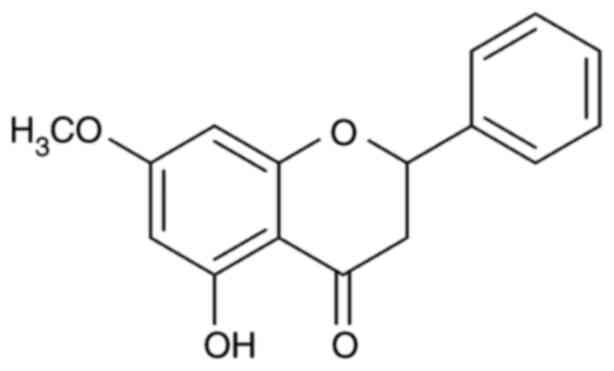
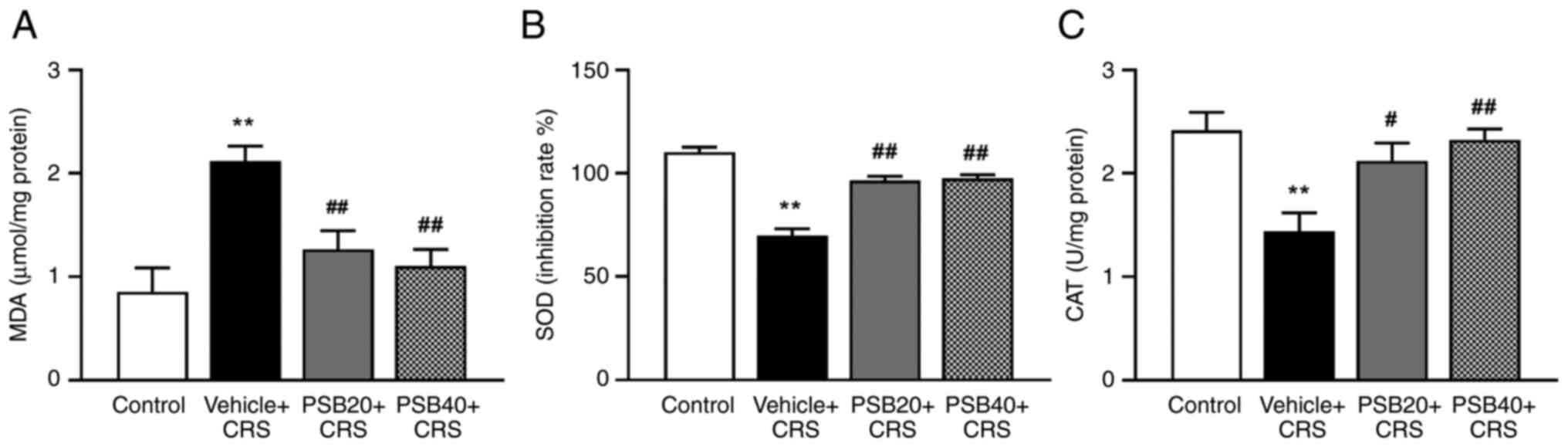
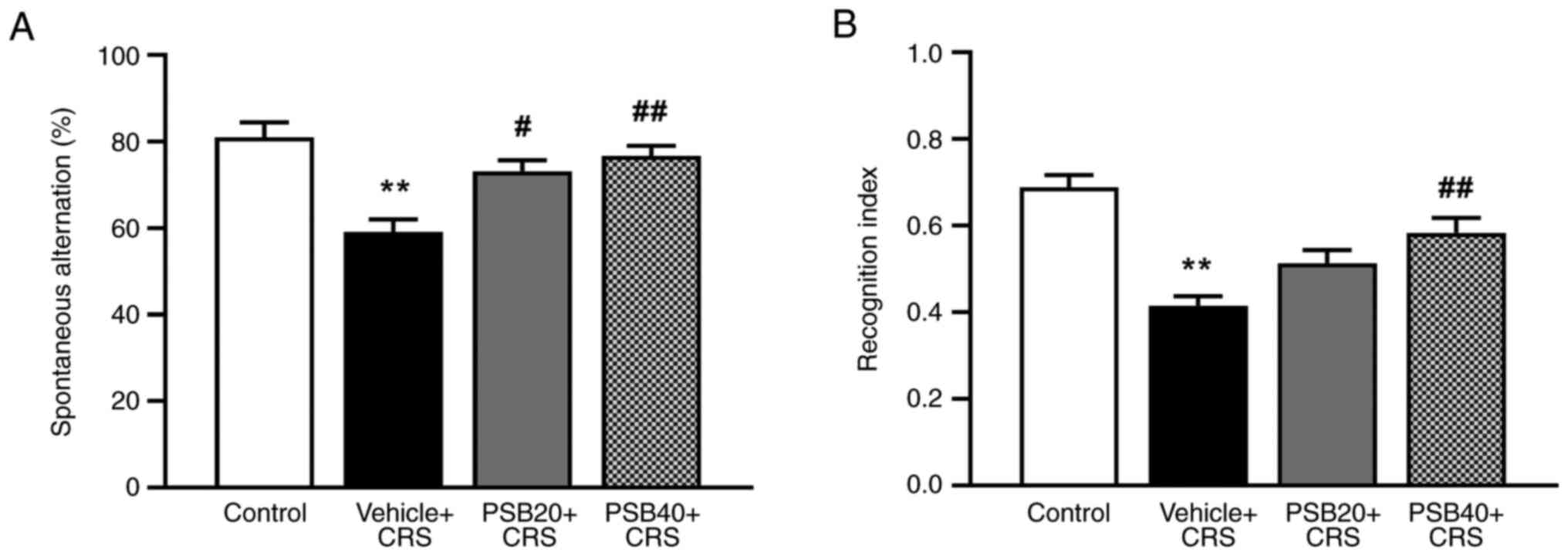
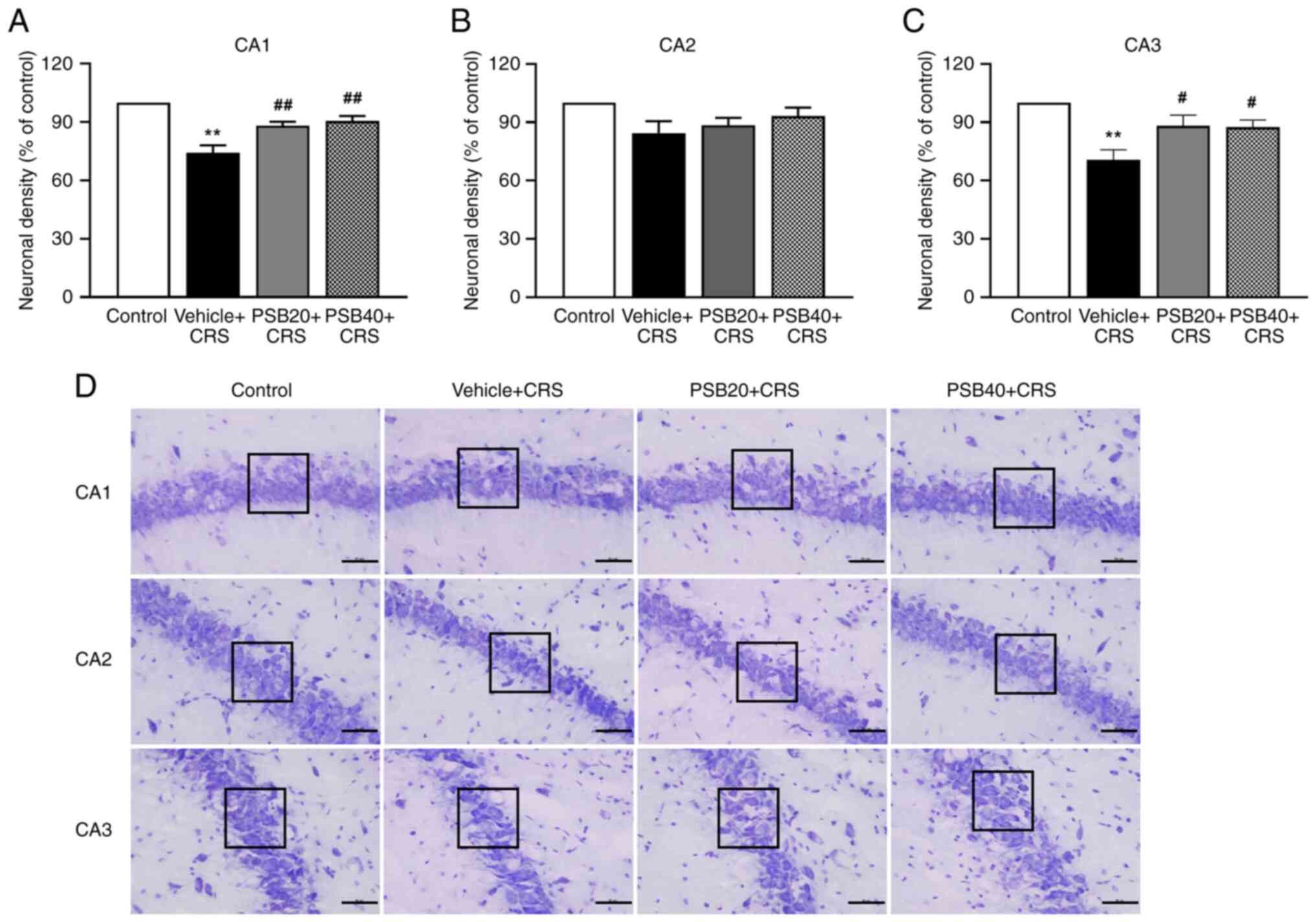
|
1
|
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M,
Farkhondeh T and Samini F: Anti-oxidative effects of curcumin on
immobilization-induced oxidative stress in rat brain, liver and
kidney. Biomed Pharmacother. 87:223–229. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Radley JJ, Kabbaj M, Jacobson L,
Heydendael W, Yehuda R and Herman JP: Stress risk factors and
stress-related pathology: Neuroplasticity, epigenetics and
endophenotypes. Stress. 14:481–497. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
de Kloet ER, Joëls M and Holsboer F:
Stress and the brain: From adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci.
6:463–475. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Briones A, Gagno S, Martisova E, Dobarro
M, Aisa B, Solas M, Tordera R and Ramírez M: Stress-induced
anhedonia is associated with an increase in Alzheimer's
disease-related markers. Br J Pharmacol. 165:897–907.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jeong YH, Park CH, Yoo J, Shin KY, Ahn SM,
Kim HS, Lee SH, Emson PC and Suh YH: Chronic stress accelerates
learning and memory impairments and increases amyloid deposition in
APPV717I-CT100 transgenic mice, an Alzheimer's disease model. FASEB
J. 20:729–731. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Najjar S, Pearlman DM, Devinsky O, Najjar
A and Zagzag D: Neurovascular unit dysfunction with blood-brain
barrier hyperpermeability contributes to major depressive disorder:
A review of clinical and experimental evidence. J
Neuroinflammation. 10(142)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huang RR, Hu W, Yin YY, Wang YC, Li WP and
Li WZ: Chronic restraint stress promotes learning and memory
impairment due to enhanced neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress in
the frontal cortex and hippocampus in male mice. Int J Mol Med.
35:553–559. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Kan H, Yin Y, Wu W, Hu W, Wang M
and Li W and Li W: Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on chronic
restraint stress induced learning and memory impairments in male
mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 120:73–81. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Morimoto M, Morita N, Ozawa H, Yokoyama K
and Kawata M: Distribution of glucocorticoid receptor
immunoreactivity and mRNA in the rat brain: An immunohistochemical
and in situ hybridization study. Neurosci Res. 26:235–269.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Smith MA: Hippocampal vulnerability to
stress and aging: Possible role of neurotrophic factors. Behav
Brain Res. 78:25–36. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Luo C, Xu H and Li XM: Quetiapine reverses
the suppression of hippocampal neurogenesis caused by repeated
restraint stress. Brain Res. 1063:32–39. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim JJ and Diamond DM: The stressed
hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 3:453–462. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Levone BR, Cryan JF and O'Leary OF: Role
of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in stress resilience. Neurobiol
Stress. 1:147–155. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
McEwen BS and Magarinos AM: Stress and
hippocampal plasticity: Implications for the pathophysiology of
affective disorders. Hum Psychopharmacol. 16 (Suppl 1):S7–S19.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McLaughlin KJ, Gomez JL, Baran SE and
Conrad CD: The effects of chronic stress on hippocampal morphology
and function: An evaluation of chronic restraint paradigms. Brain
Res. 1161:56–64. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sahin E and Gümüşlü S: Immobilization
stress in rat tissues: Alterations in protein oxidation, lipid
peroxidation and antioxidant defense system. Comp Biochem Physiol C
Toxicol Pharmacol. 144:342–347. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim GH, Kim JE, Rhie SJ and Yoon S: The
role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp
Neurobiol. 24:325–340. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang HJ, Kim KY, Kang P, Lee HS and Seol
GH: Effects of Salvia sclarea on chronic immobilization stress
induced endothelial dysfunction in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14(396)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Serrano F and Klann E: Reactive oxygen
species and synaptic plasticity in the aging hippocampus. Ageing
Res Rev. 3:431–443. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kelsey NA, Wilkins HM and Linseman DA:
Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents.
Molecules. 15:7792–7814. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kong Y, Fu YJ, Zu YG, Liu W, Wang W, Hua X
and Yang M: Ethanol modified supercritical fluid extraction and
antioxidant activity of cajaninstilbene acid and pinostrobin from
pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] leaves. Food Chem.
117:152–159. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Patel NK and Bhutani KK: Pinostrobin and
Cajanus lactone isolated from Cajanus cajan (L.) leaves
inhibits TNF-α and IL-1β production: In vitro and in vivo
experimentation. Phytomedicine. 21:946–953. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xian YF, Ip SP, Lin ZX, Mao QQ, Su ZR and
Lai XP: Protective effects of pinostrobin on β-amyloid-induced
neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 32:1223–1230.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li C, Tang B, Feng Y, Tang F, Pui-Man Hoi
M, Su Z and Ming-Yuen Lee S: Pinostrobin exerts neuroprotective
actions in neurotoxin-induced Parkinson's disease models through
Nrf2 induction. J Agric Food Chem. 66:8307–8318. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ching AYL, Wah TS, Sukari MA, Cheng Lian
GE, Rahmani M and Khalid K: Characterization of flavonoid
derivatives from Boesenbergia rotunda (L). Malaysian J Anal
Sci. 11:154–159. 2007.
|
|
26
|
Tynan RJ, Beynon SB, Hinwood M, Johnson
SJ, Nilsson M, Woods JJ and Walker FR: Chronic stress-induced
disruption of the astrocyte network is driven by structural atrophy
and not loss of astrocytes. Acta Neuropathol. 126:75–91.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Abdelwahab SI, Mohan S, Abdulla MA, Sukari
MA, Abdul AB, Taha MM, Syam S, Ahmad S and Lee KH: The methanolic
extract of Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf. and its major
compound pinostrobin induces anti-ulcerogenic property in vivo:
Possible involvement of indirect antioxidant action. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:963–970. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nakmareong S, Kukongviriyapan U,
Pakdeechote P, Donpunha W, Kukongviriyapan V, Kongyingyoes B,
Sompamit K and Phisalaphong C: Antioxidant and vascular protective
effects of curcumin and tetrahydrocurcumin in rats with
L-NAME-induced hypertension. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
383:519–529. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Góth L: A simple method for determination
of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin
Chim Acta. 196:143–151. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Johnson SJ and Walker FR: Strategies to
improve quantitative assessment of immunohistochemical and
immunofluorescent labelling. Sci Rep. 5(10607)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Galeano P, Martino Adami PV, Do Carmo S,
Blanco E, Rotondaro C, Capani F, Castaño EM, Cuello AC and Morelli
L: Longitudinal analysis of the behavioral phenotype in a novel
transgenic rat model of early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Front
Behav Neurosci. 8(321)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mooshekhian A, Sandini T, Wei Z, Van
Bruggen R, Li H, Li XM and Zhang Y: Low-field magnetic stimulation
improved cuprizone-induced depression-like symptoms and
demyelination in female mice. Exp Ther Med. 23(210)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jamali-Raeufy N, Kardgar S,
Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M and Goudarzi M: Troxerutin exerts
neuroprotection against lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced oxidative
stress and neuroinflammation through targeting SIRT1/SIRT3
signaling pathway. Metab Brain Dis. 34:1505–1513. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Batool Z, Sadir S, Liaquat L, Tabassum S,
Madiha S, Rafiq S, Tariq S, Batool TS, Saleem S, Naqvi F, et al:
Repeated administration of almonds increases brain acetylcholine
levels and enhances memory function in healthy rats while
attenuates memory deficits in animal model of amnesia. Brain Res
Bull. 120:63–74. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR and Heim
C: Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain,
behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 10:434–445.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sandi C and Pinelo-Nava MT: Stress and
memory: Behavioral effects and neurobiological mechanisms. Neural
Plast. 2007(78970)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pourheydar B, Abar M, Farjah G, Pourheydar
M and Derafshpour L: Curcumin alleviates restraint stress-induced
learning and memory deficit and activity via modulation of
biochemical, morphology changes, and apoptosis in the prefrontal
cortex and hippocampus. Behav Neurosci. 136:149–158.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
McEwen BS: The neurobiology of stress:
From serendipity to clinical relevance. Brain Res. 886:172–189.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Vyas A, Mitra R, Shankaranarayana Rao BS
and Chattarji S: Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of
dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J
Neurosci. 22:6810–6818. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M and Samini
F: Preventive effect of safranal against oxidative damage in aged
male rat brain. Exp Anim. 64:65–71. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liang S, Wang T, Hu X, Luo J, Li W, Wu X,
Duan Y and Jin F: Administration of lactobacillus helveticus NS8
improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused
by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience. 310:561–577.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M, Borji A,
Samini M and Farkhondeh T: Protective effects of carnosol against
oxidative stress induced brain damage by chronic stress in rats.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 17(249)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jiang N, Wang K, Zhang Y, Huang H, Lv JW,
Wang Q, Wang HX, Xia TJ and Liu XM: Protective effect of
ginsenoside Rb1 against chronic restraint stress (CRS)-induced
memory impairments in rats. Behav Brain Res.
405(113146)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Conrad CD, Galea LA, Kuroda Y and McEwen
BS: Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and
this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Behav Neurosci.
110:1321–1334. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu Y, Lin D, Li S, Li G, Shyamala SG,
Barish PA, Vernon MM, Pan J and Ogle WO: Curcumin reverses impaired
cognition and neuronal plasticity induced by chronic stress.
Neuropharmacology. 57:463–471. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sithisarn P, Rojsanga P, Jarikasem S,
Tanaka K and Matsumoto K: Ameliorative effects of acanthopanax
trifoliatus on cognitive and emotional deficits in olfactory
bulbectomized mice: An animal model of depression and cognitive
deficits. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013(701956)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Phachonpai W and Tongun T: Cognition
enhancing effects of Clausena lansium (Lour.) peel extract
attenuate chronic restraint stress-induced memory deficit in rats.
Heliyon. 7(e07003)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
McEwen BS and Magarinos AM: Stress effects
on morphology and function of the hippocampus. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
821:271–284. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
McEwen BS: Stress and hippocampal
plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:105–122. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Brunson KL, Kramar E, Lin B, Chen Y,
Colgin LL, Yanagihara TK, Lynch G and Baram TZ: Mechanisms of
late-onset cognitive decline after early-life stress. J Neurosci.
25:9328–9338. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Huang P, Li C, Fu T, Zhao D, Yi Z, Lu Q,
Guo L and Xu X: Flupirtine attenuates chronic restraint
stress-induced cognitive deficits and hippocampal apoptosis in male
mice. Behav Brain Res. 288:1–10. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Christian KM, Miracle AD, Wellman CL and
Nakazawa K: Chronic stress-induced hippocampal dendritic retraction
requires CA3 NMDA receptors. Neuroscience. 174:26–36.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sun DS, Zhong G, Cao HX, Hu Y, Hong XY, Li
T, Li X, Liu Q, Wang Q, Ke D, et al: Repeated restraint stress led
to cognitive dysfunction by NMDA receptor-mediated hippocampal CA3
dendritic spine impairments in juvenile sprague-dawley rats. Front
Mol Neurosci. 13(552787)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Dudek SM, Alexander GM and Farris S:
Rediscovering area CA2: Unique properties and functions. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 17:89–102. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hei M, Chen P, Wang S, Li X, Xu M, Zhu X,
Wang Y, Duan J, Huang Y and Zhao S: Effects of chronic mild stress
induced depression on synaptic plasticity in mouse hippocampus.
Behav Brain Res. 365:26–35. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Shilpa BM, Bhagya V, Harish G, Srinivas
Bharath MM and Shankaranarayana Rao BS: Environmental enrichment
ameliorates chronic immobilisation stress-induced spatial learning
deficits and restores the expression of BDNF, VEGF, GFAP and
glucocorticoid receptors. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol
Psychiatry. 76:88–100. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Araya-Callis C, Hiemke C, Abumaria N and
Flugge G: Chronic psychosocial stress and citalopram modulate the
expression of the glial proteins GFAP and NDRG2 in the hippocampus.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 224:209–222. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Czéh B, Simon M, Schmelting B, Hiemke C
and Fuchs E: Astroglial plasticity in the hippocampus is affected
by chronic psychosocial stress and concomitant fluoxetine
treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 31:1616–1626. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hughes EG, Maguire JL, McMinn MT, Scholz
RE and Sutherland ML: Loss of glial fibrillary acidic protein
results in decreased glutamate transport and inhibition of
PKA-induced EAAT2 cell surface trafficking. Brain Res Mol Brain
Res. 124:114–123. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Charoensin S, Punvittayagul C, Pompimon W,
Mevatee U and Wongpoomchai R: Toxicological and clastogenic
evaluation of pinocembrin and pinostrobin isolated from
Boesenbergia pandurata in Wistar rats. Thai J Toxicol. 25:29–40.
2010.
|
|
61
|
Tonum K, Chabang N, Fongsupa S,
Chantawarin S, Jiarpinitnun C, Tuchinda P and Soodvilai S:
Pinostrobin inhibits renal CFTR-mediated Cl- secretion
and retards cyst growth in cell-derived cyst and polycystic kidney
disease rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 148:369–376. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|