|
1
|
Fu Y, Lei C, Qibo R, Huang X, Chen Y, Wang
M and Zhang M: Insulin-like growth factor-1 and retinopathy of
prematurity: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Surv Ophthalmol.
68:1153–1165. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
García H, Villasis-Keever MA,
Zavala-Vargas G, Bravo-Ortiz JC, Pérez-Méndez A and Escamilla-Núñez
A: Global prevalence and severity of retinopathy of prematurity
over the last four decades (1985-2021): A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Arch Med Res. 55(102967)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bhatnagar A, Skrehot HC, Bhatt A, Herce H
and Weng CY: Epidemiology of retinopathy of prematurity in the US
from 2003 to 2019. JAMA Ophthalmol. 141:479–485. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chiang MF, Quinn GE, Fielder AR, Ostmo SR,
Chan RV, Berrocal A, Binenbaum G, Blair M, Campbell JP, Capone A
Jr, et al: International classification of retinopathy of
prematurity, third edition. Ophthalmology. 128:e51–e68.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Schmitz AM, Bumbaru SM, Fakhouri LS and
Zhang DQ: Long-term impairment of retinal ganglion cell function
after oxygen-induced retinopathy. Cells. 14(512)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Beccasio A, Mignini C, Caricato A,
Iaccheri B, Di Cara G, Verrotti A and Cagini C: New trends in
intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy for ROP. Eur J Ophthalmol.
32:1340–1351. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sankar BK, Amin H, Pappa P and Riaz KM:
Risk factors of retinopathy of prematurity: A prospective study.
Indian J Public Health. 69:111–114. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Karmouta R, Strawbridge JC, Langston S,
Altendahl M, Khitri M, Chu A and Tsui I: Neurodevelopmental
outcomes in infants screened for retinopathy of prematurity. JAMA
Ophthalmol. 141:1125–1132. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tan H, Blasco P, Lewis T, Ostmo S, Chiang
MF and Campbell JP: Neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants
with retinopathy of prematurity. Surv Ophthalmol. 66:877–891.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Almutairi MF, Gulden S, Hundscheid TM,
Bartoš F, Cavallaro G and Villamor E: Platelet counts and risk of
severe retinopathy of prematurity: A bayesian model-averaged
meta-analysis. Children (Basel). 10(1903)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nakayama LF, Mitchell WG, Ribeiro LZ,
Dychiao RG, Phanphruk W, Celi LA, Kalua K, Santiago APD, Regatieri
CVS and Moraes NSB: Fairness and generalisability in deep learning
of retinopathy of prematurity screening algorithms: A literature
review. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 8(e001216)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim SJ, Port AD, Swan R, Campbell JP, Chan
RVP and Chiang MF: Retinopathy of prematurity: A review of risk
factors and their clinical significance. Surv Ophthalmol.
63:618–637. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shah S, Slaney E, VerHage E, Chen J, Dias
R, Abdelmalik B, Weaver A and Neu J: Application of artificial
intelligence in the early detection of retinopathy of prematurity:
Review of the literature. Neonatology. 120:558–565. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hellström A and Hård AL: Screening and
novel therapies for retinopathy of prematurity-A review. Early Hum
Dev. 138(104846)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Diggikar S, Gurumoorthy P, Trif P, Mudura
D, Nagesh NK, Galis R, Vinekar A and Kramer BW: Retinopathy of
prematurity and neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pediatr.
11(1055813)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Collins GS, Moons KGM, Dhiman P, Riley RD,
Beam AL, Van Calster B, Ghassemi M, Liu X, Reitsma JB, van Smeden
M, et al: TRIPOD+AI statement: Updated guidance for reporting
clinical prediction models that use regression or machine learning
methods. BMJ. 385(e078378)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fernandez-Felix BM, López-Alcalde J, Roqué
M, Muriel A and Zamora J: CHARMS and PROBAST at your fingertips: A
template for data extraction and risk of bias assessment in
systematic reviews of predictive models. BMC Med Res Methodol.
23(44)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Moons KGM, Damen JAA, Kaul T, Hooft L,
Navarro CA, Dhiman P, Beam AL, Van Calster B, Celi LA, Denaxas S,
et al: PROBAST+AI: An updated quality, risk of bias, and
applicability assessment tool for prediction models using
regression or artificial intelligence methods. BMJ.
388(e082505)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fu H, Hou D, Xu R, You Q, Li H, Yang Q,
Wang H, Gao J and Bai D: Risk prediction models for deep venous
thrombosis in patients with acute stroke: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 149(104623)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kuo RYL, Harrison C, Curran TA, Jones B,
Freethy A, Cussons D, Stewart M, Collins GS and Furniss D:
Artificial intelligence in fracture detection: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Radiology. 304:50–62. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
de Jong Y, Ramspek CL, Zoccali C, Jager
KJ, Dekker FW and van Diepen M: Appraising prediction research: A
guide and meta-review on bias and applicability assessment using
the prediction model risk of bias ASsessment tool (PROBAST).
Nephrology (Carlton). 26:939–947. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J,
Welch VA, Higgins JP and Thomas J: Updated guidance for trusted
systematic reviews: A new edition of the cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
10(ED000142)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
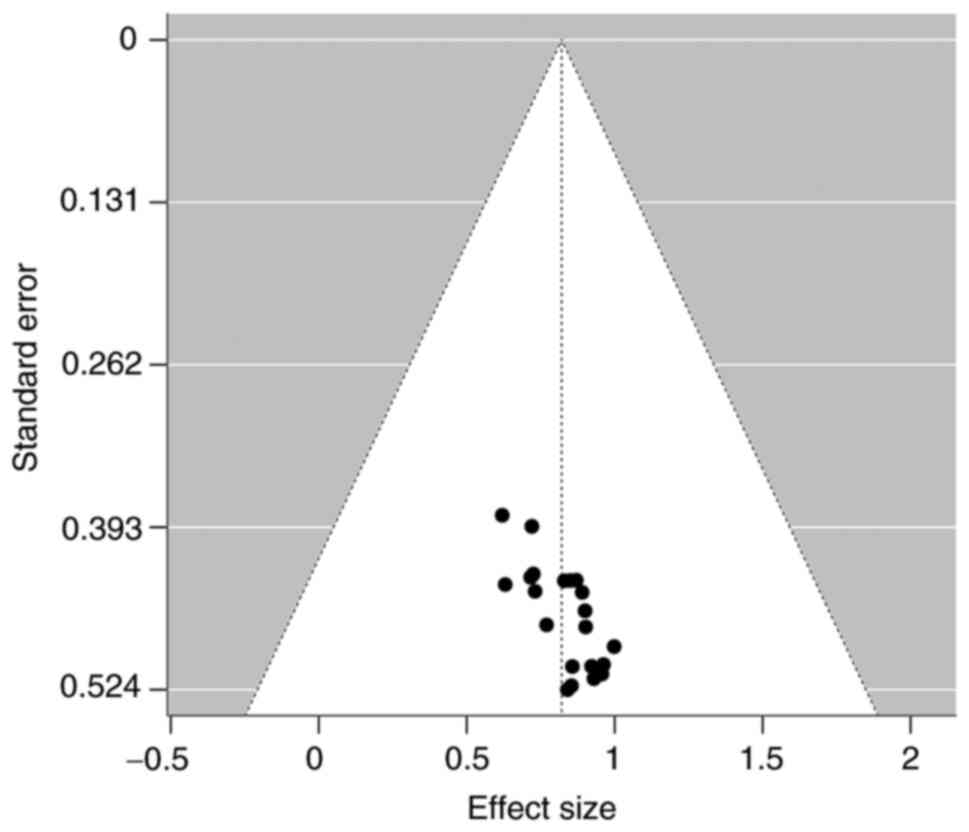
Furuya-Kanamori L, Barendregt JJ and Doi
SAR: A new improved graphical and quantitative method for detecting
bias in meta-analysis. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 16:195–203.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
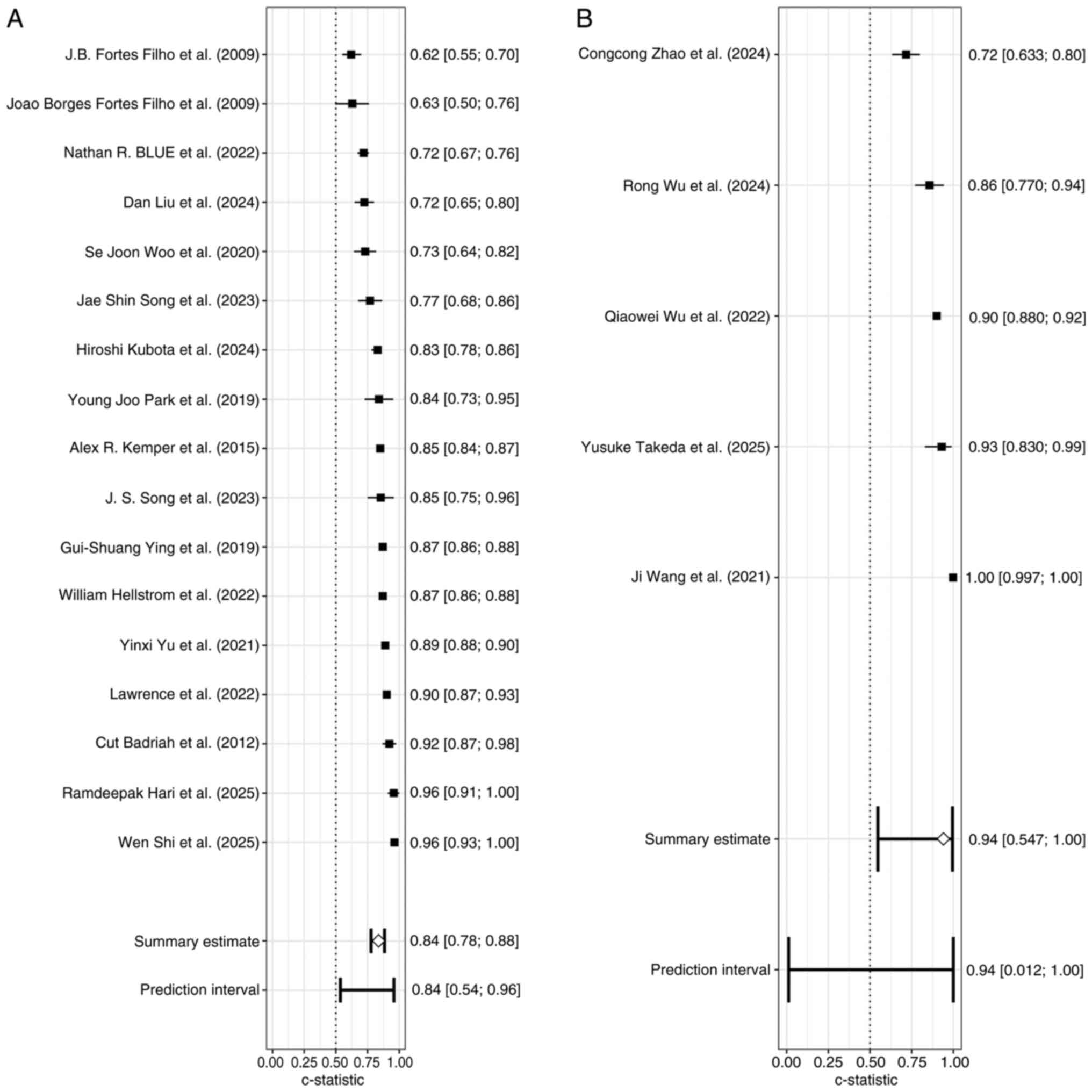
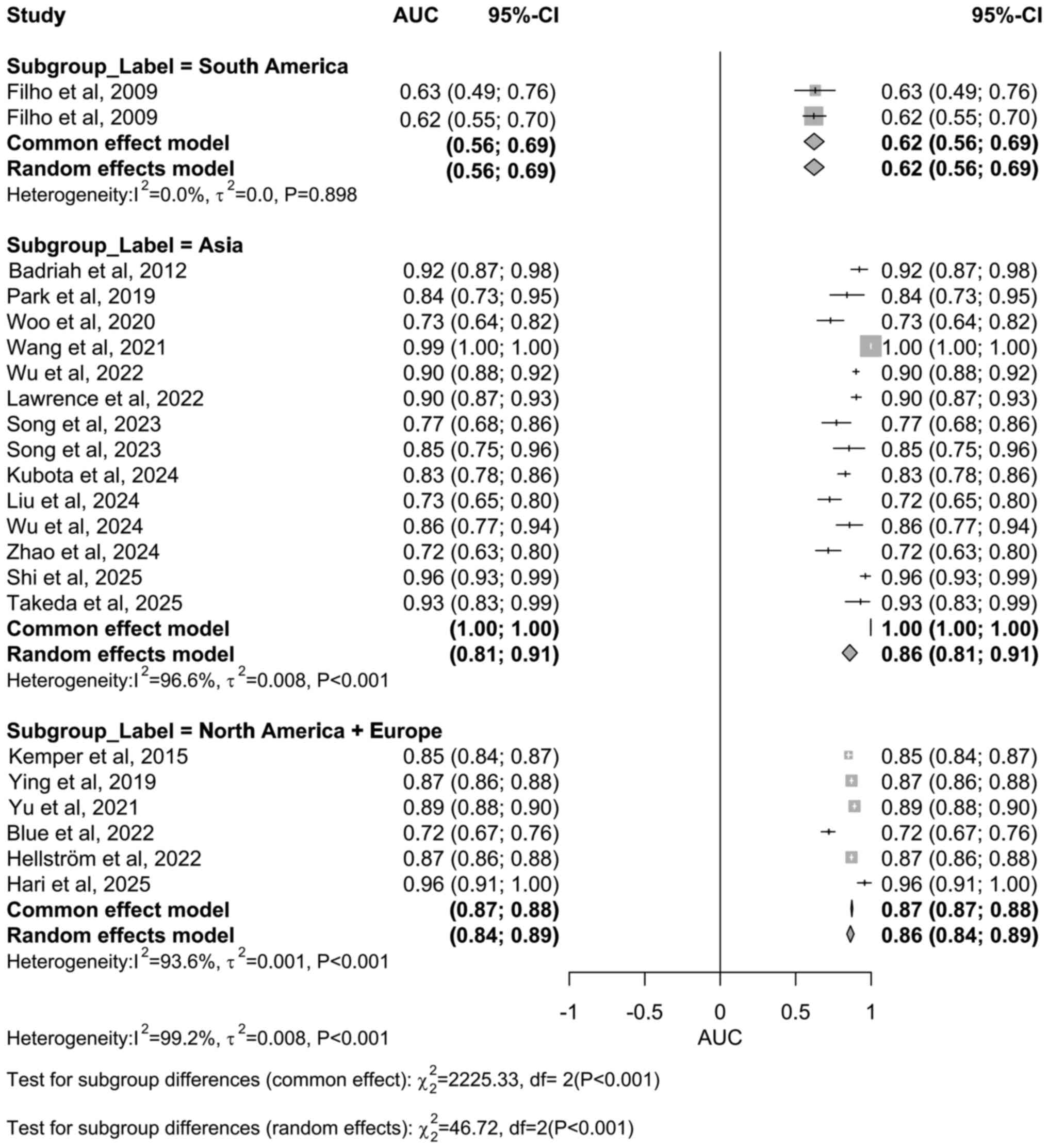
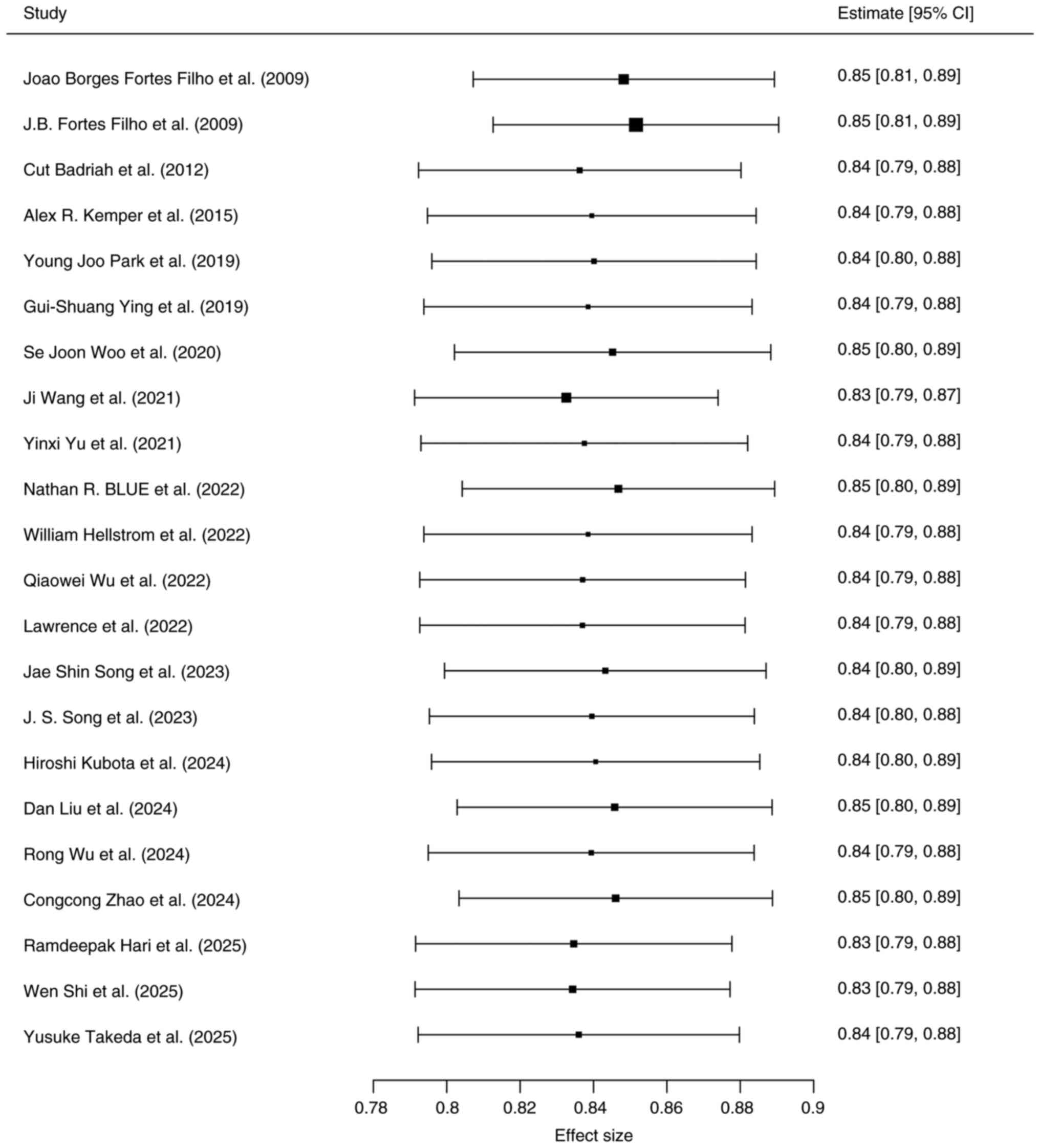
Filho JB, Bonomo PP, Maia M and Procianoy
RS: Weight gain measured at 6 weeks after birth as a predictor for
severe retinopathy of prematurity: Study with 317 very low birth
weight preterm babies. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
247:831–836. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Filho JB, Dill JC, Ishizaki A, Aguiar WW,
Silveira RC and Procianoy RS: Score for neonatal acute physiology
and perinatal extension II as a predictor of retinopathy of
prematurity: Study in 304 very-low-birth-weight preterm infants.
Ophthalmologica. 223:177–182. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Badriah C, Amir I, Elvioza E and Ifran E:
Prevalence and risk factors of retinopathy of prematurity.
Paediatrica Indonesiana. 52:138–144. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Kemper AR, Wade KC, Hornik CP, Ying GS,
Baumritter A and Quinn GE: Telemedicine Approaches to Evaluating
Acute-phase Retinopathy of Prematurity (e-ROP) Study Cooperative
Group. Retinopathy of prematurity risk prediction for infants with
birth weight less than 1251 grams. J Pediatr. 166:257–261.e2.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Owen LA, Morrison MA, Hoffman RO, Yoder BA
and DeAngelis MM: Retinopathy of prematurity: A comprehensive risk
analysis for prevention and prediction of disease. PLoS One.
12(e0171467)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gerull R, Brauer V, Bassler D, Laubscher
B, Pfister RE, Nelle M, Müller B, Roth-Kleiner M, Gerth-Kahlert C
and Adams M: Swiss Neonatal Network & Follow-up Group.
Prediction of ROP treatment and evaluation of screening criteria in
VLBW infants-a population based analysis. Pediatr Res. 84:632–638.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cerda AM, McCourt EA, Thevarajah T, Wymore
E, Lynch AM and Wagner BD: Comparison between weight gain and
Fenton preterm growth z scores in assessing the risk of retinopathy
of prematurity. J AAPOS. 23:281–283. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Park YJ, Woo SJ, Kim YM, Hong S, Lee YE
and Park KH: Immune and inflammatory proteins in cord blood as
predictive biomarkers of retinopathy of prematurity in preterm
infants. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 60:3813–3820. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ying GS, Bell EF, Donohue P, Tomlinson LA
and Binenbaum G: G-ROP Research Group. Perinatal risk factors for
the retinopathy of prematurity in postnatal growth and rop study.
Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 26:270–278. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Woo SJ, Park JY, Hong S, Kim YM, Park YH,
Lee YE and Park KH: Inflammatory and angiogenic mediators in
amniotic fluid are associated with the development of retinopathy
of prematurity in preterm infants. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
61(42)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fekri Y, Ojaghi H, Momeni N and Amani F:
Retinopathy of prematurity in Ardabil, North West of Iran:
Prevalence and risk factors. Eur J Transl Myol.
31(10063)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Ji J, Zhang M, Lin JW, Zhang G,
Gong W, Cen LP, Lu Y, Huang X, Huang D, et al: Automated
explainable multidimensional deep learning platform of retinal
images for retinopathy of prematurity screening. JAMA Netw Open.
4(e218758)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yu Y, Tomlinson LA, Binenbaum G and Ying
GS: G-Rop Study Group. Incidence, timing and risk factors of type 1
retinopathy of prematurity in a North American cohort. Br J
Ophthalmol. 105:1724–1730. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Blue NR, Allshouse AA, Grobman WA, Day RC,
Haas DM, Simhan HN, Parry S, Saade GR and Silver RM: Developing a
predictive model for perinatal morbidity among small for
gestational age infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 35:8462–8471.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hellström W, Martinsson T, Morsing E,
Gränse L, Ley D and Hellström A: Low fraction of fetal haemoglobin
is associated with retinopathy of prematurity in the very preterm
infant. Br J Ophthalmol. 106:970–974. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wu Q, Hu Y, Mo Z, Wu R, Zhang X, Yang Y,
Liu B, Xiao Y, Zeng X, Lin Z, et al: Development and validation of
a deep learning model to predict the occurrence and severity of
retinopathy of prematurity. JAMA Netw Open.
5(e2217447)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Iu LPL, Yip WWK, Lok JYC, Fan MCY, Lai
CHY, Ho M and Young AL: Prediction model to predict type 1
retinopathy of prematurity using gestational age and birth weight
(PW-ROP). Br J Ophthalmol. 107:1007–1011. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Song JS, Woo SJ, Park KH, Joo E, Kim H, Oh
E and Lee KN: Cord blood transforming growth factor-β-induced as
predictive biomarker of retinopathy of prematurity in preterm
infants. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 261:2477–2488.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Song JS, Woo SJ, Park KH, Kim H, Lee KN
and Kim YM: Association of inflammatory and angiogenic biomarkers
in maternal plasma with retinopathy of prematurity in preterm
infants. Eye (Lond). 37:1802–1809. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen S, Zhao X, Wu Z, Cao K, Zhang Y, Tan
T, Lam CT, Xu Y, Zhang G and Sun Y: Multi-risk factors joint
prediction model for risk prediction of retinopathy of prematurity.
EPMA J. 15:261–274. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kubota H, Fukushima Y, Kawasaki R, Endo T,
Hatsukawa Y, Ineyama H, Hirata K, Hirano S, Wada K and Nishida K:
Continuous oxygen saturation and risk of retinopathy of prematurity
in a Japanese cohort. Br J Ophthalmol. 108:1275–1280.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lin WC, Jordan BK, Scottoline B, Ostmo SR,
Coyner AS, Singh P, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Erdogmus D, Chan RVP, Chiang
MF and Campbell JP: Oxygenation fluctuations associated with severe
retinopathy of prematurity: Insights from a multimodal deep
learning approach. Ophthalmol Sci. 4(100417)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Liu D, Li XY, He HW, Jin KL, Zhang LX,
Zhou Y, Zhu ZM, Jiang CC, Wu HJ and Zheng SL: Nomogram to predict
severe retinopathy of prematurity in Southeast China. Int J
Ophthalmol. 17:282–288. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wu R, Chen H, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Feng S and
Lu X: Prediction models for retinopathy of prematurity occurrence
based on artificial neural network. BMC Ophthalmol.
24(323)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhao C, Sun Z, Chen H, Li K and Sun H: The
impact of blood lactic acid levels on retinopathy of prematurity
morbidity. BMC Pediatr. 24(152)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hari R, Mellacheruvu P, Nonye OC, Rastogi
A and Mydam J: Severe patent ductus arteriosus is a risk factor for
clinically significant retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth
weight infants. SN Compr Clin Med. 7(60)2025.
|
|
51
|
Shi W, Zhu L, He X, Wang S and Wang C:
Combined indicator assists in early recognition of retinopathy of
prematurity. Sci Rep. 15(8048)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Takeda Y, Kaneko Y, Sugimoto M, Yamashita
H, Sasaki A and Mitsui T: Prediction models for retinopathy of
prematurity using nonimaging machine learning approaches: A
regional multicenter study. Ophthalmol Sci.
5(100715)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wagner SK, Liefers B, Radia M, Zhang G,
Struyven R, Faes L, Than J, Balal S, Hennings C, Kilduff C, et al:
Development and international validation of custom-engineered and
code-free deep-learning models for detection of plus disease in
retinopathy of prematurity: A retrospective study. Lancet Digit
Health. 5:e340–e349. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Rashidian P, Karami S and Salehi SA: A
review on retinopathy of prematurity. Med Hypothesis Discov Innov
Ophthalmol. 13:201–212. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Maitra P, Shah PK, Campbell PJ and Rishi
P: The scope of artificial intelligence in retinopathy of
prematurity (ROP) management. Indian J Ophthalmol. 72:931–934.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Xu S, Liang Z, Du Q, Li Z, Tan G, Nie C,
Yang Y, Lv X, Zhang C and Luo X: A systematic study on the
prevention and treatment of retinopathy of prematurity in China.
BMC Ophthalmol. 18(44)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yildirim M, Coban A, Bulut O, Mercül NK
and Ince Z: Postnatal weight gain and retinopathy of prematurity in
preterm infants: A population-based retrospective cohort study. J
Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 37(2337720)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Han G, Lim DH, Kang D, Cho J, Guallar E,
Chang YS, Chung TY, Kim SJ and Park WS: Association between
retinopathy of prematurity in very-low-birth-weight infants and
neurodevelopmental impairment. Am J Ophthalmol. 244:205–215.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dammann O, Hartnett ME and Stahl A:
Retinopathy of prematurity. Dev Med Child Neurol. 65:625–631.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Engin CD, Ozturk T, Ozkan O, Oztas A,
Selver MA and Tuzun F: Prediction of retinopathy of prematurity
development and treatment need with machine learning models. BMC
Ophthalmol. 25(194)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gilbert CE: Global perspectives of
retinopathy of prematurity. Indian J Ophthalmol. 71:3431–3433.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wang J, Ying GS, Yu Y, Tomlinson L and
Binenbaum G: Racial differences in retinopathy of prematurity.
Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 30:523–531. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kim ES, Calkins KL and Chu A: Retinopathy
of prematurity: The role of nutrition. Pediatr Ann. 52:e303–e308.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
He D, Luo X, Ying B, Quinn GE, Baumritter
A, Chen Y, Ying GS and He L: Machine learning models for predicting
treatment-requiring retinopathy of prematurity in the e-ROP study.
Transl Vis Sci Technol. 14(14)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|