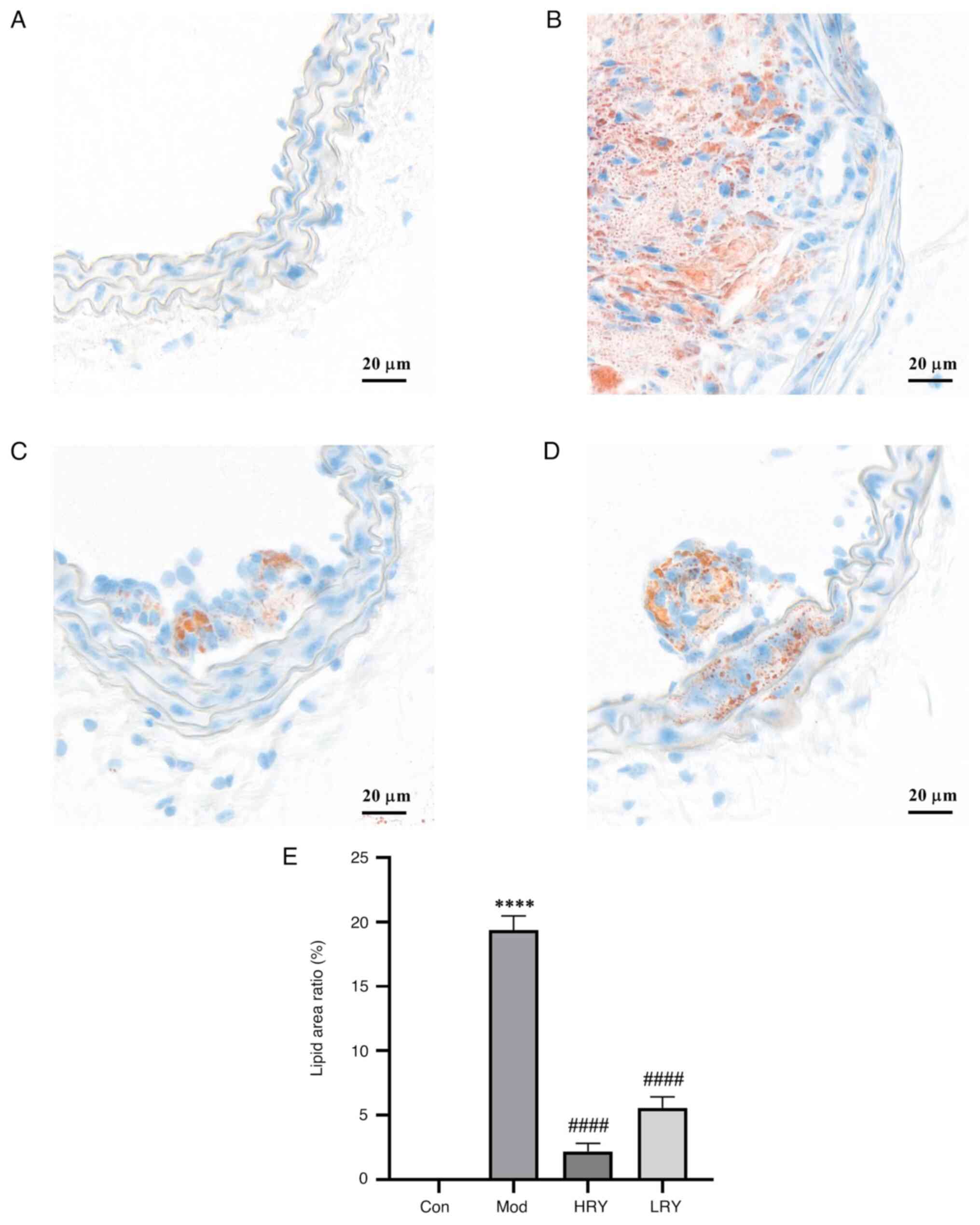
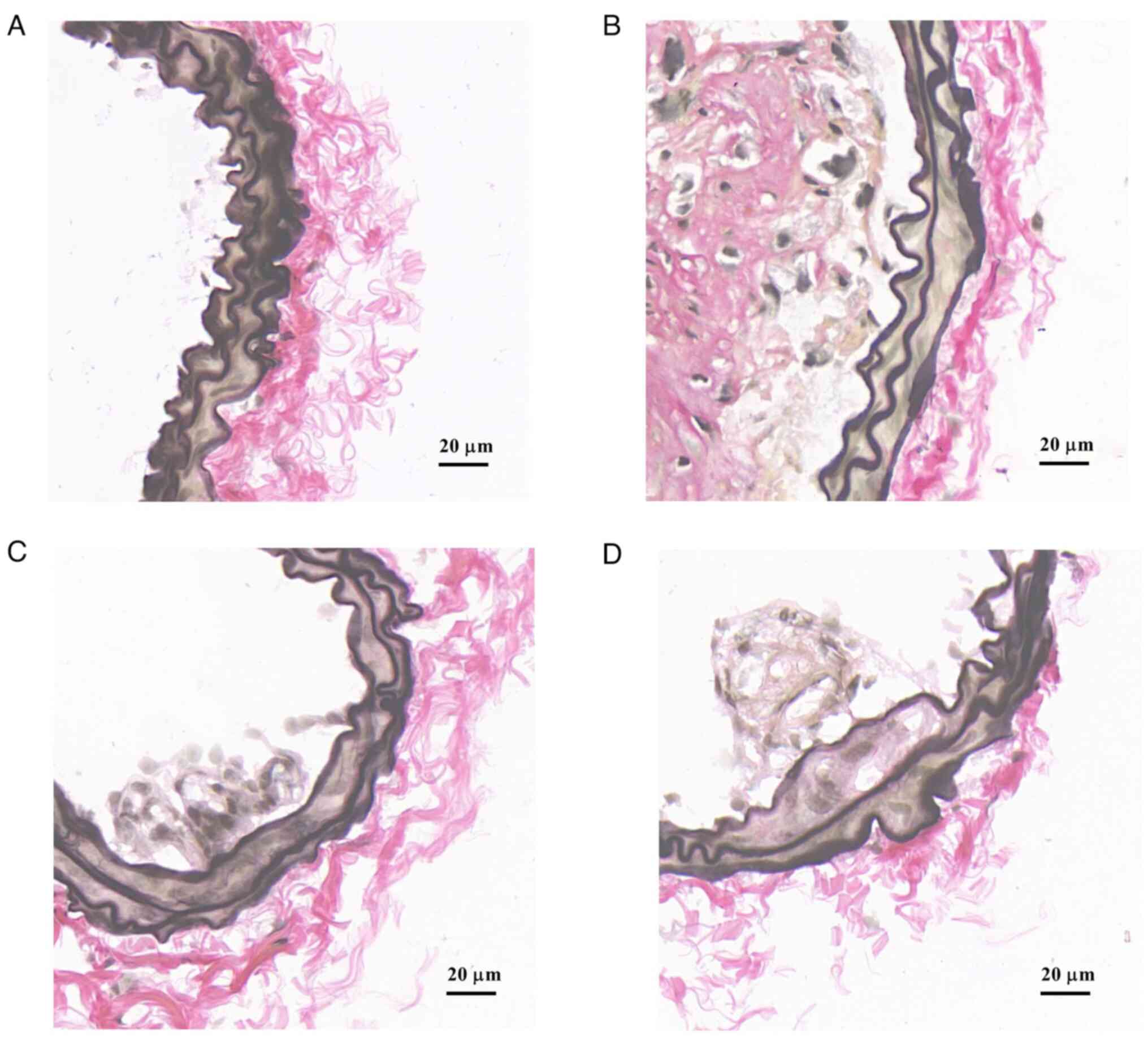
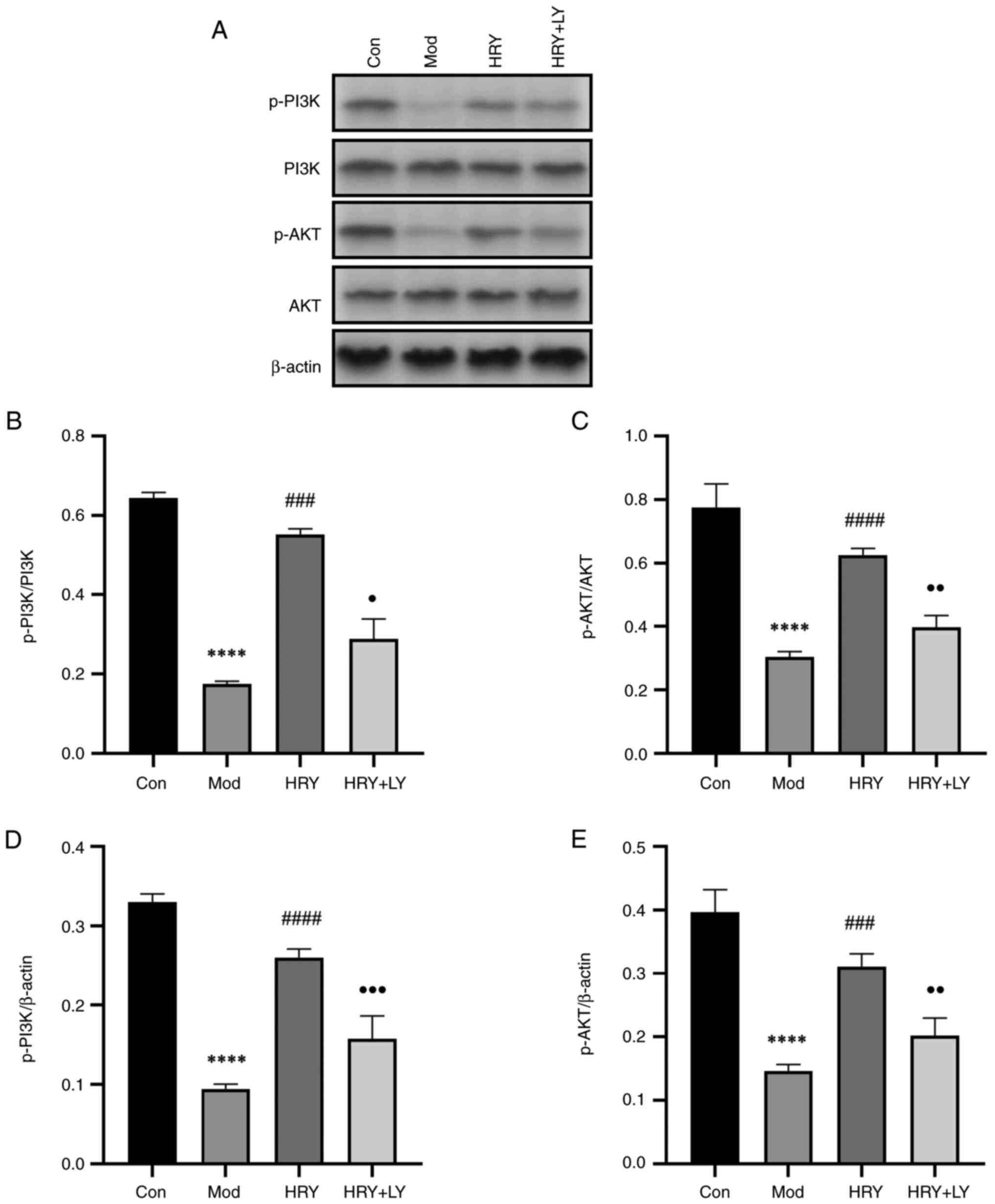
|
1
|
Chen J, Zhang X, Millican R, Sherwood J,
Martin S, Jo H, Yoon YS, Brott BC and Jun HW: Recent advances in
nanomaterials for therapy and diagnosis for atherosclerosis. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 170:142–199. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Legein B, Temmerman L, Biessen EA and
Lutgens E: Inflammation and immune system interactions in
atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:3847–3869. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Geovanini GR and Libby P: Atherosclerosis
and inflammation: Overview and updates. Clin Sci (Lond).
132:1243–1252. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Usai MV, Bosiers MJ, Bisdas T, Torsello G,
Beropoulis E, Kasprzak B, Stachmann A and Stavroulakis K: Surgical
versus endovascular revascularization of subclavian artery
arteriosclerotic disease. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 61:53–59.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sun Y, Gao Y, Zhou L, Lu Y, Zong Y, Zhu H,
Tang Y, Zheng F, Sun Y and Li Y: A multi-target protective effect
of Danggui-Shaoyao-San on the vascular endothelium of
atherosclerotic mice. BMC Complement Med Ther.
23(60)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Williams IL, Wheatcroft SB, Shah AM and
Kearney MT: Obesity, atherosclerosis and the vascular endothelium:
Mechanisms of reduced nitric oxide bioavailability in obese humans.
Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 26:754–764. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xing SS, Yang XY, Zheng T, Li WJ, Wu D,
Chi JY, Bian F, Bai XL, Wu GJ, Zhang YZ, et al: Salidroside
improves endothelial function and alleviates atherosclerosis by
activating a mitochondria-related AMPK/PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway.
Vascul Pharmacol. 72:141–152. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang R, Miao Y, Chen L, Yi S and Tan N:
De Novo transcriptome analysis reveals putative genes involved in
anthraquinone biosynthesis in Rubia yunnanensis. Genes (Basel).
13(521)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yi S, Lin Q, Zhang X, Wang J, Miao Y and
Tan N: Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for
quantitative RT-PCR analysis in Rubia yunnanensis diels based on
transcriptome data. Biomed Res Int. 2020(5824841)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Larmann J, Jurk K, Janssen H, Müller M,
Herzog C, Lorenz A, Schmitz M, Nofer JR and Theilmeier G: Hepatic
overexpression of soluble urokinase receptor (uPAR) suppresses
diet-induced atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein
receptor-deficient (LDLR-/-) mice. PLoS One.
10(e0131854)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu S, Liu Y, Liu Z, Hu Y and Jiang M: A
review of the signaling pathways of aerobic and anaerobic exercise
on atherosclerosis. J Cell Physiol. 238:866–879. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhou ZX, Ren Z, Yan BJ, Qu SL, Tang ZH,
Wei DH, Liu LS, Fu MG and Jiang ZS: The role of ubiquitin E3 ligase
in atherosclerosis. Curr Med Chem. 28:152–168. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kolovou G, Anagnostopoulou K, Mikhailidis
DP and Cokkinos DV: Apolipoprotein E knockout models. Curr Pharm
Des. 14:338–351. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nakashima Y, Plump AS, Raines EW, Breslow
JL and Ross R: ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of
atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb.
14:133–140. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gao Y, Su Y, Huo Y, Mi J, Wang X, Wang Z,
Liu Y and Zhang H: Identification of antihyperlipidemic
constituents from the roots of Rubia yunnanensis Diels. J
Ethnopharmacol. 55:1315–1321. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liou MJ and Wu TS: Triterpenoids from
Rubia yunnanensis. J Nat Prod. 65:1283–1287. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ren H, Wang X, Gao L, Niu L and Li J:
Characteristic spectrum and quantitative study of the index
components of the Yi medicine Rubia yunnanensis. Chin Med Mater.
45:1400–1404. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Yang R, Powell-Braxton L, Ogaoawara AK,
Dybdal N, Bunting S, Ohneda O and Jin H: Hypertension and
endothelial dysfunction in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:2762–2768. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nader MA, el-Agamy DS and Suddek GM:
Protective effects of propolis and thymoquinone on development of
atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arch Pharm Res.
33:637–643. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Calan M, Calan O, Gonen MS, Bilgir F,
Kebapcilar L, Kulac E, Cinali T and Bilgir O: Examination of
adhesion molecules, homocysteine and hs-CRP in patients with
polygenic hypercholesterolemia and isolated hypertriglyceridemia.
Intern Med. 50:1529–1535. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Meyer-Lindemann U, Mauersberger C, Schmidt
AC, Moggio A, Hinterdobler J, Li X, Khangholi D, Hettwer J, Gräßer
C, Dutsch A, et al: Colchicine Impacts leukocyte trafficking in
atherosclerosis and reduces vascular inflammation. Front Immunol.
13(898690)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Massberg S, Brand K, Gruner S, Page S,
Müller E, Müller I, Bergmeier W, Richter T, Lorenz M, Konrad I, et
al: A critical role of platelet adhesion in the initiation of
atherosclerotic lesion formation. J Exp Med. 196:887–896.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vega GL and Grundy SM:
Hypercholesterolemia with cholesterol-enriched LDL and normal
levels of LDL-apolipoprotein B. Effects of the step I diet and bile
acid sequestrants on the cholesterol content of LDL. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 16:517–522. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Badimon L, Vilahur G and Padro T:
Lipoproteins, platelets and atherothrombosis. Rev Esp Cardiol.
62:1161–1178. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
27
|
Calabresi L, Gomaraschi M, Simonelli S,
Bernini F and Franceschini G: HDL and atherosclerosis: Insights
from inherited HDL disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1851:13–18.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and Garcia-Cardena G:
Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Aird WC: Endothelium as an organ system.
Crit Care Med. 32 (5 Suppl):S271–S279. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Corre I, Paris F and Huot J: The p38
pathway, a major pleiotropic cascade that transduces stress and
metastatic signals in endothelial cells. Oncotarget. 8:55684–55714.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rafieian-Kopaei M, Setorki M, Doudi M,
Baradaran A and Nasri H: Atherosclerosis: Process, indicators, risk
factors and new hopes. Int J Prev Med. 5:927–946. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poznyak A, Grechko AV, Poggio P,
Myasoedova VA, Alfieri V and Orekhov AN: The diabetes
mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: The role of lipid and glucose
metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci.
21(1835)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Marchio P, Guerra-Ojeda S, Vila JM,
Aldasoro M, Victor VM and Mauricio MD: targeting early
atherosclerosis: A focus on oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2019(8563845)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Xu Q, Shi M, Gan P, Huang Q, Wang A,
Tan G, Fang Y and Liao H: Low-level laser therapy induces human
umbilical vascular endothelial cell proliferation, migration and
tube formation through activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Microvasc Res. 129(103959)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Qin L, Liu X and Meng X: CTRP3
Alleviates Ox-LDL-Induced inflammatory response and endothelial
dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cells by activating the
PI3K/Akt/eNOS Pathway. Inflammation. 42:1350–1359. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhou YJ, Xu N, Zhang XC, Zhu YY, Liu SW
and Chang YN: Chrysin improves glucose and lipid metabolism
disorders by regulating the AMPK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in
insulin-resistant HepG2 cells and HFD/STZ-Induced C57BL/6J mice. J
Agric Food Chem. 69:5618–5627. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Manning BD and Toker A: AKT/PKB signaling:
Navigating the network. Cell. 169:381–405. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Li N, Cui HH, Tian XQ, Jin C, Chen
GH and Yang YJ: Tongxinluo exerts protective effects via
anti-apoptotic and pro-autophagic mechanisms by activating AMPK
pathway in infarcted rat hearts. Exp Physiol. 102:422–435.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jing R, Zhong QQ, Long TY, Pan W and Qian
ZX: Downregulated miRNA-26a-5p induces the apoptosis of endothelial
cells in coronary heart disease by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:4940–4947. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu J, Xu P, Liu D, Wang R, Cui S, Zhang
Q, Li Y, Yang W and Zhang D: TCM Regulates PI3K/Akt signal pathway
to intervene atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2021(4854755)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Luo L, Liang H and Liu L: Myristicin
regulates proliferation and apoptosis in oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-stimulated human vascular smooth muscle cells and human
umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB
signalling pathway. Pharm Biol. 60:56–64. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Guo J, Jie W, Shen Z, Li M, Lan Y, Kong Y,
Guo S, Li T and Zheng S: SCF increases cardiac stem cell migration
through PI3K/AKT and MMP-2/-9 signaling. Int J Mol Med. 34:112–118.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|