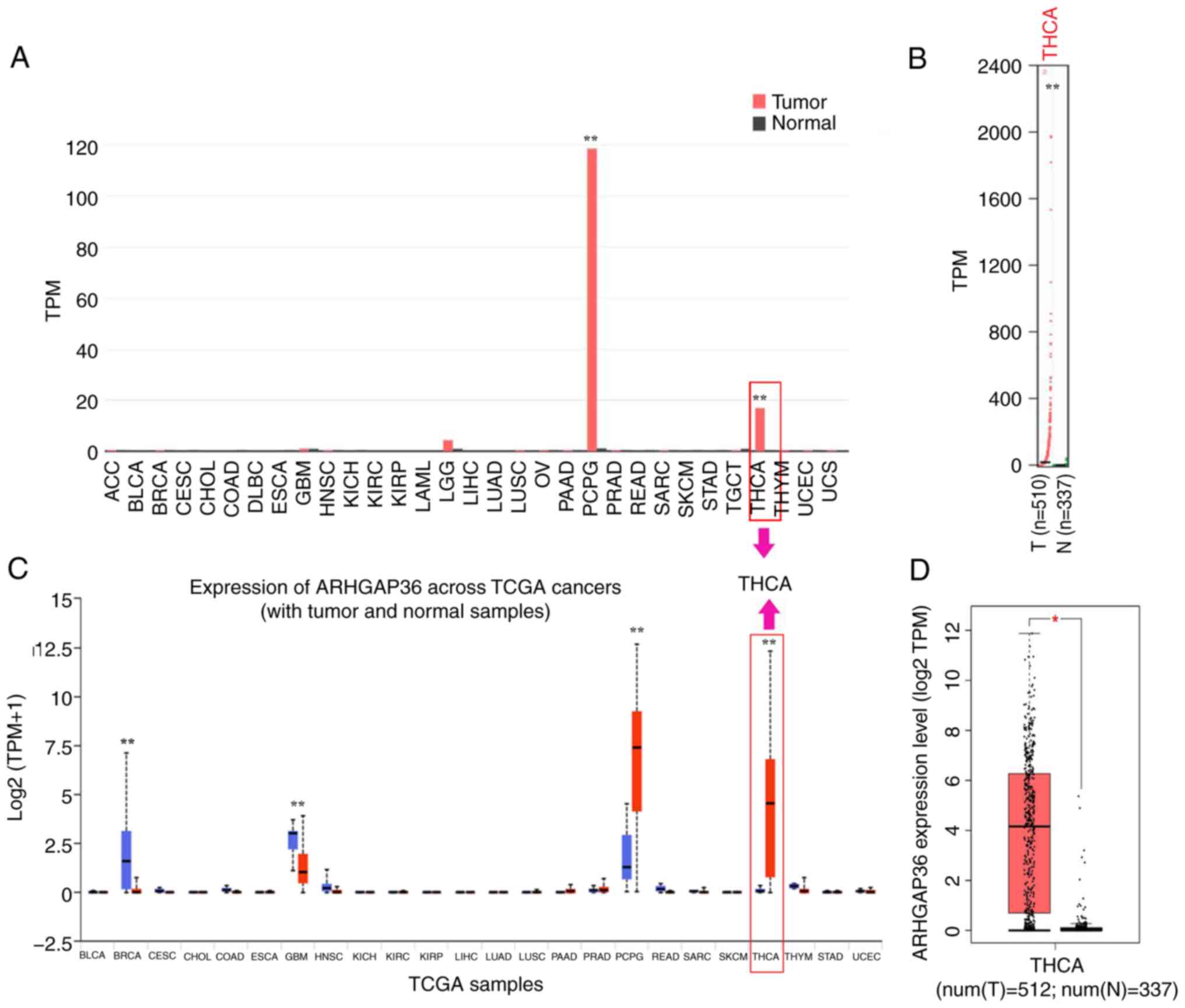
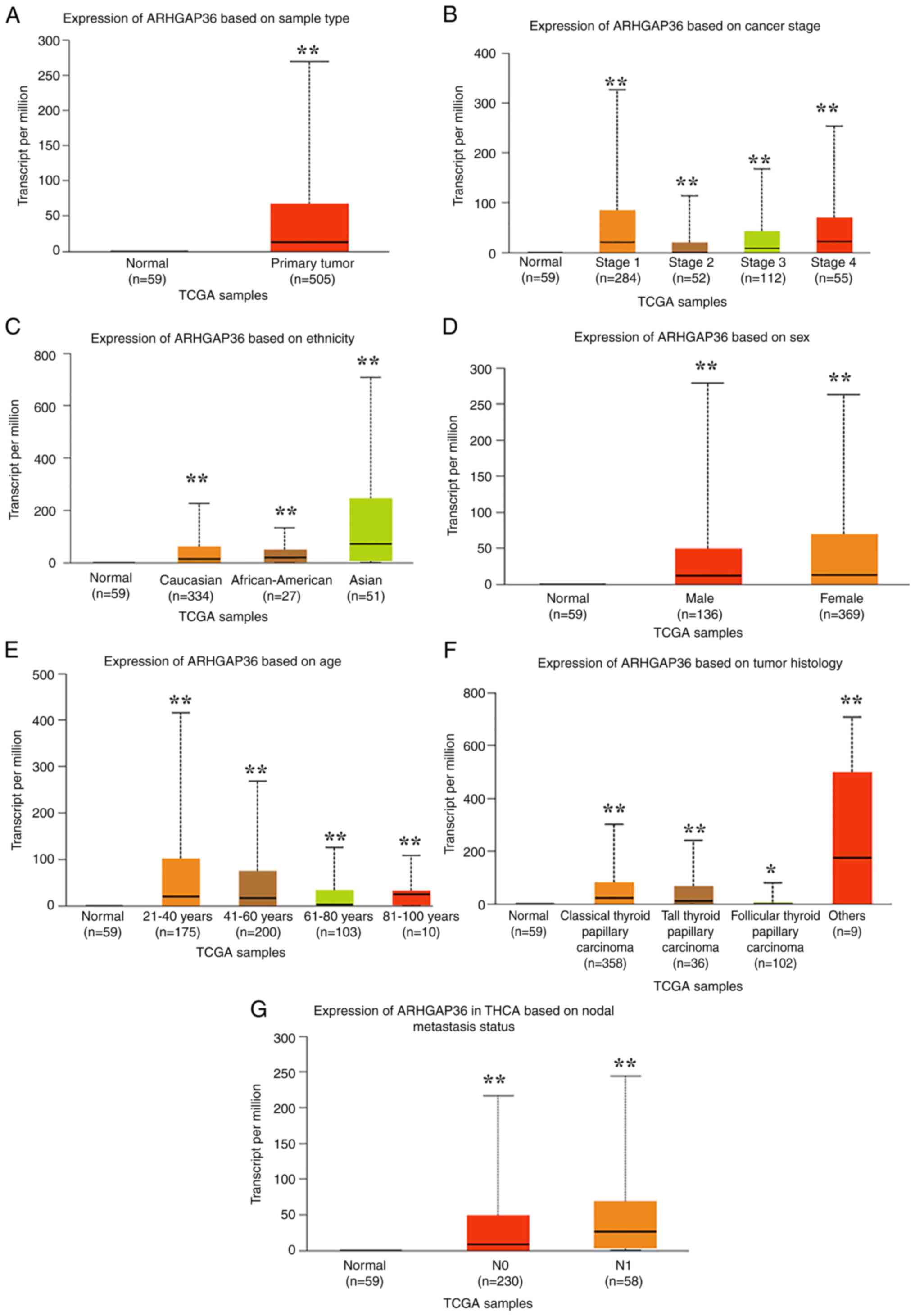
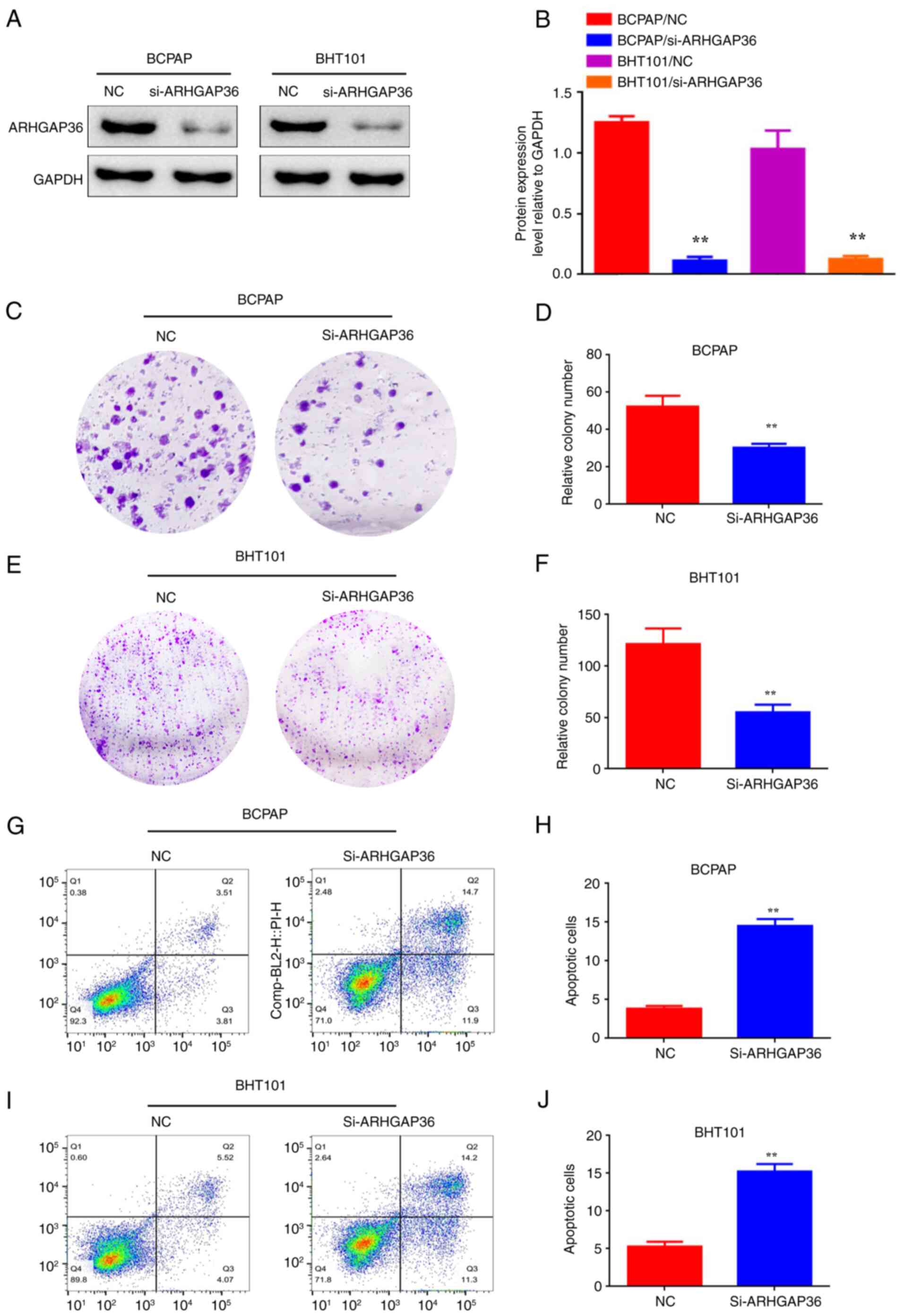
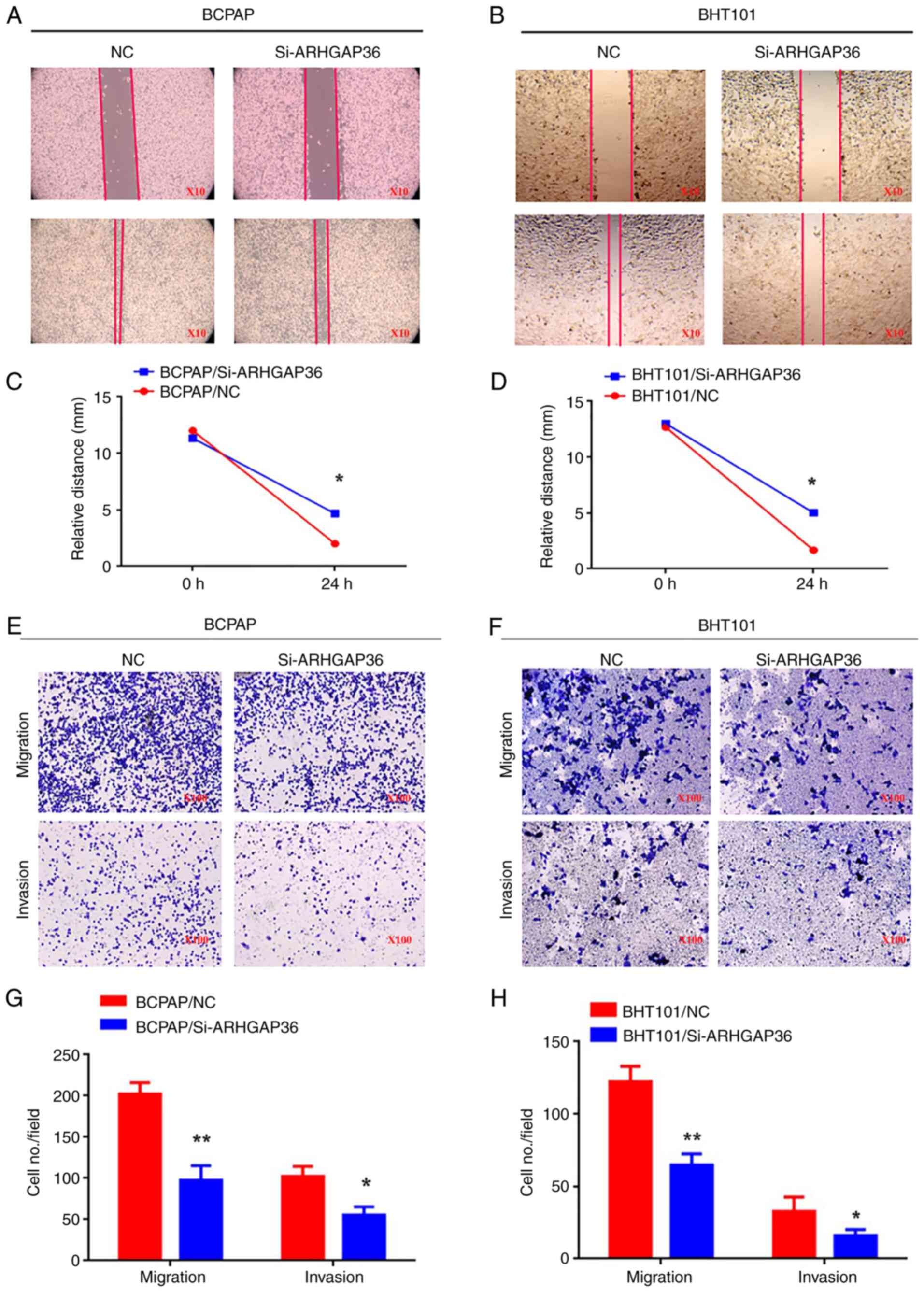
|
1
|
Wang W, Jin F, Song L, Yang J, Ye Y, Liu
J, Xu L and An P: Prediction of peripheral lymph node metastasis
(LNM) in thyroid cancer using delta radiomics derived from enhanced
CT combined with multiple machine learning algorithms. Eur J Med
Res. 30(164)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Peng X, Zhu Y, Lin S, Yu W, Zhang C, Tan
L, Long M, Luo D and Ji C: Circular RNA_0057209 acts as ceRNA to
inhibit thyroid cancer progression by promoting the STK4-mediated
hippo pathway via sponging MicroRNA-183. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(9974639)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Veschi V, Verona F, Lo Iacono M, D'Accardo
C, Porcelli G, Turdo A, Gaggianesi M, Forte S, Giuffrida D, Memeo L
and Todaro M: cancer stem cells in thyroid tumors: From the origin
to metastasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 11(566)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Croisé P, Houy S, Gand M, Lanoix J, Calco
V, Tóth P, Brunaud L, Lomazzi S, Paramithiotis E, Chelsky D, et al:
Cdc42 and Rac1 activity is reduced in human pheochromocytoma and
correlates with FARP1 and ARHGEF1 expression. Endocr Relat Cancer.
23:281–293. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shen Y, Chen G, Zhuang L, Xu L, Lin J and
Liu L: ARHGAP4 mediates the Warburg effect in pancreatic cancer
through the mTOR and HIF-1α signaling pathways. Onco Targets Ther.
12:5003–5012. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang TY and Ha MW: Silencing ARHGAP9
correlates with the risk of breast cancer and inhibits the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 119:7747–7756. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yan T, Qiu W, Song J, Fan Y and Yang Z:
ARHGAP36 regulates proliferation and migration in papillary thyroid
carcinoma cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 66:1–10. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.
Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Cell. 159:676–690. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lonsdale J, Thomas J, Salvatore M,
Phillips R, Lo E, Shad S, Hasz R, Walters G, Garcia F, Young N, et
al: The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet.
45:580–585. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Zhao R, Chen Q, Qiao P, Lu Y and Chen X: A
signature of four ferroptosis-related genes in laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res. 13:2938–2949. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yao L, Li Y, Li S, Wang M, Cao H, Xu L and
Xu Y: ARHGAP39 is a prognostic biomarker involved in immune
infiltration in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 23(440)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J and Zhang B:
LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer
types. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(D1):D956–D963. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10(1523)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Csordas A, Sipos B, Kurucova T, Volfova A,
Zamola F, Tichy B and Hicks DG: Cell tree rings: The structure of
somatic evolution as a human aging timer. Geroscience.
46:3005–3019. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tang L, Shi Y, Liao Q, Wang F, Wu H, Ren
H, Wang X, Fu W, Shou J, Wang WE, et al: Reversing metabolic
reprogramming by CPT1 inhibition with etomoxir promotes
cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration via DUSP1
ADP-ribosylation-mediated p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Acta Pharm Sin
B. 15:256–277. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yan HC and Xiang C: Aberrant expression of
BUB1B contributes to the progression of thyroid carcinoma and
predicts poor outcomes for patients. J Cancer. 13:2336–2351.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Qi F, Tang J, Cai Z, Wang G and Wang Z:
Long non-coding RNA CATIP antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA CATIP-AS1)
downregulation contributes to the progression and metastasis of
thyroid cancer via epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway.
Bioengineered. 13:7592–7606. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hong K, Cen K, Chen Q, Dai Y, Mai Y and
Guo Y: Identification and validation of a novel senescence-related
biomarker for thyroid cancer to predict the prognosis and
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 14(1128390)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Conzo G, Docimo G, Mauriello C,
Gambardella C, Esposito D, Cavallo F, Tartaglia E, Napolitano S and
Santini L: The current status of lymph node dissection in the
treatment of papillary thyroid cancer. A literature review. Clin
Ter. 164:e343–e346. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Conzo G, Mauriello C, Docimo G,
Gambardella C, Thomas G, Cavallo F, Tartaglia E, Napolitano S,
Varriale R, Rossetti G, et al: Clinicopathological pattern of lymph
node recurrence of papillary thyroid cancer. Implications for
surgery. Int J Surg. 12 (Suppl 1):S194–S197. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nano PR, Johnson TK, Kudo T, Mooney NA, Ni
J, Demeter J, Jackson PK and Chen J: Structure-activity mapping of
ARHGAP36 reveals regulatory roles for its GAP homology and
C-terminal domains. PLoS One. 16(e0251684)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Joustra SD, Heinen CA, Schoenmakers N,
Bonomi M, Ballieux BE, Turgeon MO, Bernard DJ, Fliers E, van
Trotsenburg AS, Losekoot M, et al: IGSF1 deficiency: lessons from
an extensive case series and recommendations for clinical
management. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 101:1627–1636. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Joustra SD, Andela CD, Oostdijk W, van
Trotsenburg AS, Fliers E, Wit JM, Pereira AM, Middelkoop HA and
Biermasz NR: Mild deficits in attentional control in patients with
the IGSF1 deficiency syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 84:896–903.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guan Y, Wang Y, Bhandari A, Xia E and Wang
O: IGSF1: A novel oncogene regulates the thyroid cancer
progression. Cell Biochem Funct. 37:516–524. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Koh DI, Lee M, Park YS, Shin JS, Kim J,
Ryu YS, Lee JH, Bae S, Lee MS, Hong JK, et al: The Immune
Suppressor IGSF1 as a Potential Target for Cancer Immunotherapy.
Cancer Immunol Res. 12:491–507. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu Q, You L, Nepovimova E, Heger Z, Wu W,
Kuca K and Adam V: Hypoxia-inducible factors: Master regulators of
hypoxic tumor immune escape. J Hematol Oncol. 15(77)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|