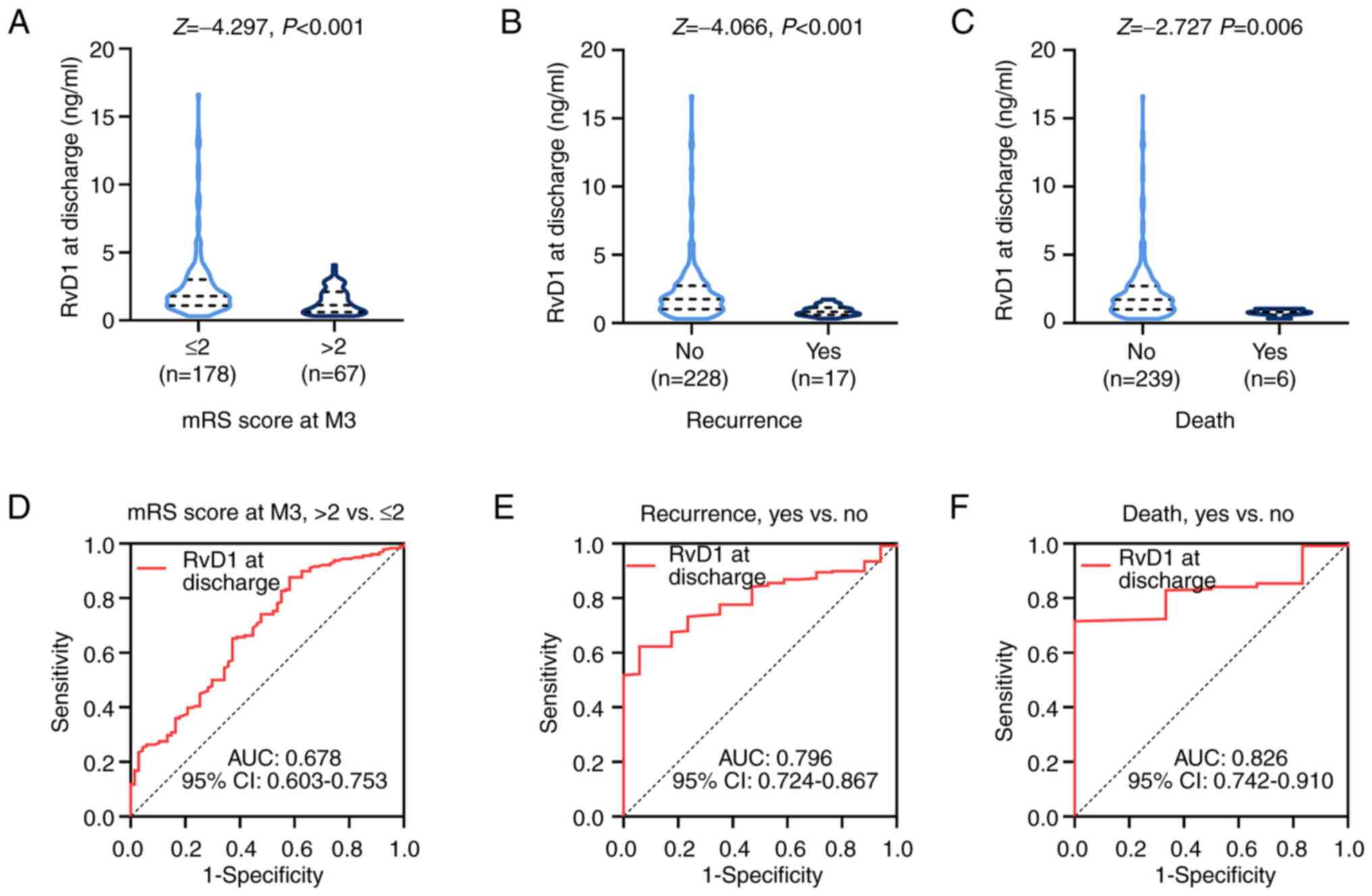
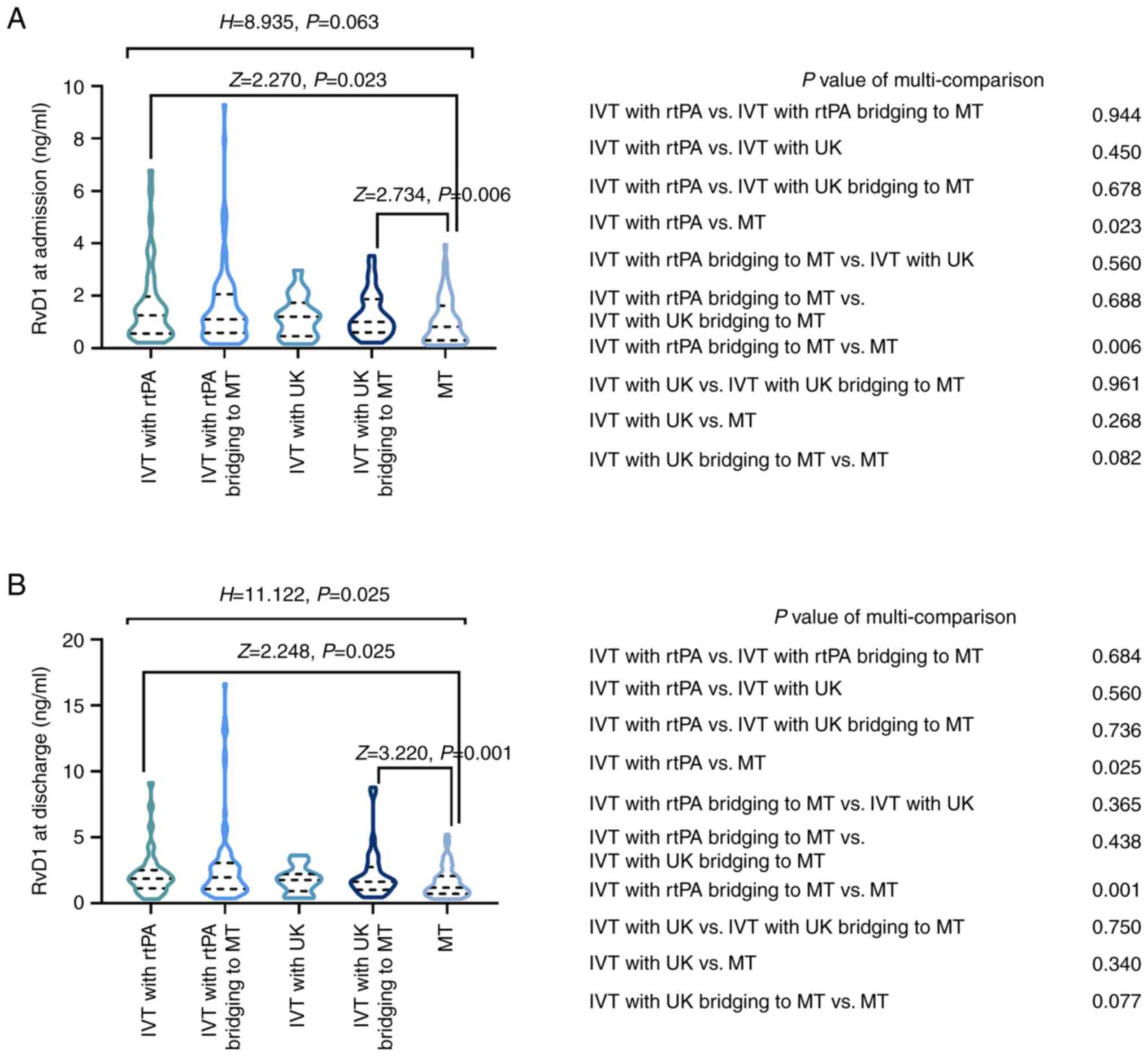
|
1
|
Bathla G, Ajmera P, Mehta PM, Benson JC,
Derdeyn CP, Lanzino G, Agarwal A and Brinjikji W: Advances in acute
ischemic stroke treatment: Current status and future directions.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 44:750–758. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tu WJ, Zhao Z, Yin P, Cao L, Zeng J, Chen
H, Fan D, Fang Q, Gao P, Gu Y, et al: Estimated Burden of stroke in
China in 2020. JAMA Netw Open. 6(e231455)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, Chen Z, Wang W,
Anderson CS, Sandercock P, Wang Y, Huang Y, Cui L, et al: Stroke in
China: Advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and
management. Lancet Neurol. 18:394–405. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Posul E, Yilmaz B, Aktas G and Kurt M:
Does neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predict active ulcerative
colitis? Wien Klin Wochenschr. 127:262–265. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Duman TT, Aktas G, Atak BM, Kocak MZ,
Erkus E and Savli H: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as an
indicative of diabetic control level in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Afr Health Sci. 19:1602–1606. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sahin S, Sarikaya S, Alcelik A, Erdem A
and Karaman KJAMM: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is a useful
predictor of atrial fibrillation in patients with diabetes
mellitus. Acta Medica Mediterranea. 29:847–851. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Aktas G, Sit M, Dikbas O, Erkol H,
Altinordu R, Erkus E and Savli H: Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio in the diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Rev Assoc Med
Bras (1992). 63:1065–1068. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khalid A, Ali Jaffar M, Khan T, Abbas Lail
R, Ali S, Aktas G, Waris A, Javaid A, Ijaz N and Muhammad N:
Hematological and biochemical parameters as diagnostic and
prognostic markers in SARS-COV-2 infected patients of Pakistan: A
retrospective comparative analysis. Hematology. 26:529–542.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bilgin S, Kurtkulagi O, Atak BM, Duman TT,
Kahveci G, Khalid A and Aktas G: Does C-reactive protein to serum
Albumin Ratio correlate with diabEtic nephropathy in patients with
Type 2 dIabetes MEllitus? The CARE TIME study. Prim Care Diabetes.
15:1071–1074. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Demirkol ME and Aktas G: C-reactive
protein to LymphocytE count ratio could be a reliable mArkeR of
thyroiditis; the CLEAR-T study. Precision Med Sci. 11:31–34.
2022.
|
|
11
|
Mojahedi MJ, Bonakdaran S, Hami M,
Sheikhian MR, Shakeri MT and Aiatollahi H: Elevated serum
C-reactive protein level and microalbuminuria in patients with type
2 diabetes mellitus. Iran J Kidney Dis. 3:12–6. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Demirkol ME, Aktas G, Bilgin S, Kahveci G,
Kurtkulagi O, Atak BM and Duman TT: C-reactive protein to
lymphocyte count ratio is a promising novel marker in hepatitis C
infection: The clear hep-c study. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992).
68:838–841. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Demirkol ME, Bilgin S, Kahveci G,
Kurtkulagi O, Atak BM, Duman TT and Aktas G: C-reactive
protein-to-lymphocyte ratio is a reliable marker in patients with
COVID-19 infection: The CLEAR COVID study. Cir Cir. 90:596–601.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Afsin H and Aktas G: Platelet to
Lymphocyte and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratios are useful in
differentiation of thyroid conditions with normal and increased
uptake. Ethiop J Health Dev. 35:149–153. 2021.
|
|
15
|
Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, Atak BM,
Bilgin S, Duman TT and Aktas G: A novel inflammatory marker for the
diagnosis of hashimoto’s thyroiditis:
Platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio. Diseases.
11(15)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Atak BM, Kahveci G, Bilgin S, Kurtkulagi O
and Kosekli MA: Platelet to lymphocyte ratio in differentiation of
benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Exp Biomed Res. 4:148–153.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Atak B, Aktas G, Duman TT, Erkus E, Kocak
MZ and Savli H: Diabetes control could through
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in hemograms. Rev Assoc Med Bras
(1992). 5:38–42. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Aktas G, Duman TT, Atak BM, Kurtkulagi O,
Bilgin S, Basaran E, Demirkol ME and Kosekli MA: Irritable bowel
syndrome is associated with novel inflammatory markers derived from
hemogram parameters. Fam Med Prim Care Rev. 22:107–110. 2020.
|
|
19
|
Aktas G: Hematological predictors of novel
Coronavirus infection. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 67 (Suppl
1):S1–S2. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu YL, Wu ZQ, Qu JF, Qiu DH, Luo GP, Yin
HP, Fang XW, Wang F and Chen YK: High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio is a predictor of poor short-term outcome in patients with
mild acute ischemic stroke receiving intravenous thrombolysis.
Brain Behav. 10(e01857)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yang Y, Xie D and Zhang Y: Increased
Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio is an Independent Predictor of
Hemorrhagic Transformation and In-Hospital Mortality among acute
ischemic stroke with large-artery atherosclerosis patients. Int J
Gen Med. 14:7545–7555. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang H, Zhang S, Xie L, Zhong Z and Yan F:
Neuroinflammation and peripheral immunity: Focus on ischemic
stroke. Int Immunopharmacol. 120(110332)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cheng Y, Zhang W, Cao W, Shao M, Lin Y,
Shao B, Yu H and Deng B: 2-BFI attenuates ischemic injury by
modulating mTOR signaling and neuroinflammation in rats. Neurosci
Lett. 750(135766)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhu H, Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Ye Y, Hu X, Gu L
and Xiong X: Inflammation-mediated angiogenesis in ischemic stroke.
Front Cell Neurosci. 15(652647)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Charabati M, Zandee S, Fournier AP, Tastet
O, Thai K, Zaminpeyma R, Lecuyer MA, Bourbonniere L, Larouche S,
Klement W, et al: MCAM+ brain endothelial cells contribute to
neuroinflammation by recruiting pathogenic CD4+ T lymphocytes.
Brain. 146:1483–1495. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Weiner HL and Selkoe DJ: Inflammation and
therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases. Nature. 420:879–884.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
von Schacky C: Importance of EPA and DHA
Blood Levels in Brain Structure and Function. Nutrients.
13(1074)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun GY, Simonyi A, Fritsche KL, Chuang DY,
Hannink M, Gu Z, Greenlief CM, Yao JK, Lee JC and Beversdorf DQ:
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): An essential nutrient and a
nutraceutical for brain health and diseases. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 136:3–13. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tulowiecka N, Kotlega D, Prowans P and
Szczuko M: The role of resolvins: EPA and DHA derivatives can be
useful in the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke. Int J
Mol Sci. 21(7628)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu G, Fiala M, Mizwicki MT, Sayre J,
Magpantay L, Siani A, Mahanian M, Chattopadhyay M, La Cava A and
Wiedau-Pazos M: Neuronal phagocytosis by inflammatory macrophages
in ALS spinal cord: Inhibition of inflammation by resolvin D1. Am J
Neurodegener Dis. 1:60–74. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu GJ, Tao T, Wang H, Zhou Y, Gao X, Gao
YY, Hang CH and Li W: Functions of resolvin D1-ALX/FPR2 receptor
interaction in the hemoglobin-induced microglial inflammatory
response and neuronal injury. J Neuroinflammation.
17(239)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li L, Cheng SQ, Sun YQ, Yu JB, Huang XX,
Dong YF, Ji J, Zhang XY, Hu G and Sun XL: Resolvin D1 reprograms
energy metabolism to promote microglia to phagocytize neutrophils
after ischemic stroke. Cell Rep. 42(112617)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Arnardottir H, Thul S, Pawelzik SC,
Karadimou G, Artiach G, Gallina AL, Mysdotter V, Carracedo M,
Tarnawski L, Caravaca AS, et al: The resolvin D1 receptor GPR32
transduces inflammation resolution and atheroprotection. J Clin
Invest. 131(e142883)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mena HA and Spite M: Proresolving receptor
tames inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest.
131(e155240)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hao J, Feng Y, Xu X, Li L, Yang K, Dai G,
Gao W, Zhang M, Fan Y, Yin T, et al: Plasma lipid mediators
associate with clinical outcome after successful endovascular
thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Immunol.
13(917974)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kotlega D, Peda B, Drozd A, Zembron-Lacny
A, Stachowska E, Gramacki J and Szczuko M: Prostaglandin E2, 9S-,
13S-HODE and resolvin D1 are strongly associated with the
post-stroke cognitive impairment. Prostaglandins Other Lipid
Mediat. 156(106576)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A,
Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW Jr, Qureshi AI,
Rosenfield K, et al: Guidelines for the early management of
patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare
professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke
Association. Stroke. 44:870–947. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Brott T, Adams HP Jr, Olinger CP, Marler
JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, Spilker J, Holleran R, Eberle R, Hertzberg
V, et al: Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: A clinical
examination scale. Stroke. 20:864–870. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC,
Schouten HJ and van Gijn J: Interobserver agreement for the
assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke. 19:604–607.
1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Suzuki K, Matsumaru Y, Takeuchi M,
Morimoto M, Kanazawa R, Takayama Y, Kamiya Y, Shigeta K, Okubo S,
Hayakawa M, et al: Effect of mechanical thrombectomy without vs
with intravenous thrombolysis on functional outcome among patients
with acute ischemic stroke: The SKIP Randomized clinical trial.
JAMA. 325:244–253. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kain V, Ingle KA, Colas RA, Dalli J,
Prabhu SD, Serhan CN, Joshi M and Halade GV: Resolvin D1 activates
the inflammation resolving response at splenic and ventricular site
following myocardial infarction leading to improved ventricular
function. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 84:24–35. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Krashia P, Cordella A, Nobili A, La
Barbera L, Federici M, Leuti A, Campanelli F, Natale G, Marino G,
Calabrese V, et al: Blunting neuroinflammation with resolvin D1
prevents early pathology in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Nat
Commun. 10(3945)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Salas-Hernandez A, Espinoza-Perez C, Vivar
R, Espitia-Corredor J, Lillo J, Parra-Flores P, Sanchez-Ferrer CF,
Peiro C and Diaz-Araya G: Resolvin D1 and E1 promote resolution of
inflammation in rat cardiac fibroblast in vitro. Mol Biol Rep.
48:57–66. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wei C, Guo S, Liu W, Jin F, Wei B, Fan H,
Su H, Liu J, Zhang N, Fang D, et al: Resolvin D1 ameliorates
Inflammation-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption After
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in rats by Modulating A20 and NLRP3
Inflammasome. Front Pharmacol. 11(610734)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gemperle C, Tran S, Schmid M, Rimann N,
Marti-Jaun J, Hartling I, Wawrzyniak P and Hersberger M: Resolvin
D1 reduces inflammation in co-cultures of primary human macrophages
and adipocytes by triggering macrophages. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 174(102363)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Titos E, Rius B, Gonzalez-Periz A,
Lopez-Vicario C, Moran-Salvador E, Martinez-Clemente M, Arroyo V
and Claria J: Resolvin D1 and its precursor docosahexaenoic acid
promote resolution of adipose tissue inflammation by eliciting
macrophage polarization toward an M2-like phenotype. J Immunol.
187:5408–5418. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Stuckey SM, Ong LK, Collins-Praino LE and
Turner RJ: Neuroinflammation as a key driver of secondary
neurodegeneration following stroke? Int J Mol Sci.
22(13101)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Roohbakhsh A, Etemad L and Karimi G:
Resolvin D1: A key endogenous inhibitor of neuroinflammation.
Biofactors. 48:1005–1026. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bisicchia E, Sasso V, Catanzaro G, Leuti
A, Besharat ZM, Chiacchiarini M, Molinari M, Ferretti E, Viscomi MT
and Chiurchiu V: Resolvin D1 Halts Remote neuroinflammation and
improves functional recovery after focal brain damage Via ALX/FPR2
Receptor-Regulated MicroRNAs. Mol Neurobiol. 55:6894–6905.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ren YZ, Zhang BZ, Zhao XJ and Zhang ZY:
Resolvin D1 ameliorates cognitive impairment following traumatic
brain injury via protecting astrocytic mitochondria. J Neurochem.
154:530–546. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jurcau A and Simion A: Neuroinflammation
in cerebral ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injuries: From
pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci.
23(14)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chen PY, Chen GC, Hsiao CL, Hsu PJ, Yang
FY, Liu CY, Tsou A, Chang WL, Liu HH and Lin SK: Comparison of
clinical features, immune-inflammatory markers, and outcomes
between patients with acute in-hospital and out-of-hospital
ischemic stroke. J Inflamm Res. 15:881–895. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
DeLong JH, Ohashi SN, O'Connor KC and
Sansing LH: Inflammatory responses after ischemic stroke. Semin
Immunopathol. 44:625–648. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Recchiuti A: Resolvin D1 and its GPCRs in
resolution circuits of inflammation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid
Mediat. 107:64–76. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Phipps MS and Cronin CA: Management of
acute ischemic stroke. BMJ. 368(l6983)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Karayigit O, Nurkoc SG, Basyigit F and
Kiziltunc E: The role of serum resolvin D1 levels in determining
the presence and prognosis of ST-Segment elevation myocardial
infarction. Med Princ Pract. 31:548–554. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Li W, Shan H, Ma Y, Lv X and Zhu S:
Prognostic significance of serum resolvin D1 levels in patients
with acute supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage: A prospective
longitudinal cohort study. Clin Chim Acta.
547(117446)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Bazan HA, Lu Y, Jun B, Fang Z, Woods TC
and Hong S: Circulating inflammation-resolving lipid mediators RvD1
and DHA are decreased in patients with acutely symptomatic carotid
disease. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 125:43–47.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fehlberg CR and Lee JK: Fibrosis in the
central nervous system: From the meninges to the vasculature. Cell
Tissue Res. 387:351–360. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|