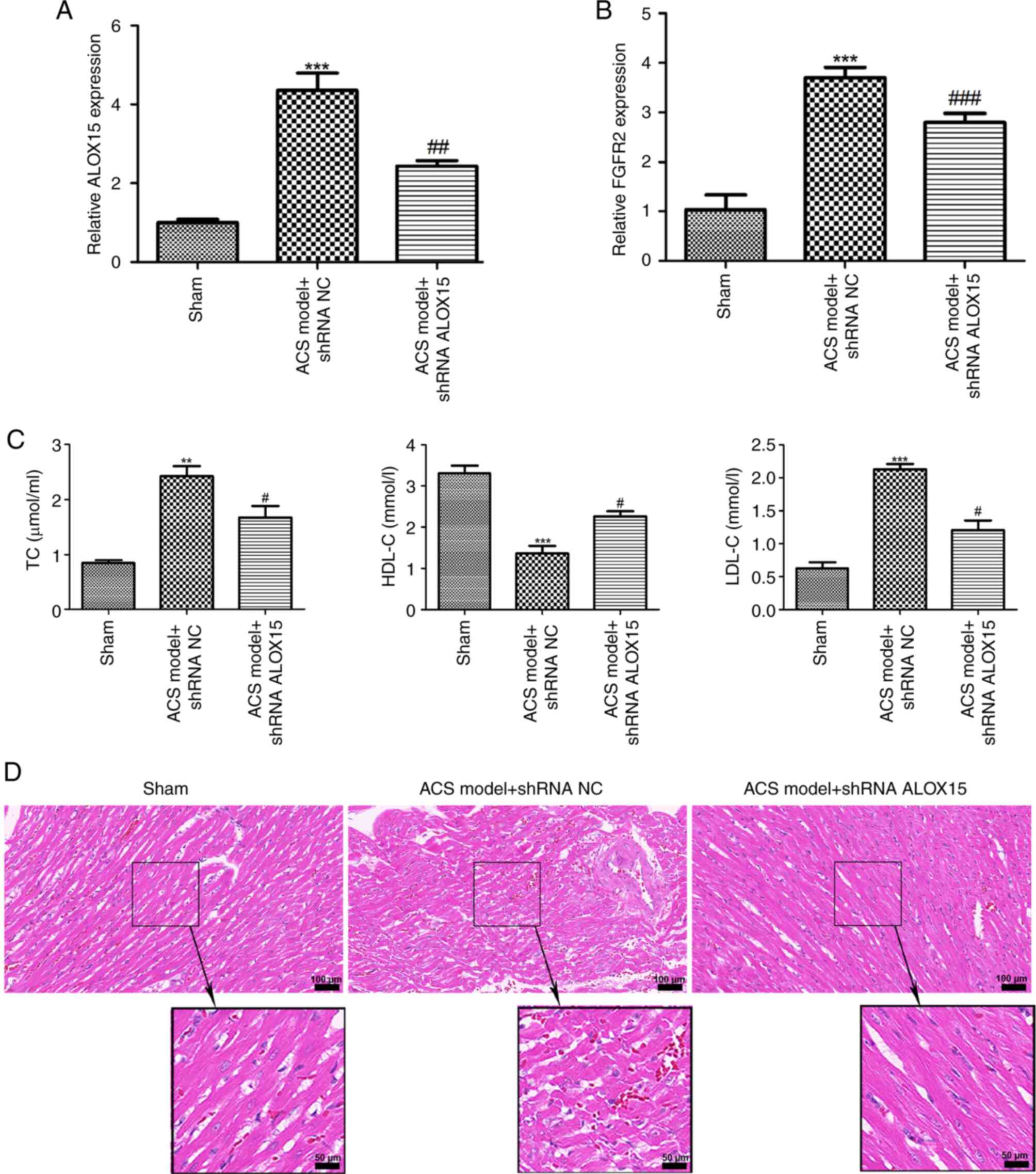
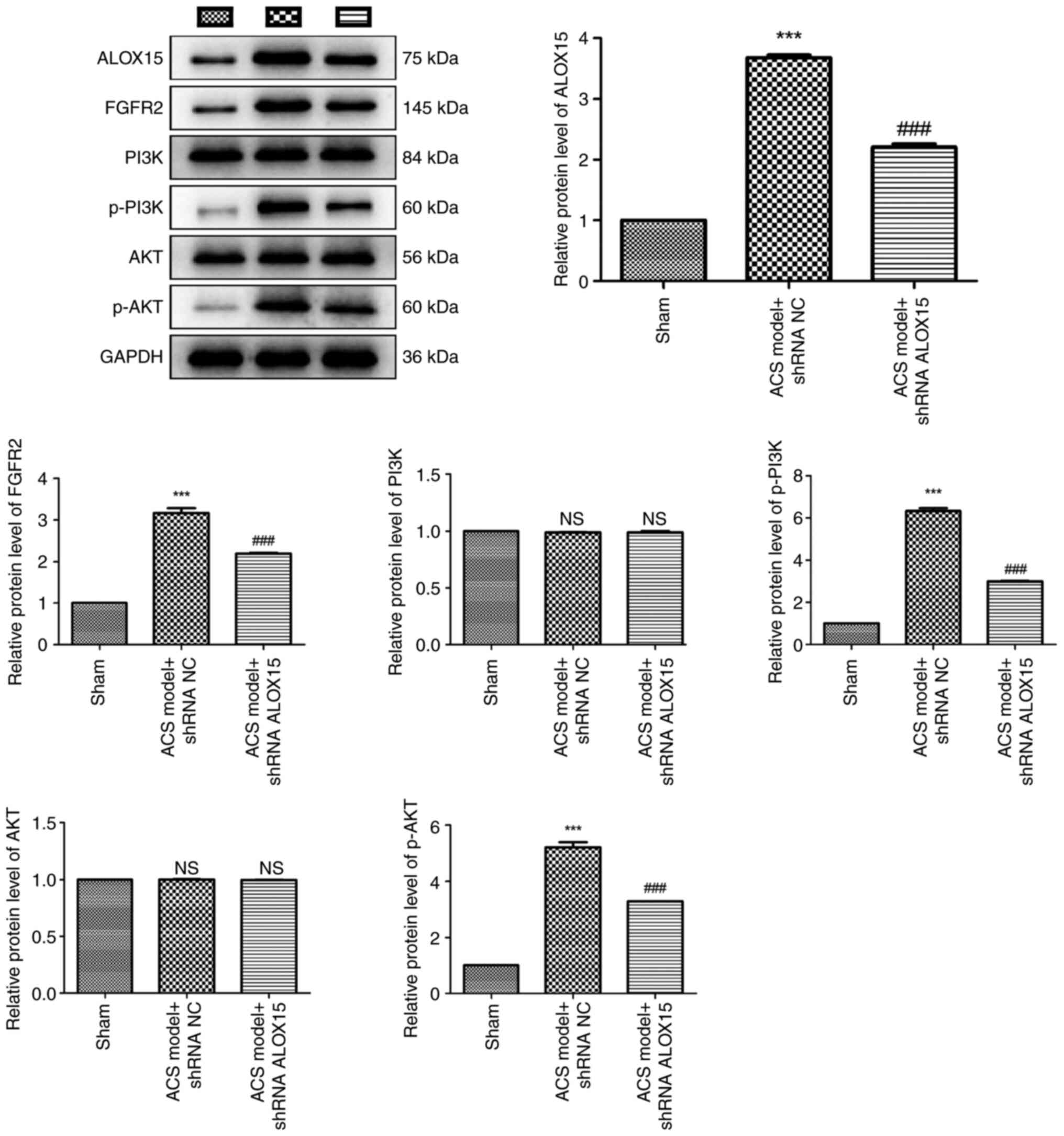
|
1
|
Dong CH, Wang ZM and Chen SY: Neutrophil
to lymphocyte ratio predict mortality and major adverse cardiac
events in acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Clin Biochem. 52:131–136. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bob-Manuel T, Ifedili I, Reed G, Ibebuogu
UN and Khouzam RN: Non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: A
comprehensive review. Curr Probl Cardiol. 42:266–305.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy
O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T,
Folliguet T, et al: 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute
coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent
ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 42:1289–1367. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Libby P and Pasterkamp G: Requiem for the
‘vulnerable plaque’. Eur Heart J. 36:2984–2987. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Makki N, Brennan TM and Girotra S: Acute
coronary syndrome. J Intensive Care Med. 30:186–200.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kaul P, Ezekowitz JA, Armstrong PW, Leung
BK, Savu A, Welsh RC, Quan H, Knudtson ML and McAlister FA:
Incidence of heart failure and mortality after acute coronary
syndromes. Am Heart J. 165:379–385 e2. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey
DE Jr, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM,
Franklin BA, et al: 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of
ST-elevation myocardial infarction: Executive summary: A report of
the American college of cardiology foundation/American heart
association task force on practice guidelines: Developed in
collaboration with the American college of emergency physicians and
society for cardiovascular angiography and interventions. Catheter
Cardiovasc Interv. 82:E1–E27. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Oliw EH: Diversity of the manganese
lipoxygenase gene family-A mini-review. Fungal Genet Biol.
163(103746)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hiltunen T, Luoma J, Nikkari T and
Yla-Herttuala S: Induction of 15-lipoxygenase mRNA and protein in
early atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation. 92:3297–3303.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kuhn H, Heydeck D, Hugou I and Gniwotta C:
In vivo action of 15-lipoxygenase in early stages of human
atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 99:888–893. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang K, Wang YY, Liu QJ, Wang H, Liu FF,
Ma ZY, Gong YQ and Li L: Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in
ALOX15 are associated with risk of coronary artery disease in a
Chinese Han population. Heart Vessels. 25:368–373. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ma XH, Liu JH, Liu CY, Sun WY, Duan WJ,
Wang G, Kurihara H, He RR, Li YF, Chen Y and Shang H:
ALOX15-launched PUFA-phospholipids peroxidation increases the
susceptibility of ferroptosis in ischemia-induced myocardial
damage. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7(288)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cai W, Liu L, Shi X, Liu Y, Wang J, Fang
X, Chen Z, Ai D, Zhu Y and Zhang X: Alox15/15-HpETE aggravates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting cardiomyocyte
ferroptosis. Circulation. 147:1444–1460. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kayama Y, Minamino T, Toko H, Sakamoto M,
Shimizu I, Takahashi H, Okada S, Tateno K, Moriya J, Yokoyama M, et
al: Cardiac 12/15 lipoxygenase-induced inflammation is involved in
heart failure. J Exp Med. 206:1565–1574. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Silbiger VN, Luchessi AD, Hirata RD,
Lima-Neto LG, Cavichioli D, Carracedo A, Brión M, Dopazo J,
García-García F, dos Santos ES, et al: Novel genes detected by
transcriptional profiling from whole-blood cells in patients with
early onset of acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta.
421:184–190. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Huang S, Guan F, Han S, Ye F, Li X
and You L: Targeting circulating lncRNA ENST00000538705.1 relieves
acute coronary syndrome via modulating ALOX15. Dis Markers.
2022(8208471)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Feng J, Yang F, Wu H, Xing C, Xue H, Zhang
L, Zhang C, Hu G and Cao H: Selenium protects against
cadmium-induced cardiac injury by attenuating programmed cell death
via PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling. Environ Toxicol. 37:1185–1197.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu D, Xiong J, Gao Y, Li J, Zhu D, Shen X,
Sun L and Wang X: Resveratrol activates PI3K/AKT to reduce
myocardial cell apoptosis and mitochondrial oxidative damage caused
by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Acta Histochem.
123(151739)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cheng Y, Shen A, Wu X, Shen Z, Chen X, Li
J, Liu L, Lin X, Wu M, Chen Y, et al: Qingda granule attenuates
angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis and
modulates the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
133(111022)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Han X, Zhang G, Chen G, Wu Y, Xu T, Xu H,
Liu B and Zhou Y: Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes angiogenesis in
myocardial infarction through suppression of PTEN and activation of
the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
287(114929)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chang H, Li C, Wang Q, Lu L, Zhang Q,
Zhang Y, Zhang N, Wang Y and Wang W: QSKL protects against
myocardial apoptosis on heart failure via PI3K/Akt-p53 signaling
pathway. Sci Rep. 7(16986)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ruan R, Li L, Li X, Huang C, Zhang Z,
Zhong H, Zeng S, Shi Q, Xia Y, Zeng Q, et al: Unleashing the
potential of combining FGFR inhibitor and immune checkpoint
blockade for FGF/FGFR signaling in tumor microenvironment. Mol
Cancer. 22(60)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Takahashi M, Umehara Y, Yue H,
Trujillo-Paez JV, Peng G, Nguyen HLT, Ikutama R, Okumura K, Ogawa
H, Ikeda S and Niyonsaba F: The antimicrobial peptide human
β-defensin-3 accelerates wound healing by promoting angiogenesis,
cell migration, and proliferation through the FGFR/JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Front Immunol. 12(712781)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Weaver A and Bossaer JB: Fibroblast growth
factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitors: A review of a novel therapeutic
class. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 27:702–710. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Farooq M, Khan AW, Kim MS and Choi S: The
role of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling in tissue repair
and regeneration. Cells. 10(3242)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mieczkowski K, Popeda M, Lesniak D, Sadej
R and Kitowska K: FGFR2 Controls growth, adhesion and migration of
nontumorigenic human mammary epithelial cells by regulation of
integrin β 1 degradation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
28(9)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yoshii T, Matsuzawa Y, Kato S, Sato R,
Hanajima Y, Kikuchi S, Nakahashi H, Konishi M, Akiyama E,
Minamimoto Y, et al: Endothelial dysfunction predicts bleeding and
cardiovascular death in acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol.
376:11–17. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jiao K, Su P and Li Y: FGFR2 modulates the
Akt/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway to improve angiotensin II-induced
hypertension-related endothelial dysfunction. Clin Exp Hypertens.
45(2208777)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Huang C, Wang R, Lu J, He Y, Wu Y, Ma W,
Xu J, Wu Z, Feng Z and Wu M: MicroRNA-338-3p as a therapeutic
target in cardiac fibrosis through FGFR2 suppression. J Clin Lab
Anal. 36(e24584)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Riccetti MR, Green J, Taylor TJ and Perl
AT: Prenatal FGFR2 signaling via PI3K/AKT specifies the
PDGFRA+ myofibroblast. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
70:63–77. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang J, Xin C, Yin G and Li J:
Taraxasterol suppresses the proliferation and tumor growth of
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells through the
FGFR2-PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 13(13072)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu S, Sun H and Sun B: MicroRNA-145 is
involved in endothelial cell dysfunction and acts as a promising
biomarker of acute coronary syndrome. Eur J Med Res.
25(2)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li J, Gong L, Zhang R, Li S, Yu H, Liu Y,
Xue Y, Huang D, Xu N, Wang Y, et al: Fibroblast growth factor 21
inhibited inflammation and fibrosis after myocardial infarction via
EGR1. Eur J Pharmacol. 910(174470)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Roth GA, Huffman MD, Moran AE, Feigin V,
Mensah GA, Naghavi M and Murray CJ: Global and regional patterns in
cardiovascular mortality from 1990 to 2013. Circulation.
132:1667–1678. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gupta A, Wang Y, Spertus JA, Geda M,
Lorenze N, Nkonde-Price C, D'Onofrio G, Lichtman JH and Krumholz
HM: Trends in acute myocardial infarction in young patients and
differences by sex and race, 2001 to 2010. J Am Coll Cardiol.
64:337–345. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, Go A,
Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern SM, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, et
al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2008 update: A report from
the American heart association statistics committee and stroke
statistics subcommittee. Circulation. 117:e25–e146. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Nichols M, Townsend N, Scarborough P and
Rayner M: Cardiovascular disease in Europe 2014: Epidemiological
update. Eur Heart J. 35(2929)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ferreira-Gonzalez I: The epidemiology of
coronary heart disease. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 67:139–144.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Menzin J, Wygant G, Hauch O, Jackel J and
Friedman M: One-year costs of ischemic heart disease among patients
with acute coronary syndromes: Findings from a multi-employer
claims database. Curr Med Res Opin. 24:461–468. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2013 update:
A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
127:143–152. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bonetti PO, Lerman LO and Lerman A:
Endothelial dysfunction: A marker of atherosclerotic risk.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:168–175. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kinlay S and Ganz P: Role of endothelial
dysfunction in coronary artery disease and implications for
therapy. Am J Cardiol. 80:11I–16I. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhu F, Wang Q, Guo C, Wang X, Cao X, Shi
Y, Gao F, Ma C and Zhang L: IL-17 induces apoptosis of vascular
endothelial cells: A potential mechanism for human acute coronary
syndrome. Clin Immunol. 141:152–160. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Stein RA: Endothelial dysfunction,
erectile dysfunction, and coronary heart disease: The
pathophysiologic and clinical linkage. Rev Urol. 5 (Suppl
7):S21–S27. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ling L, Zhao SP, Gao M, Zhou QC, Li YL and
Xia B: Vitamin C preserves endothelial function in patients with
coronary heart disease after a high-fat meal. Clin Cardiol.
25:219–224. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Singh NK and Rao GN: Emerging role of
12/15-Lipoxygenase (ALOX15) in human pathologies. Prog Lipid Res.
73:28–45. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Eisenreich A and Rauch U: PI3K inhibitors
in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Ther. 29:29–36.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ozkaynak B, Sahin I, Ozenc E, Subaşı C,
Oran DS, Totoz T, Tetikkurt ÜS, Mert B, Polat A, Okuyan E and
Karaöz E: Mesenchymal stem cells derived from epicardial adipose
tissue reverse cardiac remodeling in a rabbit model of myocardial
infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:4372–4384.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Chen L, Li S, Zhu J, You A, Huang X, Yi X
and Xue M: Mangiferin prevents myocardial infarction-induced
apoptosis and heart failure in mice by activating the Sirt1/FoxO3a
pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2944–2955. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Nagy RN, Makkos A, Baranyai T, Giricz Z,
Szabó M, Kravcsenko-Kiss B, Bereczki Z, Ágg B, Puskás LG, Faragó N,
et al: Cardioprotective microRNAs (protectomiRs) in a pig model of
acute myocardial infarction and cardioprotection by ischaemic
conditioning: MiR-450a. Br J Pharmacol. 182:396–416.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|