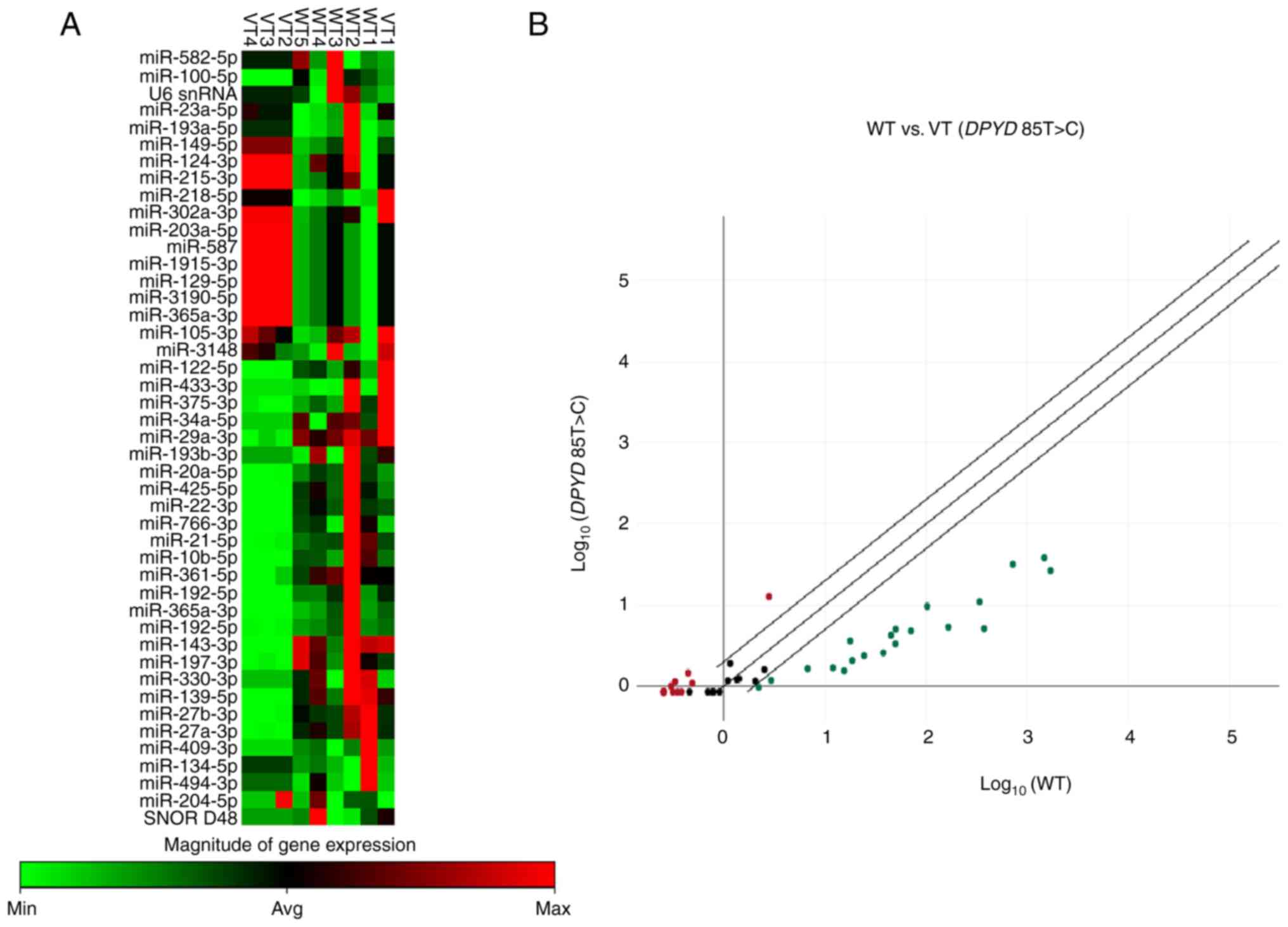
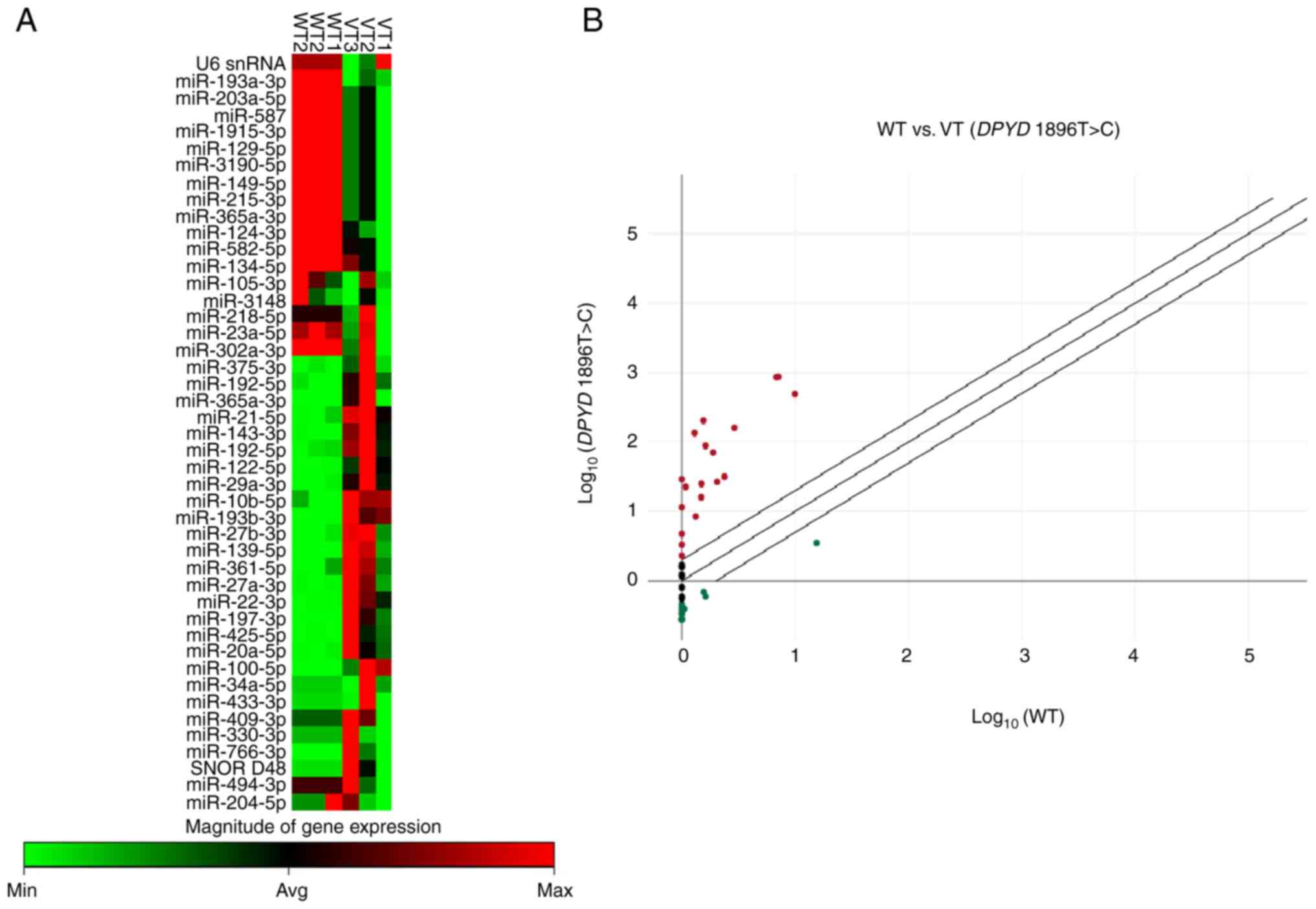
|
1
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero
A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D, Aranda Aguilar E, Bardelli A, Benson
A, Bodoky G, et al: ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol.
27:1386–1422. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Goto T, Shinmura K, Yokomizo K, Sakuraba
K, Kitamura Y, Shirahata A, Saito M, Kigawa G, Nemoto H, Sanada Y
and Hibi K: Expression levels of thymidylate synthase,
dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, and thymidine phosphorylase in
patients with colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 32:1757–1762.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amstutz U, Henricks LM, Offer SM,
Barbarino J, Schellens JHM, Swen JJ, Klein TE, McLeod HL, Caudle
KE, Diasio RB and Schwab M: Clinical pharmacogenetics
implementation consortium (CPIC) guideline for dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase genotype and fluoropyrimidine dosing: 2017 Update.
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 103:210–216. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Deac AL, Burz CC, Bocşe HF, Bocşan IC and
Buzoianu AD: A review on the importance of genotyping and
phenotyping in fluoropyrimidine treatment. Med Pharm Rep.
93:223–230. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Offer SM, Wegner NJ, Fossum C, Wang K and
Diasio RB: Phenotypic profiling of DPYD variations relevant to
5-fluorouracil sensitivity using real-time cellular analysis and in
vitro measurement of enzyme activity. Cancer Res. 73:1958–1968.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Falvella FS, Cheli S, Martinetti A,
Mazzali C, Iacovelli R, Maggi C, Gariboldi M, Pierotti MA, Di
Bartolomeo M, Sottotetti E, et al: DPD and UGT1A1 deficiency in
colorectal cancer patients receiving triplet chemotherapy with
fluoropyrimidines, oxaliplatin and irinotecan. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
80:581–588. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chan TH, Zhang JE and Pirmohamed M: DPYD
genetic polymorphisms in non-European patients with severe
fluoropyrimidine-related toxicity: A systematic review. Br J
Cancer. 131:498–514. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
He YF, Wei W, Zhang X, Li YH, Li S, Wang
FH, Lin XB, Li ZM, Zhang DS, Huang HQ, et al: Analysis of the DPYD
gene implicated in 5-fluorouracil catabolism in Chinese cancer
patients. J Clin Pharm Ther. 33:307–314. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Leung HWC and Chan ALF: Association and
prediction of severe 5-fluorouracil toxicity with dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase gene polymorphisms: A meta-analysis. Biomed Rep.
3:879–883. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Atasilp C, Vanwong N, Yodwongjane P,
Chansriwong P, Sirachainan E, Reungwetwattana T, Jinda P,
Aiempradit S, Sirilerttrakul S, Chamnanphon M, et al: Influence of
DPYD gene polymorphisms on 5-fluorouracil toxicities in Thai
colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
95(2)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sarhangi N, Rouhollah F, Niknam N, Sharifi
F, Nikfar S, Larijani B, Patrinos GP and Hasanzad M:
Pharmacogenetic DPYD allele variant frequencies: A comprehensive
analysis across an ancestrally diverse Iranian population. Daru.
32:715–727. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D and Ali S:
Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel
cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 13:57–66. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Magee P, Shi L and Garofalo M: Role of
microRNAs in chemoresistance. Ann Transl Med. 3(332)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Si W, Shen J, Zheng H and Fan W: The role
and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance.
Clin Epigenetics. 11(25)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Condrat CE, Thompson DC, Barbu MG, Bugnar
OL, Boboc A, Cretoiu D, Suciu N, Cretoiu SM and Voinea SC: miRNAs
as biomarkers in disease: latest findings regarding their role in
diagnosis and prognosis. Cells. 9(276)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ferracin M, Lupini L, Salamon I, Saccenti
E, Zanzi MV, Rocchi A, Da Ros L, Zagatti B, Musa G, Bassi C, et al:
Absolute quantification of cell-free microRNAs in cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 6:14545–14555. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li J, Liu Y, Wang C, Deng T, Liang H, Wang
Y, Huang D, Fan Q, Wang X, Ning T, et al: Serum miRNA expression
profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal
adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 5(12921)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bader El Din NG, El-Shenawy R, Moustafa
RI, Khairy A and Farouk S: Association between the expression level
of miRNA-374a and TGF-β1 in patients with colorectal cancer. World
Acad Sci J. 6(68)2024.
|
|
22
|
Okamoto K, Nozawa H, Ozawa T, Yamamoto Y,
Yokoyama Y, Emoto S, Murono K, Sasaki K, Fujishiro M and Ishihara
S: Comparative microRNA signatures based on liquid biopsy to
identify lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer patients
undergoing upfront surgery or endoscopic resection. Cell Death
Discov. 11(67)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Schwab S and Nonaka T: Circulating miRNAs
as liquid biopsy biomarkers for diagnosis in patients with
colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front
Genet. 16(1574586)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Offer SM, Butterfield GL, Jerde CR, Fossum
CC, Wegner NJ and Diasio RB: microRNAs miR-27a and miR-27b directly
regulate liver dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression through
two conserved binding sites. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:742–751.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Medwid S, Wigle TJ, Ross C and Kim RB:
Genetic variation in miR-27a Is associated with
fluoropyrimidine-associated toxicity in patients with
dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase variants after genotype-guided dose
reduction. Int J Mol Sci. 24(13284)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Meulendijks D, Henricks LM, Sonke GS,
Deenen MJ, Froehlich TK, Amstutz U, Largiadèr CR, Jennings BA,
Marinaki AM, Sanderson JD, et al: Clinical relevance of DPYD
variants c.1679T>G, c.1236G>A/HapB3, and c.1601G>A as
predictors of severe fluoropyrimidine-associated toxicity: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data.
Lancet Oncol. 16:1639–1650. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Freites-Martinez A, Santana N,
Arias-Santiago S and Viera A: Using the common terminology criteria
for adverse events (CTCAE-version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of
adverse events of anticancer therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl
Ed). 112:90–92. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO and
Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression
patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14863–14868. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wilkinson L and Friendly M: The history of
the cluster heat map. Am Statist. 63:179–184. 2009.
|
|
32
|
Mounier-Boutoille H, Boisdron-Celle M,
Cauchin E, Galmiche JP, Morel A, Gamelin E and Matysiak-Budnik T:
Lethal outcome of 5-fluorouracil infusion in a patient with a total
DPD deficiency and a double DPYD and UTG1A1 gene mutation. Br J
Clin Pharmacol. 70:280–283. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chai J, Dong W, Xie C, Wang L, Han DL,
Wang S, Guo HL and Zhang ZL: MicroRNA-494 sensitizes colon cancer
cells to fluorouracil through regulation of DPYD. IUBMB Life.
67:191–201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Van Kuilenburg ABP, Meinsma R, Zoetekouw L
and Van Gennip AH: Increased risk of grade IV neutropenia after
administration of 5-fluorouracil due to a dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase deficiency: High prevalence of the IVS14+1g>a
mutation. Int J Cancer. 101:253–258. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang H, Li YM, Zhang H and Jin X: DPYD*5
gene mutation contributes to the reduced DPYD enzyme activity and
chemotherapeutic toxicity of 5-FU: Results from genotyping study on
75 gastric carcinoma and colon carcinoma patients. Med Oncol.
24:251–258. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Raha R, Bhoyar RC, Biswal RP,
Venkatakrishnan R, Rai P, Umashankar E, Kulkarni PM, Sivasubbu S,
Scaria V and Jolly B: Opportunistic analysis of clinically
actionable DPYD gene variants in a germline testing cohort in
India. Pharmacogenomics. 1–6. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
37
|
Varma A, Jayanthi M, Dubashi B, Shewade DG
and Sundaram R: Genetic influence of DPYD*9A polymorphism on plasma
levels of 5-fluorouracil and subsequent toxicity after oral
administration of capecitabine in colorectal cancer patients of
South Indian origin. Drug Metab Pers Ther. 35:2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Detailleur S, Segelov E, Re MD and Prenen
H: Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency in patients with
severe toxicity after 5-fluorouracil: A retrospective single-center
study. Ann Gastroenterol. 34:68–72. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9(402)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dluzen DF and Lazarus P: MicroRNA
regulation of the major drug-metabolizing enzymes and related
transcription factors. Drug Metab Rev. 47:320–334. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sun X, Chen J, Chen X, Gao Q, Chen W, Zou
X, Zhang F, Gao S, Qiu S, Yue X, et al: A systematic review of
clinical validated and potential miRNA markers related to the
efficacy of fluoropyrimidine drugs. Dis Markers.
2022(1360954)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jin XH, Lu S and Wang AF: Expression and
clinical significance of miR-4516 and miR-21-5p in serum of
patients with colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 20(241)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jin RR, Zeng C and Chen Y: MiR-22-3p
regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal
cancer cells by directly targeting KDM3A through the Hippo pathway.
Histol Histopathol. 37:1241–1252. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xia SS, Zhang GJ, Liu ZL, Tian HP, He Y,
Meng CY, Li LF, Wang ZW and Zhou T: MicroRNA-22 suppresses the
growth, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through a
Sp1 negative feedback loop. Oncotarget. 8:36266–36278.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lu C, Jiang W, Hui B, Rong D, Fu K, Dong
C, Tang W and Cao H: The circ_0021977/miR-10b-5p/P21 and P53
regulatory axis suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion
in colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol. 235:2273–2285.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Talmon G and Wang J: MicroRNA-587
antagonizes 5-FU-induced apoptosis and confers drug resistance by
regulating PPP2R1B expression in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis.
6(e1845)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xiao Z, Liu Y, Li Q, Liu Q, Liu Y, Luo Y
and Wei S: EVs delivery of miR-1915-3p improves the
chemotherapeutic efficacy of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 88:1021–1031. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wu Q, Meng WY, Jie Y and Zhao H: LncRNA
MALAT1 induces colon cancer development by regulating
miR-129-5p/HMGB1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 233:6750–6757.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen Q, Meng F, Wang L, Mao Y, Zhou H, Hua
D, Zhang H and Wang W: A polymorphism in ABCC4 is related to
efficacy of 5-FU/capecitabine-based chemotherapy in colorectal
cancer patients. Sci Rep. 7(7059)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li XW, Qiu SJ and Zhang X: Overexpression
of miR-215-3p sensitizes colorectal cancer to 5-fluorouracil
induced apoptosis through regulating CXCR1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 22:7240–7250. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jafarzadeh A, Seyedmoalemi S, Dashti A,
Nemati M, Jafarzadeh S, Aminizadeh N, Vosough M, Rajabi A,
Afrasiabi A and Mirzaei H: Interplays between non-coding RNAs and
chemokines in digestive system cancers. Biomed Pharmacother.
152(113237)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tang X, Shi X, Wang N, Peng W and Cheng Z:
MicroRNA-215-3p suppresses the growth, migration, and invasion of
colorectal cancer by targeting FOXM1. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
18(1533033819874776)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hermeking H: MicroRNAs in the p53 network:
Micromanagement of tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:613–626.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Eymin B and Gazzeri S: Role of cell cycle
regulators in lung carcinogenesis. Cell Adh Migr. 4:114–123.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hong YG, Xin C, Zheng H, Huang ZP, Yang Y,
Zhou JD, Gao XH, Hao L, Liu QZ, Zhang W and Hao LQ: miR-365a-3p
regulates ADAM10-JAK-STAT signaling to suppress the growth and
metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. J Cancer. 11:3634–3644.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Al-Asadi S, Mansour H, Ataimish AJ,
Al-Kahachi R and Rampurawala J: MicroRNAs regulate tumorigenesis by
downregulating SOCS3 expression: An in silico approach. Bioinform
Biol Insights. 17(11779322231193535)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hirota T, Date Y, Nishibatake Y, Takane H,
Fukuoka Y, Taniguchi Y, Burioka N, Shimizu E, Nakamura H, Otsubo K
and Ieiri I: Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) expression is
negatively regulated by certain microRNAs in human lung tissues.
Lung Cancer. 77:16–23. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hou N, Han J, Li J, Liu Y, Qin Y, Ni L,
Song T and Huang C: MicroRNA profiling in human colon cancer cells
during 5-fluorouracil-induced autophagy. PLoS One.
9(e114779)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|