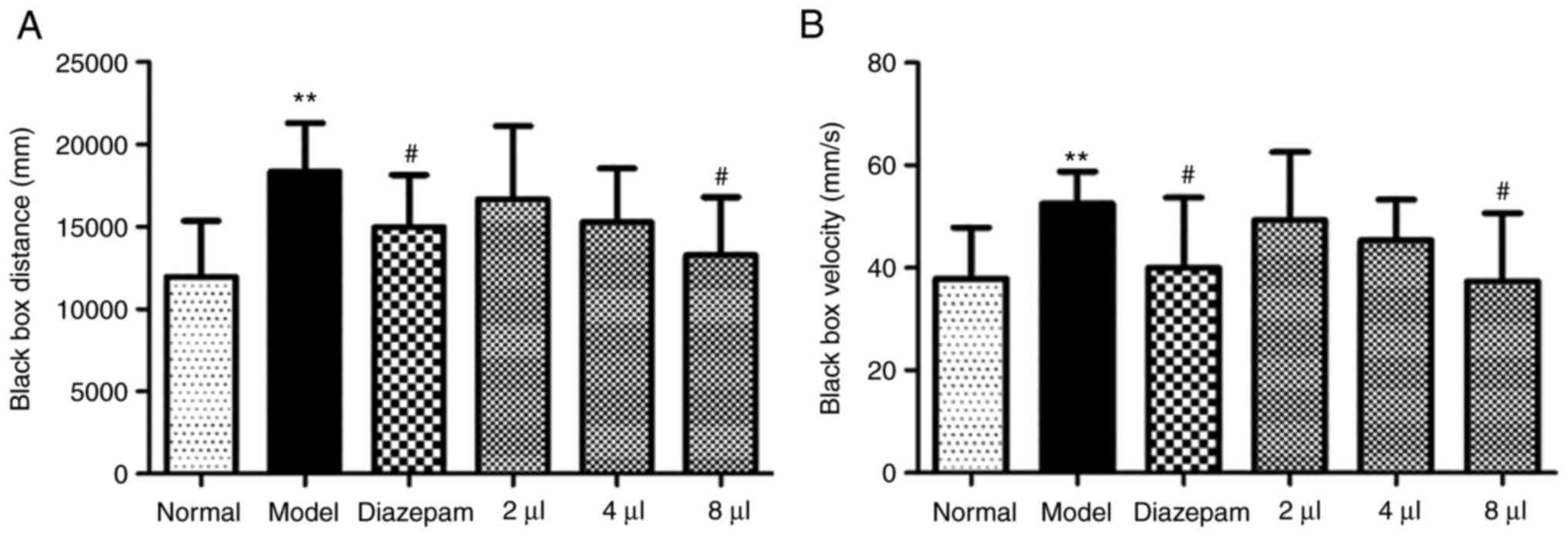
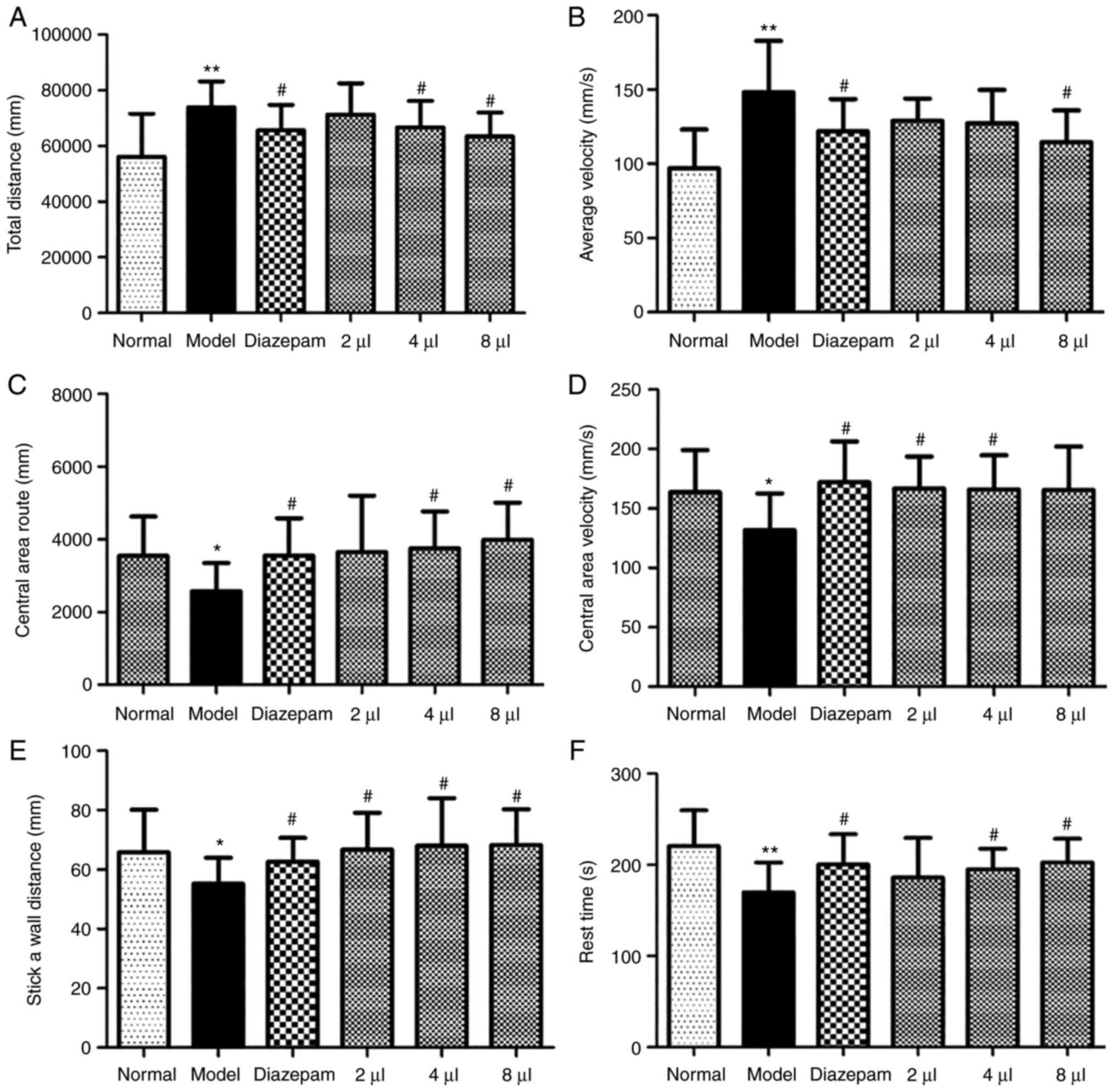
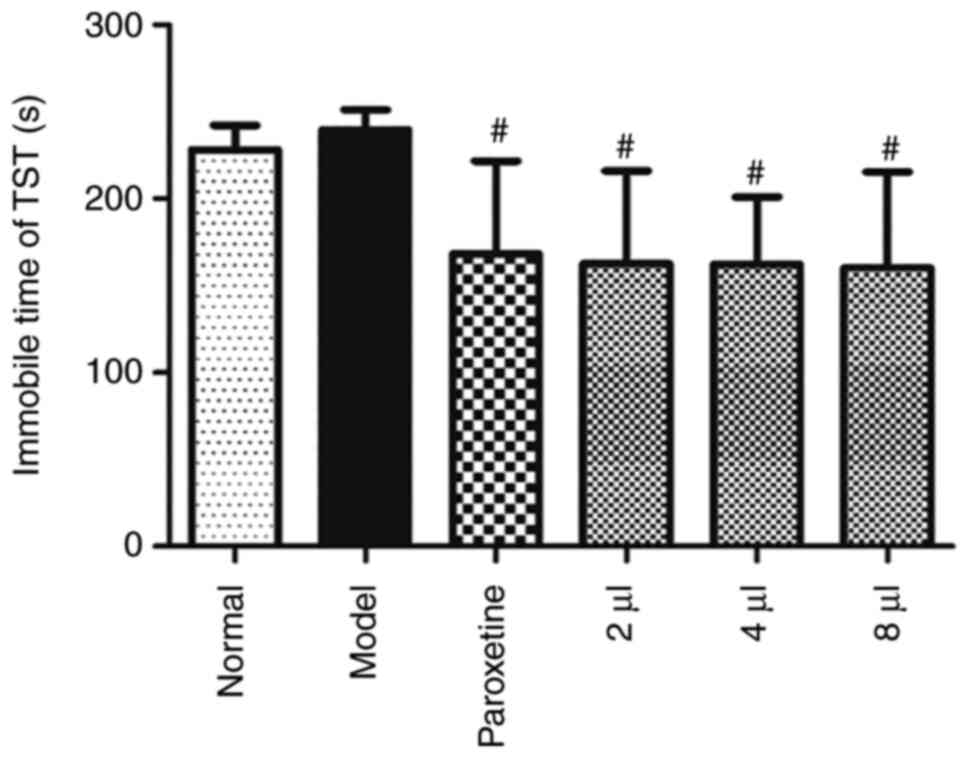
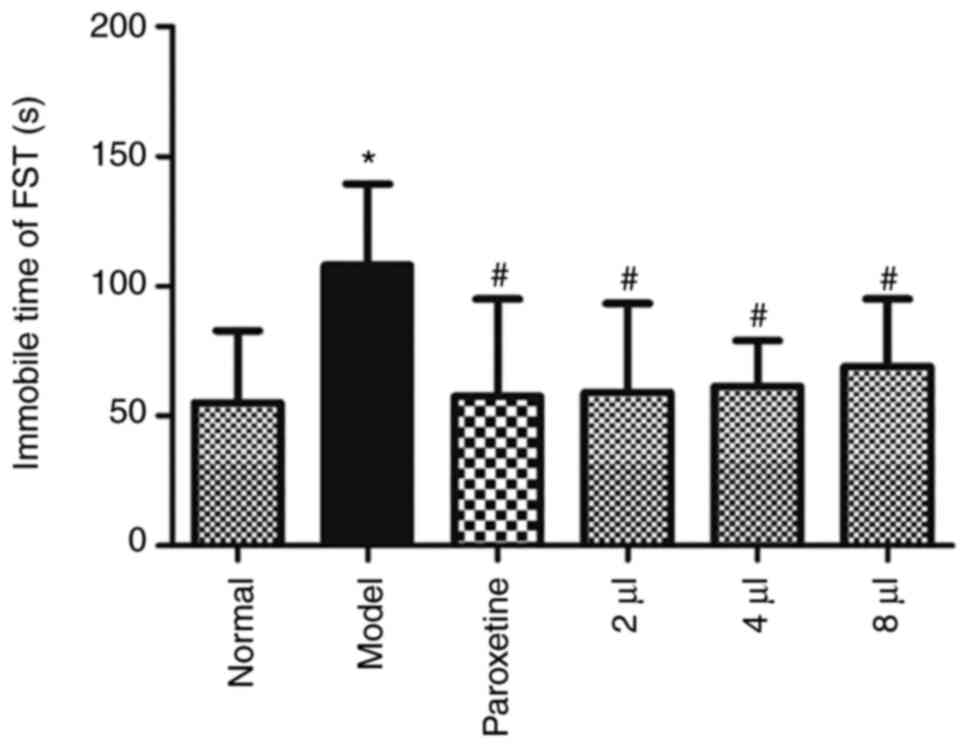
|
1
|
World Health Organization. depression and
other common mental disorders: Global health estimates. World
Health Organization, Geneva, 2017. https://doi.org/CC
BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
|
|
2
|
Guze SB and Robins E: Suicide and primary
affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry. 117:437–438. 1970.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Duman RS and Aghajanian GK: Synaptic
dysfunction in depression: Potential therapeutic targets. Science.
338:68–72. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Anisman H and Matheson K: Stress,
depression, and anhedonia: Caveats concerning animal models.
Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 29:525–546. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Grillo L: A possible role of anhedonia as
common substrate for depression and anxiety. Dep Res Treat.
2016(1598130)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Miller BR and Hen R: The current state of
the neurogenic theory of depression and anxiety. Curr Opin
Neurobiol. 30:51–58. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yu W, Wang L, Yang L, Li YJ, Wang M, Qiu
C, Yang Q, Li XB, Huang YL, Liu R and Wu YM: Activation of LXRβ
signaling in the amygdala confers anxiolytic effects through
rebalancing excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission upon acute
stress. Neurotherapeutics. 17:1253–1270. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Murrough JW, Abdallah CG and Mathew SJ:
Targeting glutamate signalling in depression: Progress and
prospects. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:472–486. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xie W, Cai L, Yu Y, Gao L, Xiao L, He Q,
Ren Z and Liu Y: Activation of brain indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
contributes to epilepsy-associated depressive-like behavior in rats
with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation.
11(41)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chaves EMC, Honório-Júnior JER, Sousa CNS,
Monteiro VS, Nonato DTT, Dantas LP, Lúcio ASSC, Barbosa-Filho JM,
Patrocínio MCA, Viana GSB and Vasconcelos SMM: The anxiolytic-like
effect of 6-styryl-2-pyrone in mice involves GABAergic mechanism of
action. Metab Brain Dis. 33:139–149. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pham TH, Defaix C, Nguyen TML,
Mendez-David I, Tritschler L, David DJ and Gardier AM: Cortical and
raphe GABAA, AMPA receptors and glial GLT-1 glutamate
transporter contribute to the sustained antidepressant activity of
ketamine. Pharmcol Biochem Beha. 192(172913)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sun H, Guan L, Zhu Z and Li H: Reduced
levels of NR1 and NR2A with depression-like behavior in different
brain regions in prenatally stressed juvenile offspring. PLoS One.
8(e81775)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gasull-Camós JL, Martínez-Torres SL,
Tarrés-Gatius M, Ozaita A, Artigas F and Castañé A: Serotonergic
mechanisms involved in antidepressant-like responses evoked by
GLT-1 blockade in rat infralimbic cortex. Neuropharmacology.
139:41–51. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
CITES: Amendments to appendices I and II
of the convention - adopted by the Conference of the Parties at its
13th meeting, Bangkok Thailand, 2-14 October, 2004.
|
|
15
|
Hashim YZ, Kerr PG, Abbas P and Mohd
Salleh H: Aquilaria spp. (agarwood) as source of health beneficial
compounds: A review of traditional use, phytochemistry and
pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol. 189:331–360. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Korinek M, Wagh VD, Lo IW, Hsu YM, Hsu HY,
Hwang TL, Wu YC, Cheng YB, Chen BH and Chang FR: Antiallergic
phorbol ester from the seeds of Aquilaria malaccensis. Int J
Mol Sci. 17(398)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
National Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 1st edition.
Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing, pp185-186,
2015.
|
|
18
|
Dahham SS, Tabana YM, Iqbal MA, Ahamed
MBK, Ezzat MO, Majid ASA and Majid AMSA: The anticancer,
antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the sesquiterpene
β-caryophyllene from the essential oil of Aquilaria crassna.
Molecules. 20:11808–11829. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang S, Wang C, Peng D, Liu X, Wu C, Guo P
and Wei J: Agarwood essential oil displays sedative-hypnotic effect
through GABAergic system. Molecules. 22(2190)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang S, Wang C, Yu Z, Wu C, Peng D, Liu X,
Liu Y, Yang Y, Guo P and Wei J: Agarwood essential oil ameliorates
restrain stress-induced anxiety and depression by inhibiting HPA
axis hyperactivity. Int J Mol Sci. 19(3468)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bahrani H, Mohamad J, Paydar MJ and Rothan
HA: Isolation and characterisation of acetylcholinesterase
inhibitors from Aquilaria subintegra for the treatment of
Alzheimer's disease (AD). Curr Alzheimer Res. 11:206–214.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huo HX, Zhu ZX, Pang DR, Li YT, Huang Z,
Shi SP, Zheng J, Zhang Q, Zhao YF, Tu PF and Li J:
Anti-neuroinflammatory sesquiterpenes from Chinese eaglewood.
Fitoterapia. 106:115–121. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang L, Qiao L, Xie D, Yuan Y, Chen N, Dai
J and Guo S: 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones from Chinese eaglewood.
Phytochemistry. 76:92–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Takemoto H, Ito M, Shiraki T, Yagura T and
Honda G: Sedative effects of vapor inhalation of agarwood oil and
spikenard extract and identification of their active components. J
Nat Med. 62:41–46. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yi Z, Wang W and Zhang J: Effects of novel
anxiolytic 4-butyl-alpha-agarofuran on levels of monoamine
neurotransmitters in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 504:39–44.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Guo JY, Wang WJ, Fang HJ, Yin DL, Sun SJ,
Liu RW and Li C: Agarofuan derivatives, their preparation,
pharmaceutical composition containing them and their use as
medicine. US Patent 6, 486, 201. Filed November 19, 1999; issued
November 26, 2002.
|
|
27
|
Yang L, Qiao L, Ji C, Xie D, Gong NB, Lu
Y, Zhang J, Dai J and Guo S: Antidepressant abietane diterpenoids
from Chinese eaglewood. J Nat Prod. 76:216–222. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Chen H, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Wei J,
Meng H, Chen W, Feng J, Gan B, Chen X, et al: Whole-tree
agarwood-inducing technique: an efficient novel technique for
producing high-quality agarwood in cultivated Aquilaria sinensis
trees. Molecules. 18:3086–3106. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Treit D and Fundytus M: Thigmotaxis as a
test for anxiolytic activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
31:959–962. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mezzomo NJ, Silveira A, Giuliani GS,
Quadros VA and Rosemberg DB: The role of taurine on anxiety-like
behaviors in zebrafish: A comparative study using the novel tank
and the light-dark tasks. Neurosci Lett. 613:19–24. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xie W, Meng X, Zhai Y, Zhou P, Ye T, Wang
Z, Sun G and Sun X: Panax notoginseng saponins: A review of its
mechanisms of antidepressant or anxiolytic effects and network
analysis on phytochemistry and pharmacology. Molecules.
23(940)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wisłowska-Stanek A, Lehner M, Skórzewska
A, Krząścik P, Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Ziemba A and Płaźnik A:
Changes in the brain expression of alpha-2 subunits of the GABA-A
receptor after chronic restraint stress in low- and high-anxiety
rats. Behav Brain Res. 253:337–345. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Modi S, Rana P, Kaur P, Rani N and Khushu
S: Glutamate level in anterior cingulate predicts anxiety in
healthy humans: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychiatry
Res. 224:34–41. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mathews DC, Henter ID and Zarate CA:
Targeting the glutamatergic system to treat major depressive
disorder: Rationale and progress to date. Drugs. 72:1313–1333.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nuss P: Anxiety disorders and GABA
neurotransmission: A disturbance of modulation. Neuropsychiatr Dis
Treat. 11:165–175. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen S, Huang X, Zeng XJ, Sieghart W and
Tietz EI: Benzodiazepine-mediated regulation of alpha1, alpha2,
beta1-3 and gamma2 GABA(A) receptor subunit proteins in the rat
brain hippocampus and cortex. Neurosciences. 93:33–44.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Dremencov E, Gur E, Lerer B and Newman ME:
Effects of chronic antidepressants and electroconvulsive shock on
serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat hippocampus. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 27:729–739. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tóth K: Glutamatergic neurotransmission in
the hippocampus. Springer, New York, 2010.
|
|
39
|
Mokler D, Morgane PJ, Luebke J and Galler
JR: Serotonin release and modulation of GABA neurotransmission in
the hippocampus of rats exposed to prenatal protein malnutrition.
Serotonin: From the Molecule to the ClinicSerotonin: From the
Molecule to the Clinic, 2000.
|
|
40
|
Pinheiro AC, da Silva AJ, Prado MA,
Cordeiro Mdo N, Richardson M, Batista MC, de Castro Junior CJ,
Massensini AR, Guatimosim C, Romano-Silva MA, et al:
Phoneutria spider toxins block ischemia-induced glutamate
release, neuronal death, and loss of neurotransmission in
hippocampus. Hippocampus. 19:1123–1129. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ferreira-Junior NC, Lagatta DC and Resstel
LBM: Glutamatergic, GABAergic, and endocannabinoid
neurotransmissions within the dorsal hippocampus modulate the
cardiac baroreflex function in rats. Pflugers Arch. 470:395–411.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Stefanits H, Milenkovic I, Mahr N,
Pataraia E, Hainfellner JA, Kovacs GG, Sieghart W, Yilmazer-Hanke D
and Czech T: GABAA receptor subunits in the human
amygdala and hippocampus: Immunohistochemical distribution of 7
subunits. J Comp Neurol. 526:324–348. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Guerriero RM, Giza CC and Rotenberg A:
Glutamate and GABA imbalance following traumatic brain injury. Curr
Neurol Neurosci Rep. 15(27)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Deidda G, Bozarth IF and Cancedda L:
Modulation of GABAergic transmission in development and
neurodevelopmental disorders: Investigating physiology and
pathology to gain therapeutic perspectives. Front Cell Neurosci.
8(119)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yu H, Li M, Zhou D, Lv D, Liao Q, Lou Z,
Shen M, Wang Z, Li M, Xiao X, et al: Vesicular glutamate
transporter 1 (VGLUT1)-mediated glutamate release and membrane
GluA1 activation is involved in the rapid antidepressant-like
effects of scopolamine in mice. Neuropharmacology. 131:209–222.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zink M, Vollmayr B, Gebicke-Haerter PJ and
Henn FA: Reduced expression of glutamate transporters vGluT1, EAAT2
and EAAT4 in learned helpless rats, an animal model of depression.
Neuropharmacology. 58:465–473. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bi LL, Wang J, Luo ZY, Chen SP, Geng F,
Chen YH, Li SJ, Yuan CH, Lin S and Gao TM: Enhanced excitability in
the infralimbic cortex produces anxiety-like behaviors.
Neuropharmacology. 72:148–156. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Poulter MO, Du L, Zhurov V, Merali Z and
Anisman H: Plasticity of the GABA(A) receptor subunit cassette in
response to stressors in reactive versus resilient mice.
Neuroscience. 165:1039–1051. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|