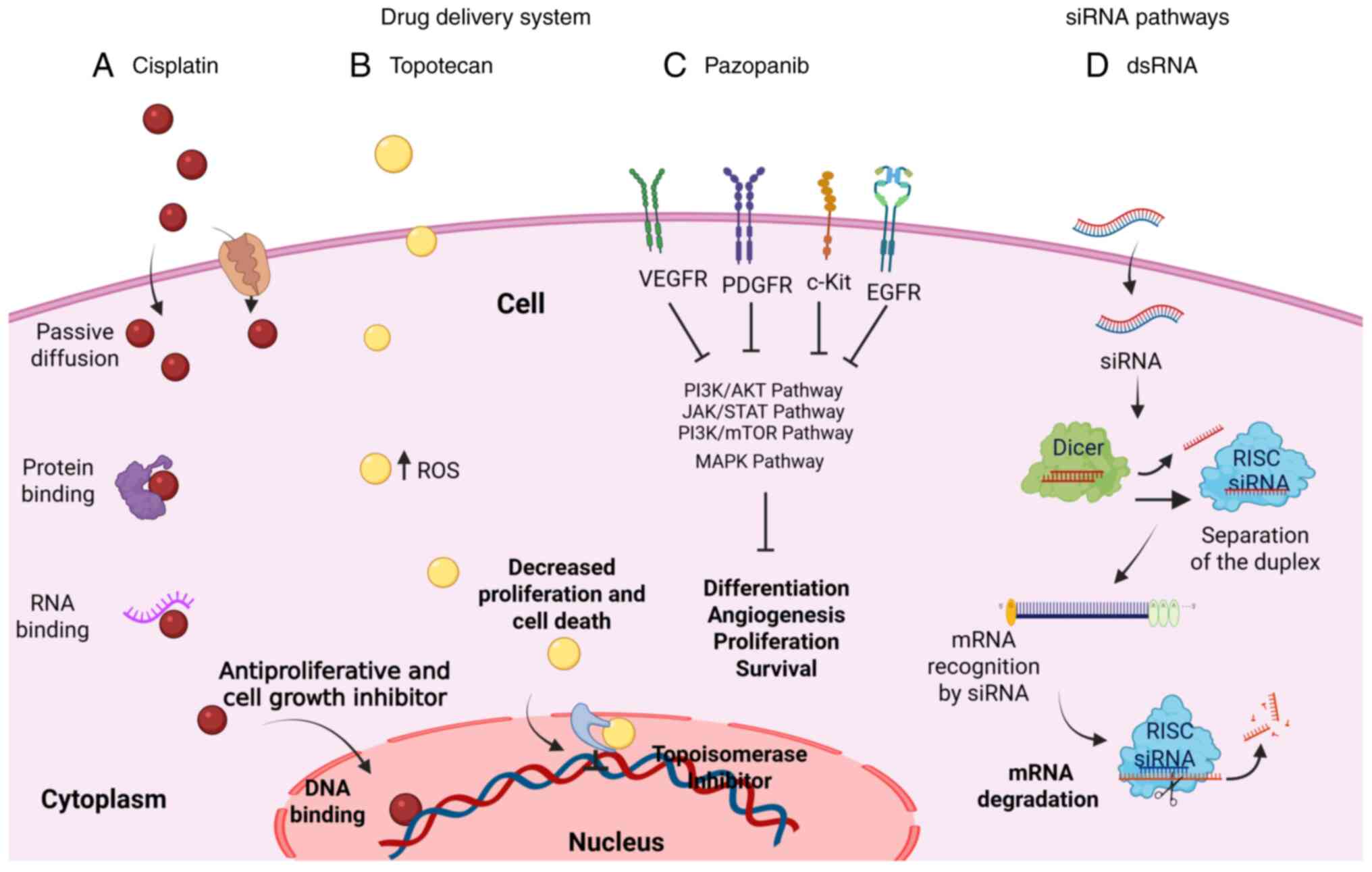
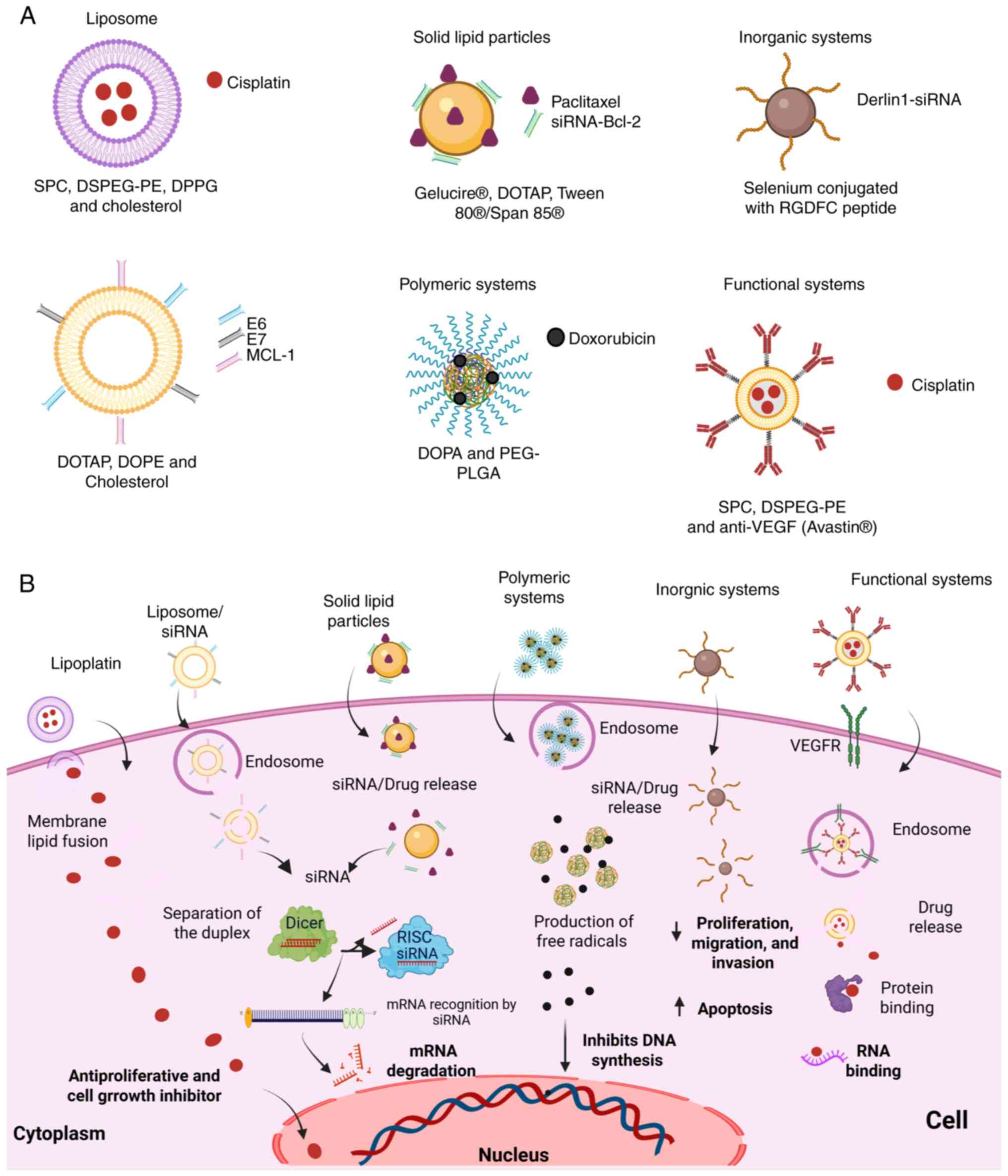
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kahue CN, Jerrell RJ and Parekh A:
Expression of human papillomavirus oncoproteins E6 and E7 inhibits
invadopodia activity but promotes cell migration in HPV-positive
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Rep (Hoboken).
1(e1125)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gonzalez SL, Stremlau M, He X, Basile JR
and Munger K: Degradation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor by
the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein is important for
functional inactivation and is separable from proteasomal
degradation of E7. J Virol. 75:7583–7591. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Narisawa-Saito M and Kiyono T: Basic
mechanisms of high-risk human papillomavirus-induced
carcinogenesis: Roles of E6 and E7 proteins. Cancer Sci.
98:1505–1511. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Snijders PJ, Steenbergen RD, Heideman DA
and Meijer CJ: HPV-mediated cervical carcinogenesis: Concepts and
clinical implications. J Pathol. 208:152–164. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yugawa T and Kiyono T: Molecular
mechanisms of cervical carcinogenesis by high-risk human
papillomaviruses: novel functions of E6 and E7 oncoproteins. Rev
Med Virol. 19:97–113. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhai L and Tumban E: Gardasil-9: A global
survey of projected efficacy. Antiviral Res. 130:101–109.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pal A and Kundu R: Human Papillomavirus E6
and E7: The cervical cancer hallmarks and targets for therapy.
Front Microbiol. 10(3116)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kumar L, Harish P, Malik PS and Khurana S:
Chemotherapy and targeted therapy in the management of cervical
cancer. Curr Probl Cancer. 42:120–128. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses and cancer:
From basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:342–350. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lizano M, Berumen J and García-Carrancá A:
HPV-related carcinogenesis: Basic concepts, viral types and
variants. Arch Med Res. 40:428–434. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tan S, de Vries EG, van der Zee AG and de
Jong S: Anticancer drugs aimed at E6 and E7 activity in
HPV-positive cervical cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 12:170–184.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, Fowler JM,
Clarke-Pearson D, Burger RA, Mannel RS, DeGeest K, Hartenbach EM
and Baergen R: Gynecologic Oncology Group. Phase III trial of
carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel
in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: A
gynecologic oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 21:3194–3200.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chang JC, Wooten EC, Tsimelzon A,
Hilsenbeck SG, Gutierrez MC, Elledge R, Mohsin S, Osborne CK,
Chamness GC, Allred DC and O'Connell P: Gene expression profiling
for the prediction of therapeutic response to docetaxel in patients
with breast cancer. Lancet. 362:362–369. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen J, Gu W, Yang L, Chen C, Shao R, Xu K
and Xu ZP: Nanotechnology in the management of cervical cancer. Rev
Med Virol. 25 (Suppl 1):S72–S83. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nanoparticles. Vocabulary. British
Standards Institution, London, 2011. Available from: https://shop.bsigroup.com/ProductDetail/?pid=000000000030214797.
|
|
17
|
Small W Jr, Bacon MA, Bajaj A, Chuang LT,
Fisher BJ, Harkenrider MM, Jhingran A, Kitchener HC, Mileshkin LR,
Viswanathan AN and Gaffney DK: Cervical cancer: A global health
crisis. Cancer. 123:2404–2412. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Balasubramaniam SD, Balakrishnan V, Oon CE
and Kaur G: Key molecular events in cervical cancer development.
Medicina (Kaunas). 55(384)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Burmeister CA, Khan SF, Schäfer G, Mbatani
N, Adams T, Moodley J and Prince S: Cervical cancer therapies:
Current challenges and future perspectives. Tumour Virus Res.
13(200238)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN and
Sankaranarayanan R: Cancer of the cervix uteri: 2021 update. Int J
Gynaecol Obstet. 155 (Suppl 1):S28–S44. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pectasides D, Kamposioras K, Papaxoinis G
and Pectasides E: Chemotherapy for recurrent cervical cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:603–613. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gopu P, Antony F, Cyriac S, Karakasis K
and Oza AM: Updates on systemic therapy for cervical cancer. Indian
J Med Res. 154:293–302. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Types of cancer treatment [Internet]. 2021
[cited June 23 th, 2021]. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types.
|
|
24
|
Targeted Cancer Therapies. 2020 [cited
June 23 th, 2021]. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/targeted-therapies.
|
|
25
|
Madaan K, Kumar S, Poonia N, Lather V and
Pandita D: Dendrimers in drug delivery and targeting:
Drug-dendrimer interactions and toxicity issues. J Pharm Bioallied
Sci. 6:139–150. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Monk BJ, Colombo N, Tewari KS, Dubot C,
Caceres MV, Hasegawa K, Shapira-Frommer R, Salman P, Yañez E, Gümüş
M, et al: First-Line pembrolizumab + chemotherapy versus placebo +
chemotherapy for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical
cancer: Final overall survival results of KEYNOTE-826. J Clin
Oncol. 41:5505–5511. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zighelboim I, Wright JD, Gao F, Case AS,
Massad LS, Mutch DG, Powell MA, Thaker PH, Eisenhauer EL, Cohn DE,
et al: Multicenter phase II trial of topotecan, cisplatin and
bevacizumab for recurrent or persistent cervical cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 130:64–68. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Suzuki K, Nagao S, Shibutani T, Yamamoto
K, Jimi T, Yano H, Kitai M, Shiozaki T, Matsuoka K and Yamaguchi S:
Phase II trial of paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab for
advanced or recurrent cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 154:554–557.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Scatchard K, Forrest JL, Flubacher M,
Cornes P and Williams C: Chemotherapy for metastatic and recurrent
cervical cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
10(Cd006469)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Moon JY, Song IC, Ko YB and Lee HJ: The
combination of cisplatin and topotecan as a second-line treatment
for patients with advanced/recurrent uterine cervix cancer.
Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e0340)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Monk BJ, Mas Lopez L, Zarba JJ, Oaknin A,
Tarpin C, Termrungruanglert W, Alber JA, Ding J, Stutts MW and
Pandite LN: Phase II, open-label study of pazopanib or lapatinib
monotherapy compared with pazopanib plus lapatinib combination
therapy in patients with advanced and recurrent cervical cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 28:3562–3569. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Segovia-Mendoza M, González-González ME,
Barrera D, Díaz L and García-Becerra R: Efficacy and mechanism of
action of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors gefitinib, lapatinib and
neratinib in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer:
preclinical and clinical evidence. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2531–2561.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rini BI: Temsirolimus, an inhibitor of
mammalian target of rapamycin. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1286–1290.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kasper B and Hohenberger P: Pazopanib: A
promising new agent in the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas.
Future Oncol. 7:1373–1383. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hamberg P, Verweij J and Sleijfer S:
(Pre-)clinical pharmacology and activity of pazopanib, a novel
multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor. Oncologist. 15:539–547.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gilbert WV and Nachtergaele S: mRNA
regulation by RNA modifications. Annu Rev Biochem. 92:175–198.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gagliardi M: Novel biodegradable
nanocarriers for enhanced drug delivery. Ther Deliv. 7:809–826.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sánchez-Meza LV, Bello-Rios C, Eloy JO,
Gómez-Gómez Y, Leyva-Vázquez MA, Petrilli R, Bernad-Bernad MJ,
Lagunas-Martínez A, Medina LA, Serrano-Bello J, et al: Cationic
liposomes carrying HPV16 E6-siRNA inhibit the proliferation,
migration, and invasion of cervical cancer cells. Pharmaceutics.
16(880)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dana P, Bunthot S, Suktham K, Surassmo S,
Yata T, Namdee K, Yingmema W, Yimsoo T, Ruktanonchai UR,
Sathornsumetee S and Saengkrit N: Active targeting liposome-PLGA
composite for cisplatin delivery against cervical cancer. Colloids
and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 196(111270)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Xu G, Shi C, Guo D, Wang L, Ling Y, Han X
and Luo J: Functional-segregated coumarin-containing telodendrimer
nanocarriers for efficient delivery of SN-38 for colon cancer
treatment. Acta Biomater. 21:85–98. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li X and Gao Y: Synergistically fabricated
polymeric nanoparticles featuring dual drug delivery system to
enhance the nursing care of cervical cancer. Process Biochem.
98:254–261. 2020.
|
|
42
|
Paul W and Sharma CP: Inorganic
nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. In: Biointegration of
Medical Implant Materials (2nd edition). Sharma CP (ed). Woodhead
Publishing, Cambridge, pp333-373, 2020.
|
|
43
|
Shi Z, Zhou Y, Fan T, Lin Y, Zhang H and
Mei L: Inorganic nano-carriers based smart drug delivery systems
for tumor therapy. Smart Mater Med. 1:32–47. 2020.
|
|
44
|
Wang W, Wang J and Ding Y: Gold
nanoparticle-conjugated nanomedicine: Design, construction, and
structure-efficacy relationship studies. J Mater Chem B.
8:4813–4830. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xia Y, Tang G, Wang C, Zhong J, Chen Y,
Hua L, Li Y, Liu H and Zhu B: Functionalized selenium nanoparticles
for targeted siRNA delivery silence Derlin1 and promote antitumor
efficacy against cervical cancer. Drug Deliv. 27:15–25.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Choi G, Piao H, Alothman ZA, Vinu A, Yun
CO and Choy JH: Anionic clay as the drug delivery vehicle: Tumor
targeting function of layered double hydroxide-methotrexate
nanohybrid in C33A orthotopic cervical cancer model. Int J
Nanomedicine. 20:337–348. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Akhtar A, Wang SX, Ghali L, Bell C and Wen
X: Effective delivery of arsenic trioxide to HPV-positive cervical
cancer cells using optimised liposomes: A size and charge study.
Int J Mol Sci. 4(1081)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Akhtar A, Ghali L, Wang SX, Bell C, Li D
and Wen X: Optimisation of folate-mediated liposomal encapsulated
arsenic trioxide for treating HPV-positive cervical cancer cells in
vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2156)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
You L, Liu X, Fang Z, Xu Q and Zhang Q:
Synthesis of multifunctional Fe3O4@PLGA-PEG nano-niosomes as a
targeting carrier for treatment of cervical cancer. Mater Sci Eng C
Mater Biol Appl. 94:291–302. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shimada H, Tyler VE and McLaughlin JL:
Biologically active acylglycerides from the berries of saw-palmetto
(Serenoa repens). J Nat Prod. 60:417–418. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Rongpan S, Phonnok S, Boondireke S,
Tripinyopap N and Wongsatayanon B: Anti-proliferative effect of
long-chain monoglyceride derivatives on human cervical carcinoma
cell line. J Med Assoc Thai. 100 (Suppl 8):S165–S172. 2017.
|
|
52
|
Boondireke S, Léonard M, Durand A and
Thanomsub Wongsatayanon B: Encapsulation of monomyristin into
polymeric nanoparticles improved its in vitro antiproliferative
activity against cervical cancer cells. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 176:9–17. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Song X, Li X, Tan Z and Zhang L: Recent
status and trends of nanotechnology in cervical cancer: A
systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Front Oncol.
14(1327851)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bakrania A, Zheng G and Bhat M:
Nanomedicine in hepatocellular carcinoma: A new frontier in
targeted cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics. 14(41)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zhou X, Lian H, Li H, Fan M, Xu W and Jin
Y: Nanotechnology in cervical cancer immunotherapy: Therapeutic
vaccines and adoptive cell therapy. Front Pharmacol.
13(1065793)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Devi S, Giri J, Makki E and Suryavanshi
MR: Navigating the novel nanoparticles: Current insights,
innovations, and future vistas in detection and treatment of
cervical cancer. Nanocomposites. 10:256–282. 2024.
|
|
57
|
Canta A, Chiorazzi A, Carozzi V, Meregalli
C, Oggioni N, Sala B, Crippa L, Avezza F, Forestieri D, Rotella G,
et al: In vivo comparative study of the cytotoxicity of a liposomal
formulation of cisplatin (lipoplatin™). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
68:1001–1008. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Xu B, Zeng M, Zeng J, Feng J and Yu L:
Meta-analysis of clinical trials comparing the efficacy and safety
of liposomal cisplatin versus conventional nonliposomal cisplatin
in nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck (SCCHN). Medicina (Baltimore).
97(e13169)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ledezma-Gallegos F, Jurado R, Mir R,
Medina LA, Mondragon-Fuentes L and Garcia-Lopez P: Liposomes
co-encapsulating cisplatin/mifepristone improve the effect on
cervical cancer: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Pharmaceutics.
12(897)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Menon S, Jayakodi S, Yadav KK, Somu P,
Isaq M, Shanmugam VK, Chaitanyakumar A and Basavegowda N:
Preparation of paclitaxel-encapsulated bio-functionalized selenium
nanoparticles and evaluation of their efficacy against cervical
cancer. Molecules. 27(7290)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Liu B, Han L, Liu J, Han S, Chen Z and
Jiang L: Co-delivery of paclitaxel and TOS-cisplatin via
TAT-targeted solid lipid nanoparticles with synergistic antitumor
activity against cervical cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 12:955–968.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Hernández-Esparza MJ, Fratoddi I, Cerra S,
Juarez-Moreno K and Huirache-Acuña R: Hybrid AuNPs-3MPS-MTX
nanosystem and its evaluation for treating cervical cancer and
melanoma. Nanoscale Adv. 5:7077–7085. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lechanteur A, Furst T, Evrard B, Delvenne
P, Piel G and Hubert P: Promoting vaginal distribution of E7 and
MCL-1 siRNA-silencing nanoparticles for cervical cancer treatment.
Mol Pharm. 14:1706–1717. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Adeyemi SA, Az-Zamakhshariy Z and Choonara
YE: In vitro prototyping of a nano-organogel for thermo-sonic
intra-cervical delivery of 5-fluorouracil-loaded solid lipid
nanoparticles for cervical cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech.
24(123)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Reddy TL, Garikapati KR, Reddy SG, Reddy
BV, Yadav JS, Bhadra U and Bhadra MP: Simultaneous delivery of
Paclitaxel and Bcl-2 siRNA via pH-Sensitive liposomal nanocarrier
for the synergistic treatment of melanoma. Sci Rep.
6(35223)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Javadi H, Lotfi AS, Hosseinkhani S,
Mehrani H, Amani J, Soheila SZ, Hojati Z and Kamali M: The
combinational effect of E6/E7 siRNA and anti-miR-182 on apoptosis
induction in HPV16-positive cervical cells. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 46 (Suppl 2):S727–S736. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Cervical Cancer Treatment by Stage. 2023
[cited january 27, 2023]. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/stages.
|
|
68
|
Kokka F, Bryant A, Brockbank E and
Jeyarajah A: Surgical treatment of stage IA2 cervical cancer.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014(CD010870)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Guimarães YM, Godoy LR, Longatto-Filho A
and Reis RD: Management of early-stage cervical cancer: A
literature review. Cancers (Basel). 14(575)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Xu C, Liu W, Hu Y, Li W and Di W:
Bioinspired tumor-homing nanoplatform for co-delivery of paclitaxel
and siRNA-E7 to HPV-related cervical malignancies for synergistic
therapy. Theranostics. 7:3325–3339. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Cho SH, Hong JH, Noh YW, Lee E, Lee CS and
Lim YT: Raspberry-like poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogel particles for
pH-dependent cell membrane passage and controlled cytosolic
delivery of antitumor drugs. Int J Nanomedicine. 11:5621–5632.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Thiruppathi R, Mishra S, Ganapathy M,
Padmanabhan P and Gulyás B: Nanoparticle functionalization and its
potentials for molecular imaging. Adv Sci (Weinh).
4(1600279)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Muhammad T, Amjad AC and Anup K: Cancer
Chemotherapy. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island, 2023.
|
|
74
|
How Chemotherapy Drugs Work [Internet].
2019 [cited November 22, 2019]. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/managing-cancer/treatment-types/chemotherapy/how-chemotherapy-drugs-work.html.
|
|
75
|
Ghasemiyeh P and Mohammadi-Samani S: Solid
lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug
delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res
Pharm Sci. 13:288–303. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Amini S, Salehi H, Setayeshmehr M and
Ghorbani M: Natural and synthetic polymeric scaffolds used in
peripheral nerve tissue engineering: Advantages and disadvantages.
Polym Adv Technol. 32:2267–2289. 2021.
|
|
77
|
Degli Esposti L, Carella F and Iafisco M:
Inorganic nanoparticles for theranostic use. In:
Electrofluidodynamic Technologies (EFDTs) for Biomaterials and
Medical Devices. Guarino V and Ambrosio L (eds). Woodhead
Publishing, Cambridge, pp351-376, 2018.
|