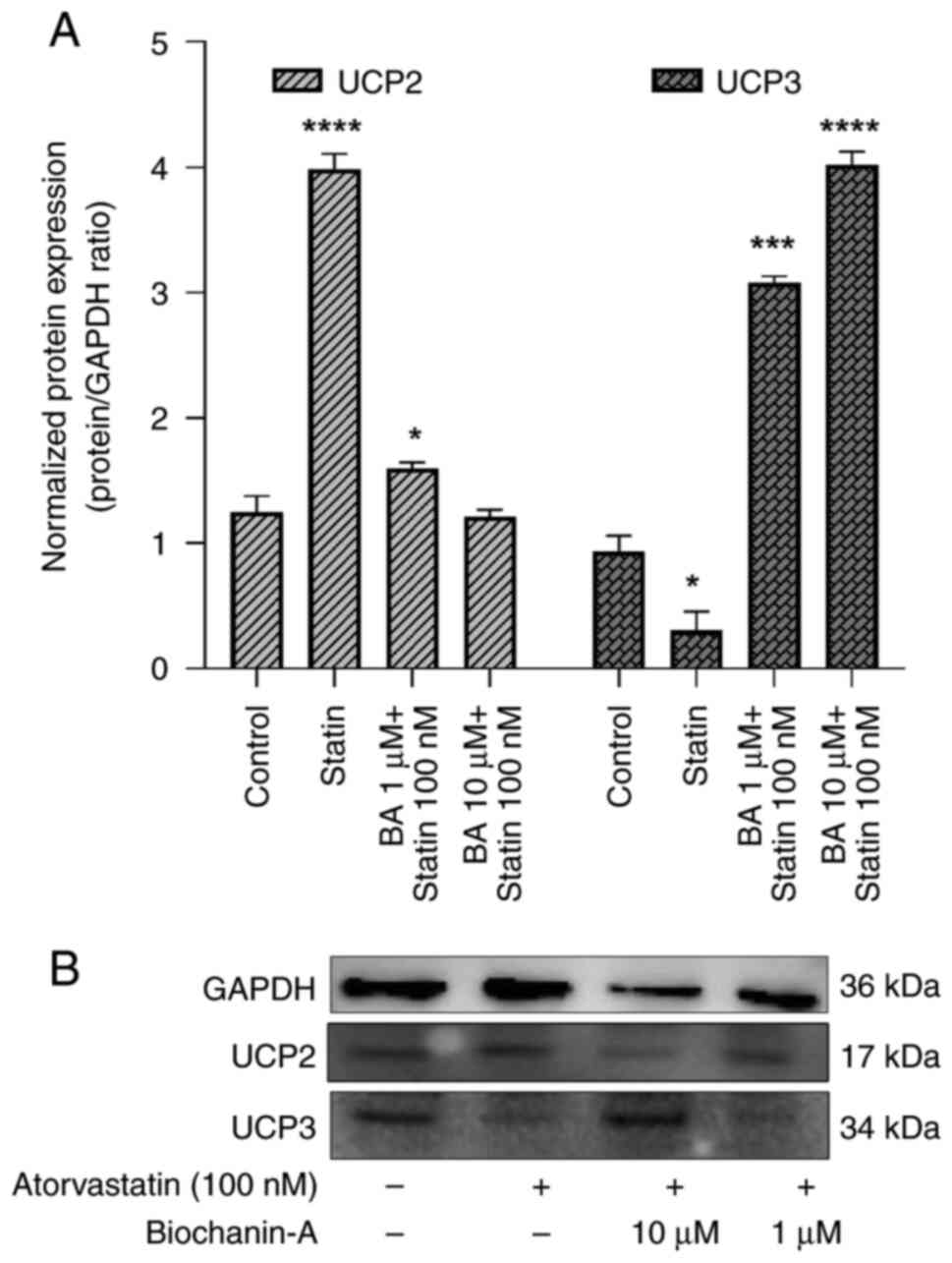
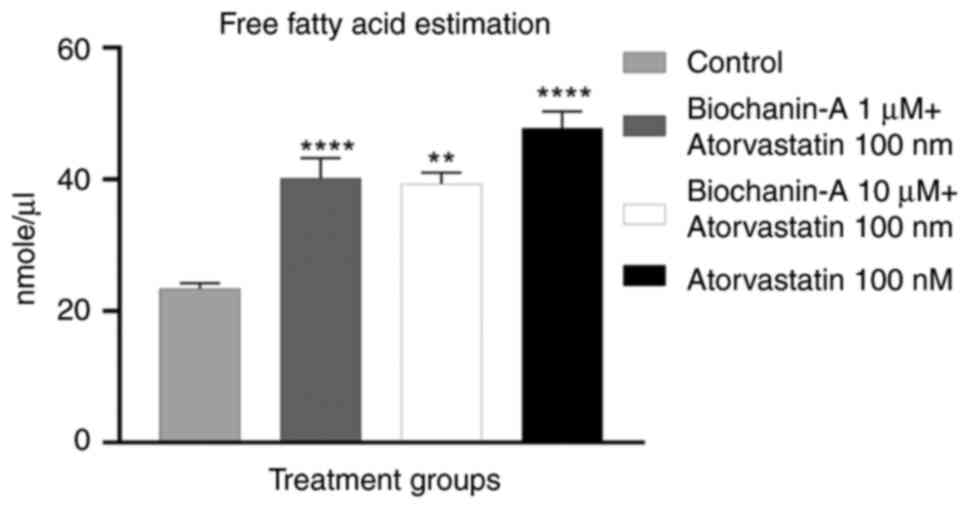
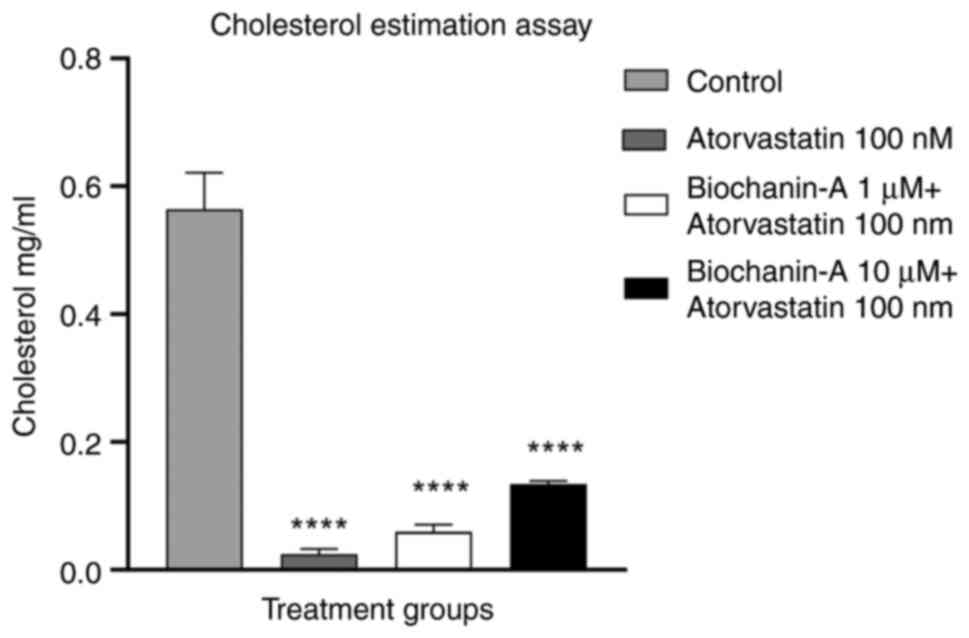
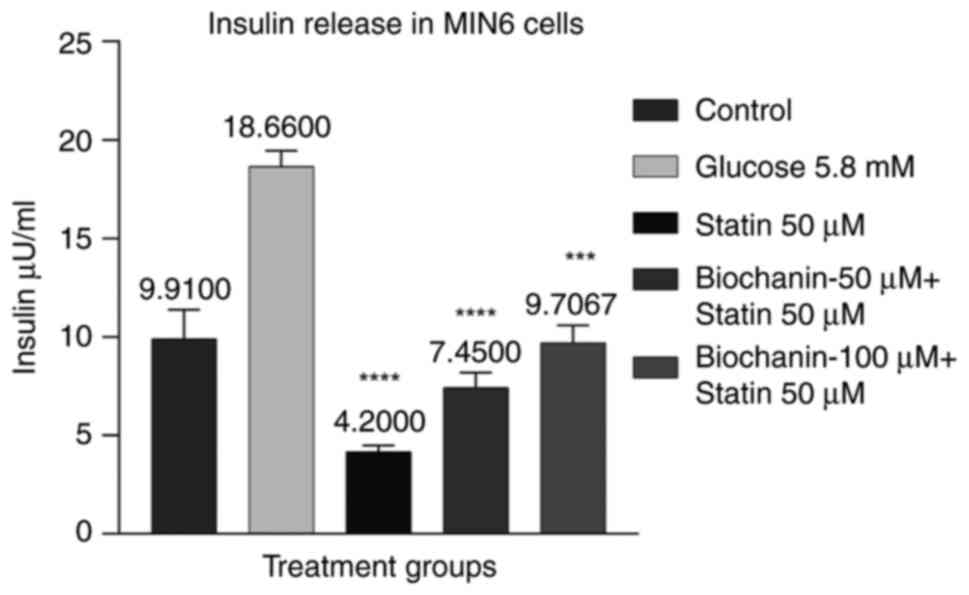
|
1
|
Steinberg D and Gotto AM Jr: Preventing
coronary artery disease by lowering cholesterol levels: Fifty years
from bench to bedside. JAMA. 282:2043–2050. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lippi G, Mattiuzzi C and Cervellin G:
Statins popularity: A global picture. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
85:1614–1615. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Taylor F, Huffman MD, Macedo AF, Moore TH,
Burke M, Davey Smith G, Ward K and Ebrahim S: Statins for the
primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database
Syst Rev. 2013(CD004816)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
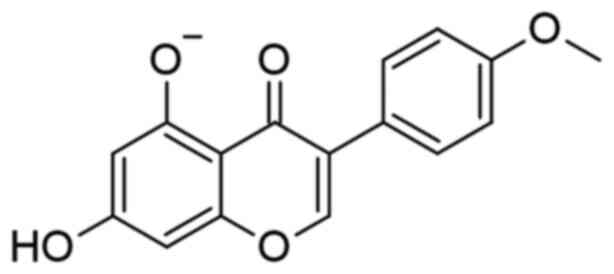
4
|
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
FDA Drug Safety Communication: Important safety label changes to
cholesterol-lowering statin drugs, 2016. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-important-safety-label-changes-cholesterol-lowering-statin-drugs.
Accessed November 25, 2020.
|
|
5
|
Ramkumar S, Raghunath A and Raghunath S:
Statin therapy : Review of safety and potential side effects. Acta
Cardiol Sin. 32:631–639. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
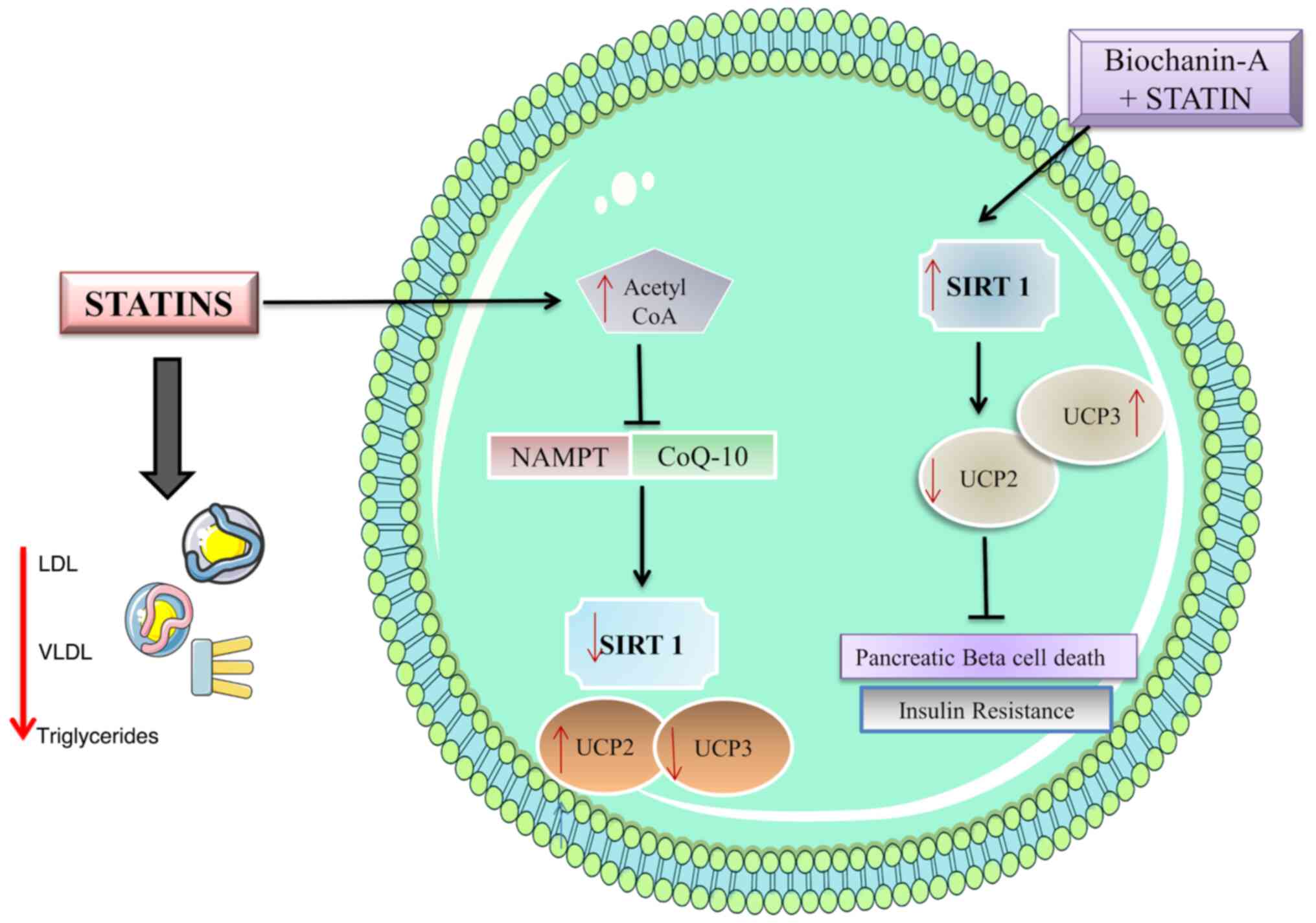
Cederberg H, Stančáková A, Yaluri N, Modi
S, Kuusisto J and Laakso M: Increased risk of diabetes with statin
treatment is associated with impaired insulin sensitivity and
insulin secretion: A 6 year follow-up study of the METSIM cohort.
Diabetologia. 58:1109–1117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sattar N, Preiss D, Murray HM, Welsh P,
Buckley BM, de Craen AJ, Seshasai SR, McMurray JJ, Freeman DJ,
Jukema JW, et al: Statins and risk of incident diabetes: A
collaborative meta-analysis of randomised statin trials. Lancet.
375:735–742. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bang CN and Okin PM: Statin treatment,
new-onset diabetes, and other adverse effects: A systematic review.
Curr Cardiol Rep. 16(461)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Khan MAB, Hashim MJ, King JK, Govender RD,
Mustafa H and Al Kaabi J: Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes-global
burden of disease and forecasted trends. J Epidemiol Glob Health.
10:107–111. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ganda OP: Statin-induced diabetes:
Incidence, mechanisms, and implications. F1000Res.
5(1499)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Keni R, Sekhar A, Gourishetti K, Nayak PG,
Kinra M, Kumar N, Shenoy RR, Kishore A and Nandakumar K: Role of
statins in new-onset diabetes mellitus: The underlying cause,
mechanisms involved, and strategies to combat. Curr Drug Targets.
22:1121–1128. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Harris CS, Harris
V, Tsai MS, Tripathi P, Abbas F, Reaven GM, Reaven PD, Snyder MP,
et al: Statins are associated with increased insulin resistance and
secretion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 41:2786–2797.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ridker PM, Pradhan A, MacFadyen JG, Libby
P and Glynn RJ: Cardiovascular benefits and diabetes risks of
statin therapy in primary prevention: An analysis from the JUPITER
trial. Lancet. 380:565–571. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Crandall JP, Mather K, Rajpathak SN,
Goldberg RB, Watson K, Foo S, Ratner R, Barrett-Connor E and
Temprosa M: Statin use and risk of developing diabetes: Results
from the diabetes prevention program. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care.
5(e000438)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kain V, Kapadia B, Misra P and Saxena U:
Simvastatin may induce insulin resistance through a novel fatty
acid mediated cholesterol independent mechanism. Sci Rep.
5(13823)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Henriksbo BD, Lau TC, Cavallari JF, Denou
E, Chi W, Lally JS, Crane JD, Duggan BM, Foley KP, Fullerton MD, et
al: Fluvastatin Causes NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated adipose insulin
resistance. Diabetes. 63:3742–3747. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liao JK and Laufs U: Pleiotropic effects
of statins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 45:89–118. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Choudhary A, Rawat U, Kumar P and Mittal
P: Pleotropic effects of statins: The dilemma of wider utilization
of statin. Egypt Hear J. 75(1)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Oesterle A, Laufs U and Liao JK:
Pleiotropic effects of statins on the cardiovascular system. Circ
Res. 120:229–243. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rajangam J, Krishnan N, Palei NN, Bhatt S,
Das MK, Das S and Mathusoothanan K: Ameliorative potential of
rosuvastatin on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating
oxidative damage in rats. Turk J Pharm Sci. 19:28–34.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rajangam J, Lakshmanan AP, Palei NN,
Elumalai K, Kotakonda M, Prakash R and Latha P: Differential
pharmacokinetic interplay of atorvastatin on lacosamide and
levetiracetam on experimental convulsions in mice. Curr Drug Metab.
24:645–655. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rajangam J and Lavanya O: Effect of
rosuvastatin on learning and memory in scopolamine induced amnesia
in Mice. Trends Med. 18:1–4. 2018.
|
|
23
|
Anuranjana PV, Beegum F, K P D, George KT,
Viswanatha GL, Nayak PG, Kanwal A, Kishore A and Shenoy RR:
Mechanisms behind the pharmacological application of biochanin-A: A
review. F1000Res. 12(107)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Oza MJ and Kulkarni YA: Biochanin A
improves insulin sensitivity and controls hyperglycemia in type 2
diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:1119–1127. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Amri J, Alaee M, Babaei R, Salemi Z,
Meshkani R, Ghazavi A, Akbari A and Salehi M: Biochanin-A has
antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, antioxidant, and protective
effects on diabetic nephropathy via suppression of TGF-β1 and PAR-2
genes expression in kidney tissues of STZ-induced diabetic rats.
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 69:2112–2121. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Azizi R, Goodarzi MT and Salemi Z: Effect
of biochanin a on serum visfatin level of streptozocin-induced
diabetic rats. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 16(e15424)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sadri H, Goodarzi MT, Salemi Z and Seifi
M: Antioxidant effects of biochanin A in streptozotocin induced
diabetic rats. Braz Arch Biol Technol. 60(e17160741)2017.
|
|
28
|
Harini R, Ezhumalai M and Pugalendi KV:
Antihyperglycemic effect of biochanin A, a soy isoflavone, on
streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 676:89–94.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shen P, Liu MH, Ng TY, Chan YH and Yong
EL: Differential effects of isoflavones, from Astragalus
membranaceus and pueraria thomsonii, on the activation of
PPARalpha, PPARgamma, and adipocyte differentiation in vitro. J
Nutr. 136:899–905. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mehrabadi ME and Salemi Z: Effect of
biochanin A on serum nesfatin-1 level in STZ induced type 1
diabetic rat. Diabetol Stoffwechs. 11(P225)2016.
|
|
31
|
Salemi Z, Ghasemi H, Morovati A and Sadri
H: Effects of biochanin A on Resistin, adiponectin and some stress
oxidative markers in normal and STZ-induced diabetic rats. Arch Med
Lab Sci. 4:9–16. 2020.
|
|
32
|
Cao Y, Jiang X, Ma H, Wang Y, Xue P and
Liu Y: SIRT1 and insulin resistance. J Diabetes Complications.
30:178–183. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou S, Tang X and Chen HZ: Sirtuins and
insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9(748)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cuyàs E, Verdura S, Llorach-Parés L,
Fernández-Arroyo S, Joven J, Martin-Castillo B, Bosch-Barrera J,
Brunet J, Nonell-Canals A, Sanchez-Martinez M and Menendez JA:
Metformin is a direct SIRT1-activating compound: computational
modeling and experimental validation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9(657)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kitada M and Koya D: SIRT1 in type 2
diabetes: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Diabetes Metab J.
37:315–325. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lou PH, Lucchinetti E, Scott KY, Huang Y,
Gandhi M, Hersberger M, Clanachan AS, Lemieux H and Zaugg M:
Alterations in fatty acid metabolism and sirtuin signaling
characterize early type-2 diabetic hearts of fructose-fed rats.
Physiol Rep. 5(e13388)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hou X, Xu S, Maitland-Toolan KA, Sato K,
Jiang B, Ido Y, Lan F, Walsh K, Wierzbicki M, Verbeuren TJ, et al:
SIRT1 regulates hepatocyte lipid metabolism through activating
AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 283:20015–20026.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kilic U, Gok O, Elibol-Can B, Uysal O and
Bacaksiz A: Efficacy of statins on sirtuin 1 and endothelial nitric
oxide synthase expression: the role of sirtuin 1 gene variants in
human coronary atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
42:321–330. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pareek A, Yeole P, Tenpe C, Chandurkar N
and Payghan R: Effect of atorvastatin and hydroxychloroquine
combination on blood glucose in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.
Indian J Pharmacol. 41:125–128. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Bordone L, Motta MC, Picard F, Robinson A,
Jhala US, Apfeld J, McDonagh T, Lemieux M, McBurney M, Szilvasi A,
et al: Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion by repressing UCP2 in
pancreatic beta cells. PLoS Biol. 4(e31)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Brault M, Ray J, Gomez YH, Mantzoros CS
and Daskalopoulou SS: Statin treatment and new-onset diabetes: A
review of proposed mechanisms. Metabolism. 63:735–745.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mollazadeh H, Tavana E, Fanni G, Bo S,
Banach M, Pirro M, von Haehling S, Jamialahmadi T and Sahebkar A:
Effects of statins on mitochondrial pathways. J Cachexia Sarcopenia
Muscle. 12:237–251. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Vichai V and Kirtikara K: Sulforhodamine B
colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc.
1:1112–1116. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Valentovic M: Atorvastatin. In: xPharm:
The comprehensive pharmacology reference. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The
Netherlands, pp1-6, 2007.
|
|
45
|
Merz KE and Thurmond DC: Role of skeletal
muscle in insulin resistance and glucose uptake. In: Comprehensive
Physiology. Wiley, pp785-809, 2020.
|
|
46
|
Hwang JT and Kim SH: Evaluation of
Anti-diabetic Effect of Biochanin A in C2C12 Myotube. Korean Soc
Biotechnol Bioeng J. 27:57–60. 2012.
|
|
47
|
Nowis D, Malenda A, Furs K, Oleszczak B,
Sadowski R, Chlebowska J, Firczuk M, Bujnicki JM, Staruch AD,
Zagozdzon R, et al: Statins impair glucose uptake in human cells.
BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2(e000017)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jiang Z, Yu B and Li Y: Effect of three
statins on glucose uptake of cardiomyocytes and its mechanism. Med
Sci Monit. 22:2825–2830. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sun B, Zhong Z, Wang F, Xu J, Xu F, Kong
W, Ling Z, Shu N, Li Y, Wu T, et al: Atorvastatin impaired glucose
metabolism in C2C12 cells partly via inhibiting
cholesterol-dependent glucose transporter 4 translocation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 150:108–119. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Carnagarin R, Dharmarajan AM and Dass CR:
Molecular aspects of glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle-A focus
on the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 417:52–62. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Galicia-Garcia U, Jebari S, Larrea-Sebal
A, Uribe KB, Siddiqi H, Ostolaza H, Benito-Vicente A and Martín C:
Statin treatment-induced development of type 2 diabetes: From
clinical evidence to mechanistic insights. Int J Mol Sci.
21(4725)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yaluri N, Modi S and Kokkola T:
Simvastatin induces insulin resistance in L6 skeletal muscle
myotubes by suppressing insulin signaling, GLUT4 expression and
GSK-3β phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 480:194–200.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sanvee GM, Panajatovic MV, Bouitbir J and
Krähenbühl S: Mechanisms of insulin resistance by simvastatin in
C2C12 myotubes and in mouse skeletal muscle. Biochem Pharmacol.
164:23–33. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bonifacio A, Sanvee GM, Brecht K,
Kratschmar DV, Odermatt A, Bouitbir J and Krähenbühl S: IGF-1
prevents simvastatin-induced myotoxicity in C2C12 myotubes. Arch
Toxicol. 91:2223–2234. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Abdul-Ghani MA and DeFronzo RA:
Pathogenesis of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2010(476279)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Elibol B and Kilic U: High levels of SIRT1
expression as a protective mechanism against disease-related
conditions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9(614)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Rousset S, Alves-Guerra MC, Mozo J, Miroux
B, Cassard-Doulcier AM, Bouillaud F and Ricquier D: The biology of
mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Diabetes. 53 (Suppl
1):S130–S135. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Azzu V and Brand MD: The on-off switches
of the mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci.
35:298–307. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kutsche HS, Schreckenberg R, Weber M,
Hirschhäuser C, Rohrbach S, Li L, Niemann B, Schulz R and Schlüter
KD: Alterations in glucose metabolism during the transition to
heart failure: The contribution of UCP-2. Cells.
9(552)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Martins AR, Nachbar RT, Gorjao R, Vinolo
MA, Festuccia WT, Lambertucci RH, Cury-Boaventura MF, Silveira LR,
Curi R and Hirabara SM: Mechanisms underlying skeletal muscle
insulin resistance induced by fatty acids: Importance of the
mitochondrial function. Lipids Health Dis. 11(30)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN and
Newsholme EA: The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin
sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus.
Lancet. 281:785–789. 1963.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Liscurn L: Chapter 15 Cholesterol
biosynthesis. Elsevier, pp409-431, 2002.
|
|
63
|
Chavez JA and Summers SA: Lipid
oversupply, selective insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity:
Molecular mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1801:252–265.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hughes RI and Aitman TJ: Genetics of the
metabolic syndrome and implications for therapy. Int Congr Ser.
1262:224–229. 2004.
|
|
65
|
Kohlmeier M: Cholesterol. In: Nutrient
Metabolism. Elsevier, pp511-526, 2003.
|
|
66
|
Li LH, Dutkiewicz EP, Huang YC, Zhou HB
and Hsu CC: Analytical methods for cholesterol quantification. J
Food Drug Anal. 27:375–386. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Gorospe CM, Carvalho G, Herrera Curbelo A,
Marchhart L, Mendes IC, Niedźwiecka K and Wanrooij PH:
Mitochondrial membrane potential acts as a retrograde signal to
regulate cell cycle progression. Life Sci Alliance.
6(e202302091)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Urbano F, Bugliani M, Filippello A,
Scamporrino A, Di Mauro S, Di Pino A, Scicali R, Noto D, Rabuazzo
AM, Averna M, et al: Atorvastatin but not pravastatin impairs
mitochondrial function in human pancreatic islets and rat β-cells.
Direct effect of oxidative stress. Sci Rep. 7(11863)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Koklesova L, Liskova A, Samec M, Zhai K,
Al-Ishaq RK, Bugos O, Šudomová M, Biringer K, Pec M, Adamkov M, et
al: Protective effects of flavonoids against mitochondriopathies
and associated pathologies: Focus on the predictive approach and
personalized prevention. Int J Mol Sci. 22(8649)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kicinska A and Jarmuszkiewicz W:
Flavonoids and mitochondria: Activation of cytoprotective pathways?
Molecules. 25(3060)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Delgado-León TG, Sálas-Pacheco JM,
Vazquez-Alaniz F, Vértiz-Hernández ÁA, López-Guzmán OD,
Lozano-Guzmán E, Martínez-Romero A, Úrtiz-Estrada N and
Cervantes-Flores M: Apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells is induced by
arsenic and atorvastatin in Wistar rats with diabetes mellitus type
2. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 46:144–149. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
McIlwain DR, Berger T and Mak TW: Caspase
functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 5(a008656)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Dawar S and Kumar S:
Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ.
22:526–539. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O and Samali A:
Cellular stress responses: Cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell
Biol. 2010(214074)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Li X: SIRT1 and energy metabolism. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:51–60. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Chalkiadaki A and Guarente L: High-fat
diet triggers inflammation-induced cleavage of SIRT1 in adipose
tissue to promote metabolic dysfunction. Cell Metab. 16:180–188.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Sun C, Zhang F, Ge X, Yan T, Chen X, Shi X
and Zhai Q: SIRT1 improves insulin sensitivity under
insulin-resistant conditions by repressing PTP1B. Cell Metab.
6:307–319. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Imai S and Yoshino J: The importance of
NAMPT/NAD/SIRT1 in the systemic regulation of metabolism and
ageing. Diabetes Obes Metab. 15 (Suppl 3):S26–S33. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Imai S and Kiess W: Therapeutic potential
of SIRT1 and NAMPT-mediated NAD biosynthesis in type 2 diabetes.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:2983–2995. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|