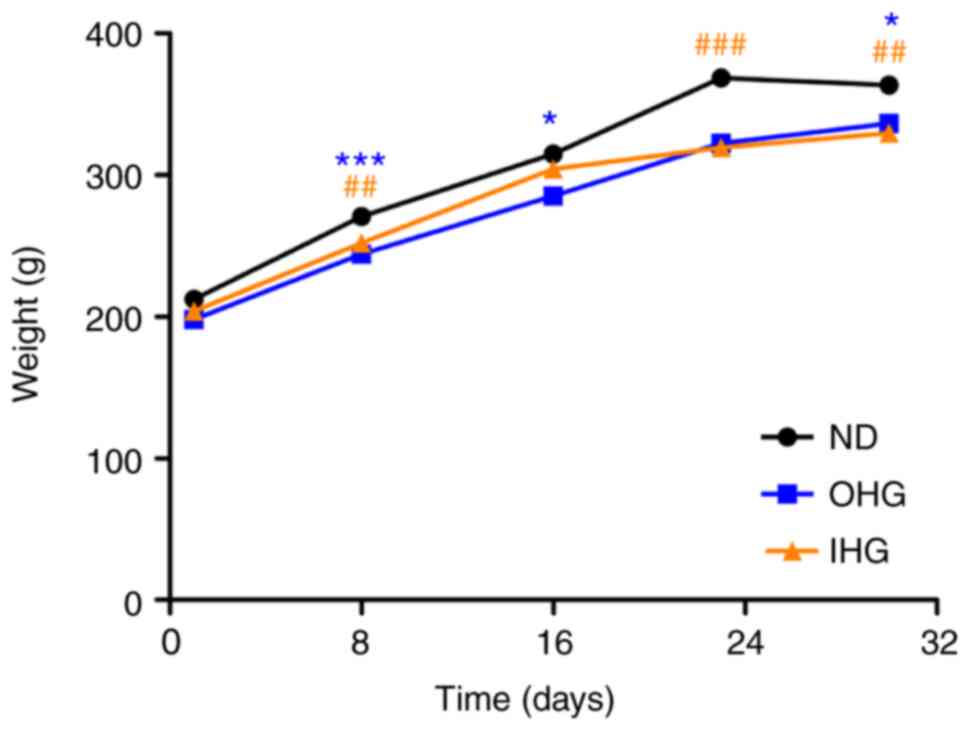
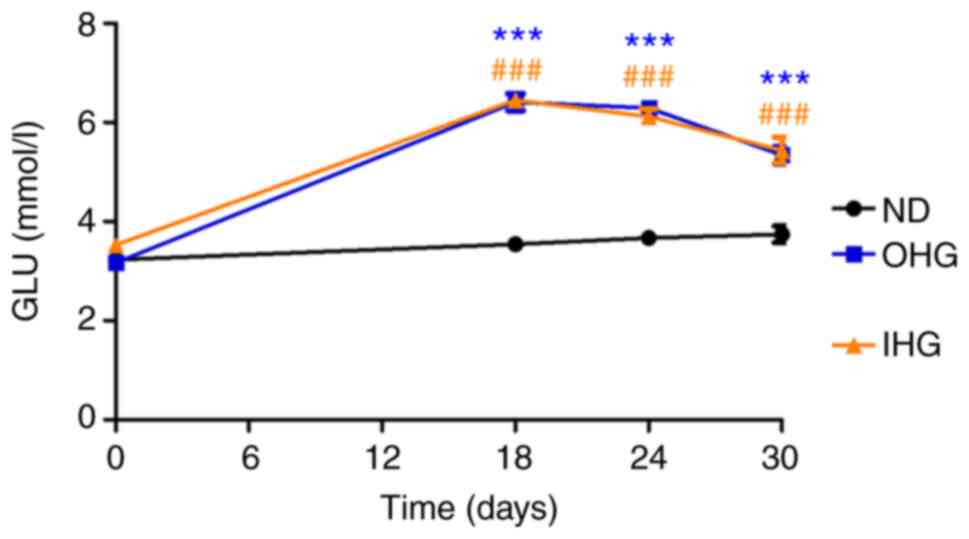
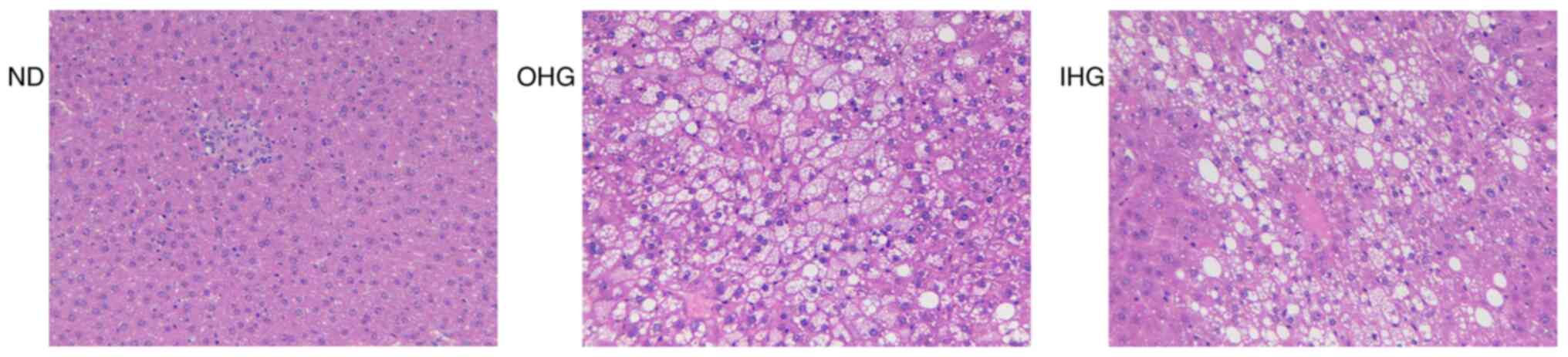
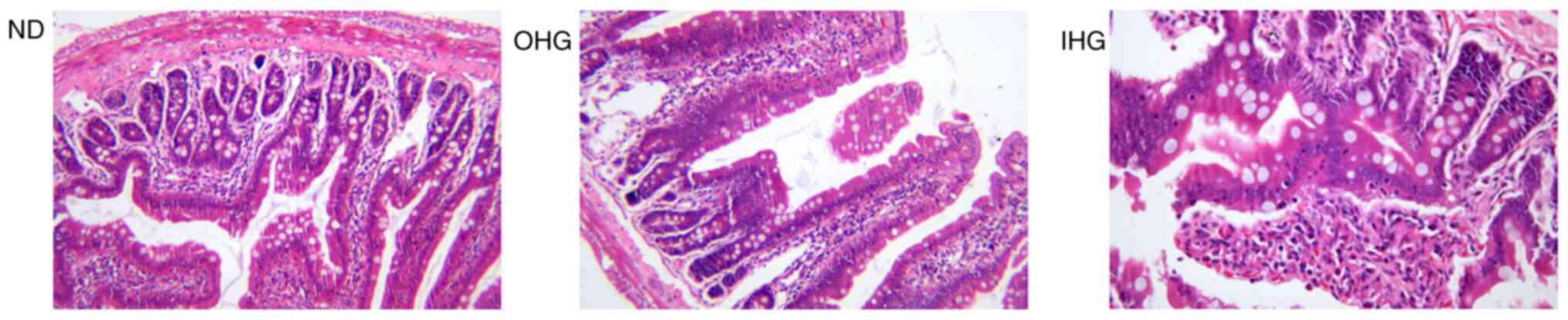
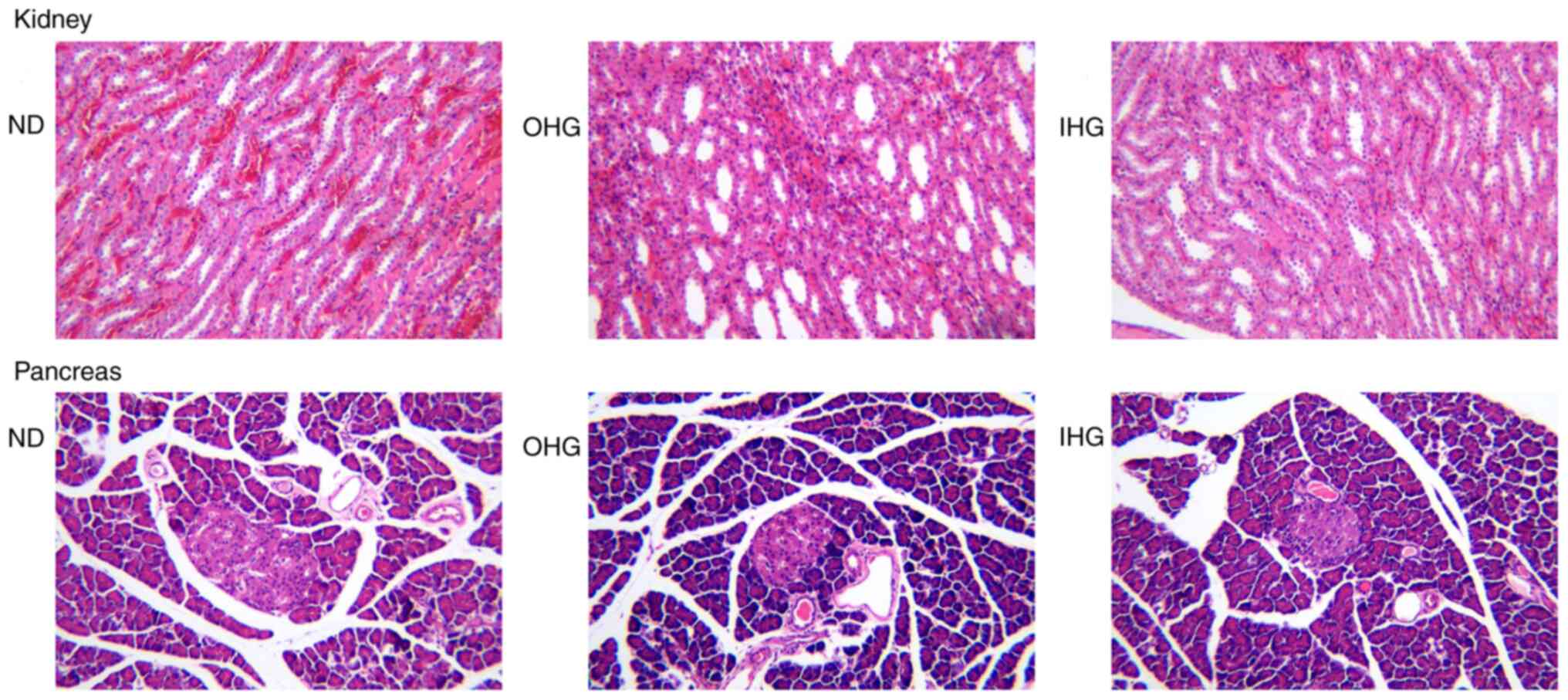
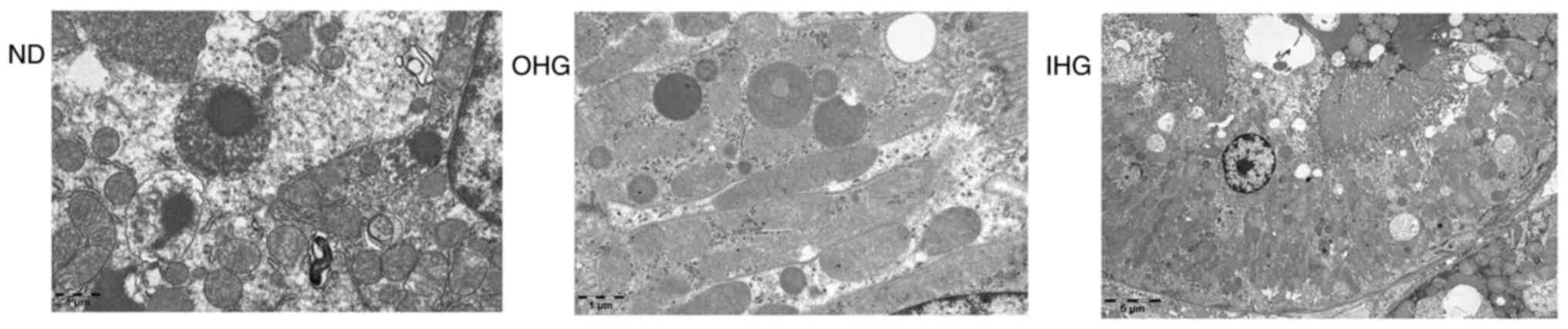
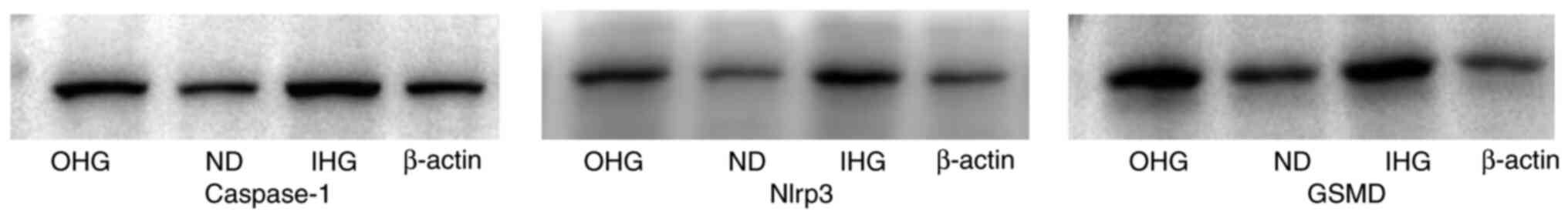
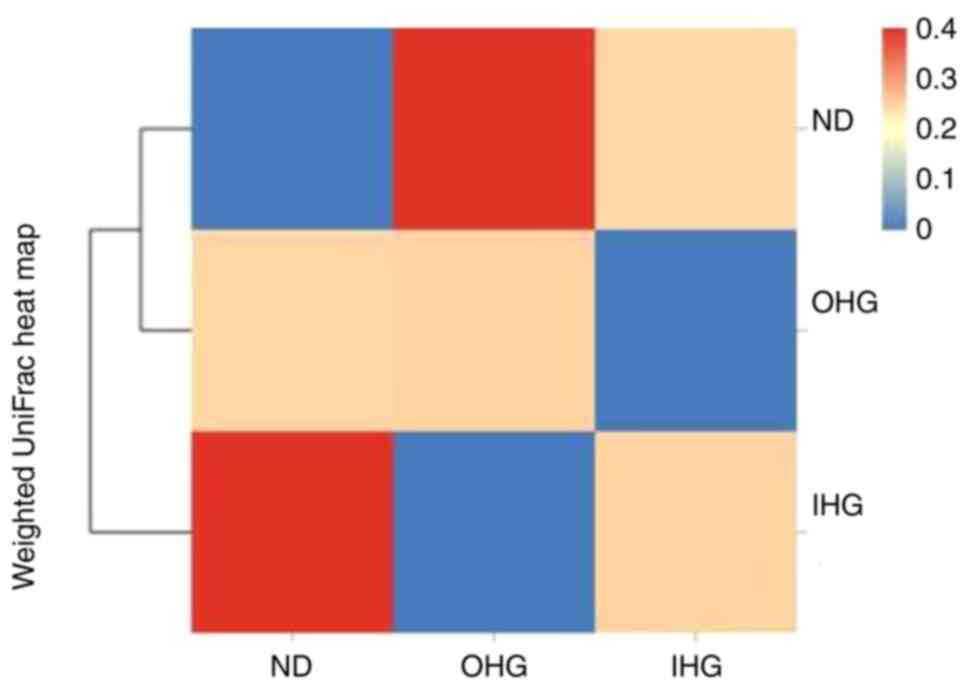
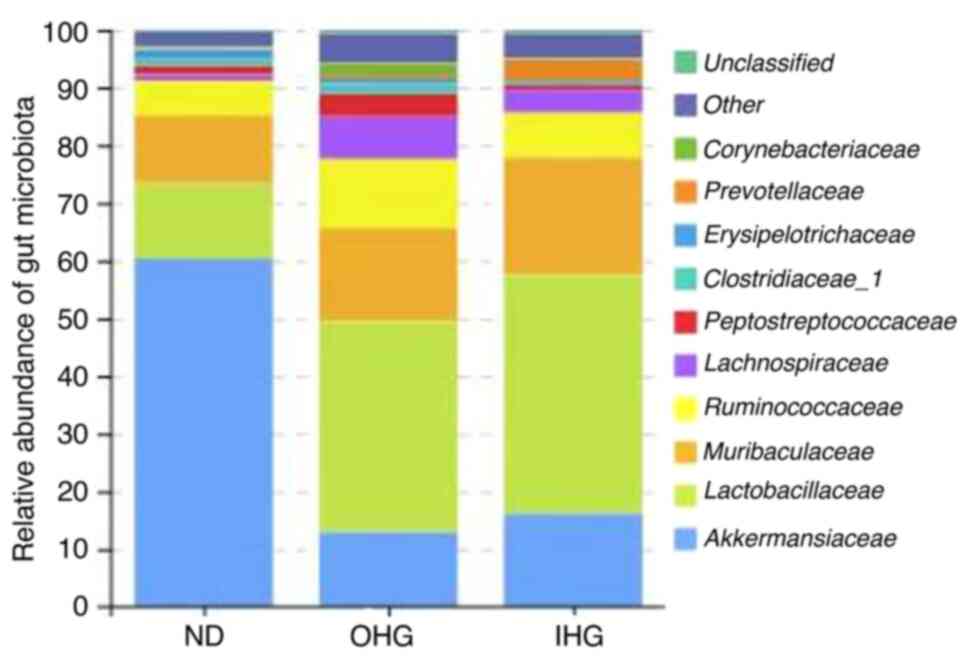
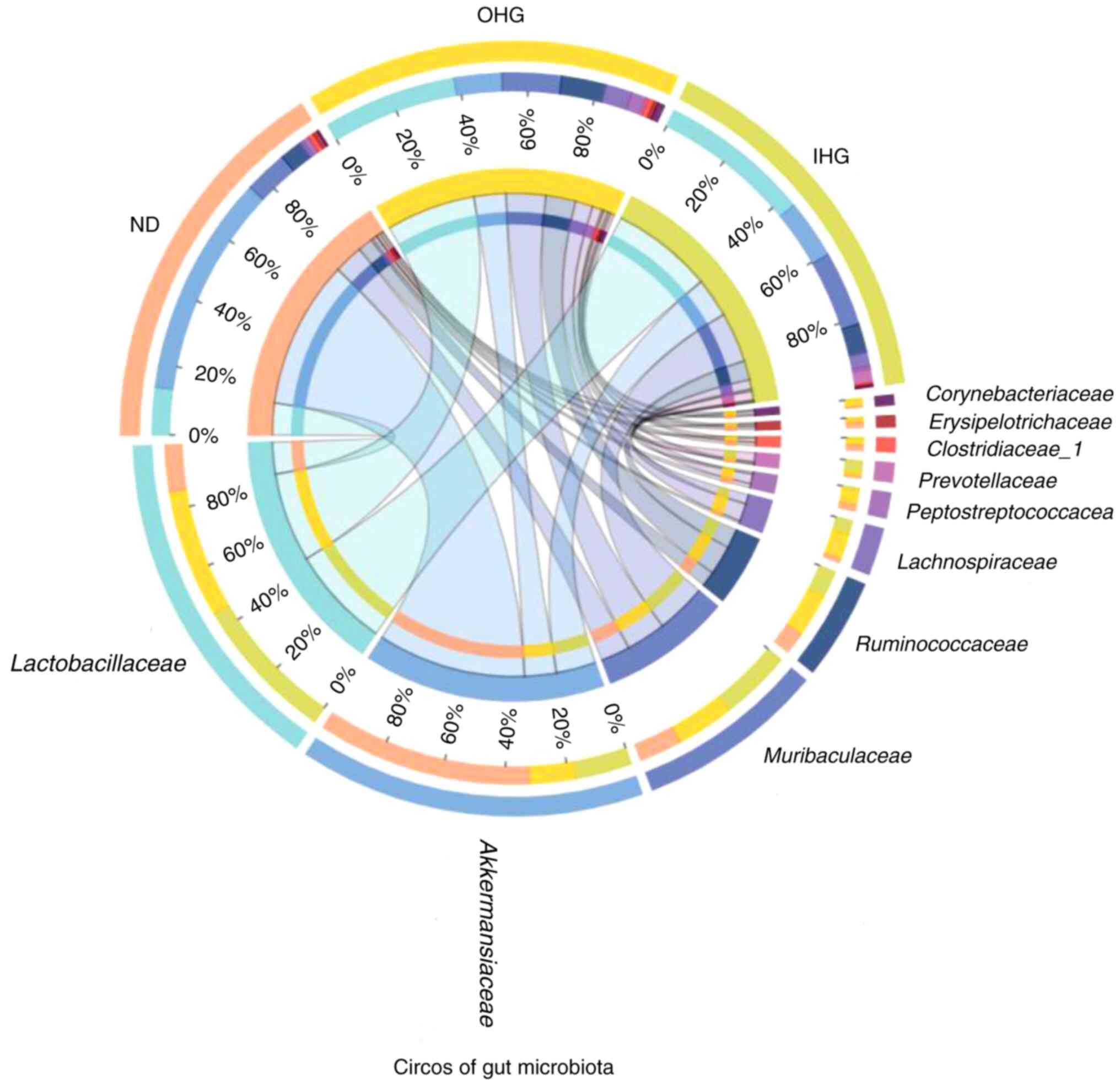
|
1
|
Dall TM, Yang W, Gillespie K, Mocarski M,
Byrne E, Cintina I, Beronja K, Semilla AP, Iacobucci W and Hogan
PF: The economic burden of elevated blood glucose levels in 2017:
Diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus,
and prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 42:1661–1668. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cowie CC: Diabetes diagnosis and control:
Missed opportunities to improve health: The 2018 Kelly West award
lecture. Diabetes Care. 42:994–1004. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Filla LA and Edwards JL: Metabolomics in
diabetic complications. Mol Biosyst. 12:1090–1105. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zou X, Zhou X, Ji L, Yang W, Lu J, Weng J,
Jia W, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, et al: The characteristics of newly
diagnosed adult early-onset diabetes: A population-based
cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 7(46534)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Riddle MC and Gerstein HC: The
cardiovascular legacy of good glycemic control: Clues about
mediators from the DCCT/EDIC study. Diabetes Care. 42:1159–1161.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gaballa M and Farag MK: Predictors of
diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Med. 8:287–296. 2013.
|
|
7
|
MacIsaac RJ and Ekinci EI: Progression of
diabetic kidney disease in the absence of albuminuria. Diabetes
Care. 42:1842–1844. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rines AK, Sharabi K, Tavares CD and
Puigserver P: Targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment
of type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:786–804.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kahl S, Gancheva S, Straßburger K, Herder
C, Machann J, Katsuyama H, Kabisch S, Henkel E, Kopf S, Lagerpusch
M, et al: Empagliflozin effectively lowers liver fat content in
well-controlled type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, phase
4, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 43:298–305.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen M, Zheng H, Xu M, Zhao L, Zhang Q,
Song J, Zhao Z, Lu S, Weng Q, Wu X, et al: Changes in hepatic
metabolic profile during the evolution of STZ-induced diabetic rats
via an 1H NMR-based metabonomic investigation. Biosci
Rep. 39(BSR20181379)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rai RC, Bagul PK and Banerjee SK: NLRP3
inflammasome drives inflammation in high fructose fed diabetic rat
liver: Effect of resveratrol and metformin. Life Sci.
253(117727)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ju M, Liu Y, Li M, Cheng M, Zhang Y, Deng
G, Kang X and Liu H: Baicalin improves intestinal microecology and
abnormal metabolism induced by high-fat diet. Eur J Pharmacol.
857(172457)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Gu Y, Ren H, Wang S, Zhong H,
Zhao X, Ma J, Gu X, Xue Y, Huang S, et al: Gut microbiome-related
effects of berberine and probiotics on type 2 diabetes (the PREMOTE
study). Nat Commun. 11(5015)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Malik VS, Willett WC and Hu FB: Global
obesity: Trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 9:13–27. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shannon C, Merovci A, Xiong J, Tripathy D,
Lorenzo F, McClain D, Abdul-Ghani M, Norton L and DeFronzo RA:
Effect of chronic hyperglycemia on glucose metabolism in subjects
with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 67:2507–2517.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tsuchiya K: Inflammasome-associated cell
death: Pyroptosis, apoptosis, and physiological implications.
Microbiol Immunol. 64:252–269. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chiu THT, Pan WH, Lin MN and Lin CL:
Vegetarian diet, change in dietary patterns, and diabetes risk: A
prospective study. Nutr Diabetes. 8(12)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Taylor R and Barnes AC: Translating
aetiological insight into sustainable management of type 2
diabetes. Diabetologia. 61:273–283. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Prasad M, Chen EW, Toh SA and Gascoigne
NRJ: Autoimmune responses and inflammation in type 2 diabetes. J
Leukoc Biol. 107:739–748. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Purnamasari D, Khumaedi AI, Soeroso Y and
Marhamah S: The influence of diabetes and or periodontitis on
inflammation and adiponectin level. Diabetes Metab Syndr.
13:2176–2182. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Biscetti F, Ferraro PM, Hiatt WR, Angelini
F, Nardella E, Cecchini AL, Santoliquido A, Pitocco D, Landolfi R
and Flex A: Inflammatory cytokines associated with failure of
lower-extremity endovascular revascularization (LER): A prospective
study of a population with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 42:1939–1945.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kheiripour N, Karimi J, Khodadadi I,
Tavilani H, Goodarzi MT and Hashemnia M: Silymarin prevents lipid
accumulation in the liver of rats with type 2 diabetes via sirtuin1
and SREBP-1c. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 29:301–308.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Taylor R, Al-Mrabeh A and Sattar N:
Understanding the mechanisms of reversal of type 2 diabetes. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 7:726–736. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ma Z, Fang L, Ungerfeld E, Li X, Zhou C,
Tan Z, Jiang L and Han X: Supplementation of rumen-protected
glucose increased the risk of disturbance of hepatic metabolism in
early postpartum holstein cows. Antioxidants (Basel).
11(469)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bril F, Portillo Sanchez P, Lomonaco R,
Orsak B, Hecht J, Tio F and Cusi K: Liver safety of statins in
prediabetes or T2DM and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Post Hoc
analysis of a randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
102:2950–2961. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tsujita M, Hossain MA, Lu R, Tsuboi T,
Okumura-Noji K and Yokoyama S: Exposure to high glucose
concentration decreases cell surface ABCA1 and HDL biogenesis in
hepatocytes. J Atheroscler Thromb. 24:1132–1149. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Leviatan S and Segal E: Identifying gut
microbes that affect human health. Nature. 587:373–374.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Haase S, Haghikia A, Wilck N, Müller DN
and Linker RA: Impacts of microbiome metabolites on immune
regulation and autoimmunity. Immunology. 154:230–238.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Botchlett R, Li H, Guo X, Qi T, Zhao J,
Zheng J, Woo SL, Pei Y, Liu M, Hu X, et al: Glucose and palmitate
differentially regulate PFKFB3/iPFK2 and inflammatory responses in
mouse intestinal epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 6(28963)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sittipo P, Shim JW and Lee YK: Microbial
metabolites determine host health and the status of some diseases.
Int J Mol Sci. 20(5296)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Do MH, Lee E, Oh MJ, Kim Y and Park HY:
High-glucose or -fructose diet cause changes of the gut microbiota
and metabolic disorders in mice without body weight change.
Nutrients. 10(761)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhou T, Heianza Y, Chen Y, Li X, Sun D,
DiDonato JA, Pei X, LeBoff MS, Bray GA, Sacks FM and Qi L:
Circulating gut microbiota metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO)
and changes in bone density in response to weight loss diets: The
POUNDS lost trial. Diabetes Care. 42:1365–1371. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee SA, Cozzi M, Bush EL and Rabb H:
Distant organ dysfunction in acute kidney injury: A review. Am J
Kidney Dis. 72:846–856. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li YJ, Chen X, Kwan TK, Loh YW, Singer J,
Liu Y, Ma J, Tan J, Macia L, Mackay CR, et al: Dietary fiber
protects against diabetic nephropathy through short-chain fatty
acid-mediated activation of G protein-coupled receptors GPR43 and
GPR109A. J Am Soc Nephrol. 31:1267–1281. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liu X, Lu J, Liao Y, Liu S, Chen Y, He R,
Men L, Lu C, Chen Z, Li S, et al: Dihydroartemisinin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting
inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother.
117(109070)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Whitt J, Woo V, Lee P, Moncivaiz J,
Haberman Y, Denson L, Tso P and Alenghat T: Disruption of
epithelial HDAC3 in intestine prevents diet-induced obesity in
mice. Gastroenterology. 155:501–513. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li L, Ma L and Fu P: Gut
microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and kidney diseases.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 11:3531–3542. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cao H, Li C, Lei L, Wang X, Liu S, Liu Q,
Huan Y, Sun S and Shen Z: Stachyose improves the effects of
berberine on glucose metabolism by regulating intestinal microbiota
and short-chain fatty acids in spontaneous type 2 diabetic KKAy
mice. Front Pharmacol. 11(578943)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Samsu N: Diabetic nephropathy: Challenges
in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Biomed Res Int.
2021(1497449)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Oshima M, Shimizu M, Yamanouchi M, Toyama
T, Hara A, Furuichi K and Wada T: Trajectories of kidney function
in diabetes: A clinicopathological update. Nat Rev Nephrol.
17:740–750. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Poznyak A, Grechko AV, Poggio P,
Myasoedova VA, Alfieri V and Orekhov AN: The diabetes
mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: The role of lipid and glucose
metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci.
21(1835)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Neves-Costa A and Moita LF: Modulation of
inflammation and disease tolerance by DNA damage response pathways.
FEBS J. 284:680–698. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gao B, Ahmad MF, Nagy LE and Tsukamoto H:
Inflammatory pathways in alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol.
70:249–259. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Mouries J, Brescia P, Silvestri A, Spadoni
I, Sorribas M, Wiest R, Mileti E, Galbiati M, Invernizzi P, Adorini
L, et al: Microbiota-driven gut vascular barrier disruption is a
prerequisite for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development. J
Hepatol. 71:1216–1228. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|