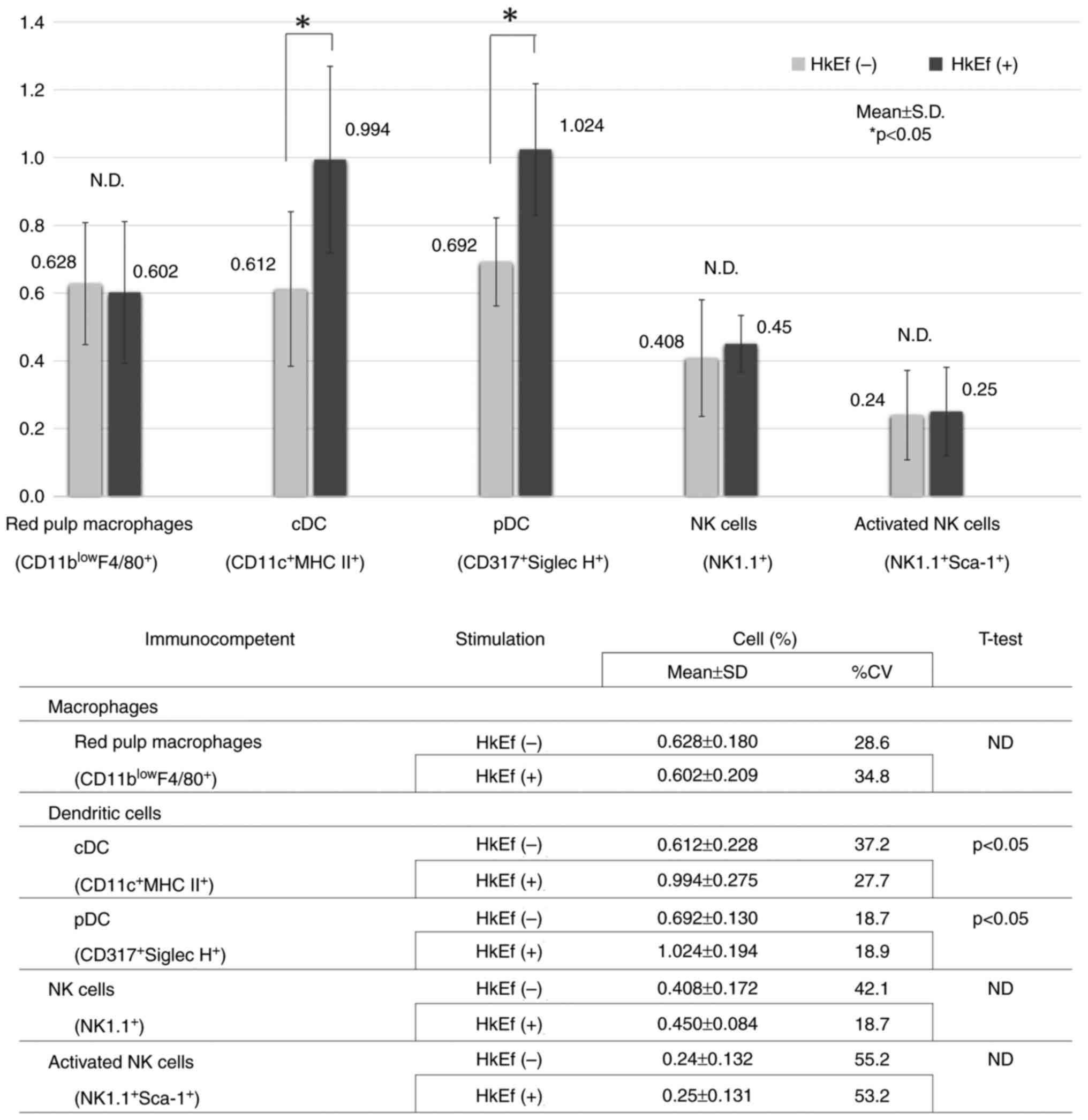
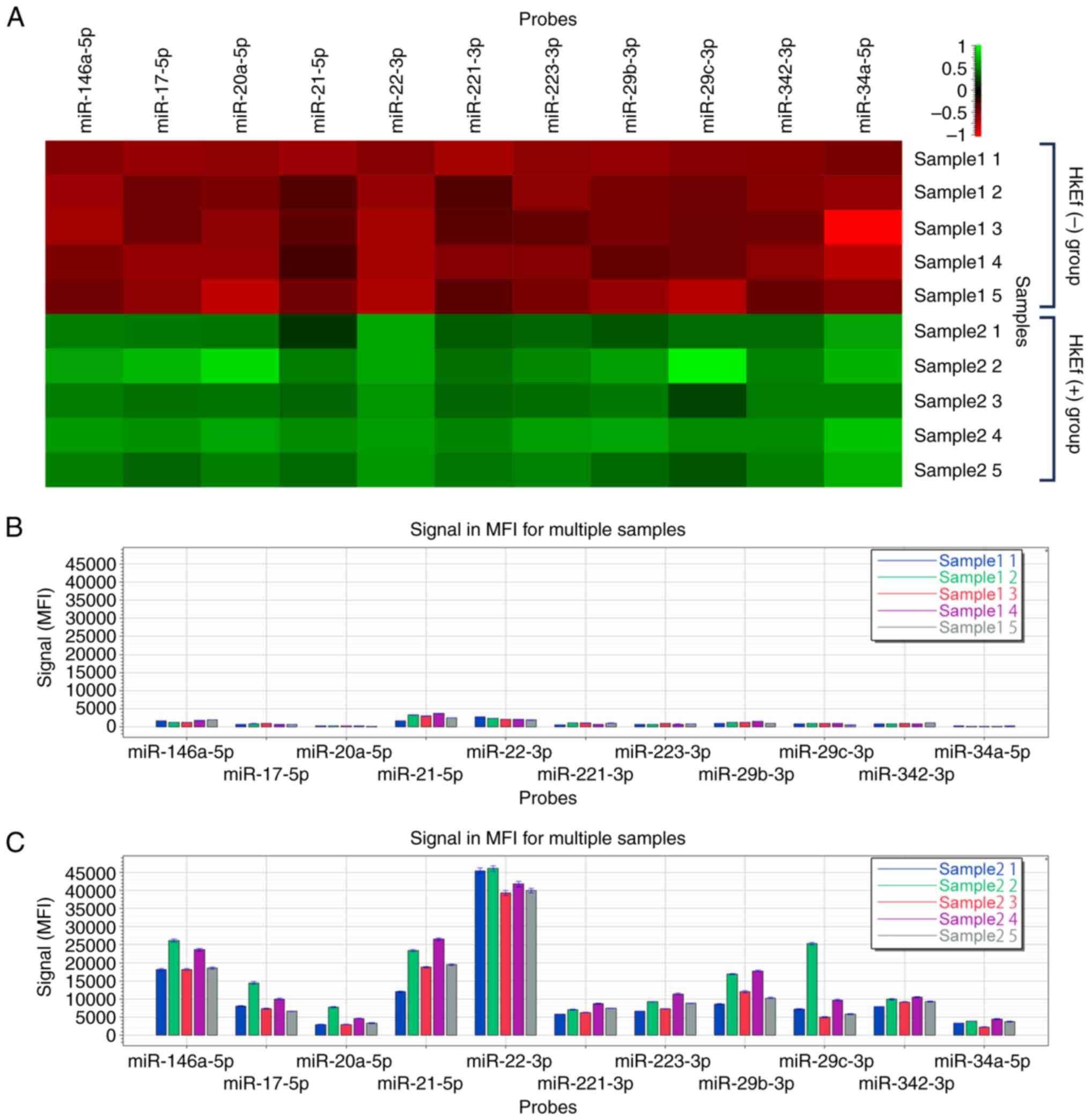
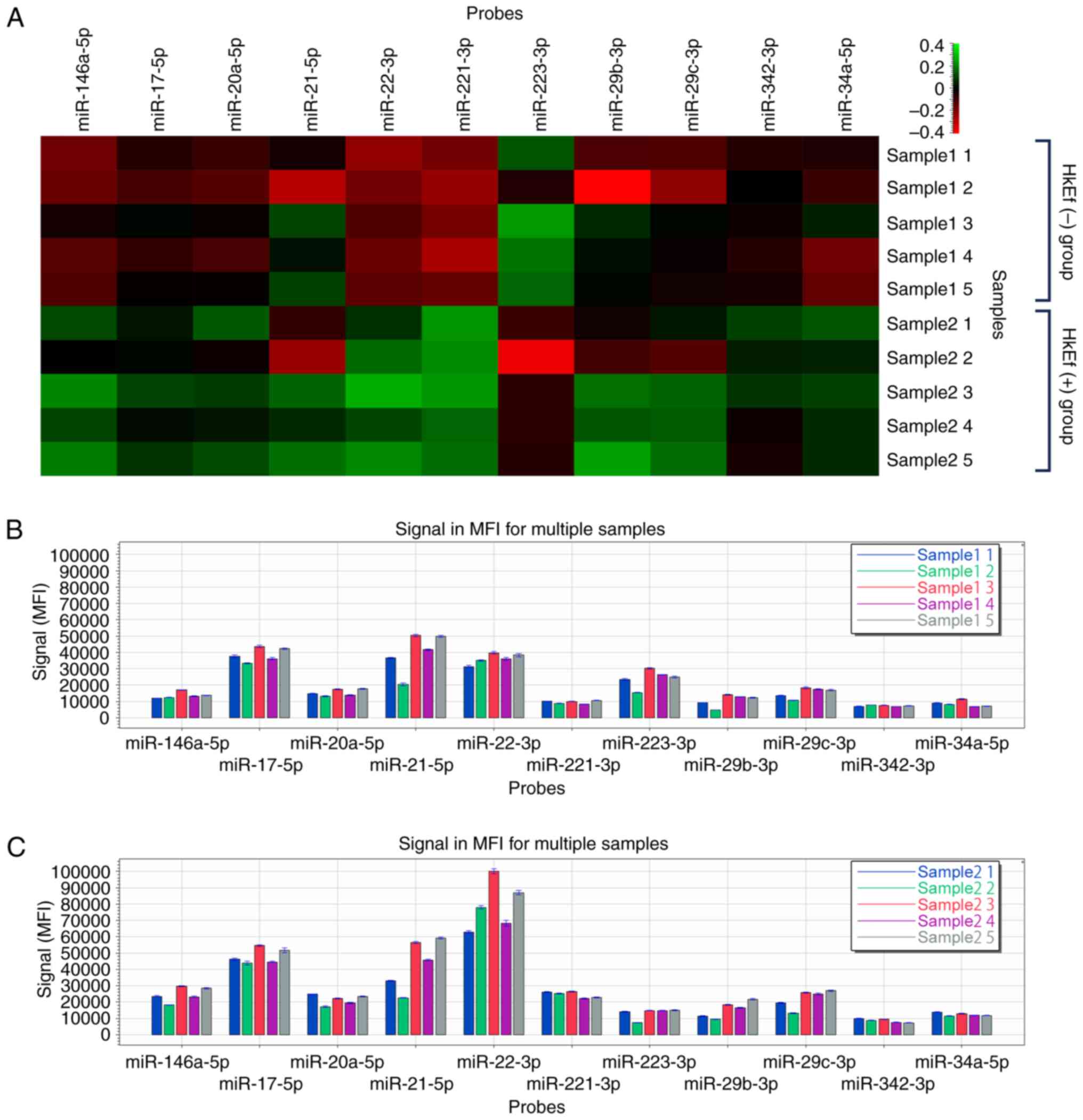
|
1
|
Inatomi T and Otomaru K: Effects of
heat-killed Enterococcus faecalis T-110 supplementation on
gut immunity, gut flora, and intestinal infection in naturally aged
hamsters. PLoS One. 15(e0240773)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Watanabe T, Hayashi K, Kan T, Ohwaki M and
Kawahara T: Anti-influenza virus effects of Enterococcus
faecalis KH2 and Lactobacillus plantarum SNK12 RNA.
Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 40:43–49. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hara K, Nakao K and Kawaguchi S: Efficacy
of heat-killed lactic acid bacteria Enterococcus faecalis on
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infected mice. J
New Rem Clin. 67:35–44. 2018.(In Japanese).
|
|
4
|
Nakao K, Hara K, Matsuo T and Kawauchi S:
Effects of heat-killed lactic acid bacteria Enterococcus
faecalis on life-threatening antibiotic-resistant bacteria in
animal models. J New Rem Clin. 69:276–287. 2020.(In Japanese).
|
|
5
|
Matsuo T, Nakao K, Hara K and Kawaguchi S:
Blood-derived exosomes released after the oral administration of
heat-killed Enterococcus faecalis activate immunity. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 86:1699–1704. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Inotsuka R, Udono M, Yamatsu A, Kim M and
Katakura Y: Exosome-mediated activation of neuronal cells triggered
by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Biosci Microb Food Health. 40:43–49.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Inotsuka R, Uchimura K, Yamatsu A, Kim M
and Katakura Y: γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) activates neuronal cells
by inducing the secretion of exosomes from intestinal cells. Food
Funct. 11:9285–9290. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sugihara Y, Onoue S, Tashiro K, Sato M,
Hasegawa T and Katakura Y: Carnosine induces intestinal cells to
secrete exosomes that activate neuronal cells. PLoS One.
14(e0217394)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeda K and Akira S:
The roles of Toll-like receptor 9, MyD88, and DNA-dependent protein
kinase catalytic subunit in the effects of two distinct CpG DNAs on
dendritic cell subsets. J Immunol. 170:3059–3064. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Steinman RM: Decisions about dendritic
cells: Past, present, and future. Annu Rev Immunol. 30:1–22.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gilliet M, Boonstra A, Paturel C,
Antonenko S, Xu XL, Trinchieri G, O'Garra A and Liu YJ: The
development of murine plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors is
differentially regulated by FLT3-ligand and granulocyte/macrophage
colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 195:953–958. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Starczynowski DT, Kuchenbauer F, Wegrzyn
J, Rouhi A, Petriv O, Hansen CL, Humphries RK and Karsan A:
MicroRNA-146a disrupts hematopoietic differentiation and survival.
Exp Hematol. 39:167–178.e4. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ueda Y, Kondo M and Kelsoe G: Inflammation
and the reciprocal production of granulocytes and lymphocytes in
bone marrow. J Exp Med. 201:1771–1780. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nagai Y, Garrett KP, Ohta S, Bahrun U,
Kouro T, Akira S, Takatsu K and Kincade PW: Toll-like receptors on
hematopoietic progenitor cells stimulate innate immune system
replenishment. Immunity. 24:801–812. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Han YC, Park CY, Bhagat G, Zhang J, Wang
Y, Fan JB, Liu M, Zou Y, Weissman IL and Gu H: microRNA-29a induces
aberrant self-renewal capacity in hematopoietic progenitors, biased
myeloid development, and acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med.
207:475–489. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Karrich JJ, Jachimowski LC, Libouban M,
Iyer A, Brandwijk K, Taanman-Kueter EW, Nagasawa M, de Jong EC,
Uittenbogaart CH and Blom B: MicroRNA-146a regulates survival and
maturation of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood.
122:3001–3009. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hong Y, Wu J, Zhao J, Wang H, Liu Y, Chen
T, Kan X, Tao Q, Shen X, Yan K and Zhai Z: miR-29b and miR-29c are
involved in Toll-like receptor control of glucocorticoid-induced
apoptosis in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS One.
8(e69926)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Buscaglia LEB and Li Y: Apoptosis and the
target genes of microRNA-21. Chin J Cancer. 30:371–380.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang A, Yang Y, Chen S, Xia F, Sun D,
Fang D, Xiong S, Jin L and Zhang J: MiR-34a promotes DCs
development and inhibits their function on T cell activation by
targeting WNT1. Oncotarget. 8:17191–17201. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hashimi ST, Fulcher JA, Chang MH, Gov L,
Wang S and Lee B: MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-34a and miR-21
and their target genes JAG1 and WNT1 in the coordinate regulation
of dendritic cell differentiation. Blood. 114:404–414.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li HS, Greeley N, Sugimoto N, Liu YJ and
Watowich SS: miR-22 controls Irf8 mRNA abundance and murine
dendritic cell development. PLoS One. 7(e52341)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kuipers H, Schnorfeil FM and Brocker T:
Differentially expressed microRNAs regulate plasmacytoid vs
conventional dendritic cell development. Mol Immunol. 48:333–340.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lu C, Huang X, Zhang X, Roensch K, Cao Q,
Nakayama KI, Blazar BR, Zeng Y and Zhou X: miR-221 and miR-155
regulate human dendritic cell development, apoptosis, and IL-12
production through targeting of p27kip1, KPC1, and SOCS-1. Blood.
117:4293–4303. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhou H, Xiao J, Wu N, Liu C, Xu J, Liu F
and Wu L: MicroRNA-223 regulates the differentiation and function
of intestinal dendritic cells and macrophages by targeting C/EBPβ.
Cell Rep. 13:1149–1160. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bros M, Youns M, Kollek V, Buchmüller D,
Bollmann F, Seo EJ, Schupp J, Montermann E, Usanova S, Kleinert H,
et al: Differentially tolerized mouse antigen presenting cells
share a common miRNA signature including enhanced mmu-miR-223-3p
expression which is sufficient to imprint a Protolerogenic State.
Front Pharmacol. 9(915)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yuan X, Berg N, Lee JW, Le TT, Neudecker
V, Jing N and Eltzschig H: MicroRNA miR-223 as regulator of innate
immunity. J Leukoc Biol. 104:515–524. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu MX, Wan WL, Hu K, Wang YF, Wang J, Zhu
XW, Yan XX, Jing HM and Ke XY: MicroRNA-223 regulates the
differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to dendritic cells.
Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 25:1275–1282. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Fontana L, Pelosi E, Greco P, Racanicchi
S, Testa U, Liuzzi F, Croce CM, Brunetti E, Grignani F and Peschle
C: MicroRNAs 17-5p-20a-106a control monocytopoiesis through AML1
targeting and M-CSF receptor upregulation. Nat Cell Biol.
9:775–787. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kim CH: Homeostatic and pathogenic
extramedullary hematopoiesis. J Blood Med. 1:13–19. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|