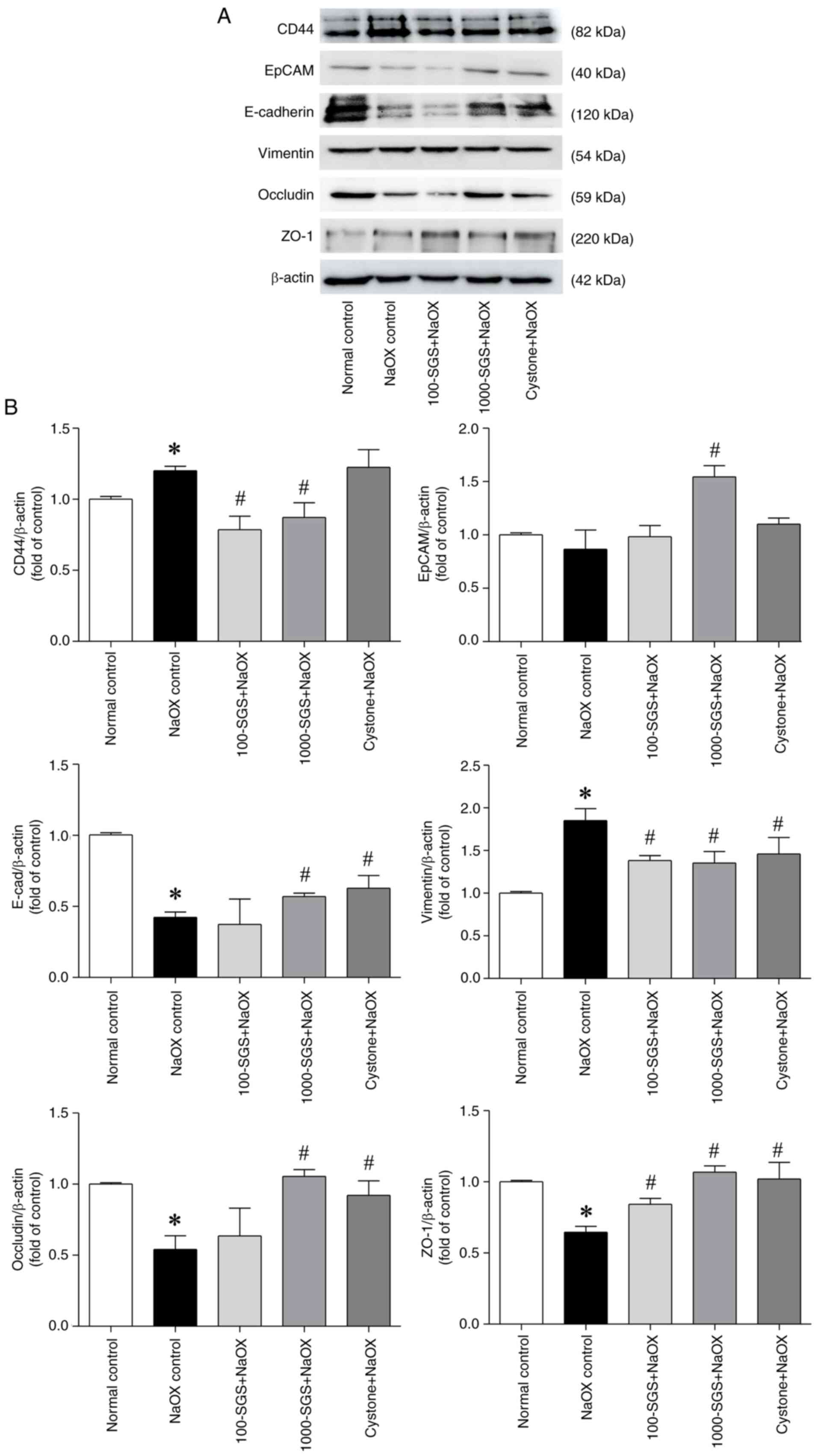
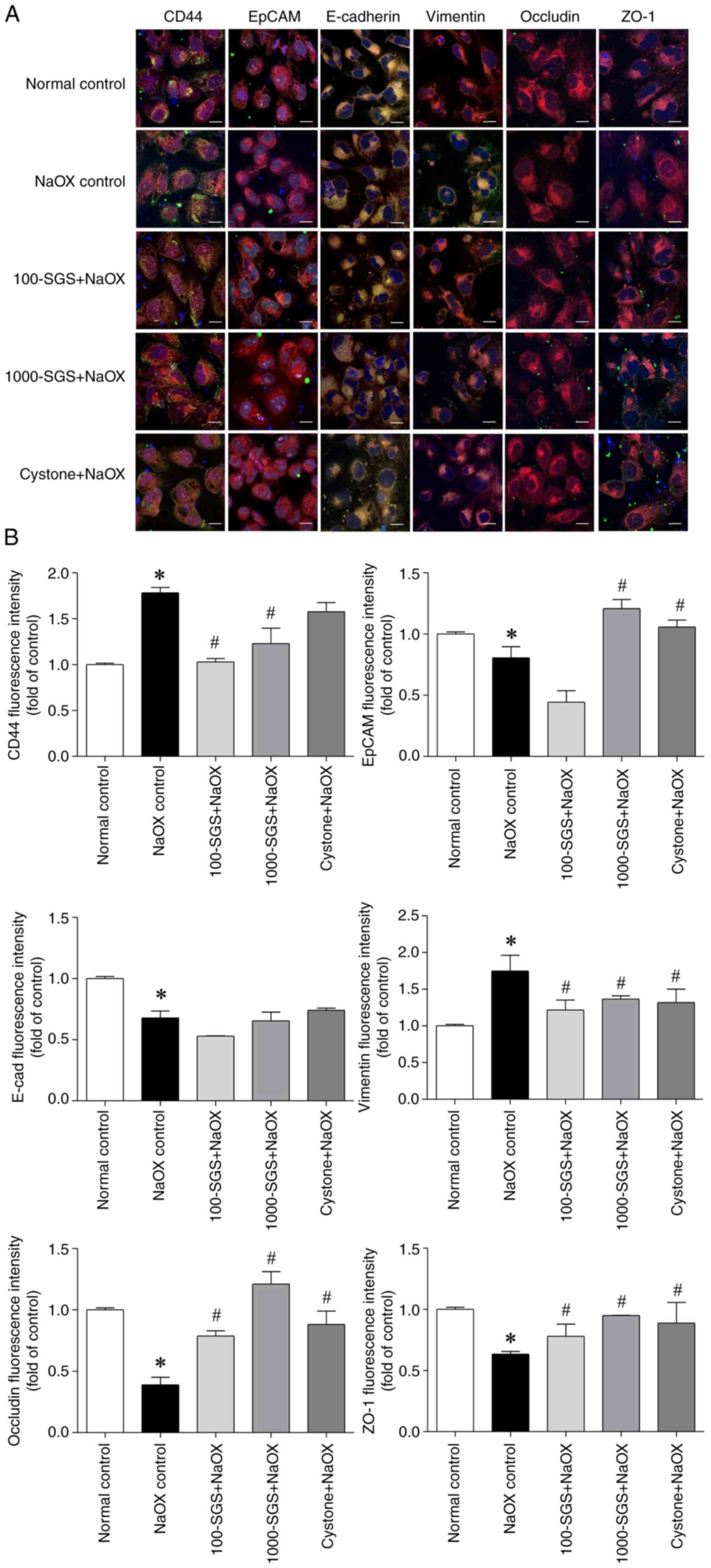
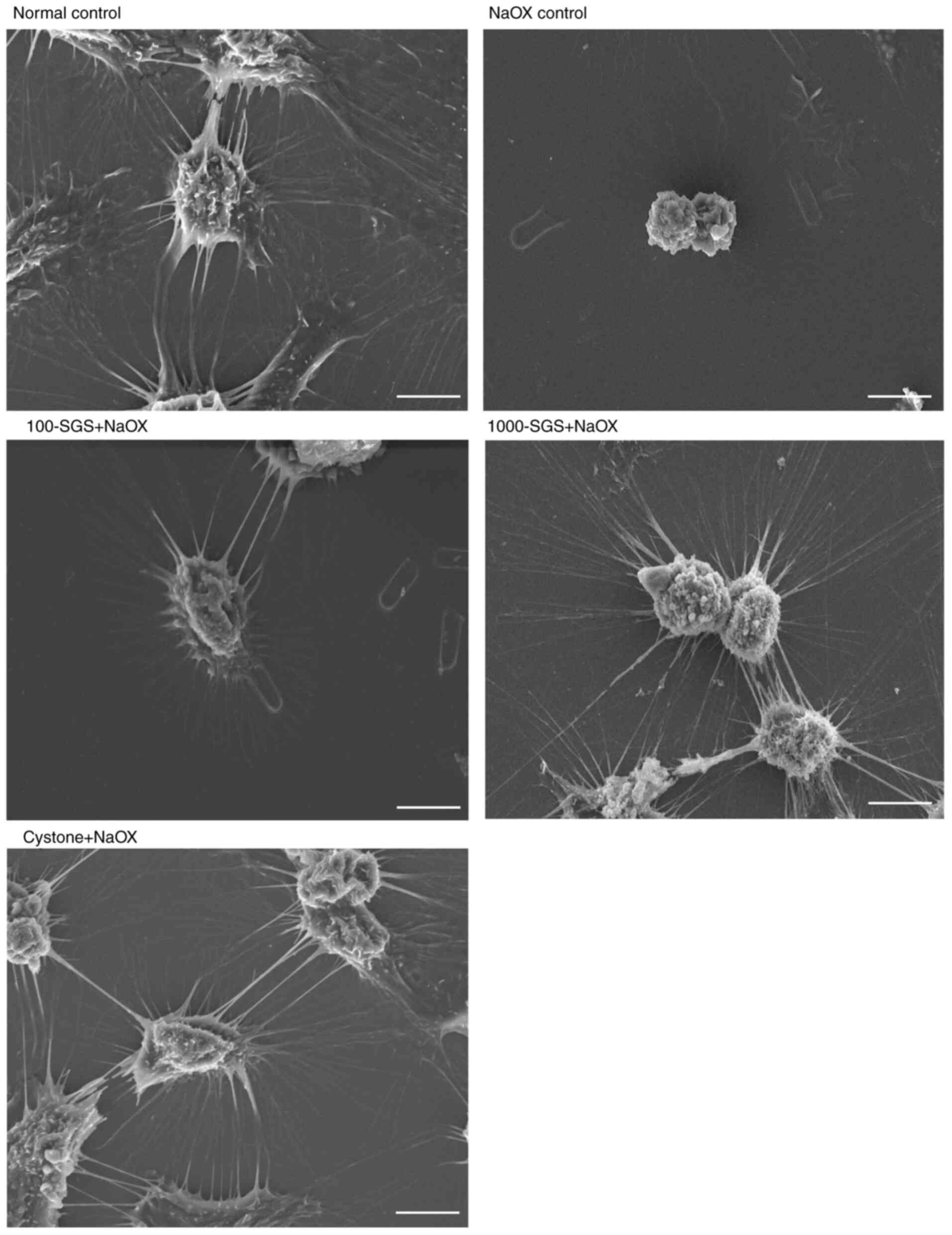
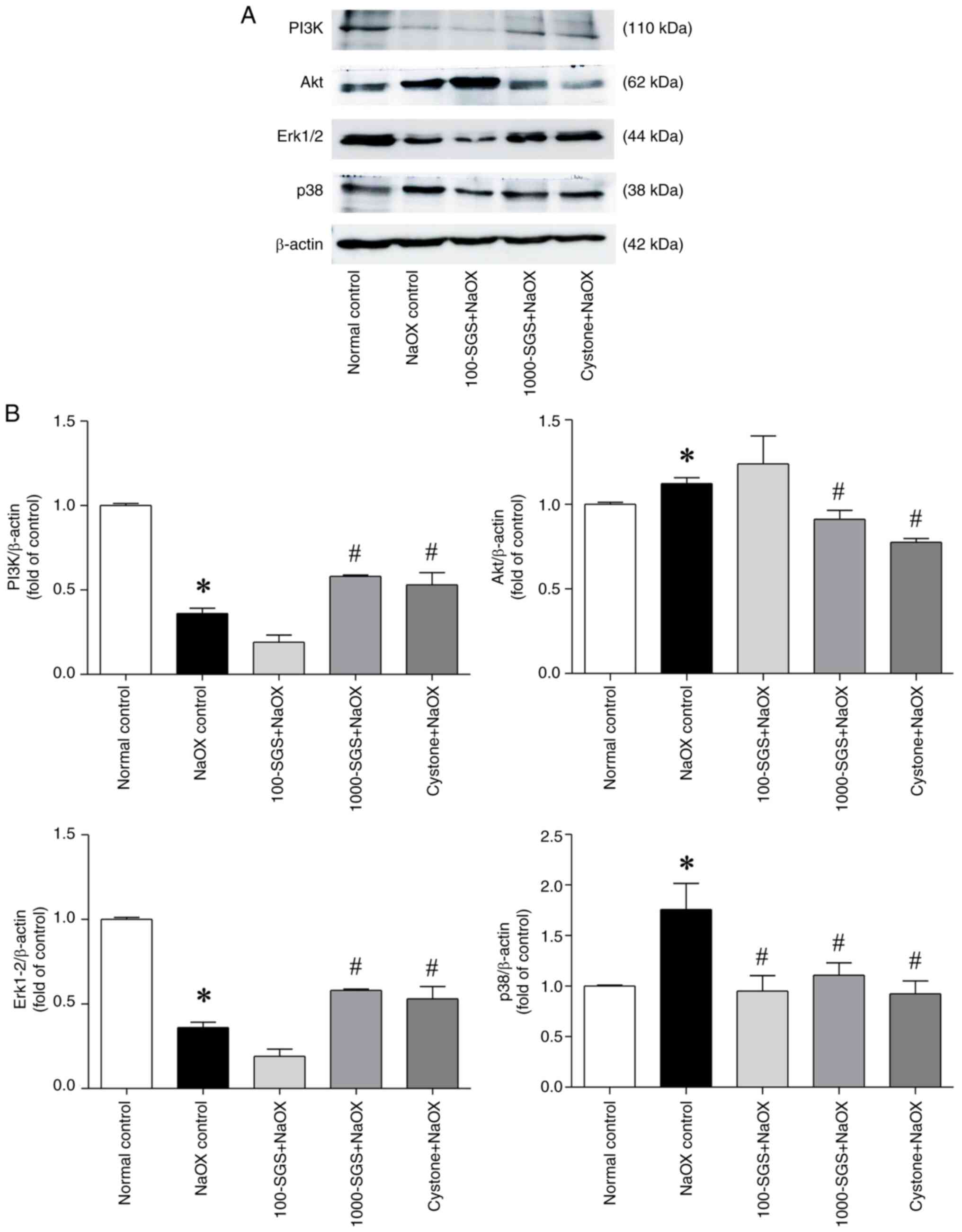
|
1
|
Yasui T, Okada A, Hamamoto S, Ando R,
Taguchi K, Tozawa K and Kohri K: Pathophysiology-based treatment of
urolithiasis. Int J Urol. 24:32–38. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pandhare RB, Shende RR, Avhad MS, Deshmukh
VK, Mohite PB, Sangameswaran B and Daude RB: Anti-urolithiatic
activity of Bryophyllum pinnatum Lam. hydroalcoholic extract
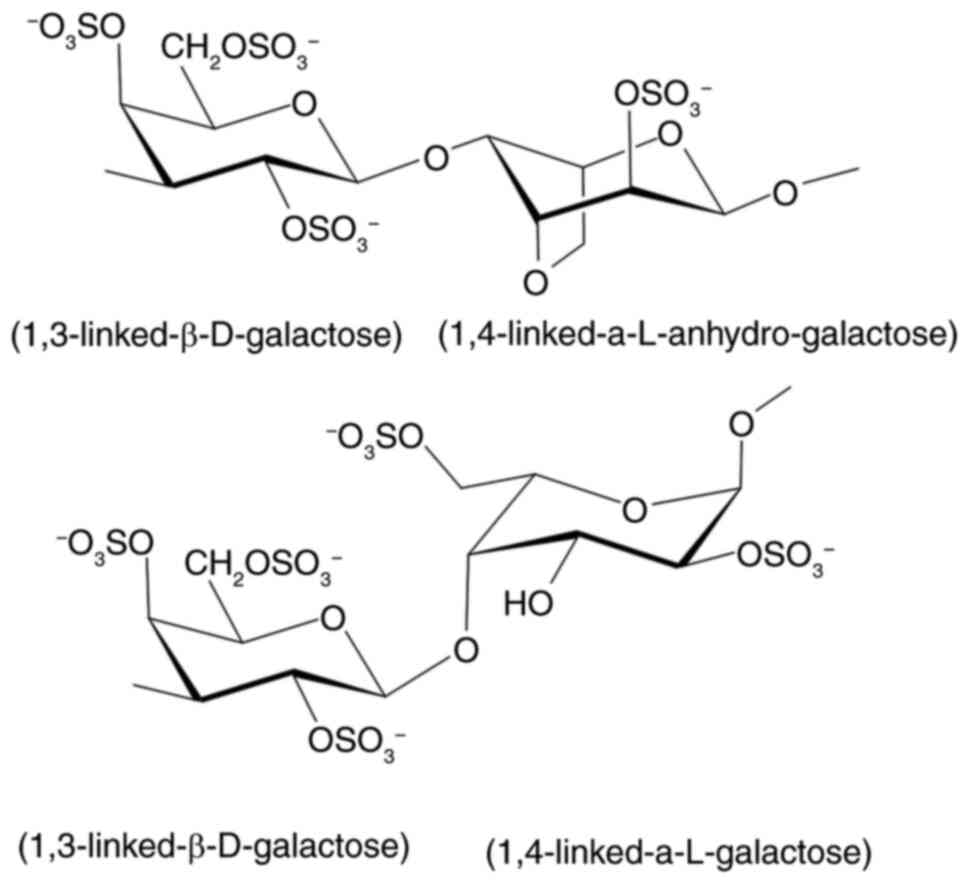
in sodium oxalate-induced urolithiasis in rats. J Tradit Complement
Med. 11:545–551. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Patel VB and Acharya N: Effect of
Macrotyloma uniflorum in ethylene glycol induced
urolithiasis in rats. Heliyon. 6(e04253)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Geraghty R, Wood K and Sayer JA: Calcium
oxalate crystal deposition in the kidney: Identification, causes
and consequences. Urolithiasis. 48:377–384. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Costa P, Blowes LM, Laly AC and Connelly
JT: Regulation of collective cell polarity and migration using
dynamically adhesive micropatterned substrates. Acta Biomater.
126:291–300. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yao W, Wang Z, Ma H, Lin Y, Liu X, Li P
and He X: Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity (EMP) in wound healing:
Exploring EMT mechanisms, regulatory network, and therapeutic
opportunities. Heliyon. 10(e34269)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jayne D, Herbert C, Anquetil V and
Teixeira G: Exploring the critical role of tight junction proteins
in kidney disease pathogenesis. Nephron. 149:240–250.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yu L, Gan X, Liu X and An R: Calcium
oxalate crystals induces tight junction disruption in distal renal
tubular epithelial cells by activating ROS/Akt/p38 MAPK signaling
pathway. Ren Fail. 39:440–451. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qi S, Wang Q, Xie B, Chen Y, Zhang Z and
Xu Y: P38 MAPK signaling pathway mediates COM crystal-induced
crystal adhesion change in rat renal tubular epithelial cells.
Urolithiasis. 48:9–18. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu RN, Zou DM, Tian MY, Li K, Du JL, Liu
MJ and Ma YZ: Effect of magnesium ammonium phosphate on the
expression of adhesion molecules in sheep renal tubular epithelial
cells. Res Vet Sci. 138:167–177. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sayed AA, Soliman A.M, Fahmy SR and Hosny
R: Antiurolithiatic effect of a polyherbal formulation against
sodium oxalate-induced urolithiasis in rats. J Basic Appl Zool.
84(15)2023.
|
|
12
|
Gopika S, Nisha MK, Gaayathiri Devi E,
Raja Rajeswari A and Vasandhlakshmi R: Evaluation of
antiurolithiatic potential of methanolic stem extract of
Spermacocce articularis L.f.: An in vitro and in vivo
approach. Pharmacogn J. 16:770–778. 2024.
|
|
13
|
Wongprasert K, Rudtanatip T and Praiboon
J: Immunostimulatory activity of sulfated galactans isolated from
the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri and development of resistance
against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish
Immunol. 36:52–60. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rudtanatip T, Pariwatthanakun C, Somintara
S, Sakaew W and Wongprasert K: Structural characterization,
antioxidant activity, and protective effect against hydrogen
peroxide-induced oxidative stress of chemically degraded Gracilaria
fisheri sulfated galactans. Int J Biol Macromol. 206:51–63.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rudtanatip T, Somintara S, Sakaew W,
El-Abid J, Cano ME, Jongsomchai K, Wongprasert K and Kovensky J:
Sulfated galactans from Gracilaria fisheri with supplementation of
octanoyl promote wound healing activity in vitro and in vivo.
Macromol Biosci. 22(e2200172)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sakaew W, Phanphak J, Somintara S, Hipkaeo
W, Wongprasert K, Kovensky J, Pariwatthanakun C and Rudtanatip T:
Increased sulfation in Gracilaria fisheri sulfated galactans
enhances antioxidant and antiurolithiatic activities and protects
HK-2 cell death induced by sodium oxalate. Mar Drugs.
20(382)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sheng GJ, Oh YI, Chang SK and Hsieh-Wilson
LC: Tunable heparan sulfate mimetics for modulating chemokine
activity. J Am Chem Soc. 135:10898–10901. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zaporozhets T and Besednova N: Prospects
for the therapeutic application of sulfated polysaccharides of
brown algae in diseases of the cardiovascular system: Review. Pharm
Biol. 54:3126–3135. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sae-Lao T, Luplertlop N, Janvilisri T,
Tohtong R, Bates DO and Wongprasert K: Sulfated galactans from the
red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri exerts anti-migration effect on
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Phytomedicine. 36:59–67. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liang KH, Tso HC, Hung SH, Kuan II, Lai
JK, Ke FY, Chuang YT, Liu IJ, Wang YP, Chen RH and Wu HC:
Extracellular domain of EpCAM enhances tumor progression through
EGFR signaling in colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 433:165–175.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Brown TC, Sankpal NV and Gillanders WE:
Functional implications of the dynamic regulation of EpCAM during
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomolecules.
11(956)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Erickson SB, Vrtiska TJ and Lieske JC:
Effect of Cystone® on urinary composition and stone
formation over a one year period. Phytomedicine. 18:863–867.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Singh A, Tandon S, Kaur T and Tandon C: In
vitro studies on calcium oxalate induced apoptosis attenuated by
Didymocarpus pedicellata. Biointerface Res Appl Chem.
12:7342–7355. 2022.
|
|
24
|
González Mosquera DM, Ortega YH, Quero PC,
Martínez RS and Luc Pieters L: Antiurolithiatic activity of
Boldoa purpurascens aqueous extract: An in vitro and in vivo
study. J Ethnopharmacol. 253(112691)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang H, Gao L, Zhao C, Fang F, Liu J, Wang
Z, Zhong Y and Wang X: The role of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in
chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol. 56:2623–2633.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kang J, Jia X, Wang N, Xiao M, Song S, Wu
S, Li Z, Wang S, Cui SW and Guo Q: Insights into the
structure-bioactivity relationships of marine sulfated
polysaccharides: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 123(107049)2022.
|
|
28
|
De Araújo L, Costa-Pessoa JM, de Ponte MC
and Oliveira-Souza M: Sodium oxalate-induced acute kidney injury
associated with glomerular and tubulointerstitial damage in rats.
Front Physiol. 11(1076)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ji Y, Fang S, Yang Y and Wu Z:
Inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling contributes to the
epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by sodium oxalate in canine
renal epithelial cells. J Anim Sci. 99:1–10. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Uwaezuoke SN: The role of adhesion
molecules in nephropathies: The diagnostic applications. Integr Mol
Med. 6:1–5. 2019.
|
|
31
|
Hu Q, Saleem K, Pandey J, Charania AN,
Zhou Y and He C: Cell adhesion molecules in fibrotic diseases.
Biomedicines. 11(1995)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Peerapen P and Thongboonkerda V: p38 MAPK
mediates calcium oxalate crystal-induced tight junction disruption
in distal renal tubular epithelial cells. Sci Rep.
3(1041)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tsuji H, Shimizu N, Nozawa M, Umekawa T,
Yoshimura K, De Velasco MA, Uemura H and Khan SR: Osteopontin
knockdown in the kidneys of hyperoxaluric rats leads to reduction
in renal calcium oxalate crystal deposition. Urolithiasis.
42:195–202. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Senbanjo LT and Chellaiah MA: CD44: A
multifunctional cell surface adhesion receptor is a regulator of
progression and metastasis of cancer cells. Front Cell Dev Biol.
5(18)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jordan AR, Racine RR, Hennig MJP and
Lokeshwar VB: The role of CD44 in disease pathophysiology and
targeted treatment. Front Immunol. 6(182)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hong SY and Qin BL: The protective role of
dietary polyphenols in urolithiasis: Insights into antioxidant
effects and mechanisms of action. Nutrients.
15(3753)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yasir F, Wahab AT and Choudhary MI:
Protective effect of dietary polyphenol caffeic acid on ethylene
glycol-induced kidney stones in rats. Urolithiasis. 46:157–166.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Zhanga J, Liu H, Yuan J, Yin Y, Wang
T, Cheng B, Sun S and Guo Z: Curcumin ameliorates
glyoxylate-induced calcium oxalate deposition and renal injuries in
mice. Phytomedicine. 61(152861)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Peerapen P and Thongboonkerd V: Protective
roles of trigonelline against oxalate-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial
cells: An in vitro study. Food Chem Toxicol.
135(110915)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang Z, Li MX, Xu CZ, Zhang Y, Deng Q, Sun
R, Hu QY, Zhang SP, Zhang JW and Liang H: Comprehensive study of
altered proteomic landscape in proximal renal tubular epithelial
cells in response to calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals. BMC
Urol. 20(136)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sun XY, Xu M and Ouyang JM: Effect of
crystal shape and aggregation of calcium oxalate monohydrate on
cellular toxicity in renal epithelial cells. ACS Omega.
2:6039–6052. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bonnici L, Suleiman S, Schembri-Wismayer P
and Cassar A: Targeting signalling pathways in chronic wound
healing. Int J Mol Sci. 25(50)2024.
|
|
43
|
Sun C, Liu M, Sun P, Yang M, Yates EA, Guo
Z and Fernig DG: Sulfated polysaccharides interact with fibroblast
growth factors and protect from denaturation. FEBS Open Bio.
9:1477–1487. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Huang L, Shen M, Morris GA and Xie J:
Sulfated polysaccharides: Immunomodulation and signaling
mechanisms. Trends Food Sci Technol. 92:1–11. 2019.
|
|
45
|
Song Q, Song C, Chen X, Xiong Y, He Z, Su
X, Zhou J, Ke H, Dong C, Liao W and Yang S: Oxalate regulates
crystal-cell adhesion and macrophage metabolism via JPT2/PI3K/AKT
signaling to promote the progression of kidney stones. J Pharm
Anal. 14(100956)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lee S, Kim MS, Jung SJ, Kim D, Park HJ and
Cho D: ERK activating peptide, AES16-2M promotes wound healing
through accelerating migration of keratinocytes. Sci Rep.
8(14398)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kasowanjete P, Kumar SSD and Houreld NN: A
review of photobiomodulation on PI3K/AKT/mTOR in wound healing. J
Photochem Photobiol. 19(100215)2024.
|
|
48
|
Ashraf R and Kumar S: Mfn2-mediated
mitochondrial fusion promotes autophagy and suppresses ovarian
cancer progression by reducing ROS through AMPK/mTOR/ ERK
signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 79(573)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Guzel A, Yunusoglu S, Calapoglu M, Candan
IA, Onaran I, Oncu M, Ergun O and Oksay T: Protective effects of
quercetin on oxidative stress-induced tubular epithelial damage in
the experimental rat hyperoxaluria model. Medicina.
57(566)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jing GH, Liu YD, Liu JN, Jin YS, Yu SL and
An RH: Puerarin prevents calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal
epithelial cell autophagy by activating the SIRT1-mediated
signaling pathway. Urolithiasis. 50:545–556. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wang Y, Zheng J, Han Y, Zhang Y, Su L, Hu
D and Fu X: JAM-A knockdown accelerates the proliferation and
migration of human keratinocytes, and improves wound healing in
rats via FAK/Erk signaling. Cell Death Dis. 9(848)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|