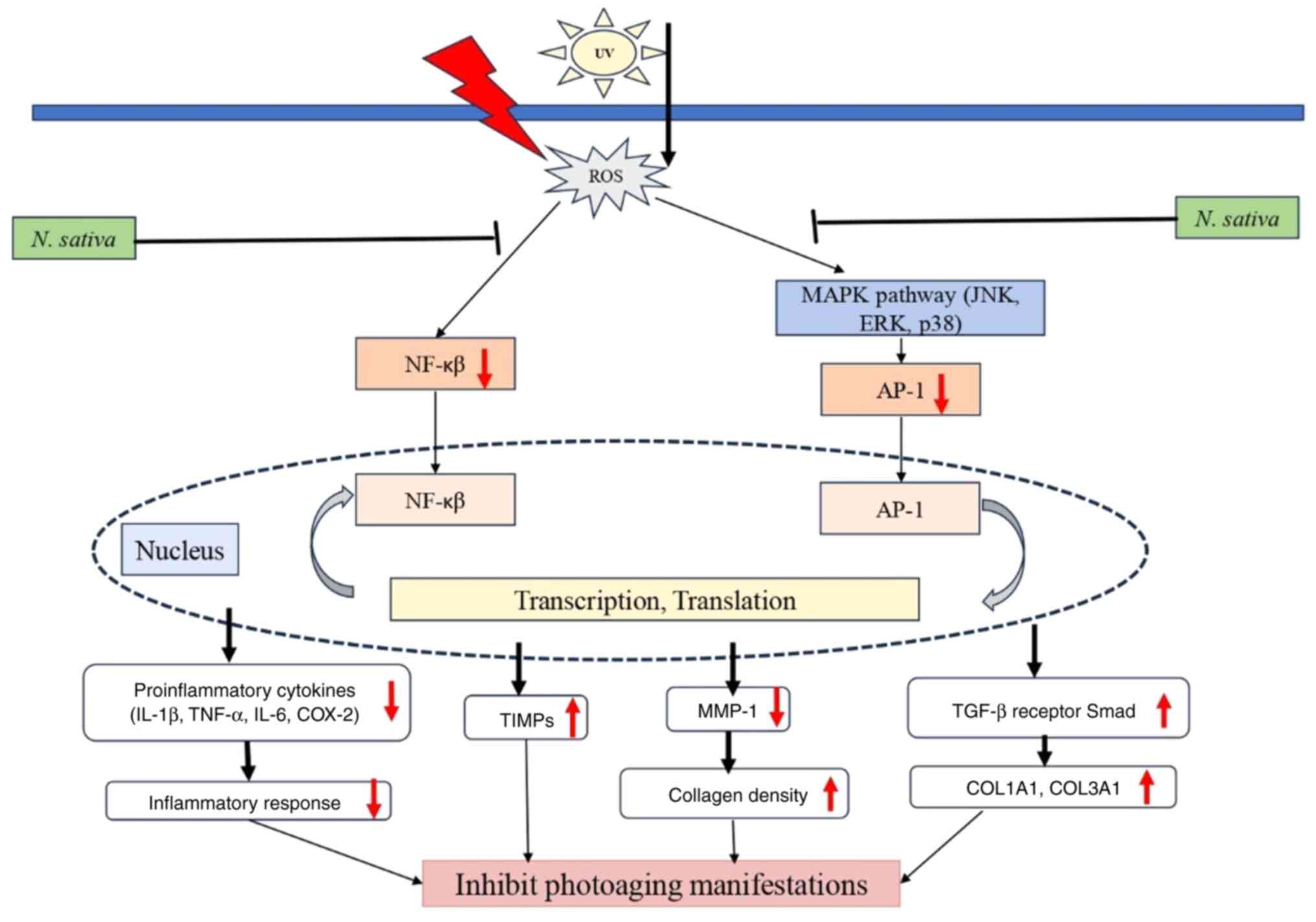
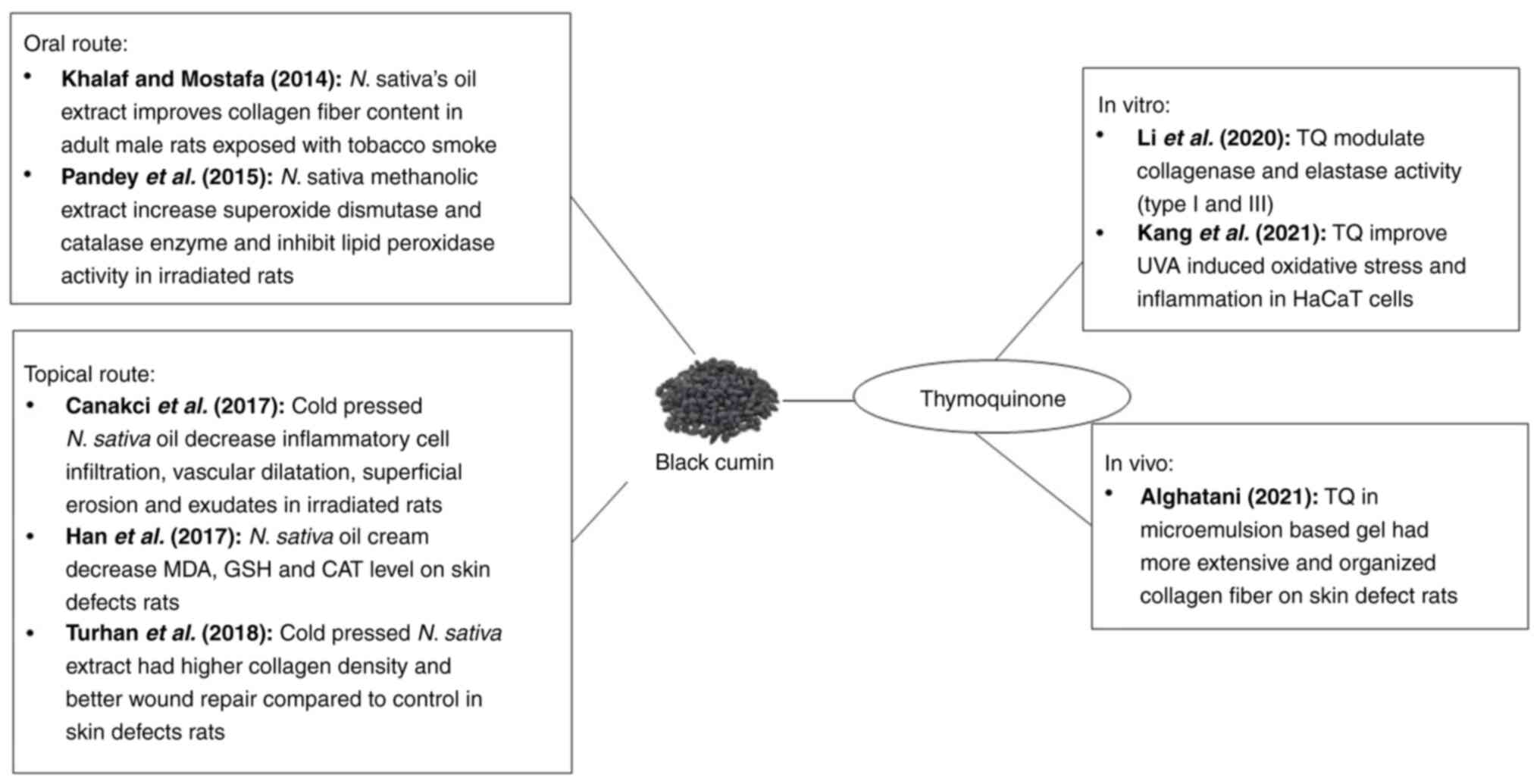
|
1
|
Mohiuddin AK: Skin aging & modern age
anti-aging strategies. Glob J Med Res. 7:15–60. 2019.
|
|
2
|
Li H, DaSilva NA, Liu W, Xu J, Dombi GW,
Dain JA, Li D, Chamcheu JC, Seeram NP and Ma H:
Thymocid®, a standardized black cumin (Nigella
sativa) seed extract, modulates collagen cross-linking,
collagenase and elastase activities, and melanogenesis in murine
B16F10 melanoma cells. Nutrients. 12(2146)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hwang E, Lee TH, Park SY, Yi TH and Kim
SY: Enzyme-modified Panax ginseng inhibits UVB-induced skin aging
through the regulation of procollagen type I and MMP-1 expression.
Food Funct. 5:265–274. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tu Y and Quan T: Oxidative stress and
human skin connective tissue aging. Cosmetics. 3(28)2016.
|
|
5
|
Ahmed OM and Mohammed MT: Oxidative
stress: The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants
in human diseases. Plant Arch. 20:4089–4095. 2020.
|
|
6
|
Ardiana M, Pikir BS, Santoso A, Hermawan
HO and Al-Farabi MJ: Effect of Nigella sativa
supplementation on oxidative stress and antioxidant parameters: A
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2020(2390706)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sudhir SP, Deshmukh VO and Verma HN:
Nigella sativa seed, a novel beauty care ingredient: A
review. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 7:3185–3196. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Adam GO and Shuaib YA: Antioxidant and
anti-tyrosinase potentials of extracts of Nigella sativa and
Senna alexandrina from sudan. J Appl Vet Sci. 7:41–45. 2022.
|
|
9
|
Shahroudi MJ, Mehri S and Hosseinzadeh H:
Anti-aging effect of Nigella sativa fixed oil on
D-galactose-induced aging in mice. J Pharmacopuncture. 20:29–35.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liang J, Lian L, Wang X and Li L:
Thymoquinone, extract from Nigella sativa seeds, protects
human skin keratinocytes against UVA-irradiated oxidative stress,
inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Mol Immunol. 135:21–27.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rizaoglu T: Effects of ozonated oils
(sesame oil, Nigella sativa oil, and hypericium perforatum
oil) on wound healing process in rats. Gov Polit Contemp Middle
East Contin Chang, pp77-116, 2018.
|
|
12
|
Huang AH and Chien AL: Photoaging: A
review of current literature. Curr Dermatol Rep. 9:22–29.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Krutmann J, Schikowski T, Morita A and
Berneburg M: Environmentally-induced (extrinsic) skin aging:
Exposomal factors and underlying mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol.
141:1096–1103. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee LY and Liu SX: Pathogenesis of
photoaging in human dermal fibroblasts. Int J Dermatol Venereol.
3:37–42. 2022.
|
|
15
|
Venkatesh S, Maymone MBC and Vashi NA:
Aging in skin of color. Clin Dermatol. 37:351–357. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Karim PL, Aryani IA and Nopriyati :
Anatomy and histologic of intrinsic aging skin. Biosci Med J Biomed
Transl Res. 5:1065–1077. 2021.
|
|
17
|
Tobin DJ: Introduction to skin aging. J
Tissue Viability. 26:37–46. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sachs DL, Varani J, Chubb H, Fligiel SEG,
Cui Y, Calderone K, Helfrich Y, Fisher GJ and Voorhees JJ: Atrophic
and hypertrophic photoaging: Clinical, histologic, and molecular
features of 2 distinct phenotypes of photoaged skin. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 81:480–488. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tanveer MA, Rashid H and Tasduq SA:
Molecular basis of skin photoaging and therapeutic interventions by
plant-derived natural product ingredients: A comprehensive review.
Heliyon. 9(e13580)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cao C, Xiao Z, Wu Y and Ge C: Diet and
skin aging-from the perspective of food nutrition. Nutrients.
12(870)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cho S: Pathogenesis and prevention of skin
aging. J Korean Med Assoc. 64:438–446. 2021.
|
|
22
|
Mohania D, Chandel S, Kumar P, Verma V,
Digvijay K, Tripathi D, Choudhury K, Mitten SK and Shah D:
Ultraviolet radiations: Skin defense-damage mechanism. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 996:71–87. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Roy C and Gies P: Ultraviolet light and
short-term hazards to the skin and eyes. Wiley Online Libr.
3:47–66. 2017.
|
|
24
|
Chen X, Yang C and Jiang G: Research
progress on skin photoaging and oxidative stress. Postepy Dermatol
Alergol. 38:931–936. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Teng Y, Yu Y, Li S, Huang Y, Xu D, Tao X
and Fan Y: Ultraviolet radiation and basal cell carcinoma: An
environmental perspective. Front Public Health.
9(666528)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Furukawa JY, Martinez RM, Morocho-Jácome
AL, Castillo-Gómez TS, Pereda-Contreras VJ, Rosado C, Velasco MVR
and Baby AR: Skin impacts from exposure to ultraviolet, visible,
infrared, and artificial lights-a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther.
23:1–7. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pittayapruek P, Meephansan J, Prapapan O,
Komine M and Ohtsuki M: Role of matrix metalloproteinases in
photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
17(868)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bernard JJ, Gallo RL and Krutmann J:
Photoimmunology: How ultraviolet radiation affects the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 19:688–701. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chambers ES and Vukmanovic-Stejic M: Skin
barrier immunity and ageing. Immunology. 160:116–125.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hart PH, Norval M, Byrne SN and Rhodes LE:
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation in the modulation of human
diseases. Annu Rev Pathol. 14:55–81. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gromkowska-Kępka KJ, Puścion-Jakubik A,
Markiewicz-Żukowska R and Socha K: The impact of ultraviolet
radiation on skin photoaging-review of in vitro studies. J Cosmet
Dermatol. 20:3427–3431. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mirończuk-Chodakowska I, Witkowska AM and
Zujko ME: Endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidants in the human body.
Adv Med Sci. 63:68–78. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Costantini D: Understanding diversity in
oxidative status and oxidative stress: The opportunities and
challenges ahead. J Exp Biol. 222(jeb194688)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
De Jager TL, Cockrell AE and Du Plessis
SS: Ultraviolet light induced generation of reactive oxygen
species. Adv Exp Med Biol. 996:15–23. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cavinato M and Jansen-Dürr P: Molecular
mechanisms of UVB-induced senescence of dermal fibroblasts and its
relevance for photoaging of the human skin. Exp Gerontol. 94:78–82.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rajendran P, Alzahrani AM, Hanieh HN,
Kumar SA, Ben Ammar R, Rengarajan T and Alhoot MA: Autophagy and
senescence: A new insight in selected human diseases. J Cell
Physiol. 234:21485–21492. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Evas O: The role of reactive oxygen
species and antioxidants in oxidative stress. Int J Res Pharm
Biosci. 56:433–437. 2016.
|
|
38
|
Madkour LH: Function of reactive oxygen
species (ROS) inside the living organisms and sources of oxidants.
Pharm Sci Anal Res J. 2(180023)2019.
|
|
39
|
Ighodaro OM and Akinloye OA: First line
defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and
glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire
antioxidant defence grid. Alexandria J Med. 54:287–293. 2018.
|
|
40
|
Galaris D, Barbouti A and Pantopoulos K:
Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: An intimate relationship.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866(118535)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Gu Y, Han J, Jiang C and Zhang Y:
Biomarkers, oxidative stress and autophagy in skin aging. Ageing
Res Rev. 59(101036)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Davinelli S, Bertoglio JC, Polimeni A and
Scapagnini G: Cytoprotective polyphenols against chronological skin
aging and cutaneous photodamage. Curr Pharm Des. 24:99–105.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cho BA, Yoo SK and Seo JS: Signatures of
photo-aging and intrinsic aging in skin were revealed by
transcriptome network analysis. Aging (Albany NY). 10:1609–1626.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shukla A and Mossman BT: Chapter 9 cell
signaling by oxidants: Pathways leading to activation of
mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and activator protein-1
(AP-1). Curr Top Membr. 61:191–209. 2008.
|
|
45
|
Singh D, Rai V and K Agrawal DK:
Regulation of collagen I and collagen III in tissue injury and
regeneration. Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 7:5–16. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang Y, Wang L, Wen X, Hao D, Zhang N, He
G and Jiang X: NF-κB signaling in skin aging. Mech Ageing Dev.
184(111160)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Pourzand C, Albieri-Borges A and Raczek
NN: Shedding a new light on skin aging, iron-and redox-homeostasis
and emerging natural antioxidants. Antioxidants (Basel).
11(471)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gendrisch F, Esser PR, Schempp CM and
Wölfle U: Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation.
Biofactors. 47:170–180. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ke Y and Wang XJ: TGFβ signaling in
photoaging and UV-induced skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol.
141:1104–1110. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ansary TM, Hossain MR, Kamiya K, Komine M
and Ohtsuki M: Inflammatory molecules associated with ultraviolet
radiation-mediated skin aging. Int J Mol Sci.
22(3974)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Cui N, Hu M and Khalil RA: Biochemical and
biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. 1st edition
Elsevier Inc., 2017.
|
|
53
|
Laronha H and Caldeira J: Structure and
function of human matrix metalloproteinases. Cells.
9(1076)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zorina A, Zorin V, Kudlay D and Kopnin P:
Molecular mechanisms of changes in homeostasis of the dermal
extracellular matrix: Both involutional and mediated by ultraviolet
radiation. Int J Mol Sci. 23(6655)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Riihilä P, Nissinen L and Kähäri VM:
Matrix metalloproteinases in keratinocyte carcinomas. Exp Dermatol.
30:50–61. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Shin JW, Kwon SH, Choi JY, Na JI, Huh CH,
Choi HR and Park KC: Molecular mechanisms of dermal aging and
antiaging approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2126)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yue J and López JM: Understanding MAPK
signaling pathways in apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci.
21(2346)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Cole MA, Quan T, Voorhees JJ and Fisher
GJ: Extracellular matrix regulation of fibroblast function:
Redefining our perspective on skin aging. J Cell Commun Signal.
12:35–43. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Rogowski-Tylman M, Narbutt J, Woźniacka A
and Lesiak A: Molecular aspects of skin aging. Literature review.
Przegl Dermatol. 103:139–142. 2016.
|
|
60
|
Kanigur Sultuybek G, Soydas T and Yenmis
G: NF-κB as the mediator of metformin's effect on ageing and
ageing-related diseases. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46:413–422.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Cheng W, Yan-Hua R, Fang-Gang N and Guo-An
Z: The content and ratio of type I and III collagen in skin differ
with age and injury. Afr J Biotechnol. 10:2524–2529. 2011.
|
|
62
|
Hwang SJ, Kim SH, Seo WY, Jeong Y, Shin
MC, Ryu D, Lee SB, Choi YJ and Kim KJ: Effects of human collagen
α-1 type I-derived proteins on collagen synthesis and elastin
production in human dermal fibroblasts. BMB Rep. 54:329–334.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Naomi R, Ridzuan PM and Bahari H: Current
insights into collagen type I. Polymers (Basel).
13(2642)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Fligiel SEG, Varani J, Datta SC, Kang S,
Fisher GJ and Voorhees JJ: Collagen degradation in
aged/photodamaged skin in vivo and after exposure to matrix
metalloproteinase-1 in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 120:842–848.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Yilmaz ÖÖ, Polat T, Tacal Aslan B and
Ulucan K: Can skin aging be reversible by anti-aging treatments
with genetic analysis? İstanbul Gelişim Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilim
Derg. 21:1242–1250. 2023.
|
|
66
|
Devos H, Zoidakis J, Roubelakis MG,
Latosinska A and Vlahou A: Reviewing the regulators of COL1A1. Int
J Mol Sci. 24(10004)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Yamaba H, Haba M, Kunita M, Sakaida T,
Tanaka H, Yashiro Y and Nakata S: Morphological change of skin
fibroblasts induced by UV Irradiation is involved in photoaging.
Exp Dermatol. 25 (Suppl 3):S45–S51. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Balasubramanian P, Prabhakaran MP,
Sireesha M and Ramakrishna S: Collagen in human tissues: Structure,
function, and biomedical implications from a tissue engineering
perspective. Adv Polym Sci. 251(173)2013.
|
|
69
|
Derby B and Akhtar R: Mechanical
properties of aging soft tissues. Eng Mater Process. 10:237–263.
2015.
|
|
70
|
Biskanaki F, Kefala V, Lazaris AC and
Rallis E: Aging and the impact of solar ultraviolet radiation on
the expression of type I and type VI collagen. Cosmetics.
10(48)2023.
|
|
71
|
Liu H, Dong J, Du R, Gao Y and Zhao P:
Collagen study advances for photoaging skin. Photodermatol
Photoimmunol Photomed. 40(e12931)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Watson RE, Gibbs NK, Griffiths CE and
Sherratt MJ: Damage to skin extracellular matrix induced by UV
exposure. Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:1063–1077. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Svobodova A, Walterova D and Vostalova J:
Ultraviolet light induced alteration to the skin. Biomed Pap Med
Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 150:25–38. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Kamata H, Honda SI, Maeda S, Chang L,
Hirata H and Karin M: Reactive oxygen species promote
TNFalpha-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting
MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell. 120:649–661. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Calvo MJ, Navarro C, Durán P, Galan-Freyle
NJ, Parra Hernández LA, Pacheco-Londoño LC, Castelanich D, Bermúdez
V and Chacin M: Antioxidants in photoaging: From molecular insights
to clinical applications. Int J Mol Sci. 25(2403)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Liu Z, Li Y, Song H, He J, Li G, Zheng Y
and Li B: Collagen peptides promote photoaging skin cell repair by
activating the TGF-β/Smad pathway and depressing collagen
degradation. Food Funct. 10:6121–6134. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ahmad MF, Ahmad FA, Ashraf SA, Saad HH,
Wahab S, Khan MI, Ali M, Mohan S, Hakeem KR and Athar MT: An
updated knowledge of black seed (Nigella sativa Linn.):
Review of phytochemical constituents and pharmacological
properties. Elsevier GmbH, 2021.
|
|
78
|
Ahmad M, Khan A, Marwat K, Zafar M, Khan
MA, Hassan U and Sultana S: Useful medicinal flora enlisted in holy
quran and ahadith. Am J Agric Environ Sci. 5:126–140. 2009.
|
|
79
|
Hannan MA, Rahman MA, Sohag AAM, Uddin MJ,
Dash R, Sikder MH, Rahman MS, Timalsina B, Munni YA, Sarker PP, et
al: Black cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A comprehensive review
on phytochemistry, health benefits, molecular pharmacology, and
safety. Nutrients. 13(1784)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Dalli M, Bekkouch O, Azizi SE, Azghar A,
Gseyra N and Kim B: Nigella sativa l. phytochemistry and
pharmacological activities: A review (2019-2021). Biomolecules.
12(20)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Eisenman SW, Zaurov DE and Struwe L:
Medicinal plants of central asia: Uzbekistan and kyrgyzstan.
Springer New York, pp1-340, 2013.
|
|
82
|
Ramadan MF: Black cumin (Nigella
sativa) oils. Elsevier Inc., 2015.
|
|
83
|
Yimer E, Tuem KB, Karim A, Rehan N, Mariod
AA, Saeed Mirghani ME and Hussein I: Nigella sativa L.
(black cumin): A promising natural remedy for wide range of
illnesses. Hindawi Publ Corp. 2019:73–80. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Javed S, Shahid AA, Haider MS, Umeera A,
Ahmad R and Mushtaq S: Nutritional, phytochemical potential and
pharmacological evaluation of Nigella sativa (kalonji) and
trachyspermum ammi (Ajwain). J Med Plants Res. 6:768–775. 2012.
|
|
85
|
Majeed A, Muhammad Z, Ahmad H, Rehmanullah
Hayat SSS, Inayat N and Siyyar S: Nigella sativa L.: Uses in
traditional and contemporary medicines-an overview. Acta Ecol Sin.
41:253–258. 2021.
|
|
86
|
Hossain MS, Sharfaraz A, Dutta A, Ahsan A,
Masud MA, Ahmed IA, Goh BH, Urbi Z, Sarker MMR and Ming LC: A
review of ethnobotany, phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology
and toxicology of Nigella sativa L. Biomed Pharmacother.
143(112182)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Fatima Shad K, Soubra W and Cordato DJ:
The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of Nigella
sativa, in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious
diseases. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 48:1445–1453. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Rajabian A and Hosseinzadeh H:
Dermatological effects of Nigella sativa and its
constituent, thymoquinone: A review. Elsevier Inc., 2020.
|
|
89
|
Benazzouz-Smail L, Achat S, Brahmi F,
Bachir-Bey M, Arab R, Lorenzo JM, Benbouriche A, Boudiab K,
Hauchard D, Boulekbache L and Madani K: Biological properties,
phenolic profile, and botanical aspect of Nigella sativa L.
and Nigella damascena L. seeds: A comparative study. Molecules.
28(571)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Hwang JR, Cartron AM and Khachemoune A: A
review of Nigella sativa plant-based therapy in dermatology.
Int J Dermatol. 60:e493–e499. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Eid AM, Elmarzugi NA, Abu Ayyash LM,
Sawafta MN and Daana HI: A review on the cosmeceutical and external
applications of Nigella sativa. J Trop Med.
2017(7092514)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Santoso ARB, Huwae TECJ, Kristianto Y and
Putera MA: Effect of thymoquinone: the extract of Nigella
sativa in accelerating soft callus formation in fracture. Int J
Res Med Sci. 7:4068–4072. 2019.
|
|
93
|
Nyemb JN, Shaheen H, Wasef L, Nyamota R,
Segueni N and El-Saber Batiha G: Black Cumin: A review of its
pharmacological effects and its main active constituent. Pharmacogn
Rev. 16:107–125. 2022.
|
|
94
|
Ali BH and Blunden G: Pharmacological and
toxicological properties of Nigella sativa. Phyther Res.
14:299–305. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Mashayekhi-Sardoo H, Rezaee R and Karimi
G: An overview of in vivo toxicological profile of thymoquinone.
Toxin Rev. 39:115–122. 2020.
|
|
96
|
Thakur S, Kaurav H and Chaudhary G:
Nigella sativa (kalonji): A black seed of miracle. Int J Res
Rev. 8:342–357. 2021.
|
|
97
|
Rahim MA, Shoukat A, Khalid W, Ejaz A,
Itrat N, Majeed I, Koraqi H, Imran M, Nisa MU, Nazir A, et al: A
narrative review on various oil extraction methods, encapsulation
processes, fatty acid profiles, oxidative stability, and medicinal
properties of black seed (Nigella sativa). Foods.
11(2826)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Nasiri N, Ilaghi Nezhad M, Sharififar F,
Khazaneha M, Najafzadeh MJ and Mohamadi N: The therapeutic effects
of Nigella sativa on skin disease: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2022(7993579)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Kalus U, Pruss A, Bystron J, Jurecka M,
Smekalova A, Lichius JJ and Kiesewetter H: Effect of Nigella
sativa (black seed) on subjective feeling in patients with
allergic diseases. Phyther Res. 17:1209–1214. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Srinivasan K: Cumin (cuminum cyminum) and
black cumin (Nigella sativa) seeds: Traditional uses,
chemical constituents, and nutraceutical effects. Food Qual Saf.
2:1–16. 2018.
|
|
101
|
Darakhshan S, Bidmeshki Pour A,
Hosseinzadeh Colagar A and Sisakhtnezhad S: Thymoquinone and its
therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol Res. 95-96:138–158.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Modarresi Chahardehi A, Ojaghi HR,
Motedayyen H and Arefnezhad R: Nano-based formulations of
thymoquinone are new approaches for psoriasis treatment: A
literature review. Front Immunol. 15(1416842)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Chen WP, Tang JL, Bao JP and Wu LD:
Thymoquinone inhibits matrix metalloproteinase expression in rabbit
chondrocytes and cartilage in experimental osteoarthritis. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 235:1425–1431. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Rasheeda K, Samyuktha D and Fathima NN:
Self-association of type I collagen directed by thymoquinone
through alteration of molecular forces. Int J Biol Macromol.
140:614–620. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Ghorbanibirgani A, Khalili A and
Rokhafrooz D: Comparing Nigella sativa oil and fish oil in
treatment of vitiligo. Iran Red Crescent Med J.
16(e4515)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Yousefi M, Barikbin B, Kamalinejad M,
Abolhasani E, Ebadi A, Younespour S, Manouchehrian M and Hejazi S:
Comparison of therapeutic effect of topical Nigella with
Betamethasone and Eucerin in hand eczema. J Eur Acad Dermatol
Venereol. 27:1498–1504. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Michalak M: Plant-derived antioxidants:
Significance in skin health and the ageing process. Int J Mol Sci.
23(585)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Rivera-Yañez CR, Ruiz-Hurtado PA,
Mendoza-Ramos MI, Reyes-Reali J, García-Romo GS, Pozo-Molina G,
Reséndiz-Albor AA, Nieto-Yañez O, René Méndez-Cruz A, Méndez-Catalá
CF and Rivera-Yañez N: Flavonoids present in propolis in the battle
against photoaging and psoriasis. Antioxidants (Basel).
10(2014)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Singh Joshan D and Singh SK:
Investigational study of juglans regia extract and quercetin
against photoaging. Biomed Aging Pathol. 3:193–200. 2013.
|
|
110
|
Sim GS, Lee BC, Cho HS, Lee JW, Kim JH,
Lee DH, Kim JH, Pyo HB, Moon DC, Oh KW, et al: Structure activity
relationship of antioxidative property of flavonoids and inhibitory
effect on matrix metalloproteinase activity in UVA-irradiated human
dermal fibroblast. Arch Pharm Res. 30:290–298. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
He X, Wan F, Su W and Xie W: Research
progress on skin aging and active ingredients. Molecules.
28(5556)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Hatahet T, Morille M, Hommoss A,
Devoisselle JM, Müller RH and Bégu S: Quercetin topical
application, from conventional dosage forms to nanodosage forms.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 108:41–53. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Choi HJ, Alam MB, Baek ME, Kwon YG, Lim JY
and Lee SH: Protection against UVB-induced photoaging by Nypa
fruticans via inhibition of MAPK/AP-1/MMP-1 signaling. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2020(2905362)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Maghsoudloo M, Aliakbari RBS and Velisdeh
ZJ: Pharmaceutical, nutritional, and cosmetic potentials of
saponins and their derivatives. Nano Micro Biosyst. 2:1–6.
2023.
|
|
115
|
Cavinato M, Waltenberger B, Baraldo G,
Grade CVC, Stuppner H and Jansen-Dürr P: Plant extracts and natural
compounds used against UVB-induced photoaging. Biogerontology.
18:499–516. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Keskin Çavdar H: Active compounds, health
effects, and extraction of unconventional plant seed oils. In:
Plant and Human Health. Ozturk M and Hakeem K (eds). Vol 2.
Springer, Cham, pp245-285, 2019.
|
|
117
|
Sarkhail P, Esmaily H, Baghaei A, Shafiee
A, Abdollahi M, Khademi Y, Madandar M and Sarkheil P: Burn healing
potential of Nigella sativa seed oil in rats. Int J Pharm
Sci Res. 2:34–40. 2011.
|
|
118
|
Pavlou P, Siamidi A, Varvaresou A and
Vlachou M: Skin care formulations and lipid carriers as skin
moisturizing agents. Cosmetics. 8(89)2021.
|
|
119
|
Choi HJ, Song BR, Kim JE, Bae SJ, Choi YJ,
Lee SJ, Gong JE, Lee HS, Lee CY, Kim BH and Hwang DY: Therapeutic
effects of cold-pressed perilla oil mainly consisting of linolenic
acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid on UV-induced photoaging in NHDF
cells and SKH-1 hairless mice. Molecules. 25(989)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Borkow G: Using copper to improve the
well-being of the skin. Curr Chem Biol. 8:89–102. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Prasad AS: Zinc is an antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory agent: Its role in human health. Front Nutr.
1(14)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Polefka TG, Bianchini RJ and Shapiro S:
Interaction of mineral salts with the skin: A literature survey.
Int J Cosmet Sci. 34:416–423. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Azab AE, Adwas A, Elsayed ASI, Adwas AA,
Elsayed ASI, Azab AE and Quwaydir FA: Oxidative stress and
antioxidant mechanisms in human body. J Appl Biotechnol Bioeng.
6:43–47. 2019.
|
|
124
|
Kaymak E, Ceylan T, Akın T, Kuloğlu N,
Sayan M, Değer N, Önal E, Yildirim AB and Karabulut D: Effect of
thymoquinone on NRF2/NF-kB/MAPK pathway in methotrexate-induced rat
testis injury. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 27:1410–1416. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Nguyen CH, Senfter D, Basilio J, Holzner
S, Stadler S, Krieger S, Huttary N, Milovanovic D, Viola K,
Simonitsch-Klupp I, et al: NF-κB contributes to MMP1 expression in
breast cancer spheroids causing paracrine PAR1 activation and
disintegrations in the lymph endothelial barrier in vitro.
Oncotarget. 6:39262–39275. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Pardo A and Selman M: MMP-1: The elder of
the family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:283–288. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Stratigos AJ and Katsambas AD: The role of
topical retinoids in the treatment of photoaging. Drugs.
65:1061–1072. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Farris PK: Topical vitamin C: A useful
agent for treating photoaging and other dermatologic conditions.
Dermatol Surg. 31:814–818. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Correia G and Magina S: Efficacy of
topical vitamin C in melasma and photoaging: A systematic review. J
Cosmet Dermatol. 22:1938–1945. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Thielitz A and Gollnick H: Topical
retinoids in acne vulgaris: Update on efficacy and safety. Am J
Clin Dermatol. 9:369–381. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Pandey N, Kumar M, Pradhan S, Mandal A and
Tripathi YB: Effect of methanolic fraction of the seeds of
Nigella sativa linn on radiation induced Gi damage in rats.
Sciforschen. 10:1–5. 2015.
|
|
132
|
Çanakci H, Yilmaz AAŞ, Canpolat MS,
Şeneldir H, Kir G, Eriş AH, Mayadagli A and Oysu Ç: Evaluation of
the effect of topical application of Nigella sativa on acute
radiation-induced nasal mucositis. J Craniofac Surg. 29:e279–e282.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Turhan Y, Arican M, Karaduman ZO, Turhal
O, Gamsizkan M, Aydin D and Ozkan K: Comparison of the effects of
Nigella sativa oil and nano-silver on wound healing in an
experimental rat model. Iran Red Cresent Med J. 21(e84650)2019.
|
|
134
|
Algahtani MS, Ahmad MZ, Shaikh IA,
Abdel-Wahab BA, Nourein IH and Ahmad J: Thymoquinone loaded topical
nanoemulgel for wound healing: Formulation design and in-vivo
evaluation. Molecules. 26(3863)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Khatoon M, Kushwaha P, Usmani S and Madan
K: Dermaceutical utilization of Nigella sativa seeds:
Applications and opportunities. Drug Res (Stuttg). 74:5–17.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Balyan P, Khan J and Ali A: Therapeutic
potential of Nigella sativa in the prevention of aggregation
and glycation of proteins. In: Black Seeds (Nigella sativa).
Khan A and Rehman M (eds). Elsevier, pp313-336, 2022.
|
|
137
|
Sun Z, Park SY, Hwang E, Zhang M, Seo SA,
Lin P and Yi TH: Thymus vulgaris alleviates UVB irradiation induced
skin damage via inhibition of MAPK/AP-1 and activation of Nrf2-ARE
antioxidant system. J Cell Mol Med. 21:336–348. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Yadav DK, Kumar S, Saloni Misra S, Yadav
L, Teli M, Sharma P, Chaudhary S, Kumar N, Choi EH, et al:
Molecular insights into the interaction of RONS and
thieno[3,2-C]pyran analogs with SIRT6/COX-2: A molecular dynamics
study. Sci Rep. 8(4777)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Shabeeb D, Musa AE, Ali HSA and Najafi M:
Curcumin protects against radiotherapy-induced oxidative injury to
the skin. Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:3159–3163. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Khalaf G and Mostafa HKK: Histological and
immunohistochemical study on the effect of passive smoking on the
skin of adult male albino rats and the possible protective role of
Nigella sativa oil. Egypt J Histol. 35:87–94. 2012.
|
|
141
|
Lee H, Hong Y and Kim M: Structural and
functional changes and possible molecular mechanisms in aged skin.
Int J Mol Sci. 22(12489)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Han MC, Durmuş AS, Sağliyan A, Günay C,
Özkaraca M, Kandemir FM, Çomakli S and Firat Öztopalan D: Effects
of Nigella sativa and hypericum perforatum on wound healing.
Turkish J Vet Anim Sci. 41:99–105. 2017.
|
|
143
|
Khatoon K, Ali A, Ahmad FJ, Hafeez Z,
Rizvi MMA, Akhter S and Beg S: Novel nanoemulsion gel containing
triple natural bio-actives combination of curcumin, thymoquinone,
and resveratrol improves psoriasis therapy: In vitro and in vivo
studies. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 11:1245–1260. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|