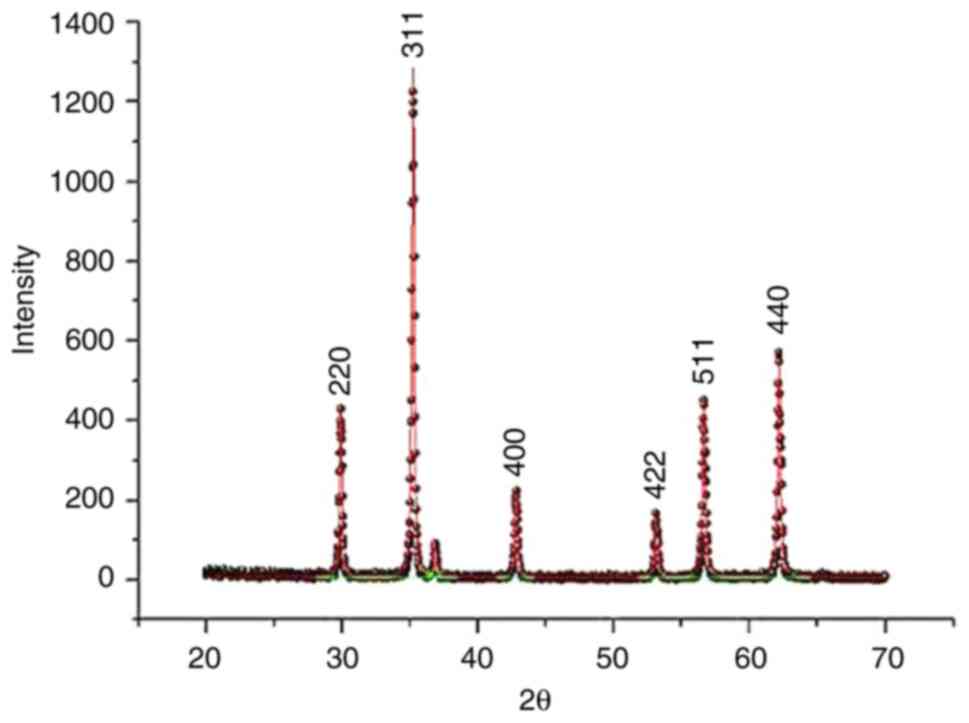
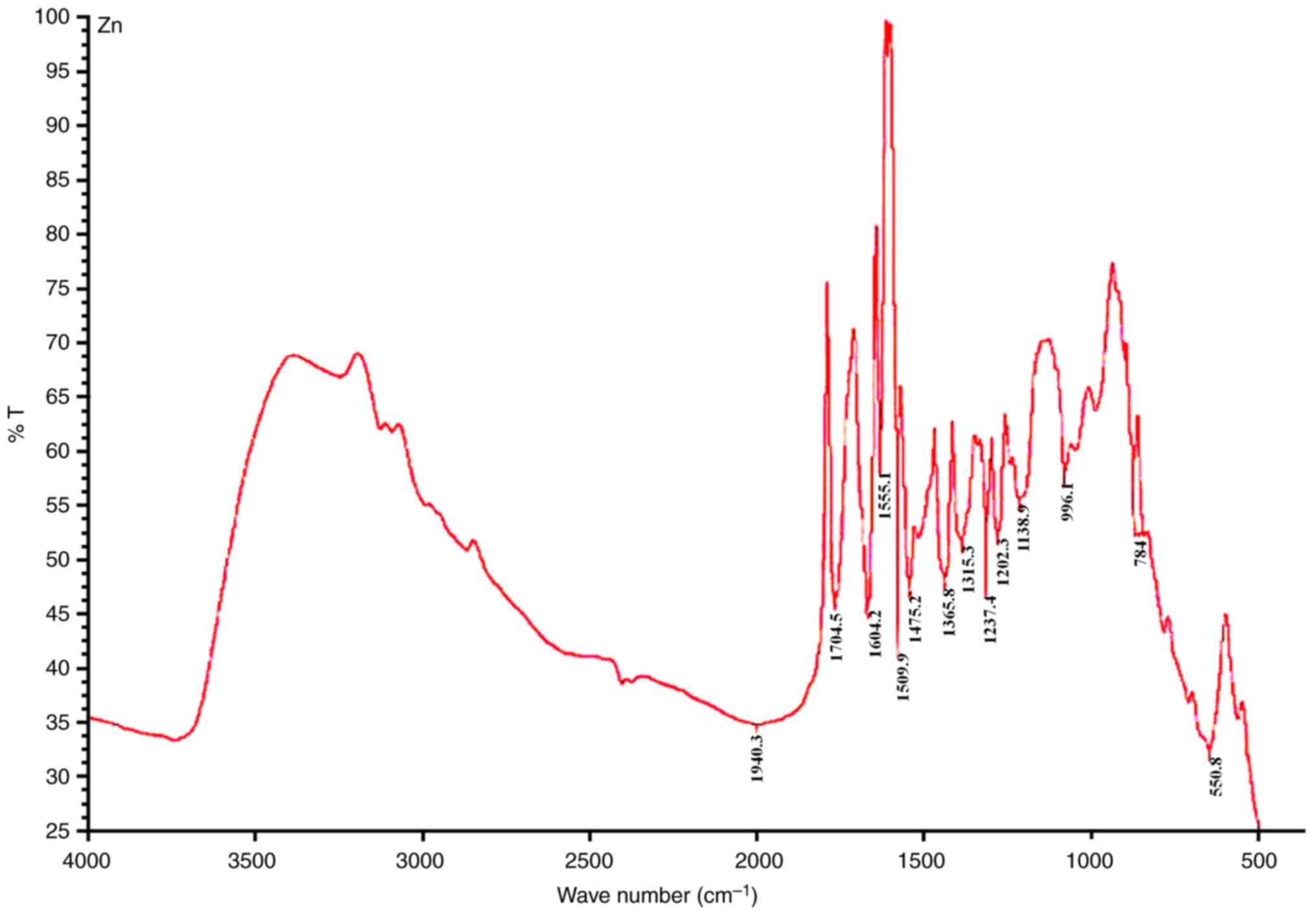
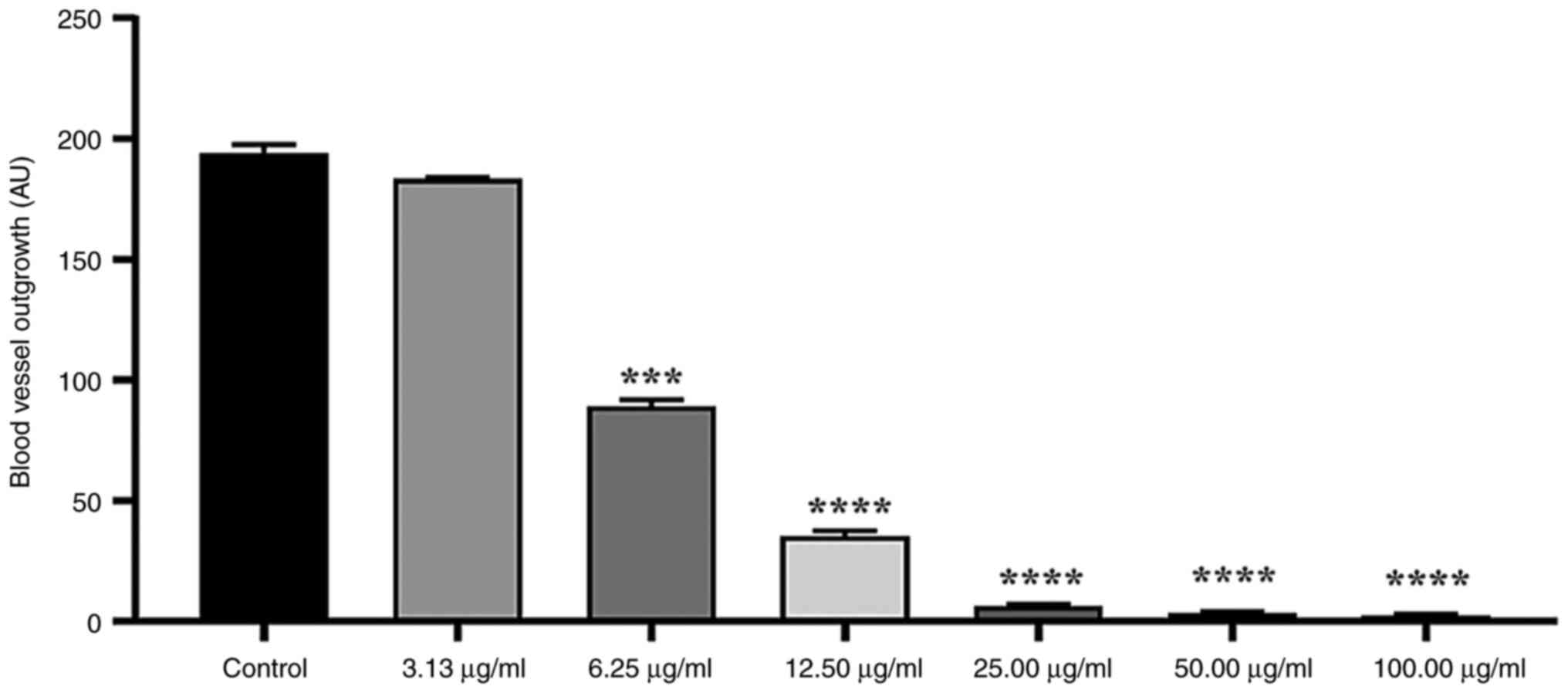
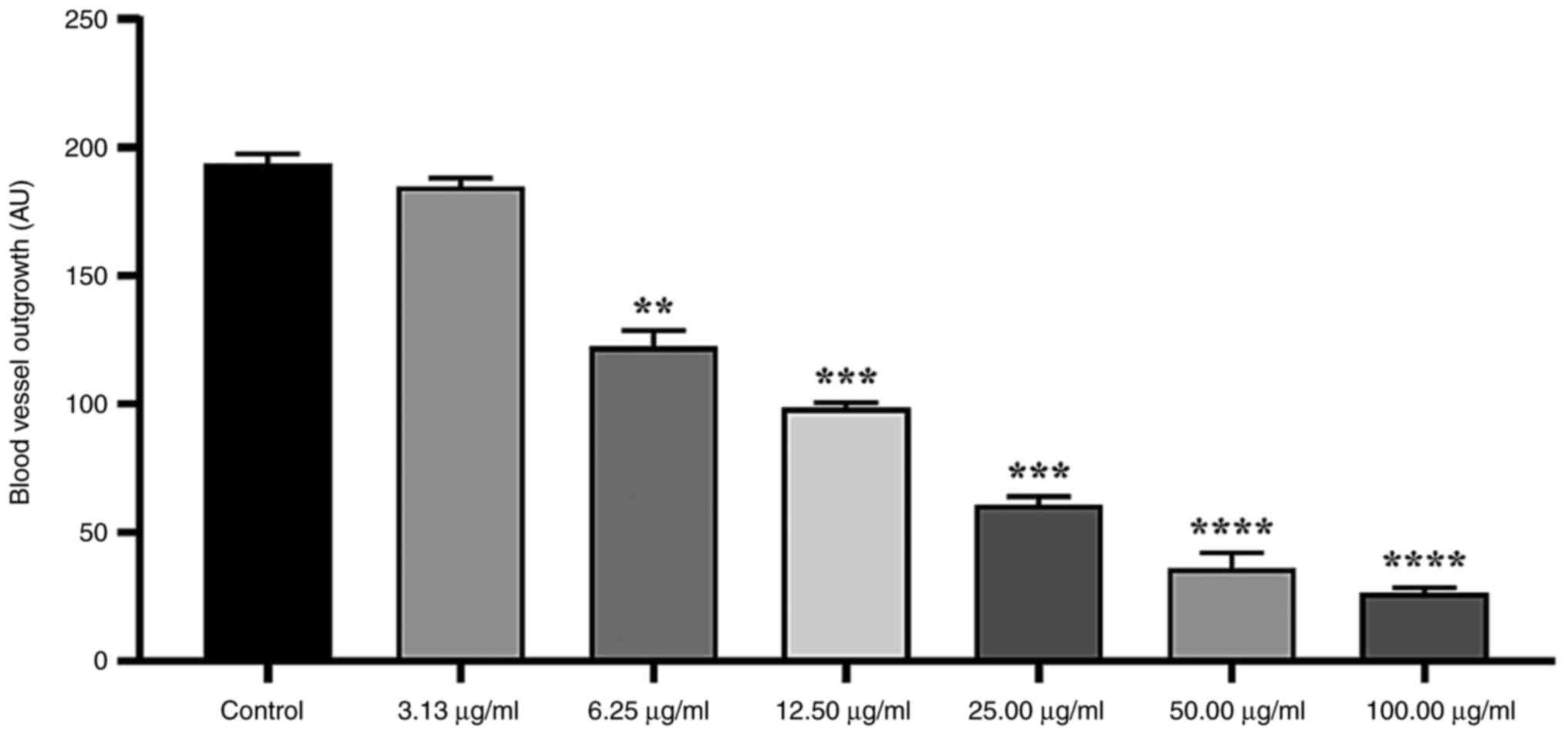
|
1
|
Rao MD and Gautam P: Synthesis and
characterization of ZnO nanoflowers using Chlamydomonas
reinhardtii: A green approach. Environmental Progress &
Sustainable Energy. 35:1020–1026. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Khan S, Mansoor S, Rafi Z, Kumari B,
Shoaib A, Saeed M, Alshehri S, Ghoneim MM, Rahamathulla M, Hani U
and Shakeel F: A review on nanotechnology: Properties,
applications, and mechanistic insights of cellular uptake
mechanisms. J Mol Liquids. 348(118008)2022.
|
|
3
|
Sogno I, Venè R, Ferrari N, De Censi A,
Imperatori A, Noonan DM, Tosetti F and Albini A: Angioprevention
with fenretinide: Targeting angiogenesis in prevention and
therapeutic strategies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 75:2–14.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mohammad GRKS, Tabrizi MH, Ardalan T,
Yadamani S and Safavi E: Green synthesis of zinc oxide
nanoparticles and evaluation of anti-angiogenesis,
anti-inflammatory and cytotoxicity properties. J Biosci.
44(30)2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adeola FO: Global impact of chemicals and
toxic substances on human health and the environment. Handbook of
Global Health, 2020: p. 1-30.
|
|
6
|
Vimalraj S, Ashokkumar T and Saravanan S:
Biogenic gold nanoparticles synthesis mediated by Mangifera indica
seed aqueous extracts exhibits antibacterial, anticancer and
anti-angiogenic properties. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:440–448.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Imade EE, Ajiboye TO, Fadiji AE, Onwudiwe
DC and Babalola OO: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles
using plantain peel extracts and the evaluation of their
antibacterial activity. Sci African. 16(e01152)2022.
|
|
8
|
Mohammadian M, Es'haghi Z and Hooshmand S:
Green and chemical synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and size
evaluation by UV-vis spectroscopy. J Nanomed Res. 7(00175)2018.
|
|
9
|
Sukhanova A, Bozrova S, Sokolov P,
Berestovoy M, Karaulov A and Nabiev I: Dependence of nanoparticle
toxicity on their physical and chemical properties. Nanoscale Res
Lett. 13(44)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Folkman J: Role of angiogenesis in tumor
growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 29 (6 Suppl 16):S15–S18.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lacerda JZ, Ferreira LC, Lopes BC,
Aristizábal-Pachón AF, Bajgelman MC, Borin TF and Zuccari DAPC:
Therapeutic potential of melatonin in the regulation of MiR-148a-3p
and angiogenic factors in breast cancer. Microrna. 8:237–247.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Melincovici CS, Boşca AB, Şuşman S,
Mărginean M, Mihu C, Istrate M, Moldovan IM, Roman AL and Mihu CM:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-key factor in normal and
pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 59:455–467.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tahvilian R, Zangeneh MM, Falahi H,
Sadrjavadi K, Jalalvand AR and Zangeneh A: Green synthesis and
chemical characterization of copper nanoparticles using Allium
saralicum leaves and assessment of their cytotoxicity, antioxidant,
antimicrobial, and cutaneous wound healing properties. Applied
Organometallic chemistry. 33(e5234)2019.
|
|
14
|
Shadmehri AA, Namvar F, Miri H, Yaghmaei P
and Moghaddam MN: Anti-Angiogenesis effect of graphene-loaded green
synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles on chick chorioalantoic
membrane. J Biotechem Tec. 17-22:2018.
|
|
15
|
Cui L, Liang J, Liu H, Zhang K and Li J:
Nanomaterials for angiogenesis in skin tissue engineering. Tissue
Eng Part B Rev. 26:203–216. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ahtzaz S, Nasir M, Shahzadi L, Amir W,
Anjum A, Iqbal F, Chaudhry AA, Yar M and ur Rehman I: A study on
the effect of zinc oxide and zinc peroxide nanoparticles to enhance
angiogenesis-pro-angiogenic grafts for tissue regeneration
applications. Materials & Design. 132:409–418. 2017.
|
|
17
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: Natural
products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981-2002. J Nat
Prod. 66:1022–1037. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
El-Shafey ES and Elsherbiny ES: The role
of apoptosis and autophagy in the insulin-enhancing activity of
oxovanadium (IV) bipyridine complex in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic mice. Biometals. 33:123–135. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
El Seedy GM, El-Shafey ES and Elsherbiny
ES: Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) fortified with Camellia sinensis
mediates apoptosis, Notch-1 signaling, and mitigates
obesity-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver. J Food Biochem: Jul 9,
2021 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
20
|
Sahan Y, Dundar AN, Aydin E, Kilci A,
Dulger D, Kaplan FB, Gocmen D and Celik G: Characteristics of
cookies supplemented with oleaster (Elaeagnus angustifolia L.)
Flour. I physicochemical, sensorial and textural properties.
Journal of Agricultural Science, 2013. 5: 160, 2013.
|
|
21
|
Ogunyemi SO, Abdallah Y, Zhang M, Fouad H,
Hong X, Ibrahim E, Masum MMI, Hossain A, Mo J and Li B: Green
synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using different plant
extracts and their antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas
oryzae pv. oryzae. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:341–352.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Choi HS, Ashitate Y, Lee JH, Kim SH,
Matsui A, Insin N, Bawendi MG, Semmler-Behnke M, Frangioni JV and
Tsuda A: Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung
airspaces to the body. Nat Biotechnol. 28:1300–1303.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gürbüz I, Ustün O, Yesilada E, Sezik E and
Kutsal O: Anti-ulcerogenic activity of some plants used as folk
remedy in Turkey. J Ethnopharmacol. 88:93–97. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chakraborty AJ, Mitra S, Tallei TE, Tareq
AM, Nainu F, Cicia D, Dhama K, Emran TB, Simal-Gandara J and
Capasso R: Bromelain a potential bioactive compound: A
comprehensive overview from a pharmacological perspective. Life
(Basel). 11(317)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yanez M, Blanchette J and Jabbarzadeh E:
Modulation of inflammatory response to implanted biomaterials using
natural compounds. Curr Pharm Des. 23:6347–6357. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Guo T, Li JY, Zhou SZ, Zhao P and
Fan MT: Four flavonoid glycosides from the pulps of Elaeagnus
angustifolia and their antioxidant activities. Adv Mater Res.
756-759:16–20. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Ahmadiani A, Hosseiny J, Semnanian S,
Javan M, Saeedi F, Kamalinejad M and Saremi S: Antinociceptive and
anti-inflammatory effects of Elaeagnus angustifolia fruit extract.
J Ethnopharmacol. 72:287–292. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mohammed FI, Al-Essa MK, Shafagoj YA and
Afifi FU: Investigation of the direct effects of the alcoholic
extract of Elaeagnus angustifolia L.(Elaeagnaceae) on dispersed
intestinal smooth muscle cells of guinea pig. Sci Pharm. 74:21–30.
2006.
|
|
29
|
Imraish A, Abu Thiab T, Al-Awaida W,
Al-Ameer HJ, Bustanji Y, Hammad H, Alsharif M and Al-Hunaiti A: In
vitro anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of
ZnFe2O4 and CrFe2O4
nanoparticles synthesized using Boswellia carteri resin. J Food
Biochem. 45(e13730)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Scherbakov AM, Vorontsova SK, Khamidullina
AI, Mrdjanovic J, Andreeva OE, Bogdanov FB, Salnikova DI, Jurisic
V, Zavarzin IV and Shirinian VZ: Novel pentacyclic derivatives and
benzylidenes of the progesterone series cause anti-estrogenic and
antiproliferative effects and induce apoptosis in breast cancer
cells. Invest New Drugs. 41:142–152. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jurisic V: Multiomic analysis of cytokines
in immuno-oncology. Expert Rev Proteomics. 17:663–674.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sanaeimehr Z, Javadi I and Namvar F:
Antiangiogenic and antiapoptotic effects of green-synthesized zinc
oxide nanoparticles using Sargassum muticum algae extraction.
Cancer Nanotechnol. 9(3)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Abdalla AME, Xiao L, Ullah MW, Yu M,
Ouyang C and Yang G: Current challenges of cancer anti-angiogenic
therapy and the promise of nanotherapeutics. Theranostics.
8:533–548. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kumar B, Smita K, Cumbal L and Debut A:
Green approach for fabrication and applications of zinc oxide
nanoparticles. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2014(523869)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tada-Oikawa S, Ichihara G, Suzuki Y,
Izuoka K, Wu W, Yamada Y, Mishima T and Ichihara S: Zn (II)
released from zinc oxide nano/micro particles suppresses
vasculogenesis in human endothelial colony-forming cells. Toxicol
Rep. 2:692–701. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|