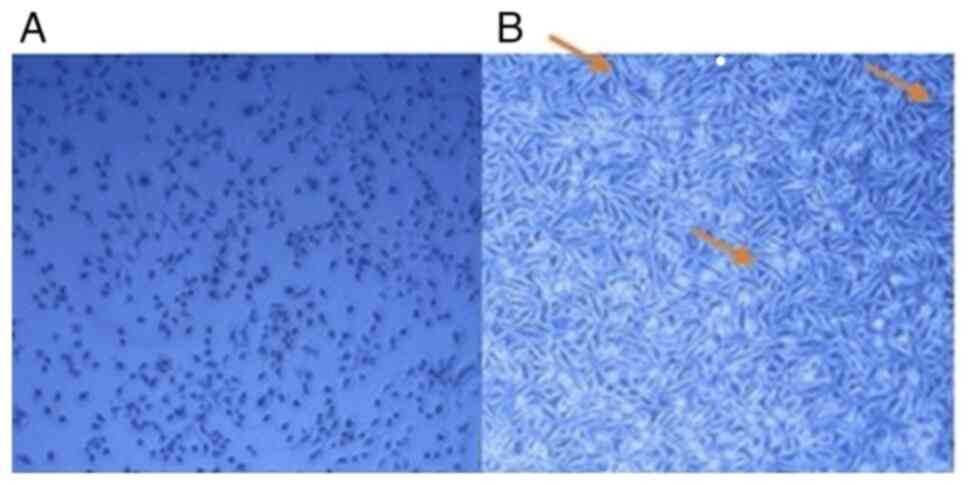
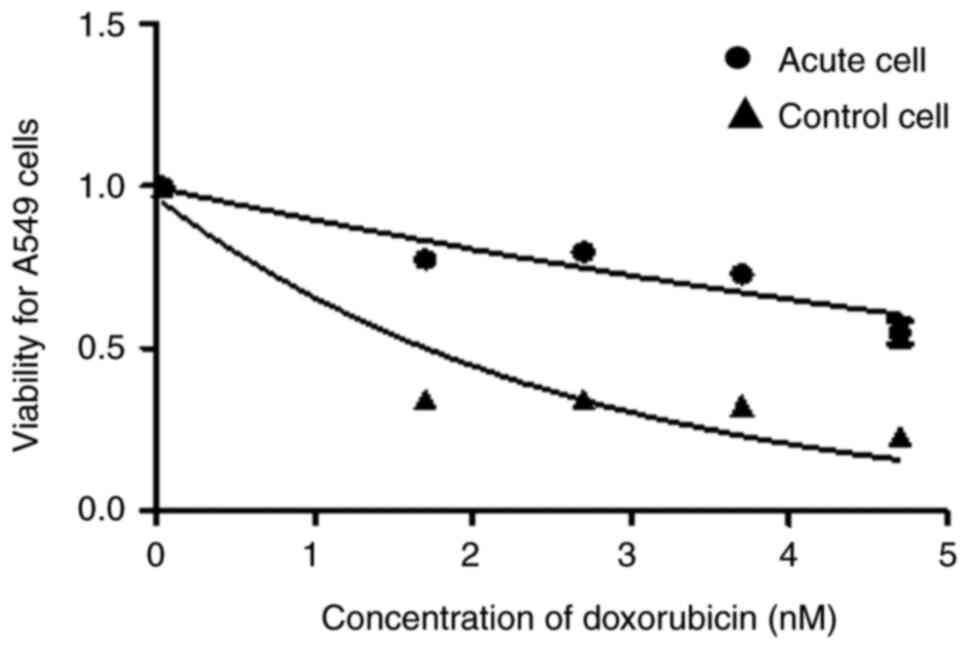
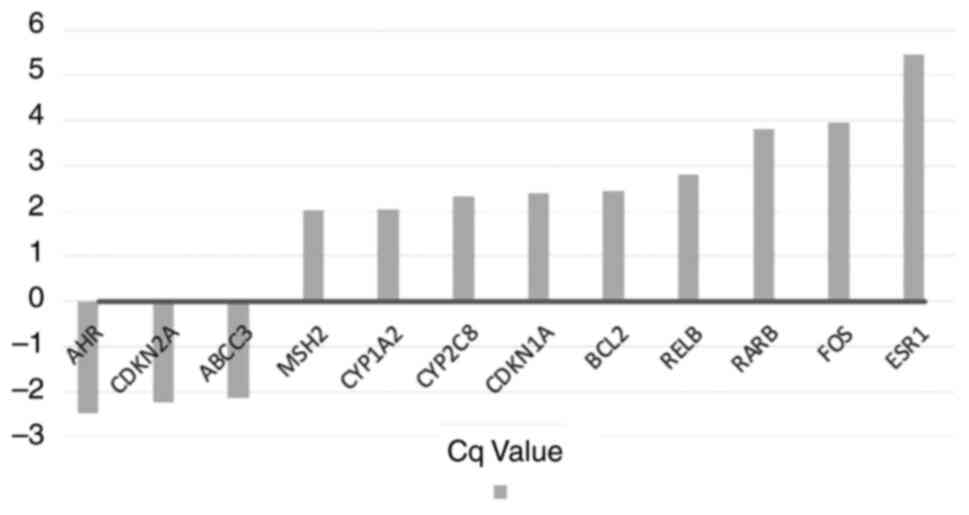
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer Statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sinha BK, Mimnaugh EG, Rajagopalan S and
Myers CE: Adriamycin activation and oxygen free radical formation
in human breast tumor cells: Protective role of glutathione
peroxidase in adriamycin resistance 1. Cancer Res. 49:3844–3848.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaupel P and Harrison L: Tumor hypoxia:
Causative factors, compensatory mechanisms, and cellular response.
Oncologist. 9 (Suppl 5):S4–S9. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Das B, Tsuchida R, Malkin D, Koren G,
Baruchel S and Yeger H: Hypoxia enhances tumor stemness by
increasing the invasive and tumorigenic side population fraction.
Stem Cells. 26:1818–1830. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen Z, Han F, Du Y, Shi H and Zhou W:
Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic interventions. Sig Transduct Target Ther.
8(70)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bayer C and Vaupel P: Acute versus chronic
hypoxia in tumors : Controversial data concerning time frames and
biological consequences. Strahlenther Onkol. 188:616–627.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Le QT, Chen E, Salim A, Cao H, Kong CS,
Whyte R, Donington J, Cannon WA, Wakelee H, Tibshirani R, et al: An
evaluation of tumor oxygenation and gene expression in patients
with early stage non-small cell lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res.
12:1507–1514. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ziółkowska-Suchanek I: Mimicking tumor
hypoxia in non-small cell lung cancer employing three-dimensional
in vitro models. Cells. 10(141)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Marhuenda E, Campillo N, Gabasa M,
Martínez-García MA, Campos-Rodríguez F, Gozal D, Navajas D, Alcaraz
J, Farré R and Almendros I: Effects of Sustained and Intermittent
Hypoxia on Human Lung Cancer Cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
61:540–544. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rouschop KM, Ramaekers CH, Schaaf MB,
Keulers TG, Savelkouls KG, Lambin P, Koritzinsky M and Wouters BG:
Autophagy is required during cycling hypoxia to lower production of
reactive oxygen species. Radiother Oncol. 92:411–416.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hsieh CH, Shyu WC, Chiang CY, Kuo JW, Shen
WC and Liu RS: NADPH oxidase subunit 4-mediated reactive oxygen
species contribute to cycling hypoxia-promoted tumor progression in
glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS One. 6(e23945)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rofstad EK, Gaustad JV, Egeland TA,
Mathiesen B and Galappathi K: Tumors exposed to acute cyclic
hypoxic stress show enhanced angiogenesis, perfusion and metastatic
dissemination. Int J Cancer. 127:1535–1546. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pires IM, Bencokova Z, Milani M, Folkes
LK, Li JL, Stratford MR, Harris AL and Hammond EM: Effects of acute
versus chronic hypoxia on DNA damage responses and genomic
instability. Cancer Res. 70:925–935. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Erler JT, Cawthorne CJ, Williams KJ,
Koritzinsky M, Wouters BG, Wilson C, Miller C, Demonacos C,
Stratford IJ and Dive C: Hypoxia-Mediated Down-Regulation of Bid
and Bax in Tumors Occurs via Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Dependent
and -Independent Mechanisms and Contributes to Drug Resistance. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:2875–2889. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vaupel P, Kelleher DK and Höckel M:
Oxygenation status of malignant tumors: Pathogenesis of hypoxia and
significance for tumor therapy. Semin Oncol. 28 (2 Suppl 8):29–35.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Al-Najjar LM, Zihlif M and Jarrar Y:
Differential molecular alterations promoting non-small cell
lungcancer under hypoxia. Genome Instab Dis. 3:108–121. 2022.
|
|
18
|
Chen YL, Yang TY, Chen KC, Wu CL, Hsu SL
and Hsueh CM: Hypoxia can impair doxorubicin resistance of
non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting MRP1 and P-gp
expression and boosting the chemosensitizing effects of MRP1 and
P-gp blockers. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 39:411–433. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chou CW, Wang CC, Wu CP, Lin YJ, Lee YC,
Cheng YW and Hsieh CH: Tumor cycling hypoxia induces
chemoresistance in glioblastoma multiforme by upregulating the
expression and function of ABCB1. Neuro Oncol. 14:1227–1238.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Green SL and Giaccia AJ: Tumor hypoxia and
the cell cycle: Implications for malignant progression and response
to therapy. Cancer J Sci Am. 4:218–223. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou SF, Wang B, Yang LP and Liu JP:
Structure, function, regulation and polymorphism and the clinical
significance of human cytochrome P450 1A2. Drug Metab Rev.
42:268–354. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
AbuHammad S and Zihlif M: Gene expression
alterations in doxorubicin resistant MCF7 breast cancer cell line.
Genomics. 101:213–220. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lei JT, Gou X, Seker S and Ellis MJ: ESR1
alterations and metastasis in estrogen receptor positive breast
cancer. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 5(38)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fialka I, Schwarz H, Reichmann E, Oft M,
Busslinger M and Beug H: The estrogen-dependent C-junER protein
causes a reversible loss of mammary epithelial cell polarity
involving a destabilization of adherens junctions. J Cell Biol.
132:1115–1132. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gartel AL and Tyner AL: The role of the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 1:639–649. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bunz F, Hwang PM, Torrance C, Waldman T,
Zhang Y, Dillehay L, Williams J, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: Disruption of p53 in human cancer cells alters the
responses to therapeutic agents. J Clin. Invest. 104:263–269.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Muhammad N, Bhattacharya S, Steele R,
Phillips N and Ray RB: Involvement of c-Fos in the promotion of
cancer stem-like cell properties in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 23:3120–3128. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sermeus A, Genin M, Maincent A, Fransolet
M, Notte A, Leclere L, Riquier H, Arnould T and Michiels C:
Hypoxia-Induced modulation of apoptosis and BCL-2 family proteins
in different cancer cell types. PLoS One. 7(e47519)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Brtko J: Role of retinoids and their
cognate nuclear receptors in breast cancer chemoprevention. Cent
Eur J Public Health. 15:3–6. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hua F, Fang N, Li X, Zhu S, Zhang W and Gu
J: A meta-analysis of the relationship between RARβ gene promoter
methylation and non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
9(e96163)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu Z, Zhang L, Ding F, Li J, Guo M, Li W,
Wang Y, Yu Z, Zhan Q, Wu M and Liu Z: 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine
induces retinoic acid receptor-beta(2) demethylation and growth
inhibition in esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
230:271–283. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pérez RJ, Benoit YD and Gudas LJ: Deletion
of retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ) impairs pancreatic endocrine
differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 319:2196–204. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ren HY, Chen B, Huang GL, Liu Y and Shen
DY: Upregulation of retinoic acid receptor-β reverses drug
resistance in cholangiocarcinoma cells by enhancing susceptibility
to apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 14:3602–3608. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Lu DG, Ma YM and Liu H: Association
between Retinoic acid receptor-β hypermethylation and NSCLC risk: A
meta-analysis and literature review. Oncotarget. 8:5814–5822.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Demchenko YN, Glebov OK, Zingone A, Keats
JJ, Bergsagel PL and Kuehl WM: Classical and/or alternative
NF-kappaB pathway activation in multiple myeloma. Blood.
115:3541–3552. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Qin H, Zhou J, Zhou P, Xu J, Tang Z, Ma H
and Guo F: Prognostic significance of RelB overexpression in
non-small cell lung cancer patients. Thorac. Cancer. 7:415–421.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Adam AP, George A, Schewe D, Bragado P,
Iglesias BV, Ranganathan AC, Kourtidis A, Conklin DS and
Aguirre-Ghiso JA: Computational identification of a
p38SAPK-regulated transcription factor network required for tumor
cell quiescence. Cancer Res. 69:5664–5672. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhao Y, Lu H, Yan A, Yang Y, Meng Q, Sun
L, Pang H, Li C, Dong X and Cai L: ABCC3 as a marker for multidrug
resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep.
3(3120)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fukuda Y and Schuetz JD: ABC transporters
and their role in nucleoside and nucleotide drug resistance.
Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1073–1083. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kirovski G, Stevens AP, Czech B, Dettmer
K, Weiss TS, Wild P, Hartmann A, Bosserhoff AK, Oefner PJ and
Hellerbrand C: Down-regulation of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase
(MTAP) induces progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via
accumulation of 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA). Am J Pathol.
178:1145–1152. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chu IM, Hengst L and Slingerland JM: The
Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer: Prognostic potential and
relevance to anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:253–267.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Semenza GL: Intratumoral hypoxia and
mechanisms ofimmune evasion mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors.
Physiology (Bethesda). 36:73–83. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|