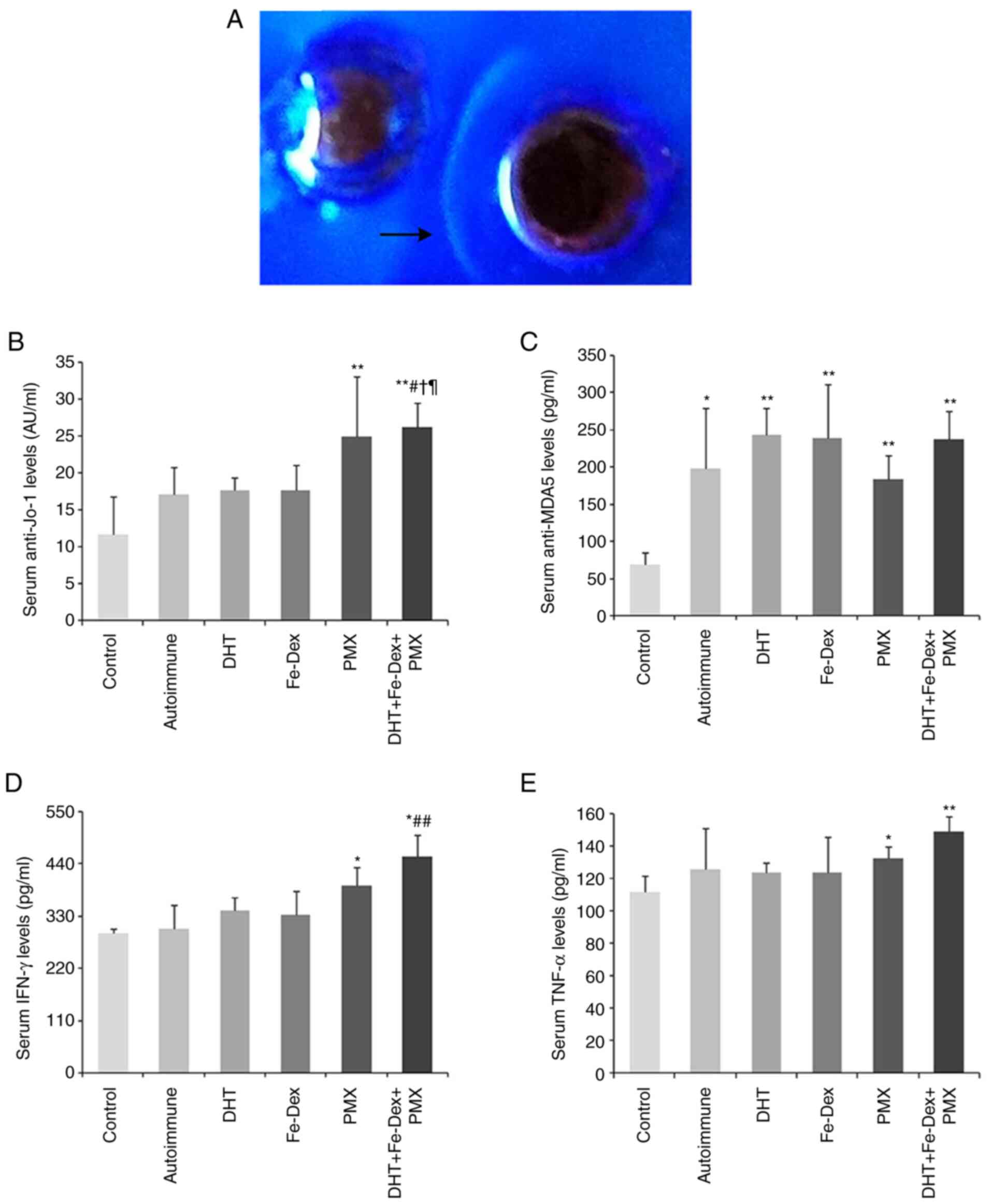
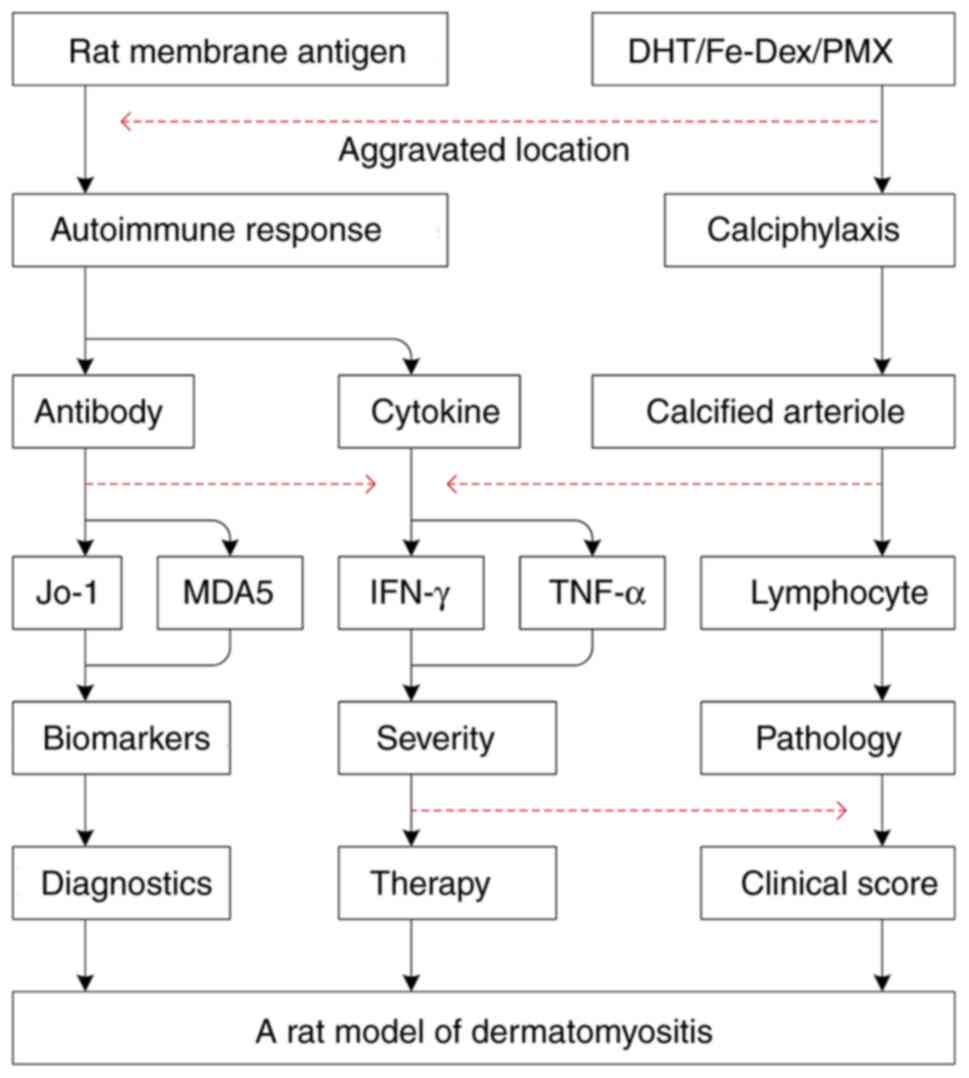
|
1
|
Santo AH, Souza JM, Pinheiro CE, Souza DC
and Sato EI: Trends in dermatomyositis- and polymyositis-related
mortality in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil, 1985-2007: Multiple
cause-of-death analysis. BMC Public Health. 10(597)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnson C, Connors GR, Oaks J, Han S,
Truong A, Richardson B, Lechtzin N, Mammen AL, Casciola-Rosen L,
Christopher-Stine L and Danoff SK: Clinical and pathologic
differences in interstitial lung disease based on antisynthetase
antibody type. Respir Med. 108:1542–1548. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
DeWane ME, Waldman R and Lu J:
Dermatomyositis: Clinical features and pathogenesis. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 82:267–281. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Smith ES, Hallman JR, DeLuca AM,
Goldenberg G, Jorizzo JL and Sangueza OP: Dermatomyositis: A
clinicopathological study of 40 patients. Am J Dermatopathol.
31:61–67. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vermaak E, Shaddick G and McHugh NJ:
Mortality In Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis: A Single Centre
Study. Arthritis Rheum-Us 65: S878-S878, 2013. https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/full-record/WOS:000325359205007.
|
|
6
|
Yang WM and Chen JJ: Advances in
biomarkers for dermatomyositis. Clin Chim Acta. 482:172–177.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun KY, Fan Y, Wang YX, Zhong YJ and Wang
GF: Prevalence of interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and
dermatomyositis: A meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Semin Arthritis
Rheum. 51:175–191. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kao L, Chung L and Fiorentino DF:
Pathogenesis of dermatomyositis: Role of cytokines and interferon.
Curr Rheumatol Rep. 13:225–232. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Selye H, Gentile G and Jean P: An
experimental model of ‘dermatomyositis’ induced by calciphylaxis.
Can Med Assoc J. 85:770–776. 1961.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aljabban J, Syed S, Rohr M, Weisleder N,
McElhanon KE, Hasan L, Safeer L, Hoffman K, Aljabban N, Mukhtar M,
et al: Investigating genetic drivers of dermatomyositis
pathogenesis using meta-analysis. Heliyon. 6(e04866)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Luo YB and Mastaglia FL: Dermatomyositis,
polymyositis and immune-mediated necrotising myopathies. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:622–632. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Okiyama N, Ichimura Y, Shobo M, Tanaka R,
Kubota N, Saito A, Ishitsuka Y, Watanabe R, Fujisawa Y, Nakamura Y,
et al: Immune response to dermatomyositis-specific autoantigen,
transcriptional intermediary factor 1γ can result in experimental
myositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:1201–1208. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A, Bettio S, Zen
M, Gatto M, Punzi L and Doria A: The clinical features, diagnosis
and classification of dermatomyositis. J Autoimmun. 48-49:122–127.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shimojima Y, Matsuda M, Ishii W, et al:
Phenotypic analysis of lymphocytes using flow cytometry in
dermatomyositis with and without interstitial pneumonia. In:
Proceeding of the 8th International Congress of Neuroimmunology:
209-212, 2006. https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/full-record/WOS:000251732700043.
|
|
15
|
Cassius C, Moguelet P, Monfort JB, Fessi
H, Michel PA, Boulahia G, Cury K, Frances C and Senet P:
Calciphylaxis in haemodialysed patients: Diagnostic value of
calcifications in cutaneous biopsy. Br J Dermatol. 178:292–293.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nemoto H, Bhopale MK, Constantinescu CS,
Schotland D and Rostami A: Skeletal muscle myosin is the
autoantigen for experimental autoimmune myositis. Exp Mol Pathol.
74:238–243. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kang J, Zhang HY, Feng GD, Feng DY and Jia
HG: Development of an improved animal model of experimental
autoimmune myositis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14457–14464.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lennon VA, Lindstrom JM and Seybold ME:
Experimental autoimmune myasthenia: A model of myasthenia gravis in
rats and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 141:1365–1375. 1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Abbas AK and Lichtman AH: Basic
immunology: Functions and disorders of the immune system. Saunders,
Philadelphia, PA, 2004.
|
|
20
|
Bodoki L, Nagy-Vincze M, Griger Z,
Betteridge Z, Szollosi L and Danko K: Four dermatomyositis-specific
autoantibodies-anti-TIF1ү, anti-NXP2, anti-SAE and anti-MDA5-in
adult and juvenile patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
in a Hungarian cohort. Autoimmun Rev. 13:1211–1219. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ishikawa Y, Iwata S, Hanami K, Nawata A,
Zhang M, Yamagata K, Hirata S, Sakata K, Todoroki Y, Nakano K, et
al: Relevance of interferon-gamma in pathogenesis of
life-threatening rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in
patients with dermatomyositis. Arthritis Res Ther.
20(240)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Giris M, Durmus H, Yetimler B, Tasli H,
Parman Y and Tuzun E: Elevated IL-4 and IFN-ү levels in muscle
tissue of patients with dermatomyositis. In Vivo. 31:657–660.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shinjo SK, de Souza FH and de Moraes JC:
Dermatomyositis and polymyositis: From immunopathology to
immunotherapy (immunobiologics). Rev Bras Reumatol. 53:101–110.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Portuguese).
|
|
24
|
Sasaki H and Kohsaka H: Current diagnosis
and treatment of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Mod Rheumatol.
28:913–921. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yang SH, Chang C and Lian ZX: Polymyositis
and dermatomyositis-challenges in diagnosis and management. J
Transl Autoimmun. 2(100018)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dalakas MC and Hohlfeld R: Polymyositis
and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 362:971–982. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Miller FW, Rider LG, Plotz PH, Isenberg DA
and Oddis CV: Diagnostic criteria for polymyositis and
dermatomyositis. Lancet. 362:1762–1763. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Goebels N, Michaelis D, Engelhardt M,
Huber S, Bender A, Pongratz D, Johnson MA, Wekerle H, Tschopp J,
Jenne D and Hohlfeld R: Differential expression of perforin in
muscle-infiltrating T cells in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J
Clin Invest. 97:2905–2910. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nigwekar SU, Kroshinsky D, Nazarian RM,
Goverman J, Malhotra R, Jackson VA, Kamdar MM, Steele DJ and
Thadhani RI: Calciphylaxis: Risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.
Am J Kidney Dis. 66:133–146. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou Q, Neubauer J, Kern JS, Grotz W, Walz
G and Huber TB: Calciphylaxis. Lancet. 383(1067)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Aghagolzadeh P, Bachtler M, Bijarnia R,
Jackson C, Smith ER, Odermatt A, Radpour R and Pasch A:
Calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells is induced by
secondary calciprotein particles and enhanced by tumor necrosis
factor-α. Atherosclerosis. 251:404–414. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mathur RV, Shortland JR and el-Nahas AM:
Calciphylaxis. Postgrad Med J. 77:557–561. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Romero-Díaz J, Vargas-Vóracková F,
Kimura-Hayama E, Cortázar-Benítez LF, Gijón-Mitre R, Criales S,
Cabiedes-Contreras J, Iñiguez-Rodríguez Mdel R, Lara-García EA,
Núñez-Alvarez C, et al: Systemic lupus erythematosus risk factors
for coronary artery calcifications. Rheumatology (Oxford).
51:110–119. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Iammatteo M, Keskin T and Jerschow E:
Evaluation of periprocedural hypersensitivity reactions. Ann
Allergy Asthma Immunol. 119:349–355.e2. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Castells M: Diagnosis and management of
anaphylaxis in precision medicine. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
140:321–333. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Javed B, Padfield P, Sperrin M, Simpson A
and Mills ENC: A protocol for a systematic review to identify
allergenic tree nuts and the molecules responsible for their
allergenic properties. Food Chem Toxicol. 106:411–416.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Dourmishev LA, Dourmishev AL and Schwartz
RA: Dermatomyositis: An association of gingival telangiectases and
anti Jo-1 antibody in the adult. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica
Adriat. 16:67–72. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sontheimer RD: MDA5 autoantibody-another
indicator of clinical diversity in dermatomyositis. Ann Transl Med.
5(160)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hoshino K, Muro Y, Sugiura K, Tomita Y,
Nakashima R and Mimori T: Anti-MDA5 and anti-TIF1-gamma antibodies
have clinical significance for patients with dermatomyositis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:1726–1733. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Arshanapalli A, Shah M, Veerula V and
Somani AK: The role of type I interferons and other cytokines in
dermatomyositis. Cytokine. 73:319–325. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Brunasso AM, Aberer W and Massone C: New
onset of dermatomyositis/polymyositis during anti-TNF-α therapies:
A systematic literature review. ScientificWorldJournal.
2014(179180)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mamyrova G, O'Hanlon TP, Sillers L, Malley
K, James-Newton L, Parks CG, Cooper GS, Pandey JP, Miller FW and
Rider LG: Childhood Myositis Heterogeneity Collaborative Study
Group. Cytokine gene polymorphisms as risk and severity factors for
juvenile dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3941–3950.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|