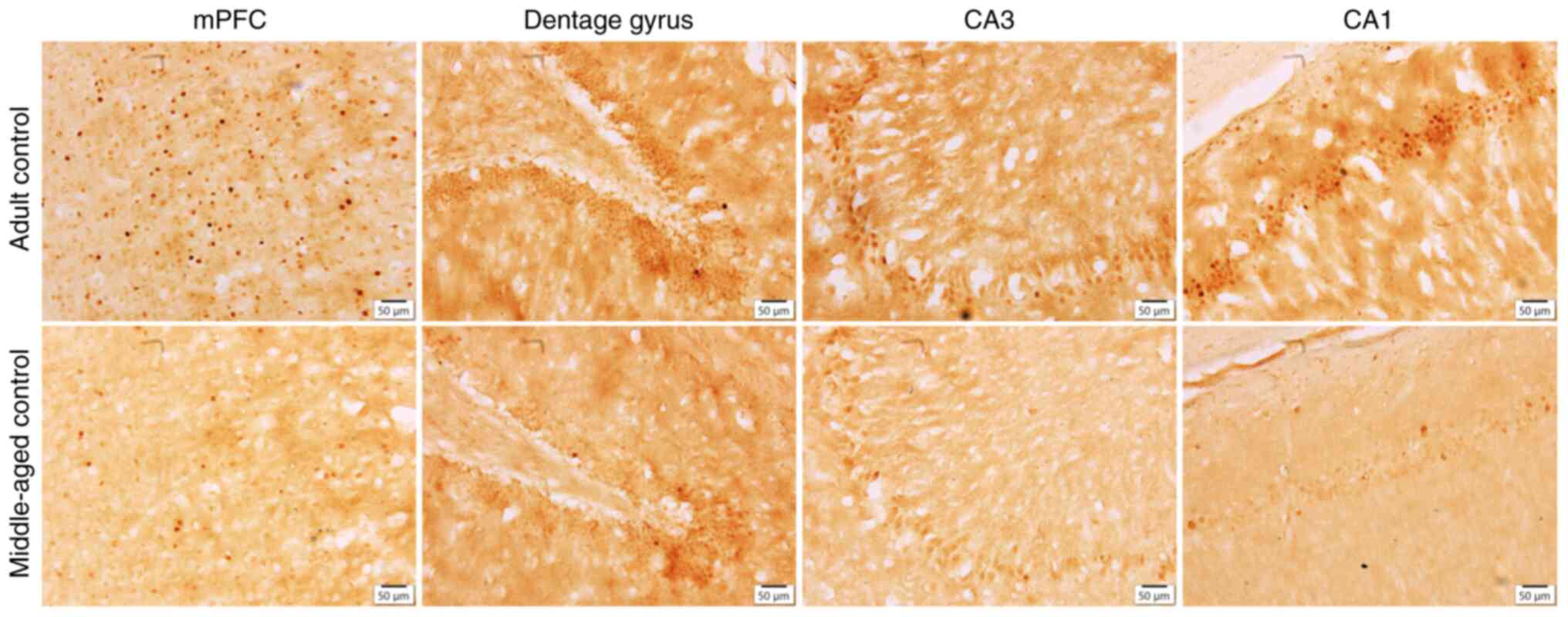
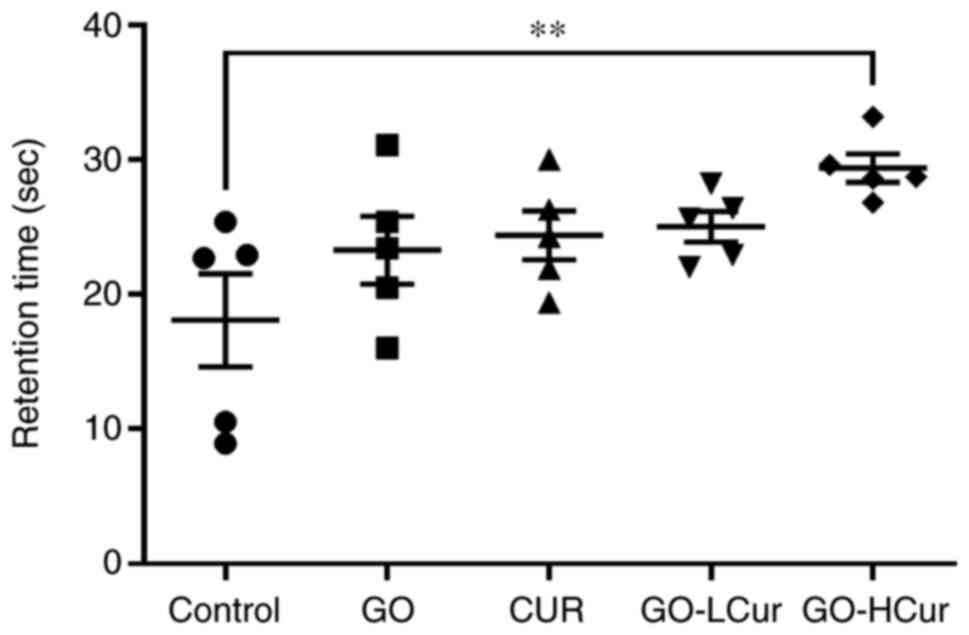
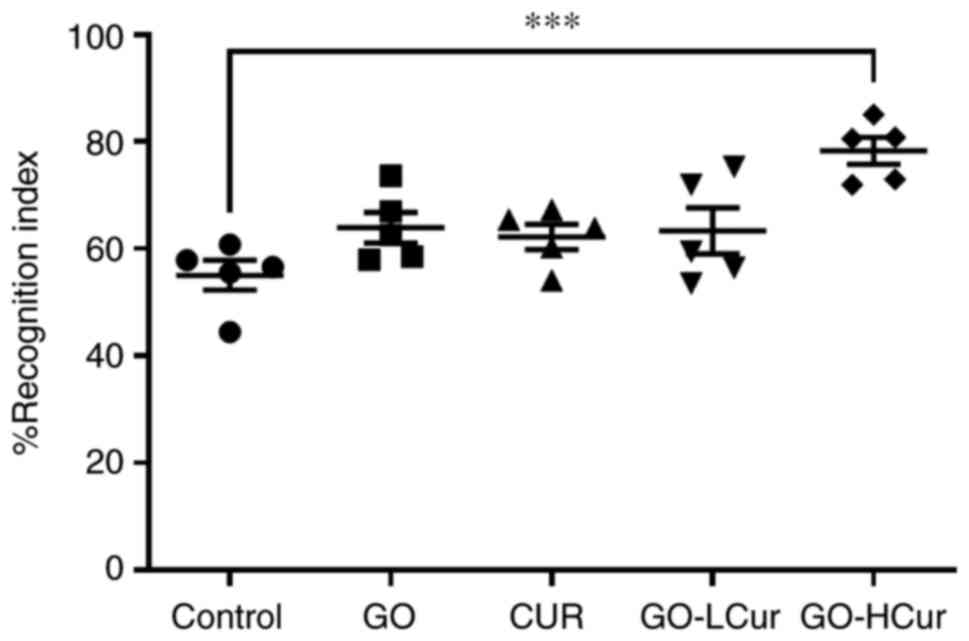
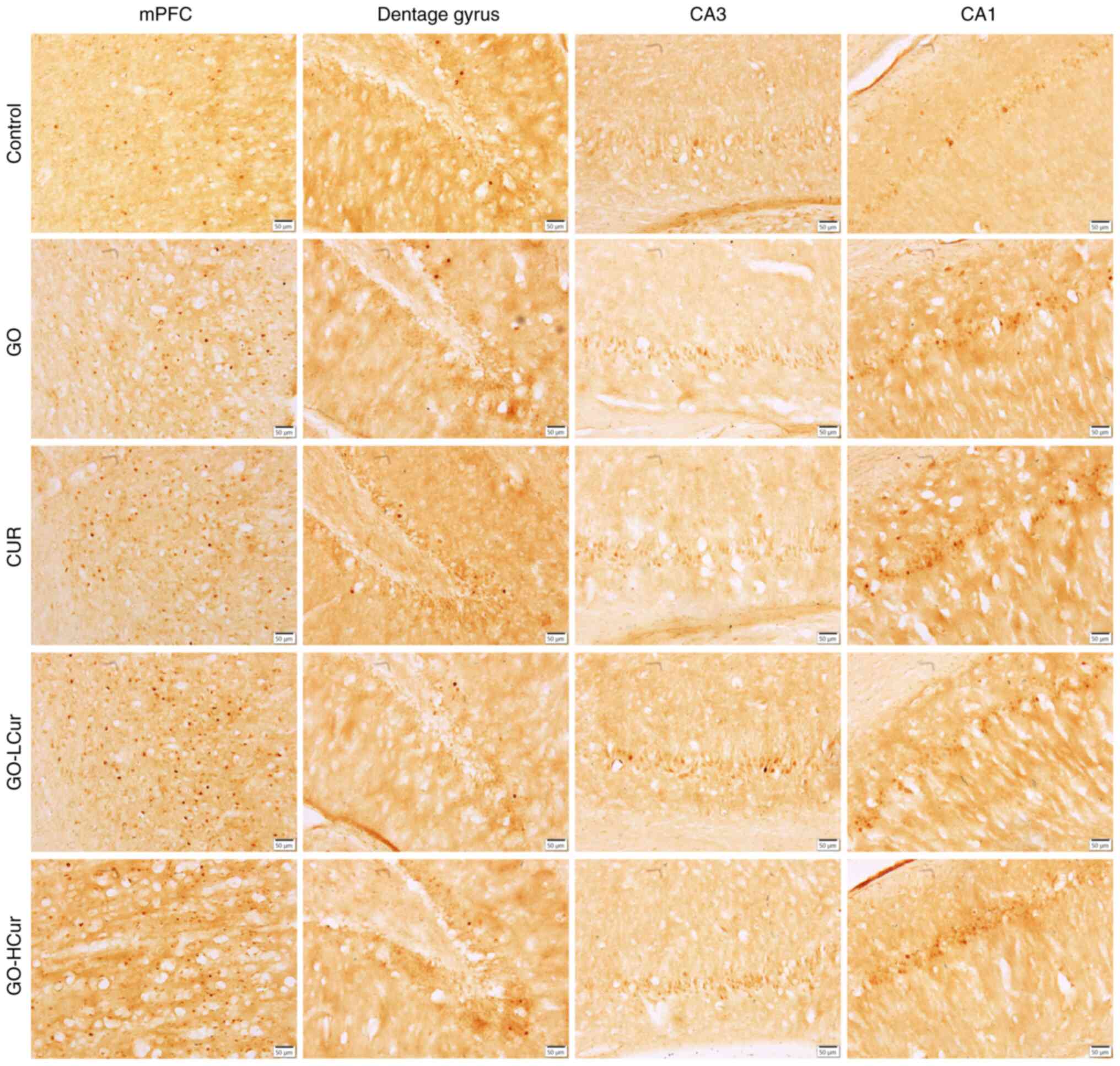
|
1
|
Hou Y, Dan X, Babbar M, Wei Y, Hasselbalch
SG, Croteau DL and Bohr VA: Ageing as a risk factor for
neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 15:565–581.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yankner BA, Lu T and Loerch P: The aging
brain. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:41–66. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gómez-Gonzalo M, Martin-Fernandez M,
Martínez-Murillo R, Mederos S, Hernández-Vivanco A, Jamison S,
Fernandez AP, Serrano J, Calero P, Futch HS, et al:
Neuron-astrocyte signaling is preserved in the aging brain. Glia.
65:569–580. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chandran R, Kumar M, Kesavan L, Jacob RS,
Gunasekaran S, Lakshmi S, Sadasivan C and Omkumar RV: Cellular
calcium signaling in the aging brain. J Chem Neuroanat. 95:95–114.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Monti DM, Rigano MM, Monti SM and Peixoto
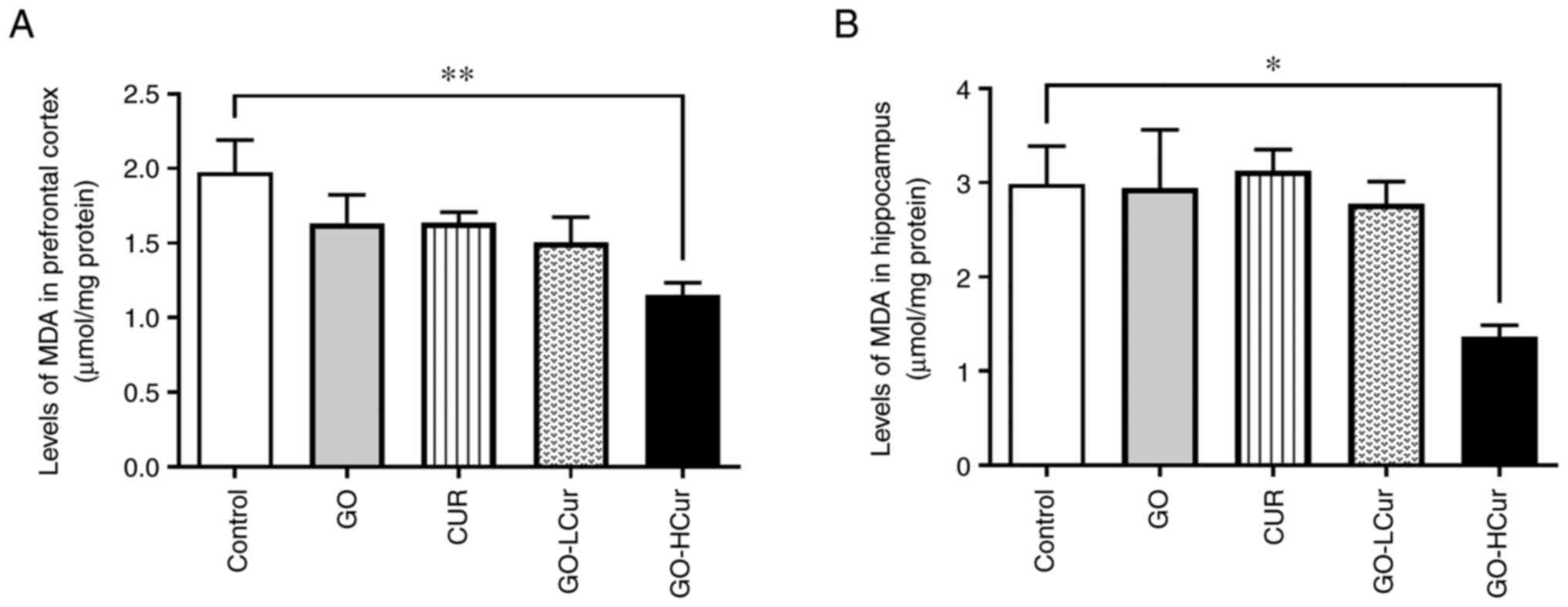
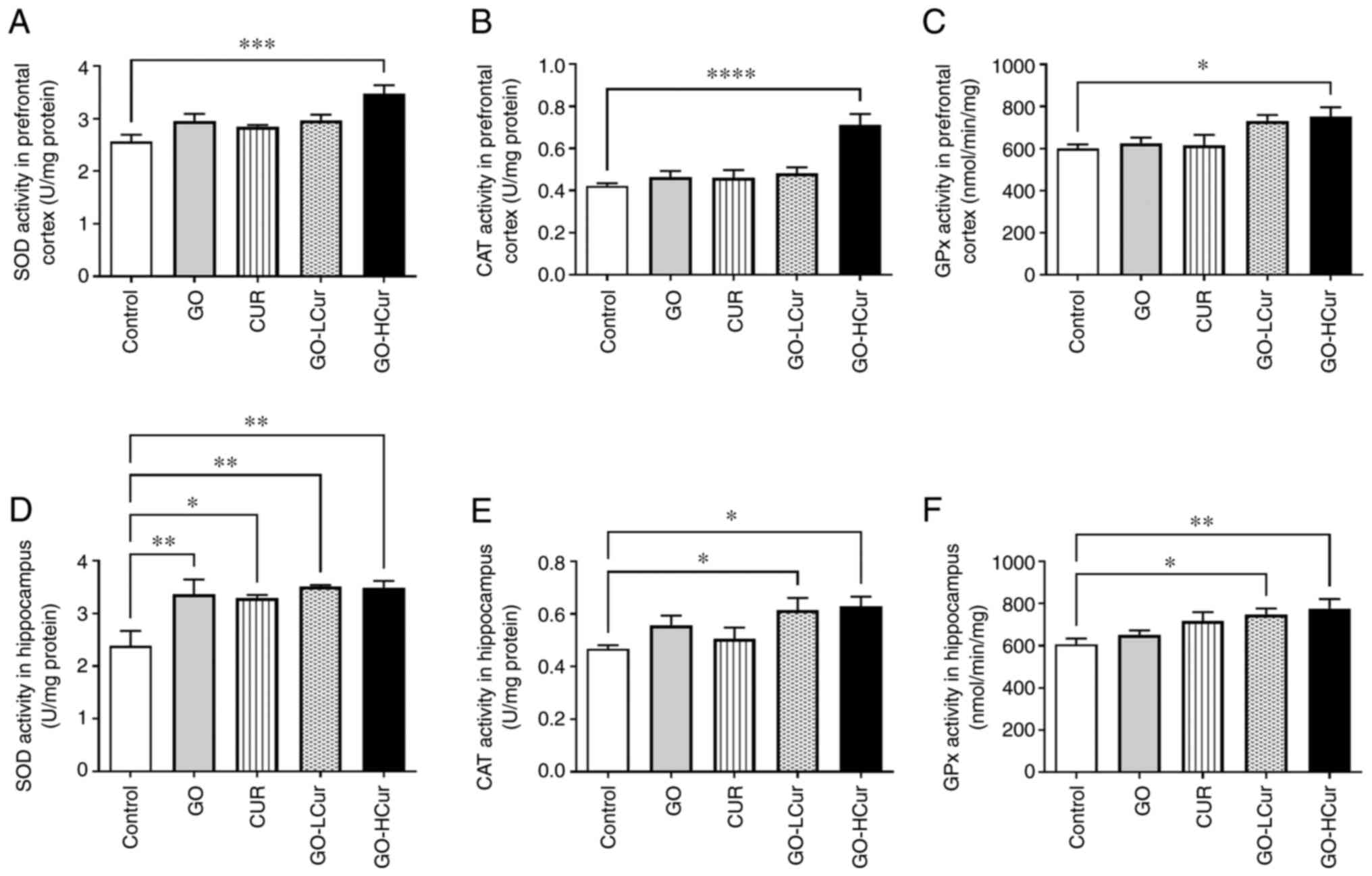
HS: Role of antioxidants in the protection from aging-related
diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019(7450693)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nikhra V: The aging brain: Recent research
and concepts. Gerontol Geriatr Stud. 1:1–11. 2017.
|
|
7
|
Vaiserman A, Koliada A, Zayachkivska A and
Lushchak O: Curcumin: A therapeutic potential in ageing-related
disorders. PharmaNutrition. 14(100226)2020.
|
|
8
|
Benameur T, Soleti R, Panaro MA, La Torre
ME, Monda V, Messina G and Porro C: Curcumin as prospective
anti-aging natural compound: Focus on brain. Molecules.
26(4794)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M,
Farkhondeh T and Samini F: Anti-oxidative effects of curcumin on
immobilization-induced oxidative stress in rat brain, liver and
kidney. Biomed Pharmacother. 87:223–229. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Suryanarayana P, Satyanarayana A,
Balakrishna N, Kumar PU and Reddy GB: Effect of turmeric and
curcumin on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Med Sci Monit. 13:BR286–BR292.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rungratanawanich W, Abate G, Serafini MM,
Guarienti M, Catanzaro M, Marziano M, Memo M, Lanni C and Uberti D:
Characterization of the antioxidant effects of γ-oryzanol:
Involvement of the Nrf2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev: Mar 14, 2018
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
12
|
Wang YX, Li Y, Sun AM, Wang FJ and Yu GP:
Hypolipidemic and antioxidative effects of aqueous enzymatic
extract from rice bran in rats fed a high-fat and -cholesterol
diet. Nutrients. 6:3696–3710. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Islam A, Rebello L and Chepyala S: Review
on nanoformulations of curcumin (Curcuma longa Linn.): Special
emphasis on Nanocurcumin®. Int J Nat Life Sci. 3:1–12. 2019.
|
|
14
|
Hettiarachchi SS, Dunuweera SP, Dunuweera
AN and Rajapakse RMG: Synthesis of curcumin nanoparticles from raw
turmeric rhizome. ACS Omega. 6:8246–8252. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rawal T, Mishra N, Jha A, Bhatt A, Tyagi
RK, Panchal S and Butani S: Chitosan nanoparticles of
gamma-oryzanol: Formulation, optimization, and in vivo evaluation
of anti-hyperlipidemic activity. AAPS PharmSciTech. 19:1894–1907.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rodsuwan U, Pithanthanakul U, Thisayakorn
K, Uttapap D, Boonpisuttinant K, Vatanyoopaisarn S, Thumthanaruk B
and Rungsardthong V: Preparation and characterization of gamma
oryzanol loaded zein nanoparticles and its improved stability. Food
Sci Nutr. 9:616–624. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Morris R: Developments of a water-maze
procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci
Methods. 11:47–60. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dodart JC, Bales KR, Gannon KS, Greene SJ,
DeMattos RB, Mathis C, DeLong CA, Wu S, Wu X, Holtzman DM and Paul
SM: Immunization reverses memory deficits without reducing brain
Abeta burden in Alzheimer's disease model. Nat Neurosci. 5:452–457.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu J, Edamatsu R, Kabuto H and Mori A:
Antioxidant action of guilingji in the brain of rats with
FeCl3-induced epilepsy. Free Radic Biol Med. 9:451–454.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Marklund S and Marklund G: Involvement of
the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and
a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem.
47:469–474. 1974.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Beers RF Jr and Sizer IW: A
spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen
peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 195:133–140. 1952.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamezah HS, Durani LW, Ibrahim NF,
Yanagisawa D, Kato T, Shiino A, Tanaka S, Damanhuri HA, Ngah WZW
and Tooyama I: Volumetric changes in the aging rat brain and its
impact on cognitive and locomotor functions. Exp Gerontol.
99:69–79. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Garg G, Singh S, Singh AK and Rizvi SI:
N-acetyl-l-cysteine attenuates oxidative damage and
neurodegeneration in rat brain during aging. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 96:1189–1196. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Khairy EY and Attia MM: Protective effects
of vitamin D on neurophysiologic alterations in brain aging: Role
of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Nutr Neurosci.
24:650–659. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pyo IS, Yun S, Yoon YE, Choi JW and Lee
SJ: Mechanisms of aging and the preventive effects of resveratrol
on age-related diseases. Molecules. 25(4649)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fischer R and Maier O: Interrelation of
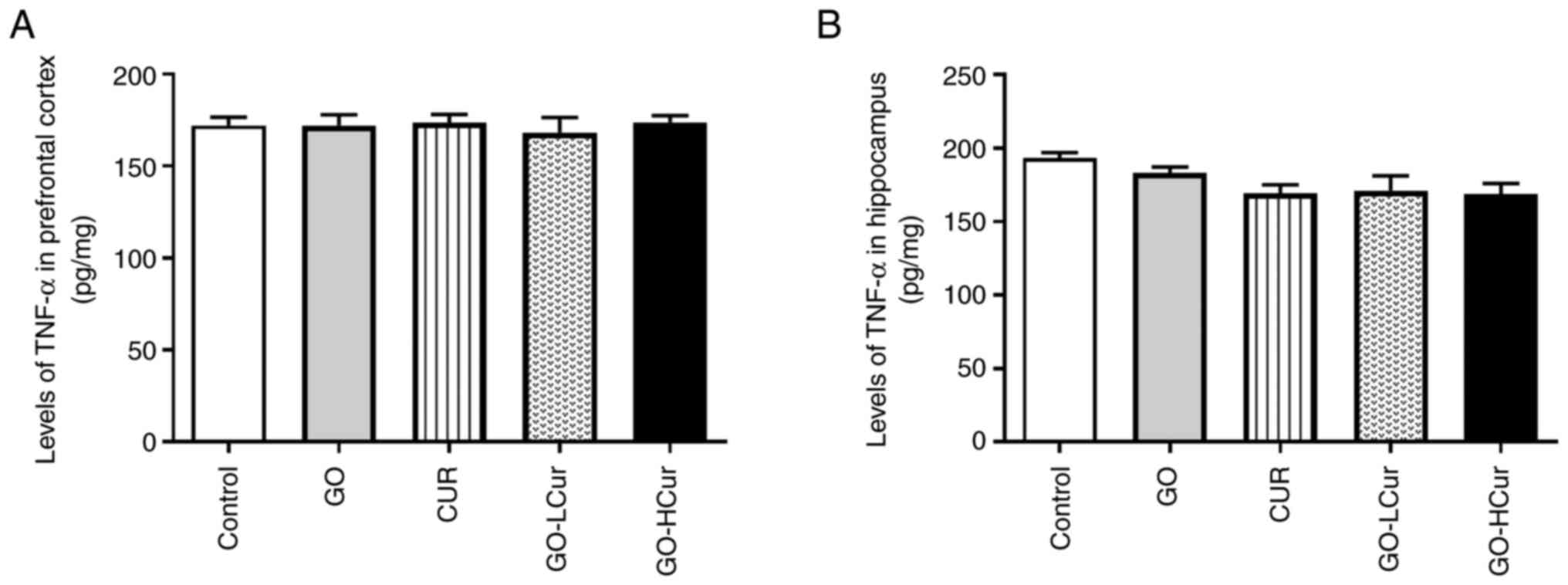
oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease:
Role of TNF. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015(610813)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Anyanwu EC: Neurochemical changes in the
aging process: Implications in medication in the elderly.
ScientificWorldJournal. 7:1603–1610. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huang TT, Leu D and Zou Y: Oxidative
stress and redox regulation on hippocampal-dependent cognitive
functions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 576:2–7. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tönnies E and Trushina E: Oxidative
stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers
Dis. 57:1105–1121. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mastinu A, Bonini SA, Rungratanawanich W,
Aria F, Marziano M, Maccarinelli G, Abate G, Premoli M, Memo M and
Uberti D: Gamma-oryzanol prevents LPS-induced brain inflammation
and cognitive impairment in adult mice. Nutrients.
11(728)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Xing H, Zhao Y and Ma Z:
Pharmaceutical dispersion techniques for dissolution and
bioavailability enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs.
Pharmaceutics. 10(74)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jara MO, Warnken ZN and Williams RO III:
Amorphous solid dispersions and the contribution of nanoparticles
to in vitro dissolution and in vivo testing: Niclosamide as a case
study. Pharmaceutics. 13(97)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Oliveira VDS, de Almeida AS, Albuquerque
IDS, Duarte FÍC, Queiroz BCSH, Converti A and Lima ÁAND:
Therapeutic applications of solid dispersions for drugs and new
molecules: In vitro and in vivo activities. Pharmaceutics.
12(933)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rungratanawanich W, Cenini G, Mastinu A,
Sylvester M, Wilkening A, Abate G, Bonini SA, Aria F, Marziano M,
Maccarinelli G, et al: γ-Oryzanol improves cognitive function and
modulates hippocampal proteome in mice. Nutrients.
11(753)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Birben E, Sahiner UM, Sackesen C, Erzurum
S and Kalayci O: Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World
Allergy Organ J. 5:9–19. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cui X, Song H and Su J: Curcumin
attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats through
induction of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 and heme
oxygenase-1. Exp Ther Med. 14:1512–1518. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Massaad CA and Klann E: Reactive oxygen
species in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and memory.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:2013–2054. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Gallo FT, Katche C, Morici JF, Medina JH
and Weisstaub NV: Immediate early genes, memory and psychiatric
disorders: Focus on c-Fos, Egr1 and Arc. Front Behav Neurosci.
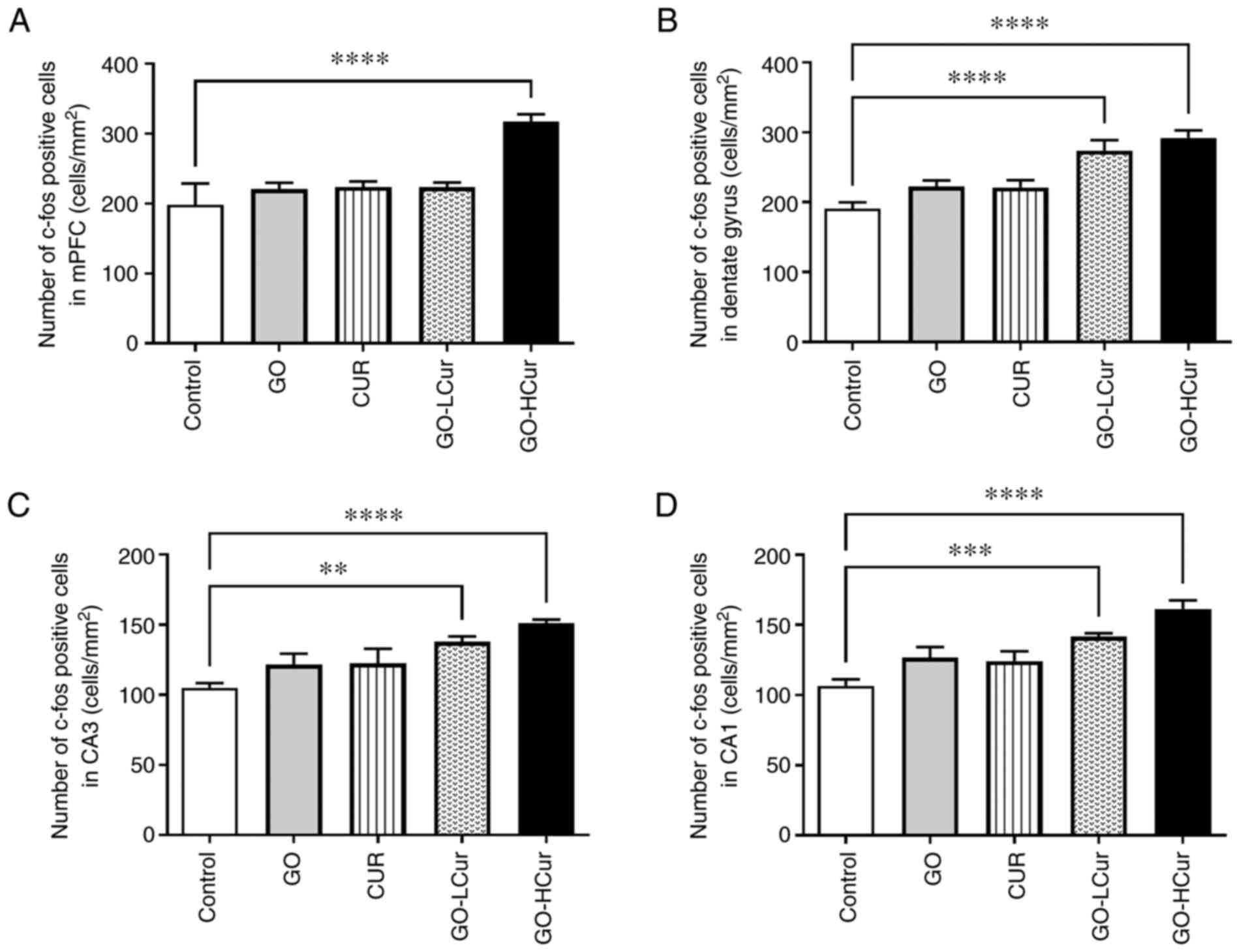
12(79)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|