|
1
|
Trbovich M, Romo T, Polk M, Koek W, Kelly
C, Stowe S, Kraus S and Kellogg D: The treatment of neurogenic
lower urinary tract dysfunction in persons with spinal cord injury:
An open label, pilot study of anticholinergic agent vs mirabegron
to evaluate cognitive impact and efficacy. Spinal Cord Ser Cases.
7(50)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang YC, Chen YL, Huang CC, Ho CH, Huang
YT, Wu MP, Ou MJ, Yang CH and Chen PJ: Cumulative use of
therapeutic bladder anticholinergics and the risk of dementia in
patients with lower urinary tract symptoms: A nationwide 12-year
cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 19(380)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cameron AP: Medical management of
neurogenic bladder with oral therapy. Transl Androl Urol. 5:51–62.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
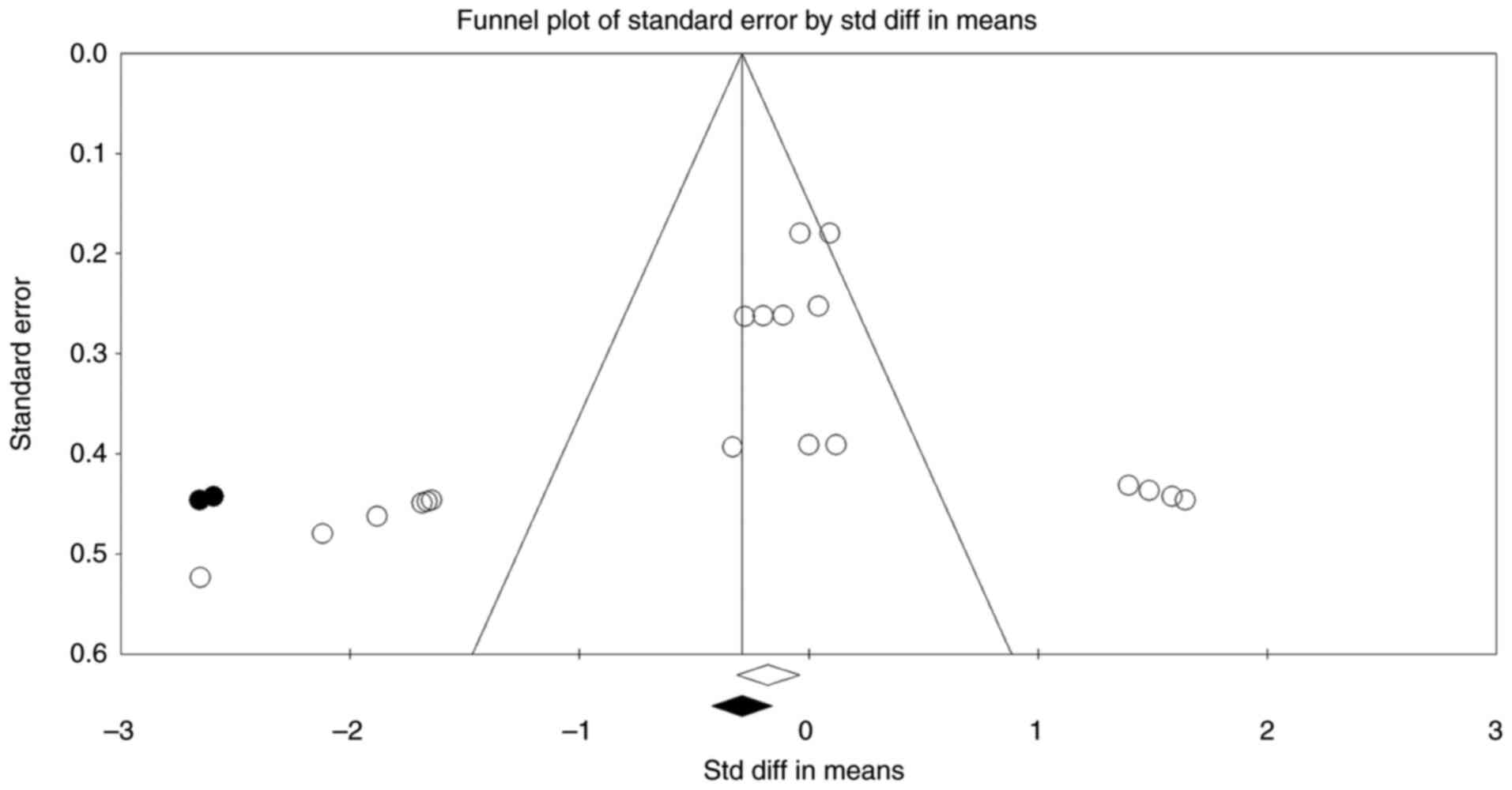
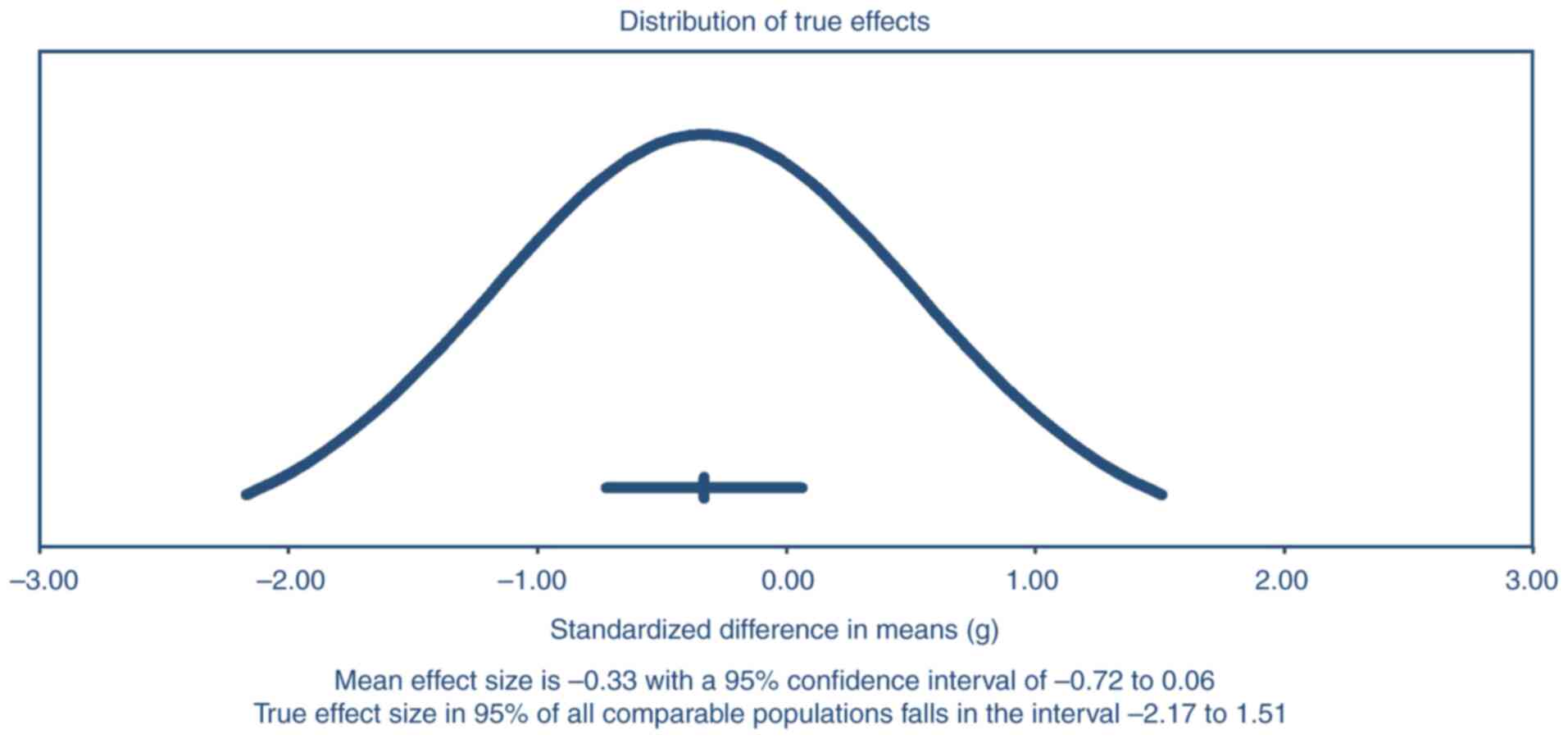
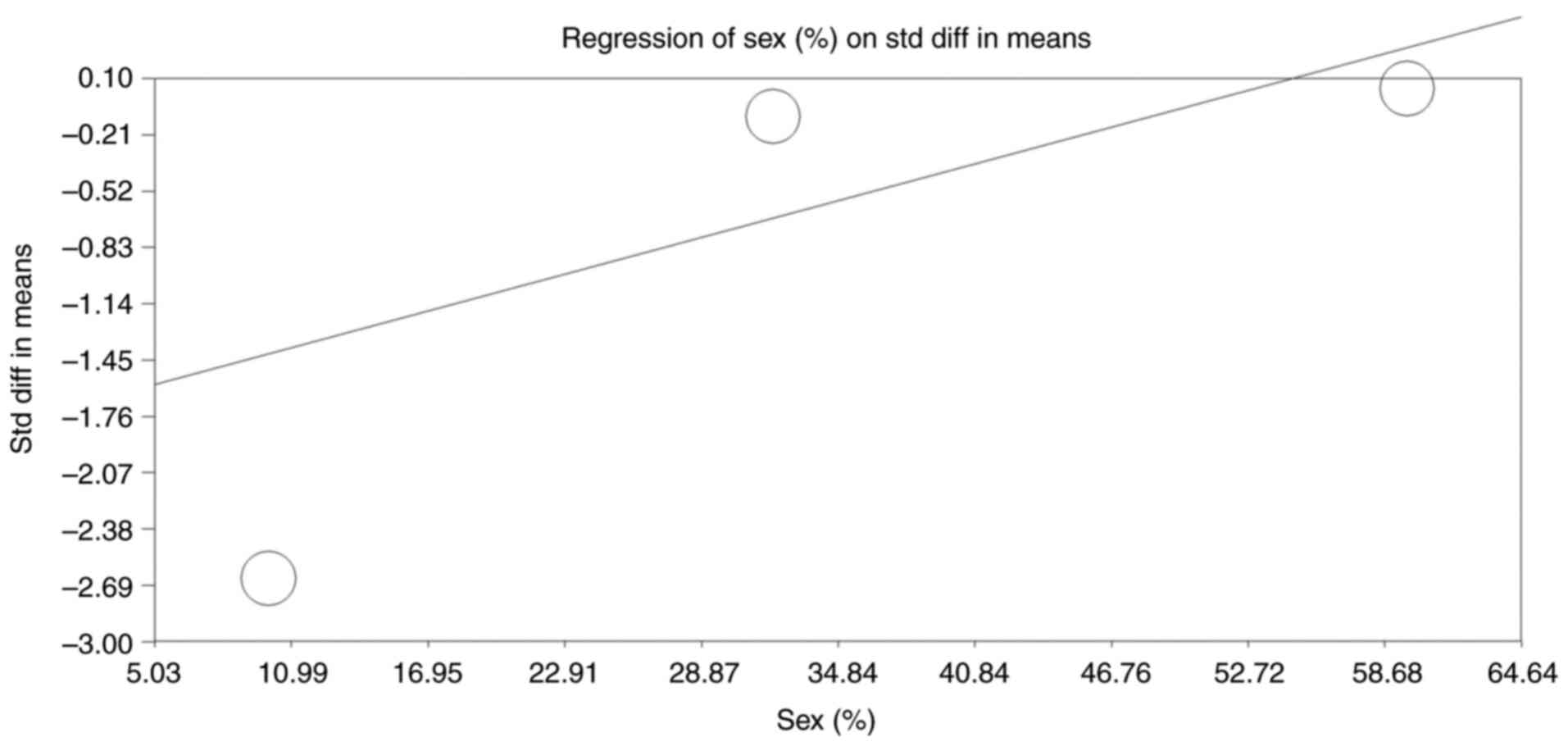
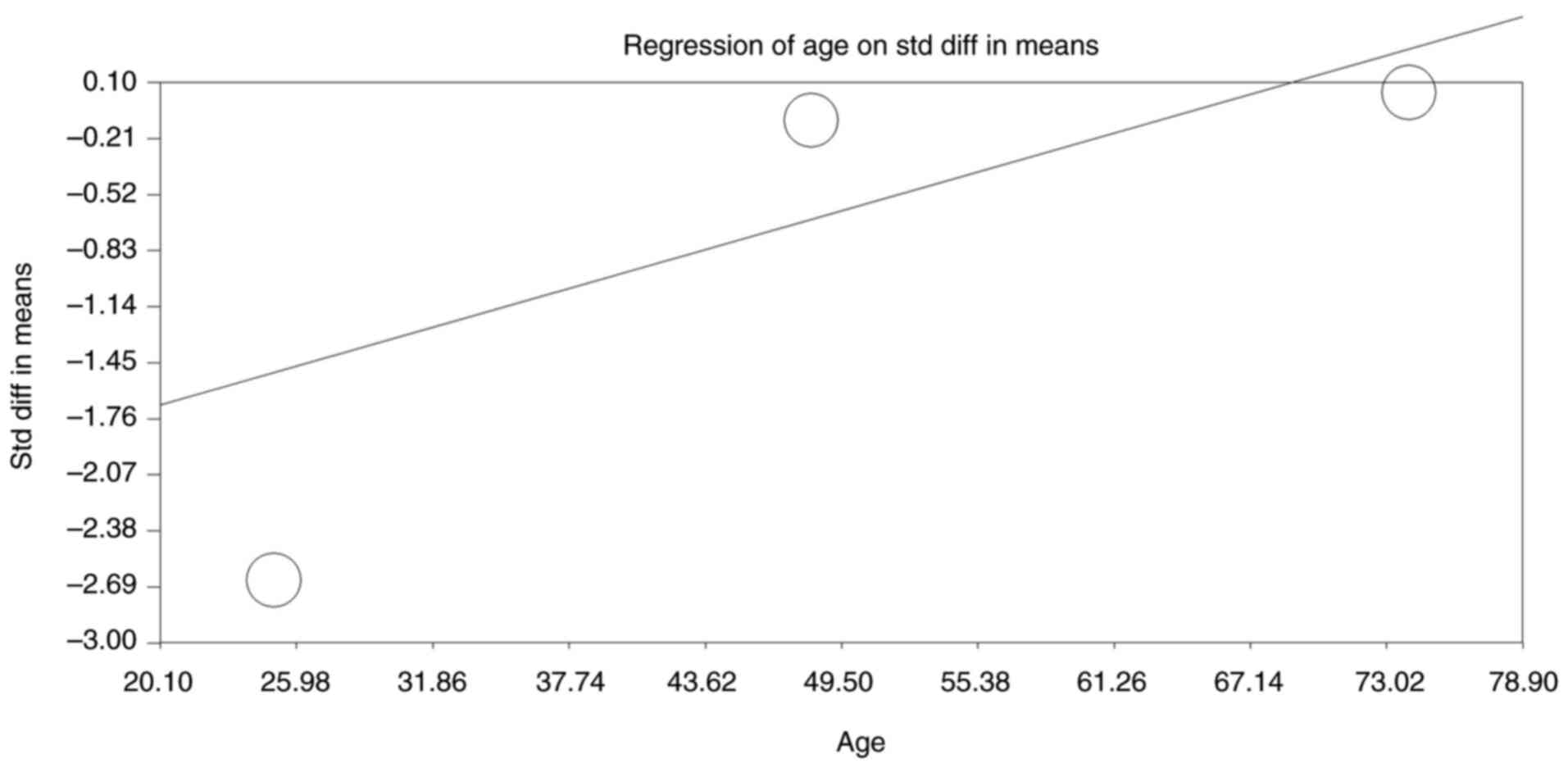
Sakakibara R, Tateno F, Yano M, Takahashi
O, Sugiyama M, Ogata T, Haruta H, Kishi M, Tsuyusaki Y, Yamamoto T,
et al: Imidafenacin on bladder and cognitive function in neurologic
OAB patients. Clin Auton Res. 23:189–195. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Richardson K, Fox C, Maidment I, Steel N,
Loke YK, Arthur A, Myint PK, Grossi CM, Mattishent K, Bennett K, et
al: Anticholinergic drugs and risk of dementia: Case-control study.
BMJ. 361(k1315)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Coupland CAC, Hill T, Dening T, Morriss R,
Moore M and Hippisley-Cox J: Anticholinergic drug exposure and the
risk of dementia: A nested case-control study. JAMA Intern Med.
179:1084–1093. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Morrow SA, Rosehart H, Sener A and Welk B:
Anti-cholinergic medications for bladder dysfunction worsen
cognition in persons with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci.
385:39–44. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Harvey PD: Domains of cognition and their
assessment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 21:227–237. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Oleksy P, Zieliński K, Buczkowski B,
Sikora D, Góralczyk E, Zając A, Mąka M, Papież Ł and Kamiński J:
Cognitive function tests: Application of MMSE and MoCA in various
clinical settings-a brief overview. Qual Sport. 34(56285)2024.
|
|
10
|
Benedict RH, DeLuca J, Phillips G, LaRocca
N, Hudson LD and Rudick R: Multiple Sclerosis Outcome Assessments
Consortium. Validity of the symbol digit modalities test as a
cognition performance outcome measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult
Scler. 23:721–733. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
von Hippel PT: The heterogeneity statistic
I(2) can be biased in small meta-analyses. BMC Med Res Methodol.
15(35)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Borenstein M: In a meta-analysis, the
I-squared statistic does not tell us how much the effect size
varies. J Clin Epidemiol. 152:281–284. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krebs J, Scheel-Sailer A, Oertli R and
Pannek J: The effects of antimuscarinic treatment on the cognition
of spinal cord injured individuals with neurogenic lower urinary
tract dysfunction: A prospective controlled before-and-after study.
Spinal Cord. 56:22–27. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dettori JR, Norvell DC and Chapman JR:
Fixed-effect vs random-effects models for meta-analysis: 3 Points
to consider. Global Spine J. 12:1624–1626. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Majdi A, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Rahigh Aghsan
S, Farajdokht F, Vatandoust SM, Namvaran A and Mahmoudi J:
Amyloid-β, tau, and the cholinergic system in Alzheimer's disease:
Seeking direction in a tangle of clues. Rev Neurosci. 31:391–413.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Naseri A, Sadigh-Eteghad S,
Seyedi-Sahebari S, Hosseini MS, Hajebrahimi S and Salehi-Pourmehr
H: Cognitive effects of individual anticholinergic drugs: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Dement Neuropsychol.
17(e20220053)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu XS: Sample size and the precision of
the confidence interval in meta-analyses. Ther Innov Regul Sci.
49:593–598. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Spineli LM and Pandis N: Prediction
interval in random-effects meta-analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial
Orthop. 157:586–588. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Talebi M, Majdi A, Kamari F and
Sadigh-Eteghad S: The cambridge neuropsychological test automated
battery (CANTAB) versus the minimal assessment of cognitive
function in multiple sclerosis (MACFIMS) for the assessment of
cognitive function in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler
Relat Disord. 43(102172)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Motavalli A, Majdi A, Hosseini L, Talebi
M, Mahmoudi J, Hosseini SH and Sadigh-Eteghad S: Pharmacotherapy in
multiple sclerosis-induced cognitive impairment: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Mult Scler Relat Disord.
46(102478)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Callegari E, Malhotra B, Bungay PJ,
Webster R, Fenner KS, Kempshall S, LaPerle JL, Michel MC and Kay
GG: A comprehensive non-clinical evaluation of the CNS penetration
potential of antimuscarinic agents for the treatment of overactive
bladder. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 72:235–246. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han L, Agostini JV and Allore HG:
Cumulative anticholinergic exposure is associated with poor memory
and executive function in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc.
56:2203–2310. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sittironnarit G, Ames D, Bush AI, Faux N,
Flicker L, Foster J, Hilmer S, Lautenschlager NT, Maruff P, Masters
CL, et al: Effects of anticholinergic drugs on cognitive function
in older Australians: Results from the AIBL study. Dement Geriatr
Cogn Disord. 31:173–178. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Georgiou R, Lamnisos D and Giannakou K:
Anticholinergic burden and cognitive performance in patients with
schizophrenia: A systematic literature review. Front Psychiatry.
12(779607)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Trenaman SC, Bowles SK, Andrew MK and
Goralski K: The role of sex, age and genetic polymorphisms of CYP
enzymes on the pharmacokinetics of anticholinergic drugs. Pharmacol
Res Perspect. 9(e00775)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sartori LGF, Nunes BM, Farah D, Oliveira
LM, Novoa CCT, Sartori MGF and Fonseca MCM: Mirabegron and
anticholinergics in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome: A
meta-analysis. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 45:337–346. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Abrams P, Kelleher C, Staskin D, Kay R,
Martan A, Mincik I, Newgreen D, Ridder A, Paireddy A and van Maanen
R: Combination treatment with mirabegron and solifenacin in
patients with overactive bladder: Exploratory responder analyses of
efficacy and evaluation of patient-reported outcomes from a
randomized, double-blind, factorial, dose-ranging, phase II study
(SYMPHONY). World J Urol. 35:827–838. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
van Enst WA, Ochodo E, Scholten RJPM,
Hooft L and Leeflang MM: Investigation of publication bias in
meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy: A meta-epidemiological
study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 14(70)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Munkholm K and Paludan-Müller AS: Caution
is advised when interpreting subgroup analyses.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 46(1551)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reinold J, Schäfer W, Christianson L,
Barone-Adesi F, Riedel O and Pisa FE: Anticholinergic burden and
fractures: A protocol for a methodological systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 9(e030205)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pieper NT, Grossi CM, Chan WY, Loke YK,
Savva GM, Haroulis C, Steel N, Fox C, Maidment ID, Arthur AJ, et
al: Anticholinergic drugs and incident dementia, mild cognitive
impairment and cognitive decline: A meta-analysis. Age Ageing.
49:939–947. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|