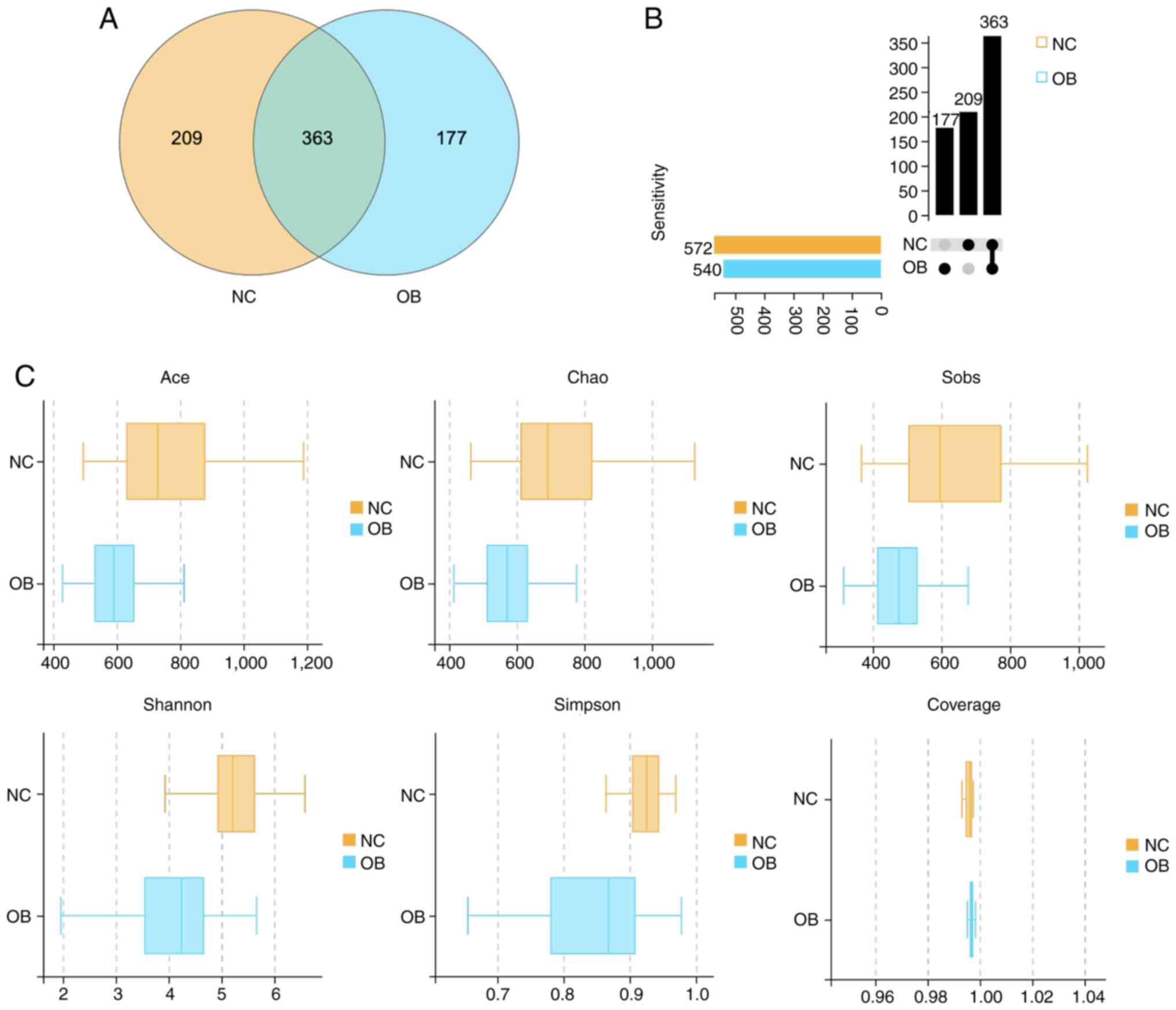
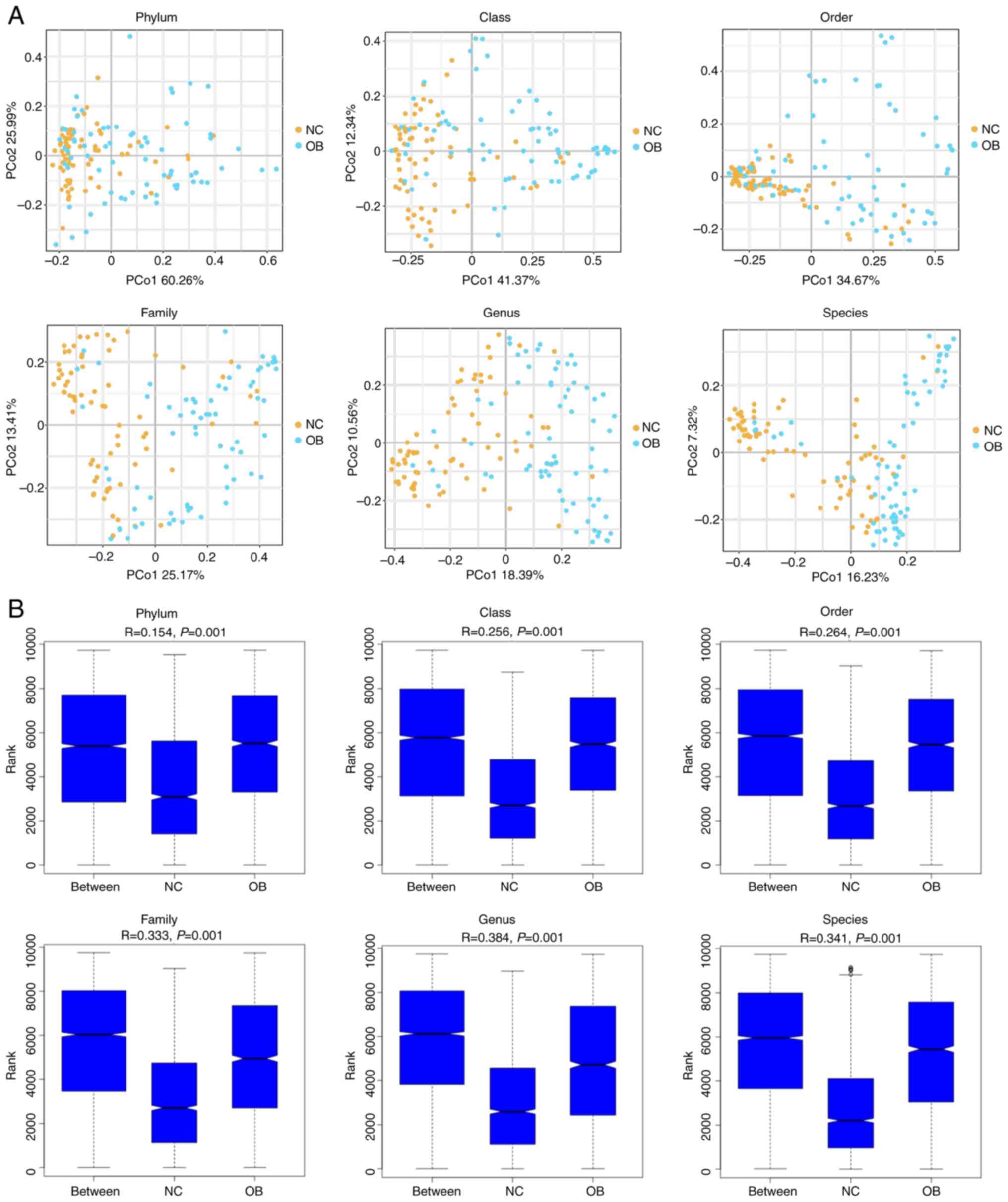
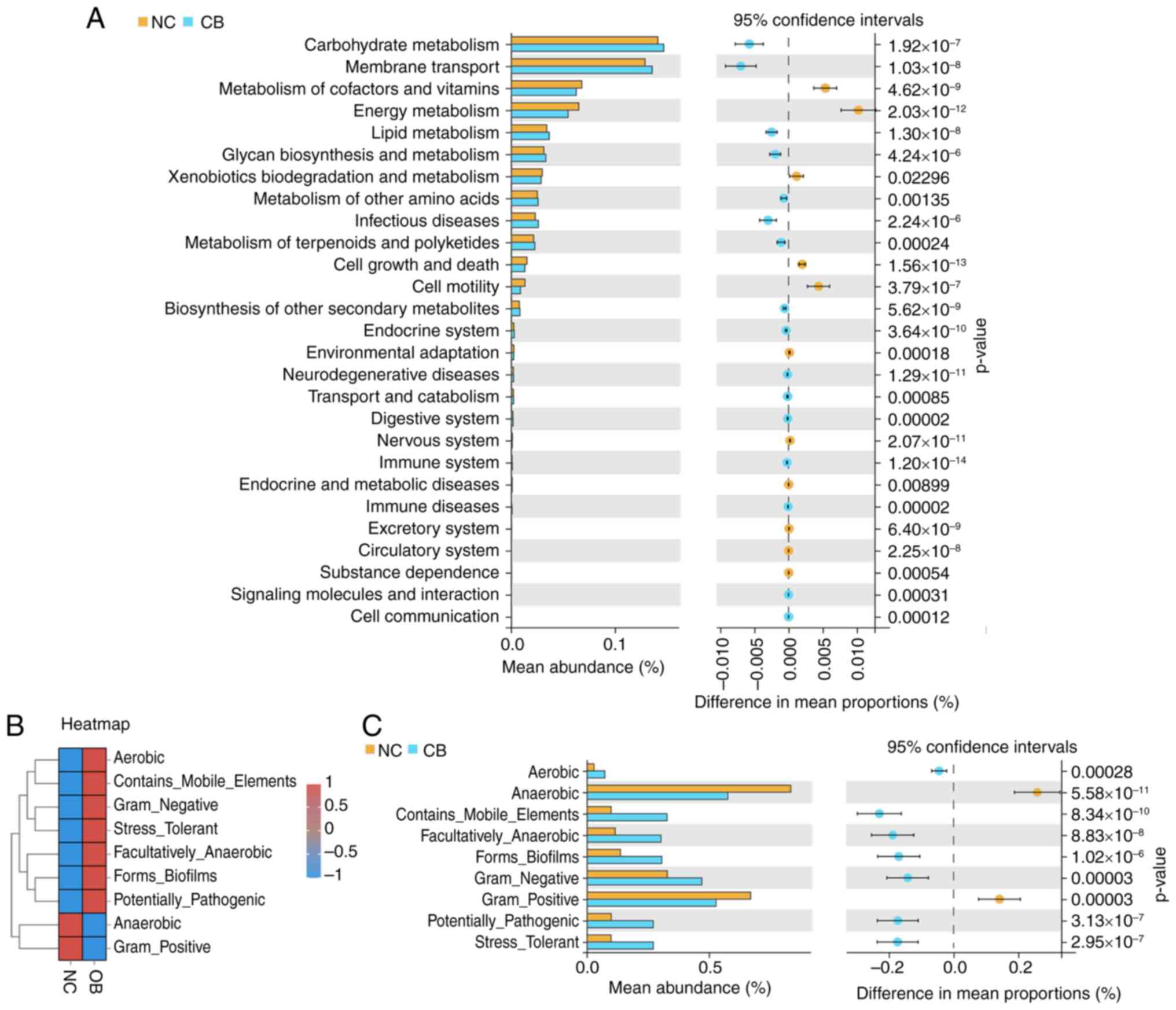
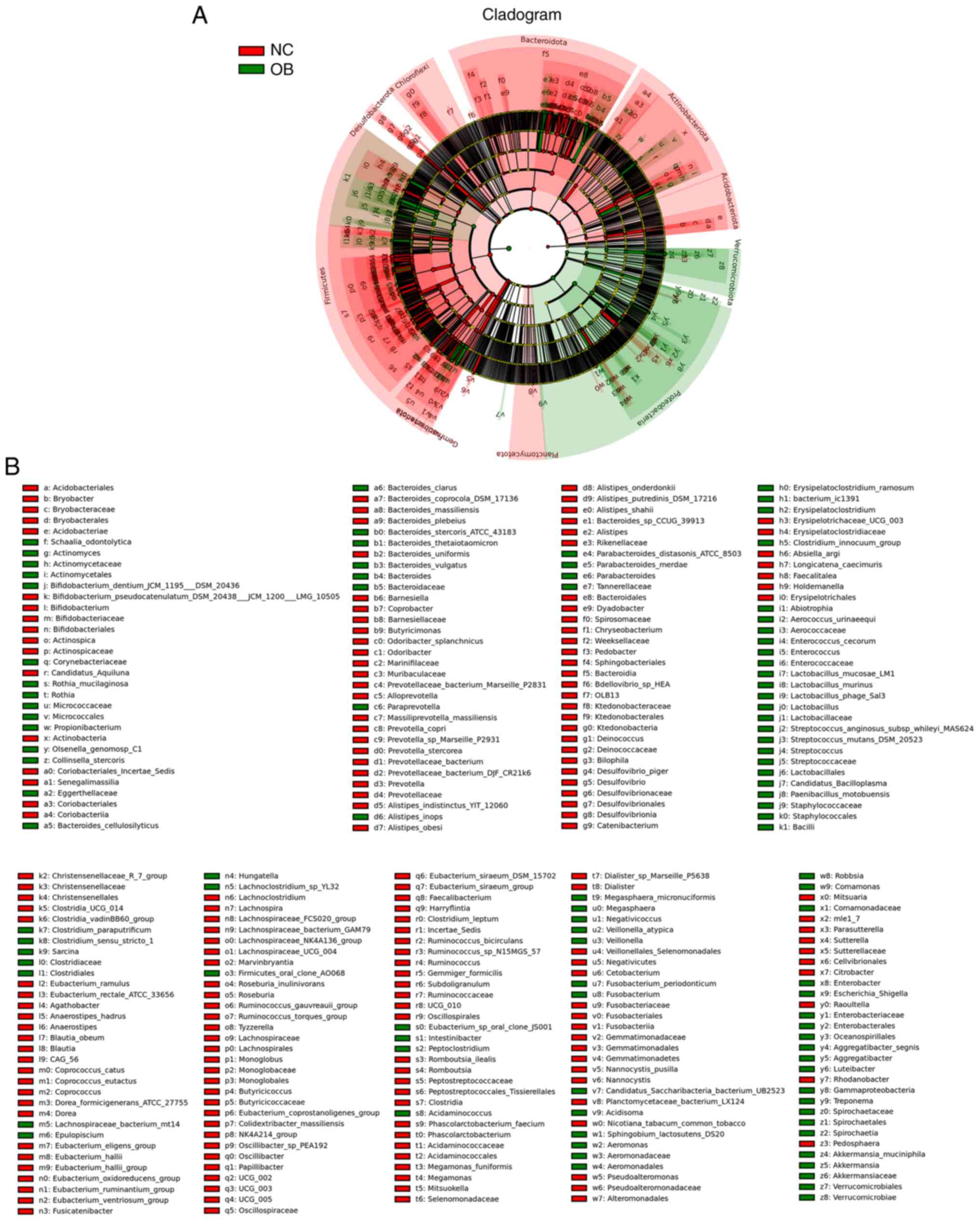
|
1
|
Wong F: Management of refractory ascites.
Clin Mol Hepatol. 29:16–32. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhao R, Lu J, Shi Y, Zhao H, Xu K and
Sheng J: Current management of refractory ascites in patients with
cirrhosis. J Int Med Res. 46:1138–1145. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zaccherini G, Tufoni M, Iannone G and
Caraceni P: Management of ascites in patients with cirrhosis: An
update. J Clin Med. 10(5226)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rajesh S, George T, Philips CA, Ahamed R,
Kumbar S, Mohan N, Mohanan M and Augustine P: Transjugular
intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhosis: An exhaustive
critical update. World J Gastroenterol. 26:5561–5596.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Debernardi Venon W, Lo Pumo S, Imperatrice
B, Giorgi M, Righi D, Fonio P, Saracco GM and Marzano A:
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in refractory
ascites: Clinical impact of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 33 (1S Suppl 1):e464–e470.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gu L, Yin X, Cheng Y, Wang X, Zhang M, Zou
X, Wang L, Zhuge Y and Zhang F: Overweight/Obesity increases the
risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular
intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients. J Pers Med.
13(682)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tranah TH, Edwards LA, Schnabl B and
Shawcross DL: Targeting the gut-liver-immune axis to treat
cirrhosis. Gut. 70:982–994. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Usuda H, Okamoto T and Wada K: Leaky gut:
Effect of dietary fiber and fats on microbiome and intestinal
barrier. Int J Mol Sci. 22(7613)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ma L, Ni Y, Wang Z, Tu W, Ni L, Zhuge F,
Zheng A, Hu L, Zhao Y, Zheng L and Fu Z: Spermidine improves gut
barrier integrity and gut microbiota function in diet-induced obese
mice. Gut Microbes. 12:1–19. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Guan H, Zhang X, Kuang M and Yu J: The
gut-liver axis in immune remodeling of hepatic cirrhosis. Front
Immunol. 13(946628)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nishimura N, Kaji K, Kitagawa K, Sawada Y,
Furukawa M, Ozutsumi T, Fujinaga Y, Tsuji Y, Takaya H, Kawaratani
H, et al: Intestinal permeability is a mechanical rheostat in the
pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. Int J Mol Sci.
22(6921)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Larrue H, Vinel JP and Bureau C:
Management of severe and refractory ascites. Clin Liver Dis.
25:431–440. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Helil AS, Haile SA, Birhanu Y, Desalegn H,
Desalegn DM, Geremew RA, Gebreyohannes Z, Mohammed A,
Wondimagegnehu DD, Ayana G, et al: Bacterial profile, drug
resistance pattern, clinical and laboratory predictors of ascites
infection in cirrhosis patients. BMC Infect Dis.
24(528)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Han S, Guiberson ER, Li Y and Sonnenburg
JL: High-throughput identification of gut microbiome-dependent
metabolites. Nat Protoc. 19:2180–2205. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Beyoğlu D, Simillion C, Storni F, De
Gottardi A and Idle JR: A metabolomic analysis of cirrhotic
ascites. Molecules. 27(3935)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guidelines on the management of ascites
and complications in cirrhosis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.
25:664–677. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Chen Y, Yang F, Lu H, Wang B, Chen Y, Lei
D, Wang Y, Zhu B and Li L: Characterization of fecal microbial
communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology.
54:562–572. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Althubaiti A: Sample size determination: A
practical guide for health researchers. J Gen Fam Med. 24:72–78.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Malik M, Hnatkova K, Batchvarov V, Gang Y,
Smetana P and Camm AJ: Sample size, power calculations, and their
implications for the cost of thorough studies of drug induced QT
interval prolongation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 27:1659–1669.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Biau DJ, kernéis S and Porcher R:
Statistics in brief: The importance of sample size in the planning
and interpretation of medical research. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
466:2282–2288. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Weissenborn K: Hepatic encephalopathy:
Definition, clinical grading and diagnostic principles. Drugs. 79
(Suppl 1):S5–S9. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Biggins SW, Angeli P, Garcia-Tsao G, Ginès
P, Ling SC, Nadim MK, Wong F and Kim WR: Diagnosis, evaluation, and
management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and
hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 practice guidance by the American
Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology.
74:1014–1048. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Delanaye P, Björk J, Courbebaisse M, Couzi
L, Ebert N, Eriksen BO, Dalton RN, Dubourg L, Gaillard F, Garrouste
C, et al: Performance of Creatinine-based equations to estimate
glomerular filtration rate with a methodology adapted to the
context of drug dosage adjustment. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
88:2118–2117. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Heidrich V, Inoue LT, Asprino PF, Bettoni
F, Mariotti ACH, Bastos DA, Jardim DLF, Arap MA and Camargo AA:
Choice of 16S ribosomal RNA primers impacts male urinary microbiota
profiling. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 12(862338)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bharti R and Grimm DG: Current challenges
and best-practice protocols for microbiome analysis. Brief
Bioinform. 22:178–193. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kryukov K, Imanishi T and Nakagawa S:
Nanopore sequencing data analysis of 16S rRNA genes using the
GenomeSync-GSTK system. Methods Mol Biol. 2632:215–226.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang T, Li H, Ma S, Cao J, Liao H, Huang
Q and Chen W: The newest Oxford Nanopore R10.4.1 full-length 16S
rRNA sequencing enables the accurate resolution of species-level
microbial community profiling. Appl Environ Microbiol.
89(e0060523)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Fan X, Shi H, Li J, Zhang M, Zhao
J and Su X: Comprehensive assessment of 16S rRNA gene amplicon
sequencing for microbiome profiling across multiple habitats.
Microbiol Spectr. 11(e0056323)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bozza S, Nunzi E, Frias-Mazuecos A,
Pieraccini G, Pariano M, Renga G, Mencacci A, Talesa VN, Antognelli
C, Puccetti P, et al: SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with Age-
and Gender-specific changes in the nasopharyngeal microbiome. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 29(59)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Johnson JS, Spakowicz DJ, Hong BY,
Petersen LM, Demkowicz P, Chen L, Leopold SR, Hanson BM, Agresta
HO, Gerstein M, et al: Evaluation of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for
species and Strain-level microbiome analysis. Nat Commun.
10(5029)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sanschagrin S and Yergeau E:
Next-generation sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicons. J
Vis Exp: 51709, 2014 doi: 10.3791/51709.
|
|
32
|
Shi P, Liu J, Liang A, Zhu W, Fu J and Wu
X, Peng Y, Yuan S and Wu X: Application of metagenomic
next-generation sequencing in optimizing the diagnosis of ascitic
infection in patients with liver cirrhosis. BMC Infect Dis.
24(503)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shi YJ, Sheng KW, Zhao HN, Liu C and Wang
H: Toll-like receptor 2 deficiency exacerbates dextran sodium
sulfate-induced intestinal injury through Marinifilaceae-dependent
attenuation of cell cycle signaling. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
29(338)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gitto S, Vizzutti F, Baldi S, Campani C,
Navari N, Falcini M, Venturi G, Montanari S, Roccarina D, Arena U,
et al: Transjugular intrahepatic Porto-systemic shunt positively
influences the composition and metabolic functions of the gut
microbiota in cirrhotic patients. Dig Liver Dis. 55:622–628.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Beyoğlu D, Popov YV and Idle JR: The
metabolomic footprint of liver fibrosis. Cells.
13(1333)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Singh R, Zogg H, Wei L, Bartlett A,
Ghoshal UC, Rajender S and Ro S: Gut microbial dysbiosis in the
pathogenesis of gastrointestinal dysmotility and metabolic
disorders. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 27:19–34. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Seo SK and Kwon B: Immune regulation
through tryptophan metabolism. Exp Mol Med. 55:1371–1379.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ye J, Bi X, Deng S, Wang X, Liu Z, Suo Q,
Wu J, Chen H, Wang Y, Qian K, et al: Hypoxanthine is a metabolic
biomarker for inducing GSDME-dependent pyroptosis of endothelial
cells during ischemic stroke. Theranostics. 14:6071–687.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Roehlen N, Crouchet E and Baumert TF:
Liver fibrosis: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives.
Cells. 9(875)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sak JJ, Prystupa A, Bis-Wencel H, Kiciński
P, Luchowska-Kocot D, Krukowski H, Nowicki GJ and Panasiuk L:
Oxidative stress-induced growth inhibitor 1 in alcohol-induced
liver cirrhosis. Ann Agric Environ Med. 28:676–680. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Blachier F: Metabolism of dietary
substrates by intestinal bacteria and consequences for the host
intestine. In: Metabolism of alimentary compounds by the intestinal
microbiota and health. Springer, pp45-144, 2023.
|
|
42
|
Alonso-Peña M, Espinosa-Escudero R,
Herraez E, Briz O, Cagigal ML, Gonzalez-Santiago JM, Ortega-Alonso
A, Fernandez-Rodriguez C, Bujanda L, Calvo Sanchez M, et al:
Beneficial effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with acyl-CoA
oxidase 2 (ACOX2) deficiency-associated hypertransaminasemia.
Hepatology. 76:1259–1274. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Guan Z, Li Y, Hu S, Mo C, He D, Huang Z
and Liao M: Screening and identification of differential
metabolites in serum and urine of bamaxiang pigs bitten by
trimeresurus stejnegeri based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS metabolomics
technology. J Toxicol Sci. 47:389–407. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|