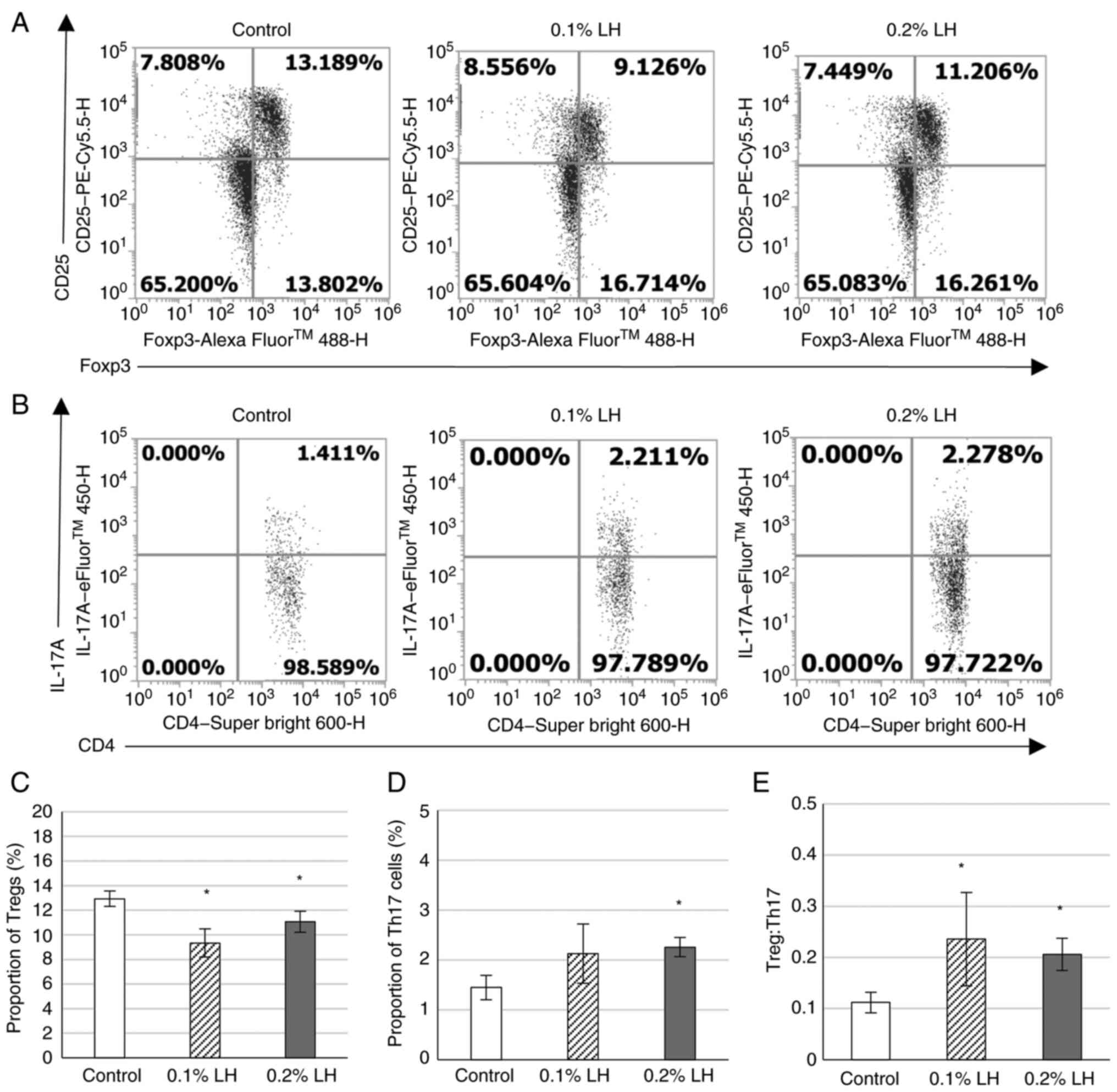
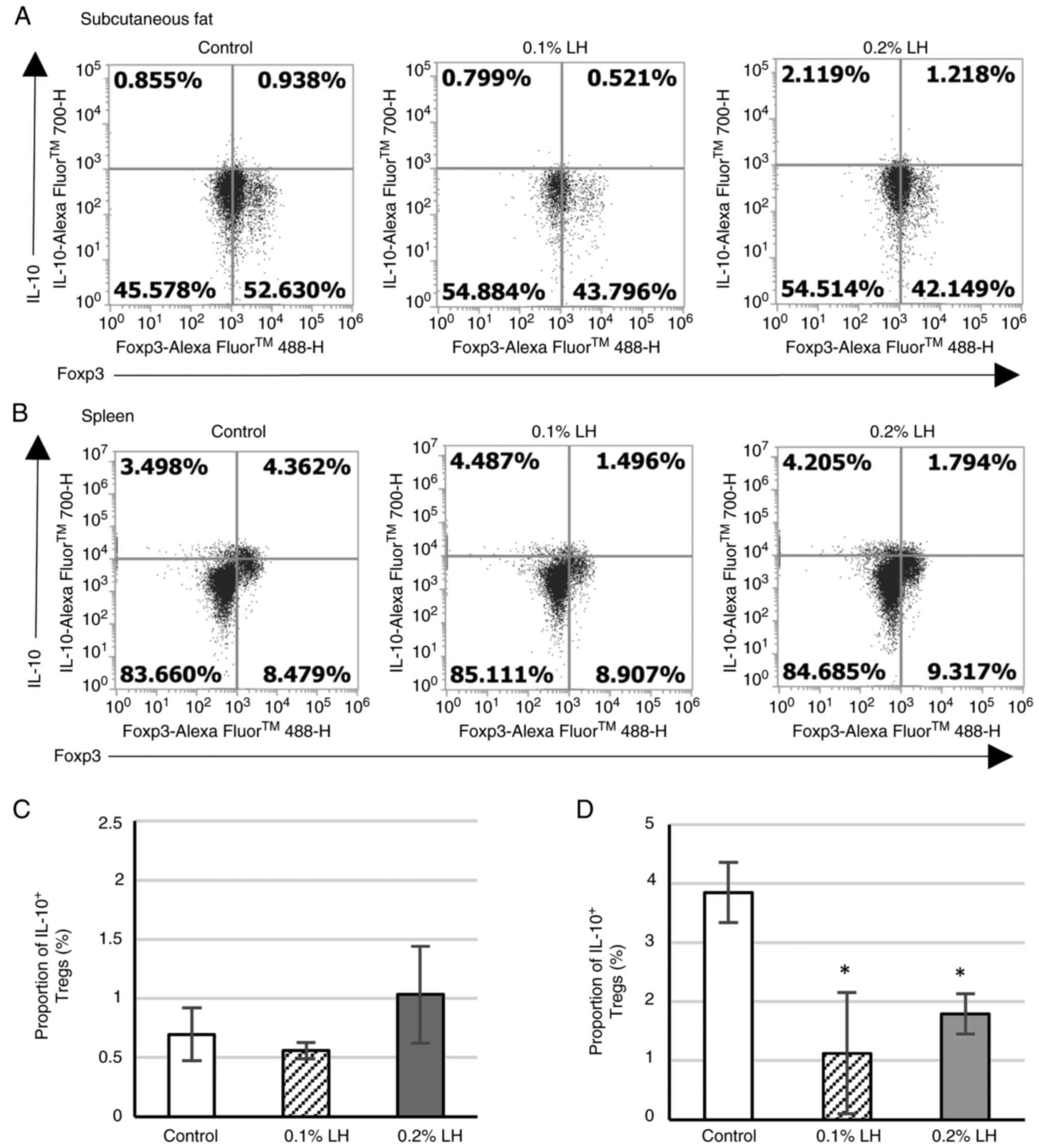
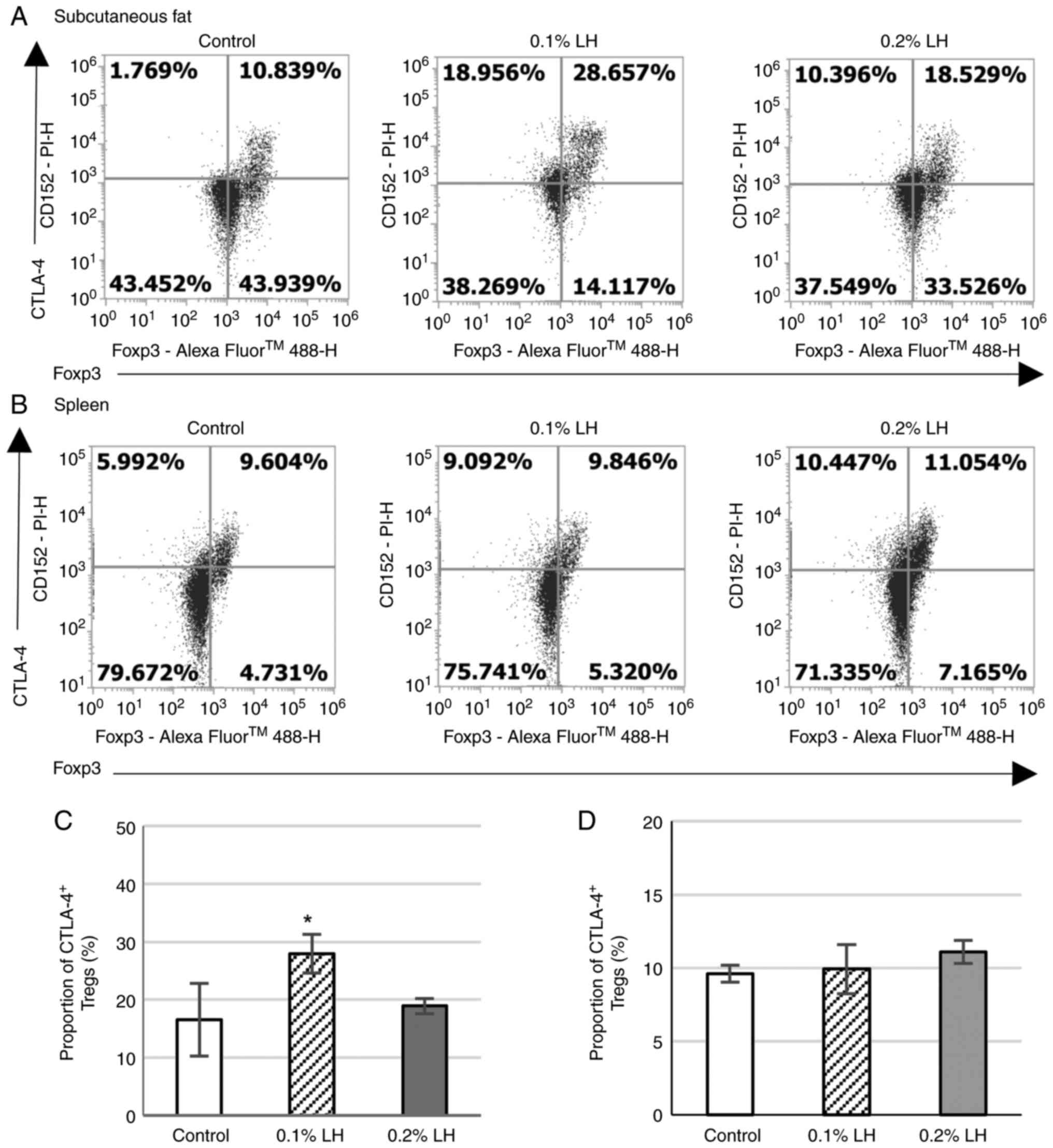
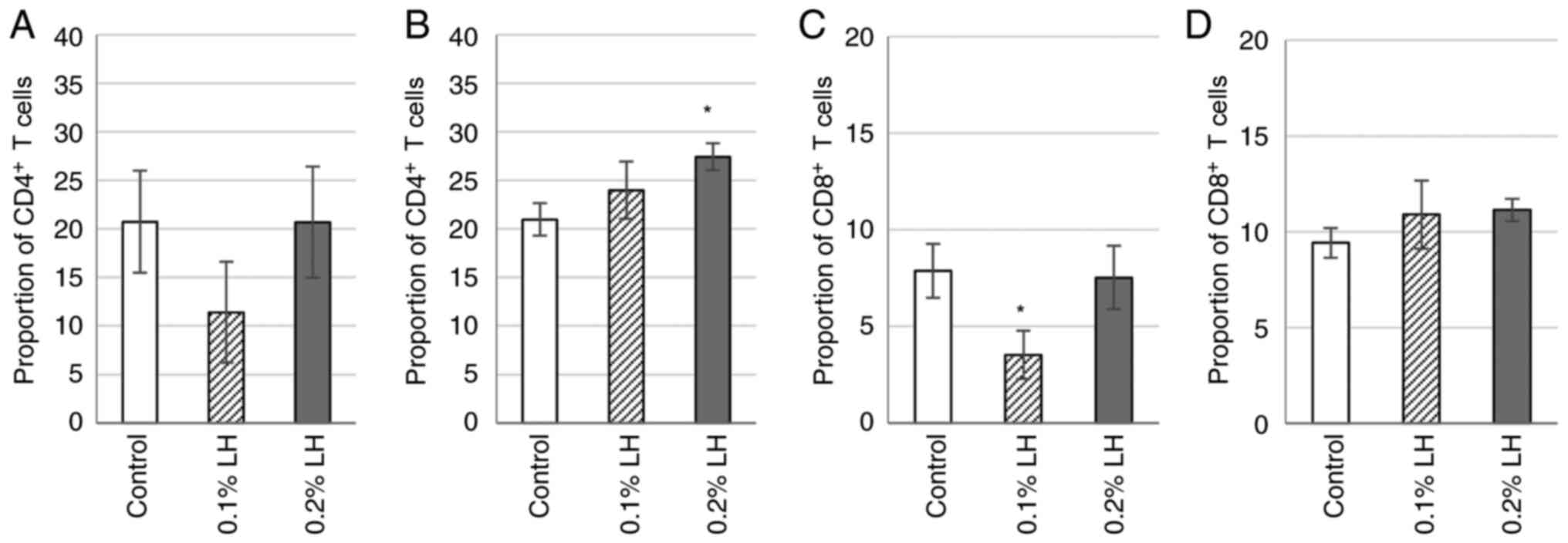
|
1
|
Surmi BK and Hasty AH: Macrophage
infiltration into adipose tissue: Initiation, propagation and
remodeling. Future Lipidol. 3:545–556. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Olefsky JM and Glass CK: Macrophages,
inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:219–246.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shimobayashi M, Albert V, Woelnerhanssen
B, Frei IC, Weissenberger D, Meyer-Gerspach AC, Clement N, Moes S,
Colombi M, Meier JA, et al: Insulin resistance causes inflammation
in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 128:1538–1550. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL and Saltiel AR:
Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage
polarization. J Clin Invest. 117:175–184. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jiang C, Ting AT and Seed B: PPAR-gamma
agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines.
Nature. 391:82–86. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fooks AN, Beppu LY, Frias AB and D'Cruz
LM: Adipose tissue regulatory T cells: Differentiation and
function. Int Rev Immunol. 42:323–333. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shen N, Wang T, Gan Q, Liu S, Wang L and
Jin B: Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution,
biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem.
383(132531)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yuan D, Guo Y, Pu F, Yang C, Xiao X, Du H,
He J and Lu S: Opportunities and challenges in enhancing the
bioavailability and bioactivity of dietary flavonoids: A novel
delivery system perspective. Food Chem. 430(137115)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mukai R, Fujikura Y, Murota K, Uehara M,
Minekawa S, Matsui N, Kawamura T, Nemoto H and Terao J: Prenylation
enhances quercetin uptake and reduces efflux in Caco-2 cells and
enhances tissue accumulation in mice fed long-term. J Nutr.
143:1558–1564. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
American Veterinary Medical Association
(AVMA): AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2020
edition. American Veterinary Medical Association, Schaumburg, IL,
2020.
|
|
11
|
Lee SJ, Hossaine MDA and Park SC: A
potential anti-inflammation activity and depigmentation effect of
Lespedeza bicolor extract and its fractions. Saudi J Biol
Sci. 23:9–14. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mariadoss AVA, Park S, Saravanakumar K,
Sathiyaseelan A and Wang MH: Phytochemical profiling, in vitro
antioxidants, and antidiabetic efficacy of ethyl acetate fraction
of Lespedeza cuneata on streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 30:60976–60993. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim NK, Park HM, Lee J, Ku KM and Lee CH:
Seasonal Variations of metabolome and tyrosinase inhibitory
activity of Lespedeza maximowiczii during growth periods. J
Agric Food Chem. 63:8631–8639. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bae J, Lee D, Lee TK, Song JH, Lee JS, Lee
S, Yoo SW, Kang KS, Moon E, Lee S and Kim KH:
(-)-9'-O-(α-l-Rhamnopyranosyl)lyoniresinol from Lespedeza
cuneata suppresses ovarian cancer cell proliferation through
induction of apoptosis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 28:122–128.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee JH, Parveen A, Do MH, Lim Y, Shim SH
and Kim SY: Lespedeza cuneata protects the endothelial
dysfunction via eNOS phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
in HUVECs. Phytomedicine. 48:1–9. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Konno T, Sasaki K, Kobayashi K and Murata
T: Indirubin promotes adipocyte differentiation and reduces lipid
accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells via peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor γ activation. Mol Med Rep. 21:1552–1560. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Blois MS: Antioxidant determinations by
the use of a stable free radical. Nature. 181:1199–1200. 1958.
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi K, Tang YT and Sasaki K:
Paeoniflorin, a constituent of Kami-shoyo-san, suppresses blood
glucose levels in postmenopausal diabetic mice by promoting the
secretion of estradiol from adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Rep.
32(101335)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Daynes RA and Jones DC: Emerging roles of
PPARS in inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:748–759.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hardwick JP, Osei-Hyiaman D, Wiland H,
Abdelmegeed MA and Song BJ: PPAR/RXR regulation of fatty acid
metabolism and fatty acid omega-hydroxylase (CYP4) isozymes:
Implications for prevention of lipotoxicity in fatty liver disease.
PPAR Res. 2009(952734)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Andrade ML, Gilio GR, Perandini LA,
Peixoto AS, Moreno MF, Castro É, Oliveira TE, Vieira TS,
Ortiz-Silva M, Thomazelli CA, et al: PPARγ-induced upregulation of
subcutaneous fat adiponectin secretion, glyceroneogenesis and BCAA
oxidation requires mTORC1 activity. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell
Biol Lipids. 1866(158967)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wu Z, Xie Y, Morrison RF, Bucher NL and
Farmer SR: PPARgamma induces the insulin-dependent glucose
transporter GLUT4 in the absence of C/EBPalpha during the
conversion of 3T3 fibroblasts into adipocytes. J Clin Invest.
101:22–32. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Way JM, Harrington WW, Kathleen KB,
Gottschalk WK, Sundseth SS, Mansfield TA, Ramachandran RK, Willson
TM and Kliewer SA: Comprehensive messenger ribonucleic acid
profiling reveals that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma activation has coordinate effects on gene expression in
multiple insulin-sensitive tissues. Endocrinology. 142:1269–1277.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gilleron J, Bouget G, Ivanov S, Meziat C,
Ceppo F, Vergoni B, Djedaini M, Soprani A, Dumas K, Jacquel A, et
al: Rab4b deficiency in T cells promotes adipose Treg/Th17
imbalance, adipose tissue dysfunction, and insulin resistance. Cell
Rep. 25:3329–3341.e5. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Oliveira-Marques V, Marinho HS, Cyrne L
and Antunes F: Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by
H2O2: A major role for a simple chemical
process in a complex biological response. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:2043–2053. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sun C, Mao S, Chen S, Zhang W and Liu C:
PPARs-orchestrated metabolic homeostasis in the adipose tissue. Int
J Mol Sci. 22(8974)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shinohara S and Fujimori K: Promotion of
lipogenesis by PPARγ-activated FXR expression in adipocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 527:49–55. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bogacka I, Ukropcova B, McNeil M, Gimble
JM and Smith SR: Structural and functional consequences of
mitochondrial biogenesis in human adipocytes in vitro. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 90:6650–6656. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Ferrari SM, Colaci
M, Ruffilli I, Sebastiani M and Fallahi P: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ agonists reduce cell
proliferation and viability and increase apoptosis in systemic
sclerosis fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol. 168:129–135. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP
and Malik AB: Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue
injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1126–1167. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yu D, Liu JQ, Mo LH, Luo XQ, Liu ZQ, Wu
GH, Yang LT, Liu DB, Wang S, Liu ZG and Yang PC: Specific
antigen-guiding exosomes inhibit food allergies by inducing
regulatory T cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 98:639–649. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Martin H: Role of PPAR-gamma in
inflammation. Prospects for therapeutic intervention by food
components. Mutat Res. 690:57–63. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Katafuchi T, Holland WL, Kollipara RK,
Kittler R, Mangelsdorf DJ and Kliewer SA: PPARγ-K107 SUMOylation
regulates insulin sensitivity but not adiposity in mice. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 115:12102–12111. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wiedemann SJ, Trimigliozzi K, Dror E,
Meier DT, Molina-Tijeras JA, Rachid L, Foll CL, Magnan C, Schulze
F, Stawiski M, et al: The cephalic phase of insulin release is
modulated by IL-1β. Cell Metab. 34:991–1003,e6. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cawthorn WP and Sethi JK: TNF-alpha and
adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett. 582:117–131. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Smith U and Kahn BB: Adipose tissue
regulates insulin sensitivity: Role of adipogenesis, de novo
lipogenesis and novel lipids. J Inter Med. 280:465–475.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest.
112:1796–1808. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Carey AL, Steinberg GR, Macaulay SL,
Thomas WG, Holmes AG, Ramm G, Prelovsek O, Hohnen-Behrens C, Watt
MJ, James DE, et al: Interleukin-6 increases insulin-stimulated
glucose disposal in humans and glucose uptake and fatty acid
oxidation in vitro via AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes.
55:2688–2697. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW and
Hotamisligil GS: Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance
in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature. 389:610–614.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lumeng CN, Maillard I and Saltiel AR:
T-ing up inflammation in fat. Nat Med. 15:846–847. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen LW, Chen PH, Tang CH and Yen JH:
Adipose-derived stromal cells reverse insulin resistance through
inhibition of M1 expression in a type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse
model. Stem Cell Re Ther. 13(357)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fujii M, Inoguchi T, Batchuluun B,
Sugiyama N, Kobayashi K, Sonoda N and Takayanagi R: CTLA-4Ig
immunotherapy of obesity-induced insulin resistance by manipulation
of macrophage polarization in adipose tissues. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 438:103–109. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K,
Yamashita H, Ohsugi M, Otsu M, Hara K, Ueki K, Sugiura S, et al:
CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and
adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nature Med. 15:914–920.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shin JH, Shin DW and Noh M:
Interleukin-17A inhibits adipocyte differentiation in human
mesenchymal stem cells and regulates pro-inflammatory responses in
adipocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1835–1844. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cipolletta D, Feuerer M, Li A, Kamei N,
Lee J, Shoelson SE, Benoist C and Mathis D: PPAR-γ is a major
driver of the accumulation and phenotype of adipose tissue Treg
cells. Nature. 486:549–553. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lei J, Hasegawa H, Matsumoto T and
Yasukawa M: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and γ
agonists together with TGF-β convert human CD4+CD25-T cells into
functional Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 185:7186–7198.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sun L, Fu J and Zhou Y: Metabolism
controls the balance of Th17/T-regulatory cells. Front Immunol.
8(1632)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Maciolek JA, Pasternak JA and Wilson HL:
Metabolism of activated T lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 27:60–74.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Miao Y, Zhang C, Yang L, Zeng X, Hu Y, Xue
X, Dai Y and Wei Z: The activation of PPARγ enhances Treg responses
through up-regulating CD36/CPT1-mediated fatty acid oxidation and
subsequent N-glycan branching of TβRII/IL-2Rα. Cell Commun Signal.
20(48)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li C, Muñoz-Rojas AR, Wang G, Mann AO,
Benoist C and Mathis D: PPARγ marks splenic precursors of multiple
nonlymphoid-tissue Treg compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118(e2025197118)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jeong W, Jung JY, Kim SC and Im WT:
Ginsenoside F2 for prophylaxis and treatment of liver disease.
European patent EP2992933A1. Filed September 4, 2015; issued March
9, 2016.
|
|
52
|
Lin Z, Wang Z, Hegarty JP, Lin TR, Wang Y,
Deiling S, Wu R, Thomas NJ and Floros J: Genetic association and
epistatic interaction of the interleukin-10 signaling pathway in
pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol.
23:4897–4909. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Fay NC, Muthusamy BP, Nyugen LP, Desai RC,
Taverner A, MacKay J, Seung M, Hunter T, Liu K, Chandalia A, et al:
A novel fusion of IL-10 engineered to traffic across intestinal
epithelium to treat colitis. J Immunol. 205:3191–3204.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Saraiva M, Vieira P and O'Garra A: Biology
and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J Exp Med.
217(e20190418)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Vidal PM, Lemmens E, Dooley D and Hendrix
S: The role of ‘anti-inflammatory’ cytokines in axon regeneration.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:1–12. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Rajbhandari P, Thomas BJ, Feng AC, Hong C,
Wang J, Vergnes L, Sallam T, Wang B, Sandhu J, Seldin MM, et al:
IL-10 signaling remodels adipose chromatin architecture to limit
thermogenesis and energy expenditure. Cell. 172:218–233.e17.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Acosta JR, Tavira B, Douagi I, Kulyté A,
Arner P, Rydén M and Laurencikiene J: Human-specific function of
IL-10 in adipose tissue linked to insulin resistance. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 104:4552–4562. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ramos-Ramírez P, Malmhäll C, Johansson K,
Lötvall J and Bossios A: Weight gain alters adiponectin receptor 1
expression on adipose tissue-resident helios+ regulatory T cells.
Scand J Immunol. 83:244–254. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ramos-Ramirez P, Malmhäl C, Tliba O,
Rådinger M and Bossios A: Adiponectin/AdipoR1 axis promotes IL-10
release by human regulatory T cells. Front Immunol.
12(677550)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wu X, Tian J and Wang S: Insight into
non-pathogenic Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol.
9(1112)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Fang W, Deng Z, Benadjaoud F, Yang D, Yang
C and Shi GP: Regulatory T cells promote adipocyte beiging in
subcutaneous adipose tissue. FASEB J. 34:9755–9770. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Klotz L, Burgdorf S, Dani I, Saijo K,
Flossdorf J, Hucke S, Alferink J, Novak N, Beyer M, Mayer G, et al:
The nuclear receptor PPAR gamma selectively inhibits Th17
differentiation in a T cell-intrinsic fashion and suppresses CNS
autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 206:2079–2089. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Chang YC, Hee SW and Chuang LM: T helper
17 cells: A new actor on the stage of type 2 diabetes and aging? J
Diabetes Investig. 12:909–913. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Miyase T, Sano M, Nakai H, Muraoka M,
Nakazawa M, Suzuki M, Yoshino K, Nishihara Y and Tanai J:
Antioxidants from Lespedeza homoloba. (I). Phytochemistry.
52:303–310. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Miyase T, Sano M, Yoshio K and Nonaka K:
Antioxidants from Lespedeza homoloba (II). Phytochemistry.
52:311–319. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Terao J and Mukai R: Prenylation modulates
the bioavailability and bioaccumulation of dietary flavonoids. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 559:12–16. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Longo N, Frigeni M and Pasquali M:
Carnitine transport and fatty acid oxidation. Biochem Biophys Acta.
1863:2422–2435. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sultan AA, Rattray Z and Rattray NJW:
Toxicometabolomics-based cardiotoxicity evaluation of
Thiazolidinedione exposure in human-derived cardiomyocytes.
Metabolomics. 20(24)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Home PD, Pocock SJ, Beck-Nielsen H, Curtis
PS, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Jones NP, Komajda M and McMurray JJ:
RECORD Study Team. Rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiovascular
outcomes in oral agent combination therapy for type 2 diabetes
(RECORD): A multicentre, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet.
373:2125–2135. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJA,
Erdmann E, Massi-Benedetti M, Moules IK, Skene AM, Tan MH, Lefèbvre
PJ, Murray GD, et al: Secondary prevention of macrovascular events
in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive study
(PROspective pioglitAzone clinical trial in macroVascular events):
A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 366:1279–1289.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Yong EL, Cheong WF, Huang Z, Thu WPP,
Cazenave-Gassiot A, Seng KY and Logan S: Randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial to examine the safety, pharmacokinetics
and effects of epimedium prenylflavonoids, on bone specific
alkaline phosphatase and the osteoclast adaptor protein TRAF6 in
post-menopausal women. Phytomedicine. 91(153680)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|