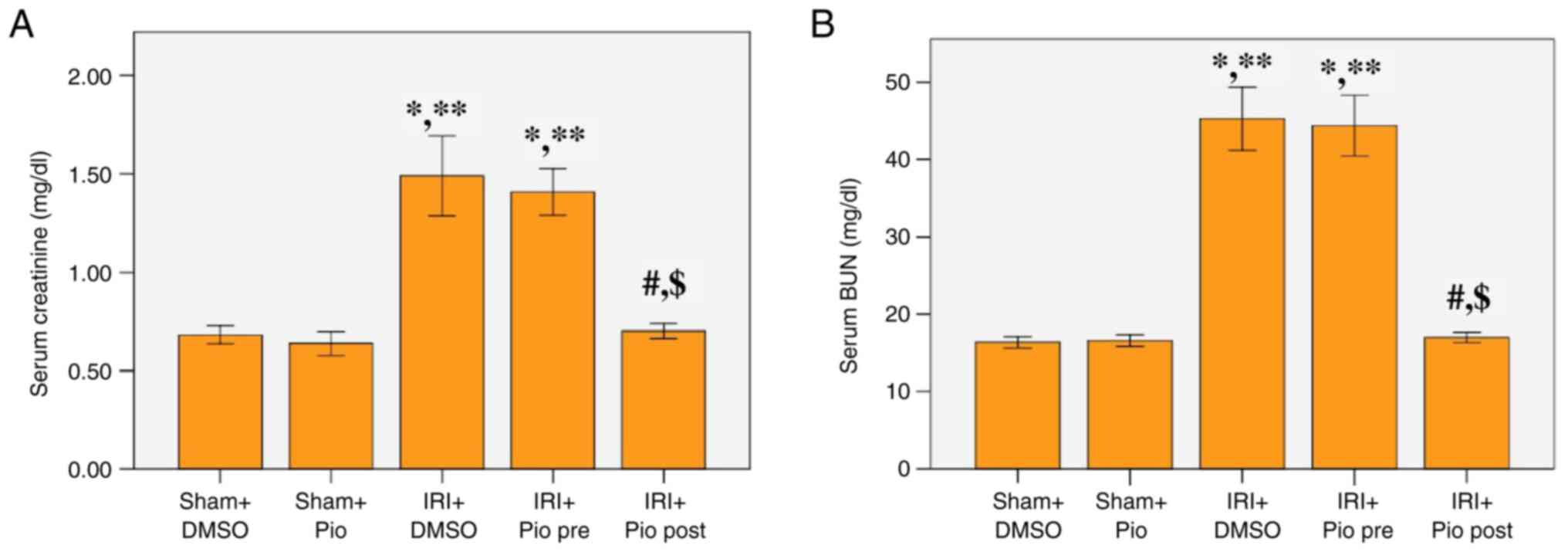
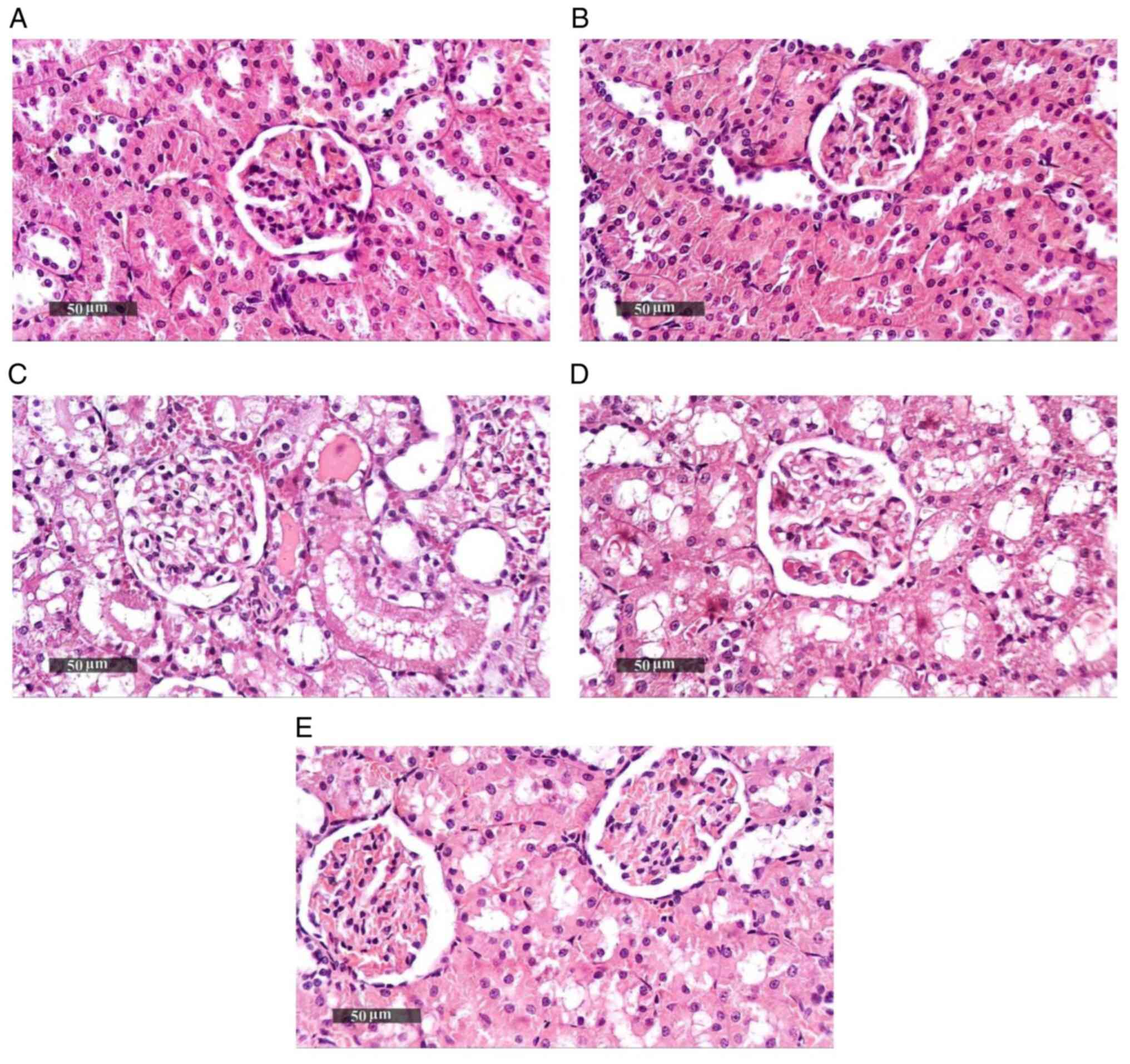
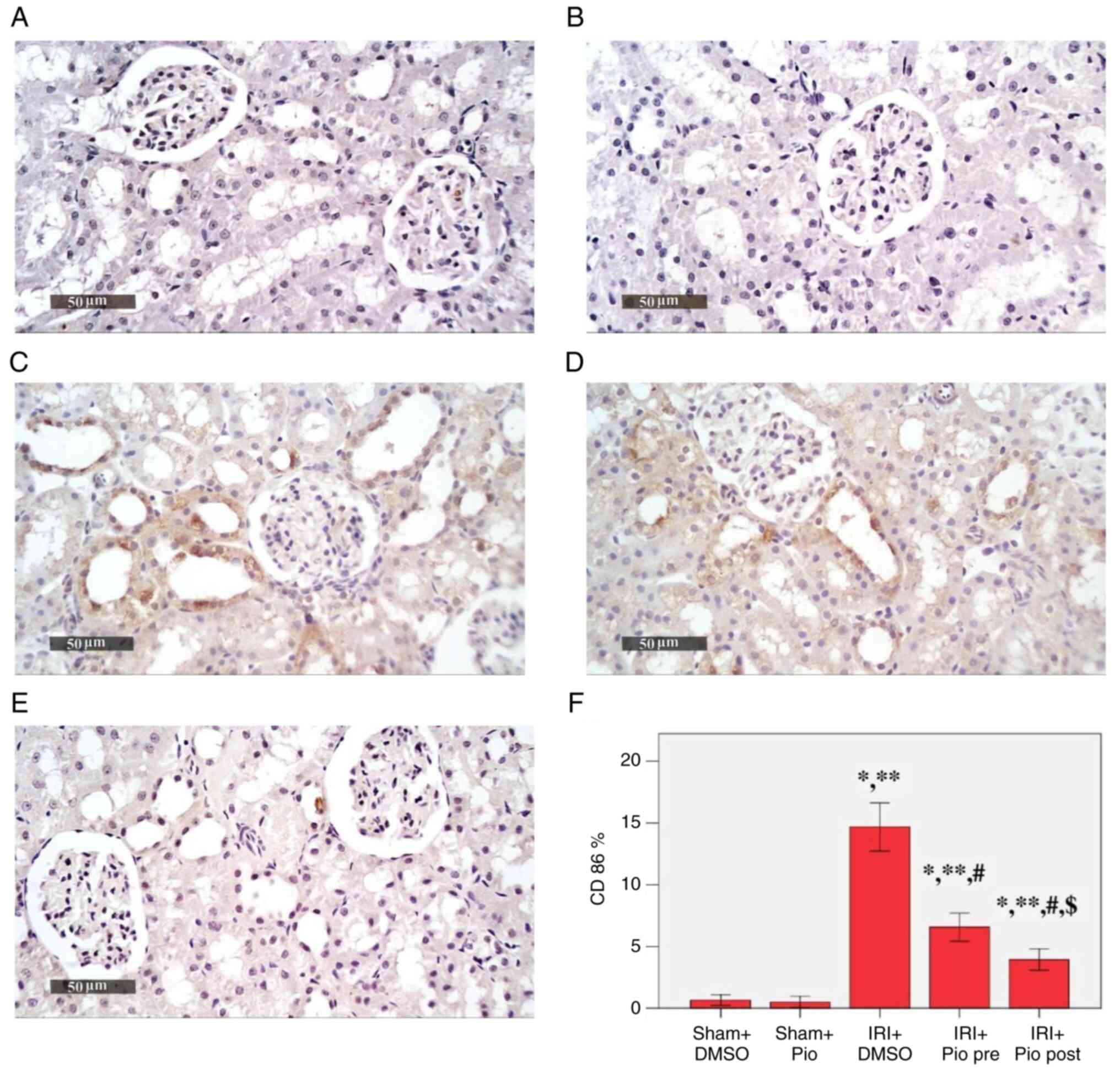
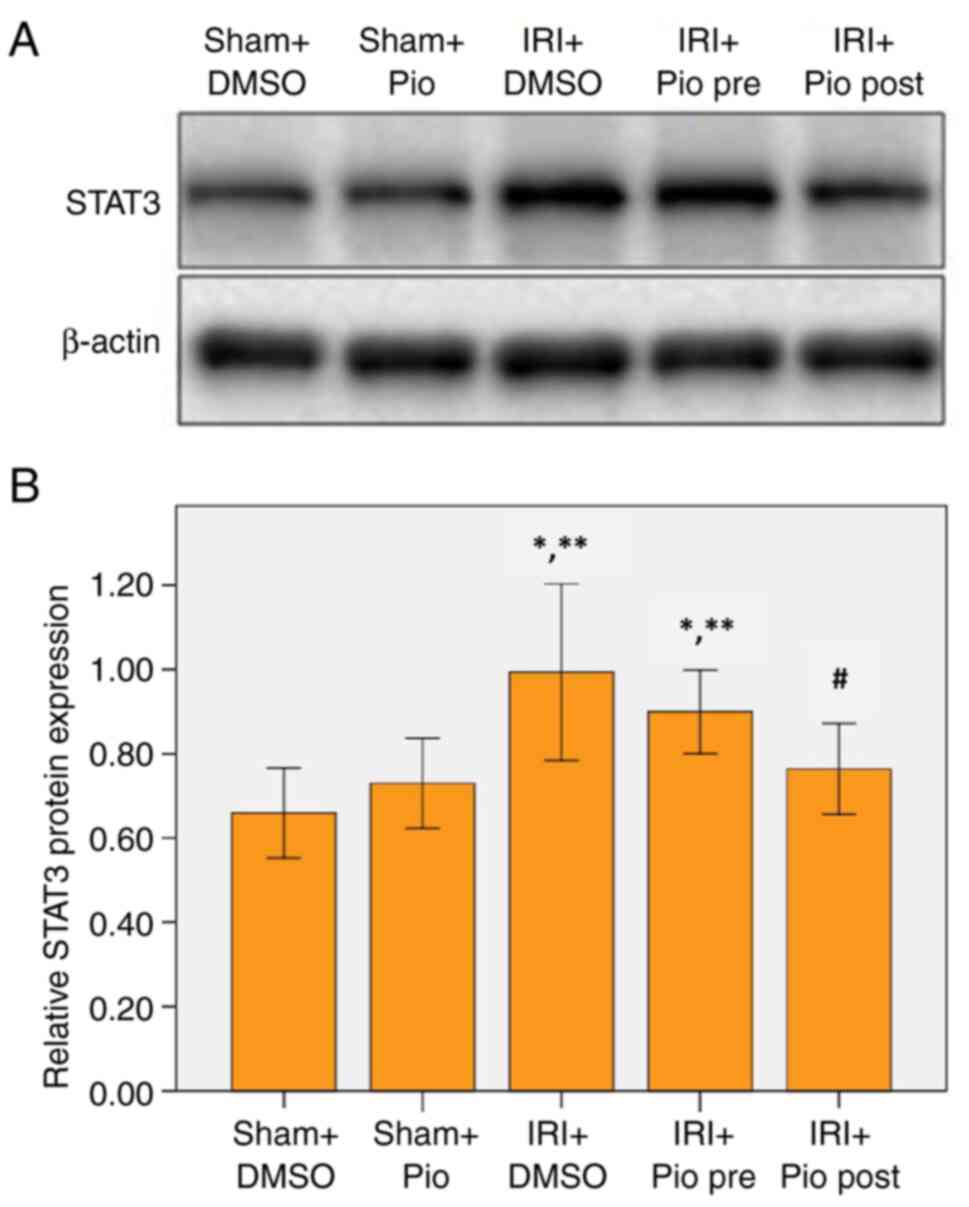
|
1
|
Han SJ and Lee HT: Mechanisms and
therapeutic targets of ischemic acute kidney injury. Kidney Res
Clin Pract. 38:427–440. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jia P, Xu S, Ren T, Pan T, Wang X, Zhang
Y, Zou Z, Guo M, Zeng Q, Shen B and Ding X: LncRNA IRAR regulates
chemokines production in tubular epithelial cells thus promoting
kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis.
13(562)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sharfuddin AA and Molitoris BA:
Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol.
7:189–200. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Funk JA and Schnellmann RG: Persistent
disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis after acute kidney injury.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F853–F864. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bonventre JV and Zuk A: Ischemic acute
renal failure: An inflammatory disease? Kidney Int. 66:480–485.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Chang J, Yao B, Niu A, Kelly E,
Breeggemann MC, Abboud Werner SL, Harris RC and Zhang MZ: Proximal
tubule-derived colony stimulating factor-1 mediates polarization of
renal macrophages and dendritic cells, and recovery in acute kidney
injury. Kidney Int. 88:1274–1282. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huen SC, Huynh L, Marlier A, Lee Y,
Moeckel GW and Cantley LG: GM-CSF promotes macrophage alternative
activation after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 26:1334–1345. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cinelli MA, Do HT, Miley GP and Silverman
RB: Inducible nitric oxide synthase: Regulation, structure, and
inhibition. Med Res Rev. 40:158–189. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Joles JA, Vos IH, Gröne HJ and Rabelink
TJ: Inducible nitric oxide synthase in renal transplantation.
Kidney Int. 61:872–875. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mark LA, Robinson AV and Schulak JA:
Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase reduces renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Surg Res. 129:236–241.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chatterjee PK, Patel NS, Kvale EO,
Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H and Thiemermann C:
Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase reduces renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 61:862–871.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Levillain O, Balvay S and Peyrol S:
Localization and differential expression of arginase II in the
kidney of male and female mice. Pflugers Arch. 449:491–503.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Marselli L, Bosi E, De Luca C, Del Guerra
S, Tesi M, Suleiman M and Marchetti P: Arginase 2 and polyamines in
human pancreatic beta cells: Possible role in the pathogenesis of
type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 22(12099)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Marathe C, Bradley MN, Hong C, Lopez F,
Ruiz de Galarreta CM, Tontonoz P and Castrillo A: The arginase II
gene is an anti-inflammatory target of liver X receptor in
macrophages. J Biol Chem. 281:32197–32206. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhong Z, Wen Z and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3: A
STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in
response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science.
264:95–98. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar
KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S and Sung B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and
cancer: How intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1171:59–76. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Billing U, Jetka T, Nortmann L, Wundrack
N, Komorowski M, Waldherr S, Schaper F and Dittrich A: Robustness
and information transfer within IL-6-induced JAK/STAT signalling.
Commun Biol. 2(27)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zheng C, Huang L, Luo W, Yu W, Hu X, Guan
X, Cai Y, Zou C, Yin H, Xu Z, et al: Inhibition of STAT3 in tubular
epithelial cells prevents kidney fibrosis and nephropathy in
STZ-induced diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis. 10(848)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Feng X, Lu TC, Chuang PY, Fang W, Ratnam
K, Xiong H, Ouyang X, Shen Y, Levy DE, Hyink D, et al: Reduction of
Stat3 activity attenuates HIV-induced kidney injury. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 20:2138–2146. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pang M, Ma L, Gong R, Tolbert E, Mao H,
Ponnusamy M, Chin YE, Yan H, Dworkin LD and Zhuang S: A novel STAT3
inhibitor, S3I-201, attenuates renal interstitial fibroblast
activation and interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy.
Kidney Int. 78:257–268. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Si Y, Bao H, Han L, Shi H, Zhang Y, Xu L,
Liu C, Wang J, Yang X, Vohra A and Ma D: Dexmedetomidine protects
against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting the
JAK/STAT signaling activation. J Transl Med. 11(141)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhao X, Zhang E, Ren X, Bai X, Wang D, Bai
L, Luo D, Guo Z, Wang Q and Yang J: Edaravone alleviates cell
apoptosis and mitochondrial injury in ischemia-reperfusion-induced
kidney injury via the JAK/STAT pathway. Biol Res.
53(28)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu MJ, Feng D, Wang H, Guan Y, Yan X and
Gao B: IL-22 ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by
targeting proximal tubule epithelium. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:967–977.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dube S, Matam T, Yen J, Mang HE, Dagher
PC, Hato T and Sutton TA: Endothelial STAT3 modulates protective
mechanisms in a mouse ischemia-reperfusion model of acute kidney
injury. J Immunol Res. 2017(4609502)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pace J, Paladugu P, Das B, He JC and
Mallipattu SK: Targeting STAT3 signaling in kidney disease. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 316:F1151–F1161. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Park JY, Yoo KD, Bae E, Kim KH, Lee JW,
Shin SJ, Lee JS, Kim YS and Yang SH: Blockade of STAT3 signaling
alleviates the progression of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney
disease through antiapoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
322:F553–F572. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kersten S, Desvergne B and Wahli W: Roles
of PPARs in health and disease. Nature. 405:421–424.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Park EJ, Park SY, Joe EH and Jou I:
15d-PGJ2 and rosiglitazone suppress Janus kinase-STAT inflammatory
signaling through induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
(SOCS1) and SOCS3 in glia. J Biol Chem. 278:14747–14752.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kapadia R, Yi JH and Vemuganti R:
Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of
PPAR-gamma agonists. Front Biosci. 13:1813–1826. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang D, Shi L, Xin W, Xu J, Xu J, Li Q, Xu
Z, Wang J, Wang G, Yao W, et al: Activation of PPARγ inhibits
pro-inflammatory cytokines production by upregulation of miR-124 in
vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:726–731.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sun Y, Li Q, Gui H, Xu DP, Yang YL, Su DF
and Liu X: MicroRNA-124 mediates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory
action through inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory
cytokines. Cell Res. 23:1270–1283. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Committee for the Update of the Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, Institute for Laboratory
Animal Research, Division on Earth and Life Studies, National
Research Council. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals.
8th edition. National Academies Press, 2010.
|
|
34
|
Hu H, Zou C, Xi X, Shi Z, Wang G and Huang
X: Protective effects of pioglitazone on renal ischemia-reperfusion
injury in mice. J Surg Res. 178:460–465. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zou C, Hu H, Xi X, Shi Z, Wang G and Huang
X: Pioglitazone protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
by enhancing antioxidant capacity. J Surg Res. 184:1092–1095.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
El-Nabarawy NA, Gouda AS, Khattab MA and
Rashed LA: Effects of nitrite graded doses on hepatotoxicity and
nephrotoxicity, histopathological alterations, and activation of
apoptosis in adult rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
27:14019–14032. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lucena-Aguilar G, Sánchez-López AM,
Barberán-Aceituno C, Carrillo-Ávila JA, López-Guerrero JA and
Aguilar-Quesada R: DNA source selection for downstream applications
based on DNA quality indicators analysis. Biopreserv Biobank.
14:264–270. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zuk A and Bonventre JV: Recent advances in
acute kidney injury and its consequences and impact on chronic
kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 28:397–405.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ding C, Zheng J, Wang B, Li Y, Xiang H,
Dou M, Qiao Y, Tian P, Ding X and Xue W: Exosomal MicroRNA-374b-5p
from tubular epithelial cells promoted M1 macrophages activation
and worsened renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 8(587693)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Liu BC, Tang TT, Lv LL and Lan HY: Renal
tubule injury: A driving force toward chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Int. 93:568–579. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen W, Xi X, Zhang S, Zou C, Kuang R, Ye
Z, Huang Y and Hu H: Pioglitazone protects against renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury via the AMP-activated protein
kinase-regulated autophagy pathway. Front Pharmacol.
9(851)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zou G, Zhou Z, Xi X, Huang R and Hu H:
Pioglitazone ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via
inhibition of NF-κB activation and inflammation in rats. Front
Physiol. 12(707344)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li Q, Tian Z, Wang M, Kou J, Wang C, Rong
X, Li J, Xie X and Pang X: Luteoloside attenuates neuroinflammation
in focal cerebral ischemia in rats via regulation of the
PPARγ/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
66:309–316. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ding Y, Kang J, Liu S, Xu Y and Shao B:
The protective effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front
Neurol. 11(588516)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hiben MG, de Haan L, Spenkelink B,
Wesseling S, Vervoort J and Rietjens IMCM: Induction of peroxisome
proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ) mediated gene expression
and inhibition of induced nitric oxide production by Maerua
subcordata (Gilg) DeWolf. BMC Complement Med Ther.
20(80)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Hong W, Hu S, Zou J, Xiao J, Zhang X, Fu
C, Feng X and Ye Z: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
prevents the production of NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain
containing 3 inflammasome and interleukin 1β in HK-2 renal tubular
epithelial cells stimulated by monosodium urate crystals. Mol Med
Rep. 12:6221–6226. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ramirez-Moral I, Ferreira BL, de Vos AF
and van der Poll T: Post-treatment with the PPAR-γ agonist
pioglitazone inhibits inflammation and bacterial growth during
Klebsiella pneumonia. Respir Res. 22(230)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Crosby MB, Svenson J, Gilkeson GS and
Nowling TK: A novel PPAR response element in the murine iNOS
promoter. Mol Immunol. 42:1303–1310. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Yin F, Zheng PQ, Zhao LQ, Wang YZ, Miao
NJ, Zhou ZL, Cheng Q, Chen PP, Xie HY, Li JY, et al: Caspase-11
promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the cleavage of
pannexin1 in acute kidney disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 43:86–95.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang Y, Yu B, Wang L, Yang M, Xia Z, Wei
W, Zhang F and Yuan X: Pioglitazone ameliorates glomerular NLRP3
inflammasome activation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice with
diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 12(e0181248)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Li R, Wang X, Fu Q and Ma S:
Umbelliferone ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via
upregulating the PPAR gamma expression and suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3
inflammasome. Neurosci Lett. 600:182–187. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Meng QQ, Feng ZC, Zhang XL, Hu LQ, Wang M,
Zhang HF and Li SM: PPAR-γ activation exerts an anti-inflammatory
effect by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome in spinal cord-derived
neurons. Mediators Inflamm. 2019(6386729)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Bartesaghi S and Radi R: Fundamentals on
the biochemistry of peroxynitrite and protein tyrosine nitration.
Redox Biol. 14:618–625. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang M, Deng J, Lai H, Lai Y, Meng G, Wang
Z, Zhou Z, Chen H, Yu Z, Li S and Jiang H: Vagus nerve stimulation
ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting
NF-κB activation and iNOS protein expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020(7106525)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Korkmaz A and Kolankaya D: Inhibiting
inducible nitric oxide synthase with rutin reduces renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Can J Surg. 56:6–14. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Aydogdu N, Erbas H, Atmaca G, Erten O and
Kaymak K: Melatonin reduces nitric oxide via increasing arginase in
rhabdomyolysis-induced acute renal failure in rats. Ren Fail.
28:435–440. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Erbas H, Aydogdu N and Kaymak K: Effects
of N-acetylcysteine on arginase, ornithine and nitric oxide in
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Res. 50:523–527.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Waeckerle-Men Y, Starke A, Wahl PR and
Wüthrich RP: Limited costimulatory molecule expression on renal
tubular epithelial cells impairs T cell activation. Kidney Blood
Press Res. 30:421–429. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hagerty DT, Evavold BD and Allen PM:
Regulation of the costimulator B7, not class II major
histocompatibility complex, restricts the ability of murine kidney
tubule cells to stimulate CD4+ T cells. J Clin Invest.
93:1208–1215. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Breda PC, Wiech T, Meyer-Schwesinger C,
Grahammer F, Huber T, Panzer U, Tiegs G and Neumann K: Renal
proximal tubular epithelial cells exert immunomodulatory function
by driving inflammatory CD4+ T cell responses. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 317:F77–F89. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Niemann-Masanek U, Mueller A, Yard BA,
Waldherr R and van der Woude FJ: B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD 86)
expression in human tubular epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro.
Nephron. 92:542–556. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Xiao YT, Wang J, Lu W, Cao Y and Cai W:
Downregulated expression of microRNA-124 in pediatric intestinal
failure patients modulates macrophages activation by inhibiting
STAT3 and AChE. Cell Death Dis. 7(e2521)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Koukos G, Polytarchou C, Kaplan JL,
Morley-Fletcher A, Gras-Miralles B, Kokkotou E, Baril-Dore M,
Pothoulakis C, Winter HS and Iliopoulos D: MicroRNA-124 regulates
STAT3 expression and is down-regulated in colon tissues of
pediatric patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology.
145:842–852.e2. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wang S, Wu G, Han Y, Song P, Chen J, Wu Y,
Yang J and Liang P: miR-124 regulates STAT3-mediated cell
proliferation, migration and apoptosis in bladder cancer. Oncol
Lett. 16:5875–5881. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Lin S, Liu Q, Wen J, Bai K, Guo Y and Wang
J: Mir-124 attenuates STAT3-mediated TH17 differentiation in
colitis-driven colon cancer. Front Oncol. 10(570128)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|