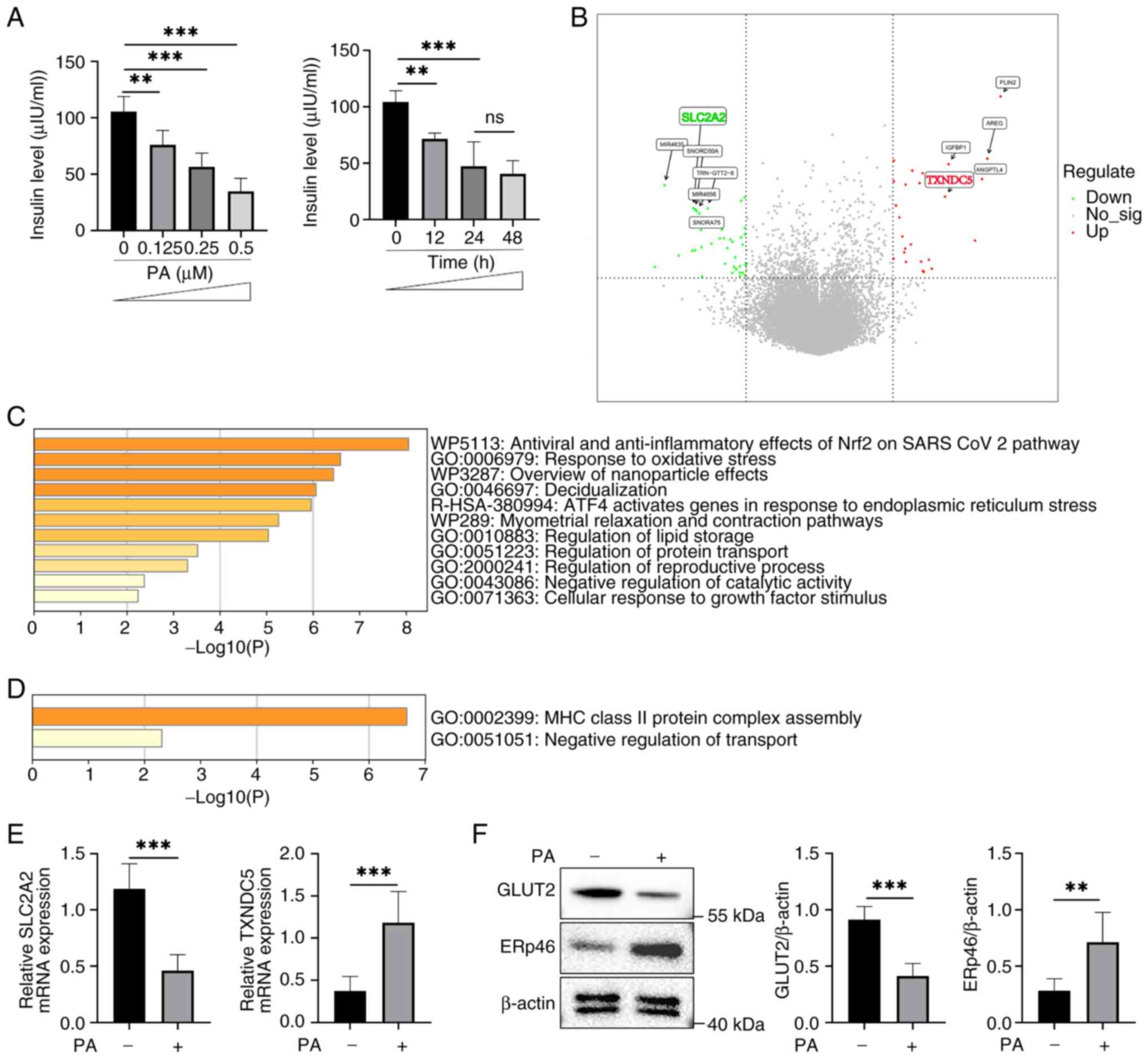
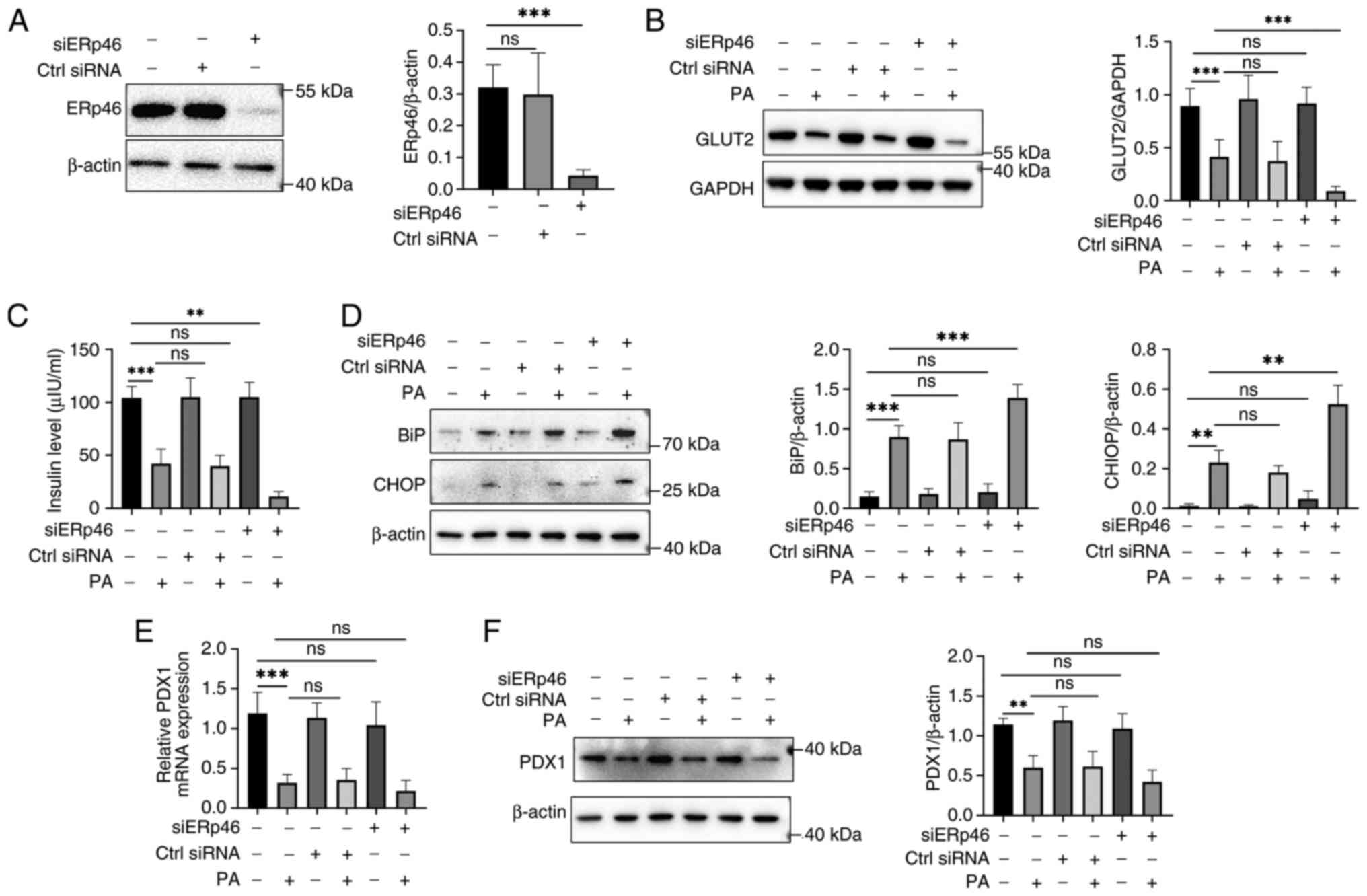
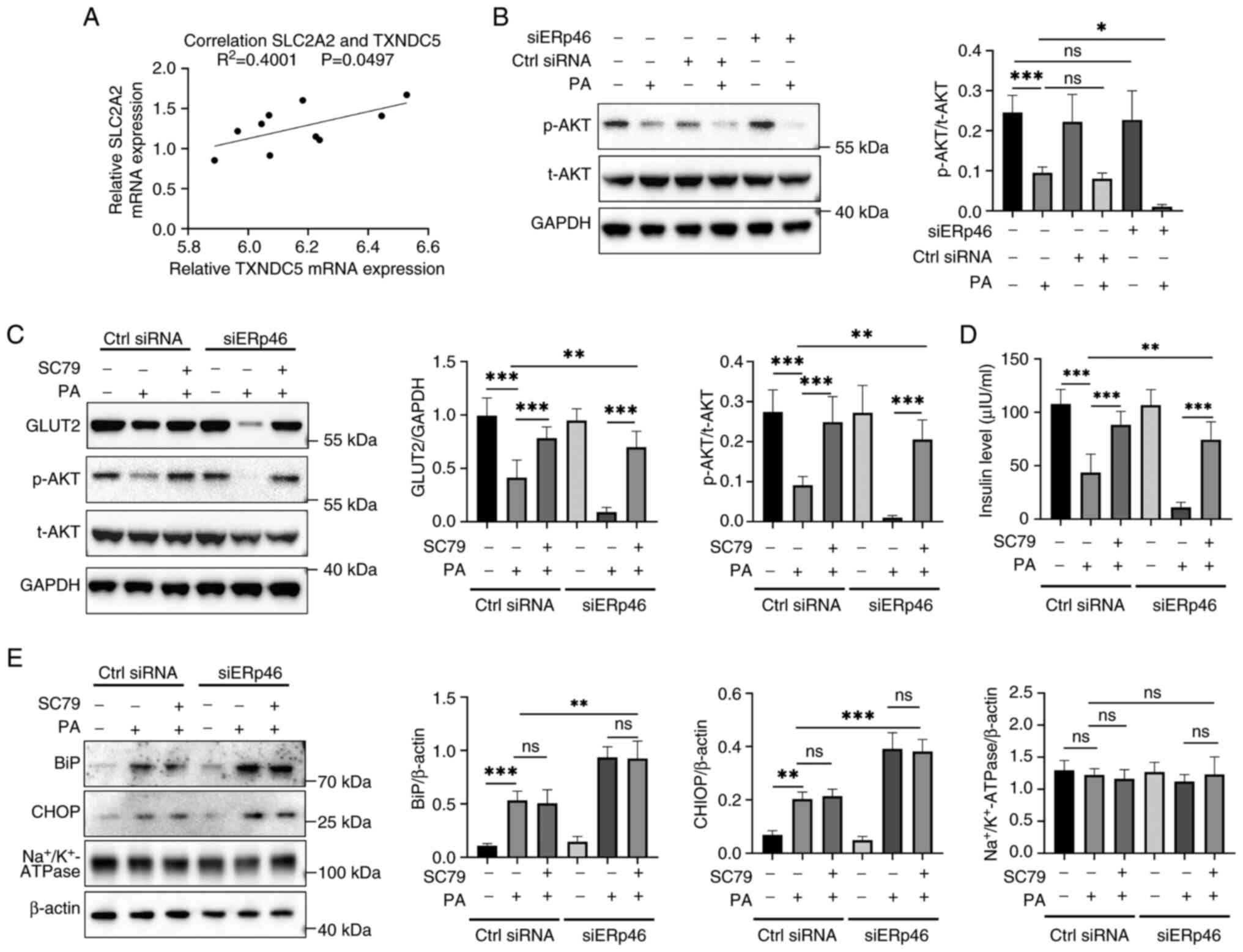
|
1
|
Heald AH, Stedman M, Davies M, Livingston
M, Alshames R, Lunt M, Rayman G and Gadsby R: Estimating life years
lost to diabetes: Outcomes from analysis of National diabetes audit
and office of National statistics data. Cardiovasc Endocrinol
Metab. 9:183–185. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M,
Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et
al: IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes
prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 183(109119)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the International diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157(107843)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Piché ME, Tchernof A and Després JP:
Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ
Res. 126:1477–1500. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Eizirik DL, Pasquali L and Cnop M:
Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus: Different
pathways to failure. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 16:349–362.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Thorens B: GLUT2, glucose sensing and
glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia. 58:221–232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mueckler M and Thorens B: The SLC2 (GLUT)
family of membrane transporters. Mol Aspects Med. 34:121–138.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Thorens B, Guillam MT, Beermann F,
Burcelin R and Jaquet M: Transgenic reexpression of GLUT1 or GLUT2
in pancreatic beta cells rescues GLUT2-null mice from early death
and restores normal glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J Biol
Chem. 275:23751–23758. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Guillam MT, Dupraz P and Thorens B:
Glucose uptake, utilization, and signaling in GLUT2-null islets.
Diabetes. 49:1485–1491. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lytrivi M, Castell AL, Poitout V and Cnop
M: Recent insights into mechanisms of β-cell lipo- and
glucolipotoxicity in type 2 diabetes. J Mol Biol. 432:1514–1534.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Prentki M, Peyot ML, Masiello P and
Madiraju SRM: Nutrient-induced metabolic stress, adaptation,
detoxification, and toxicity in the pancreatic β-cell. Diabetes.
69:279–290. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ashcroft FM and Rorsman P: Diabetes
mellitus and the β cell: The last ten years. Cell. 148:1160–1171.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xie T, So WY, Li XY and Leung PS:
Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against lipotoxicity-induced
pancreatic β-cell dysfunction via regulation of AMPK signaling and
lipid metabolism. Clin Sci (Lond. 133:2029–2044. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Biden TJ, Robinson D, Cordery D, Hughes WE
and Busch AK: Chronic effects of fatty acids on pancreatic
beta-cell function: New insights from functional genomics.
Diabetes. 53 (Suppl 1):S159–S165. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cnop M: Fatty acids and glucolipotoxicity
in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Biochem Soc Trans.
36:348–352. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Barlow J, Jensen VH, Jastroch M and
Affourtit C: Palmitate-induced impairment of glucose-stimulated
insulin secretion precedes mitochondrial dysfunction in mouse
pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 473:487–496. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Manukyan L, Ubhayasekera SJ, Bergquist J,
Sargsyan E and Bergsten P: Palmitate-induced impairments of β-cell
function are linked with generation of specific ceramide species
via acylation of sphingosine. Endocrinology. 156:802–812.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cnop M, Foufelle F and Velloso LA:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends Mol Med.
18:59–68. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
El-Assaad W, Buteau J, Peyot ML, Nolan C,
Roduit R, Hardy S, Joly E, Dbaibo G, Rosenberg L and Prentki M:
Saturated fatty acids synergize with elevated glucose to cause
pancreatic beta-cell death. Endocrinology. 144:4154–4163.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang XY, Zhu BR, Jia Q, Li YM, Wang T and
Wang HY: Cinnamtannin D1 protects pancreatic β-cells from
glucolipotoxicity-induced apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy in
vitro and in vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 68:12617–12630.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Omar-Hmeadi M and Idevall-Hagren O:
Insulin granule biogenesis and exocytosis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
78:1957–1970. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Back SH, Kang SW, Han J and Chung HT:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the β-cell pathogenesis of type 2
diabetes. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012(618396)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Eizirik DL, Cardozo AK and Cnop M: The
role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr
Rev. 29:42–61. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee JH and Lee J: Endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) stress and its role in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and
senescence in type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci.
23(4843)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hung CT, Tsai YW, Wu YS, Yeh CF and Yang
KC: The novel role of ER protein TXNDC5 in the pathogenesis of
organ fibrosis: mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications.
J Biomed Sci. 29(63)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Li H and Chang X: The role and
mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases. Eur J Med Res.
27(145)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Okumura M, Kadokura H and Inaba K:
Structures and functions of protein disulfide isomerase family
members involved in proteostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Free
Radic Biol Med. 83:314–322. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Duivenvoorden WCM, Hopmans SN, Austin RC
and Pinthus JH: Endoplasmic reticulum protein ERp46 in prostate
adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 13:3624–3630. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bidooki SH, Navarro MA, Fernandes SCM and
Osada J: Thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5): Friend or Foe?
Curr Issues Mol Biol. 46:3134–3163. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rutter GA, Pullen TJ, Hodson DJ and
Martinez-Sanchez A: Pancreatic β-cell identity, glucose sensing and
the control of insulin secretion. Biochem J. 466:203–218.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lampropoulou E, Lymperopoulou A and
Charonis A: Reduced expression of ERp46 under diabetic conditions
in β-cells and the effect of liraglutide. Metabolism. 65:7–15.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cnop M, Abdulkarim B, Bottu G, Cunha DA,
Cunha DA, Igoillo-Esteve M, Masini M, Turatsinze JV, Griebel T,
Villate O, Santin I, et al: RNA sequencing identifies dysregulation
of the human pancreatic islet transcriptome by the saturated fatty
acid palmitate. Diabetes. 63:1978–1993. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen CW, Guan BJ, Alzahrani MR, Gao Z, Gao
L, Bracey S, Wu J, Mbow CA, Jobava R, Haataja L, et al: Adaptation
to chronic ER stress enforces pancreatic β-cell plasticity. Nat
Commun. 13(4621)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jiang H, Thapa P, Hao Y, Ding N,
Alshahrani A and Wei Q: Protein disulfide isomerases function as
the missing link between diabetes and cancer. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 37 (16-18):1191–1205. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B and Kahn CR:
Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin
action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:85–96. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Camaya I, Donnelly S and O'Brien B:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in pancreatic β-cells to
enhance their survival and function: An emerging therapeutic
strategy for type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes. 14:247–260.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dalle S and Abderrahmani A: Receptors and
signaling pathways controlling beta-cell function and survival as
targets for anti-diabetic therapeutic strategies. Cells.
13(1244)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Back SH and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes. Annu Rev Biochem. 81:767–793.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hetz C and Papa FR: The unfolded protein
response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. 69:169–181.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3460–3470.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hetz C, Zhang K and Kaufman RJ:
Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein
response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:421–438. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M,
Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Görgün CZ and Hotamisligil GS: Chemical
chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a
mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 313:1137–1140.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gao Y, Ryu H, Lee H, Kim YJ, Lee JH and
Lee J: ER stress and unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling
modulate GLP-1 receptor signaling in the pancreatic islets. Mol
Cells. 47(100004)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xing D, Zhou Q, Wang Y and Xu J: Effects
of tauroursodeoxycholic acid and 4-phenylbutyric acid on selenium
distribution in mice model with type 1 diabetes. Biol Trace Elem
Res. 201:1205–1213. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yong J, Johnson JD, Arvan P, Han J and
Kaufman RJ: Therapeutic opportunities for pancreatic β-cell ER
stress in diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 17:455–467.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Celik C, Lee SYT, Yap WS and Thibault G:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipids in health and diseases.
Prog Lipid Res. 89(101198)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen X and Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment.
Nat Rev Cancer. 21:71–88. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ren J, Bi Y, Sowers JR, Hetz C and Zhang
Y: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in
cardiovascular diseases. Nat Rev Cardiol. 18:499–521.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Tarantino G and Citro V: Crosstalk between
the spleen and other organs/systems: Downstream signaling events.
Immuno. 4:479–501. 2024.
|
|
52
|
Zhang J, Deng Z, Jin L, Yang C, Liu J,
Song H, Han W and Si Y: Spleen-derived anti-inflammatory cytokine
IL-10 stimulated by adipose tissue-derived stem cells protects
against type 2 diabetes. Stem Cells Dev. 26:1749–1758.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gotoh K, Inoue M, Masaki T, Chiba S,
Shimasaki T, Ando H, Fujiwara K, Katsuragi I, Kakuma T, Seike M, et
al: A novel anti-inflammatory role for spleen-derived
interleukin-10 in obesity-induced inflammation in white adipose
tissue and liver. Diabetes. 61:1994–2003. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Malik A, Bagchi AK, Jassal DS and Singal
PK: Interleukin-10 mitigates doxorubicin-induced endoplasmic
reticulum stress as well as cardiomyopathy. Biomedicines.
10(890)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Marafon BB, Pinto AP, de Sousa Neto IV, da
Luz CM, Pauli JR, Cintra DE, Ropelle ER, Simabuco FM, Pereira de
Moura L, de Freitas EC, et al: The role of interleukin-10 in
mitigating endoplasmic reticulum stress in aged mice through
exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 327:E384–E395.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|