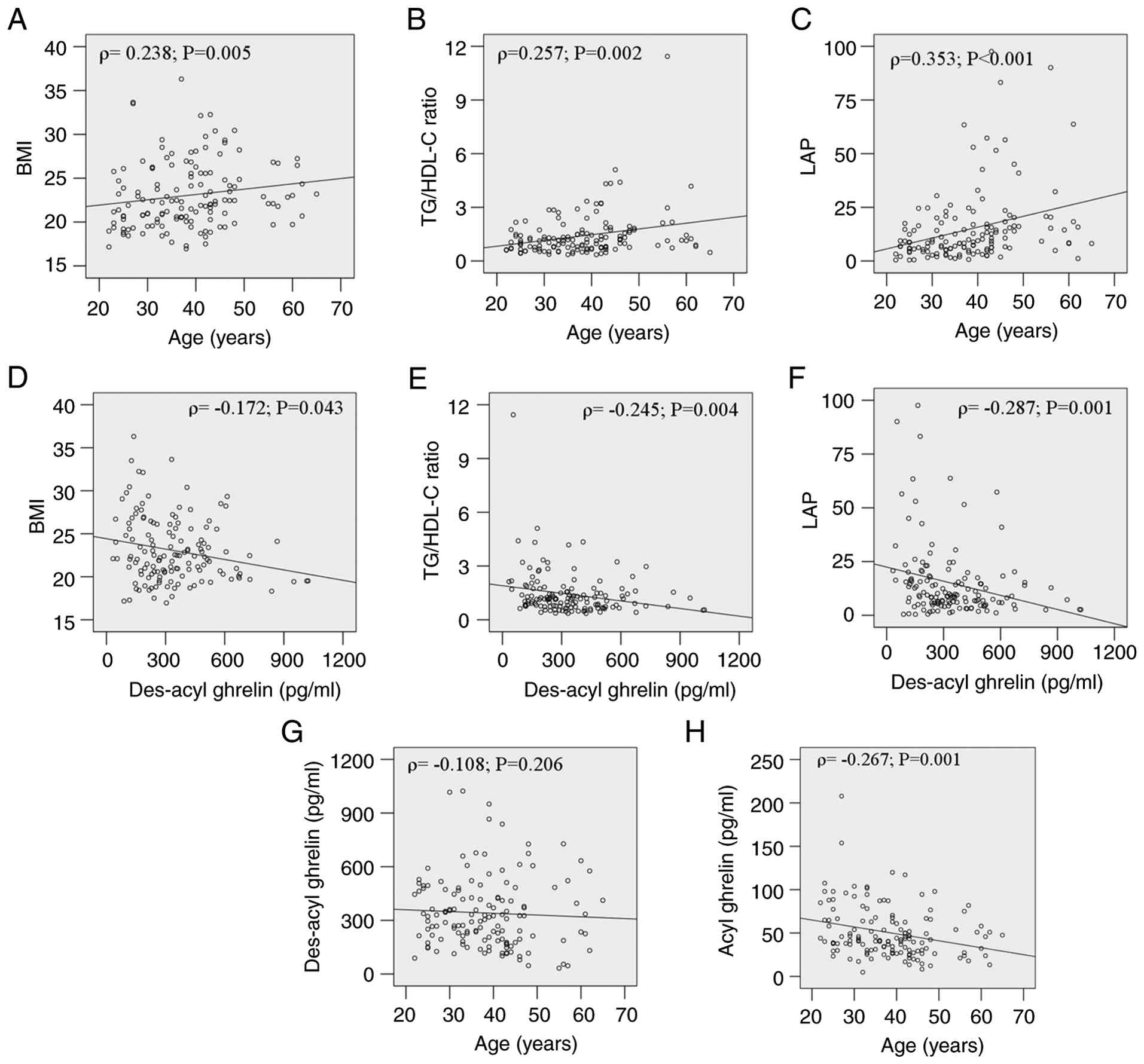
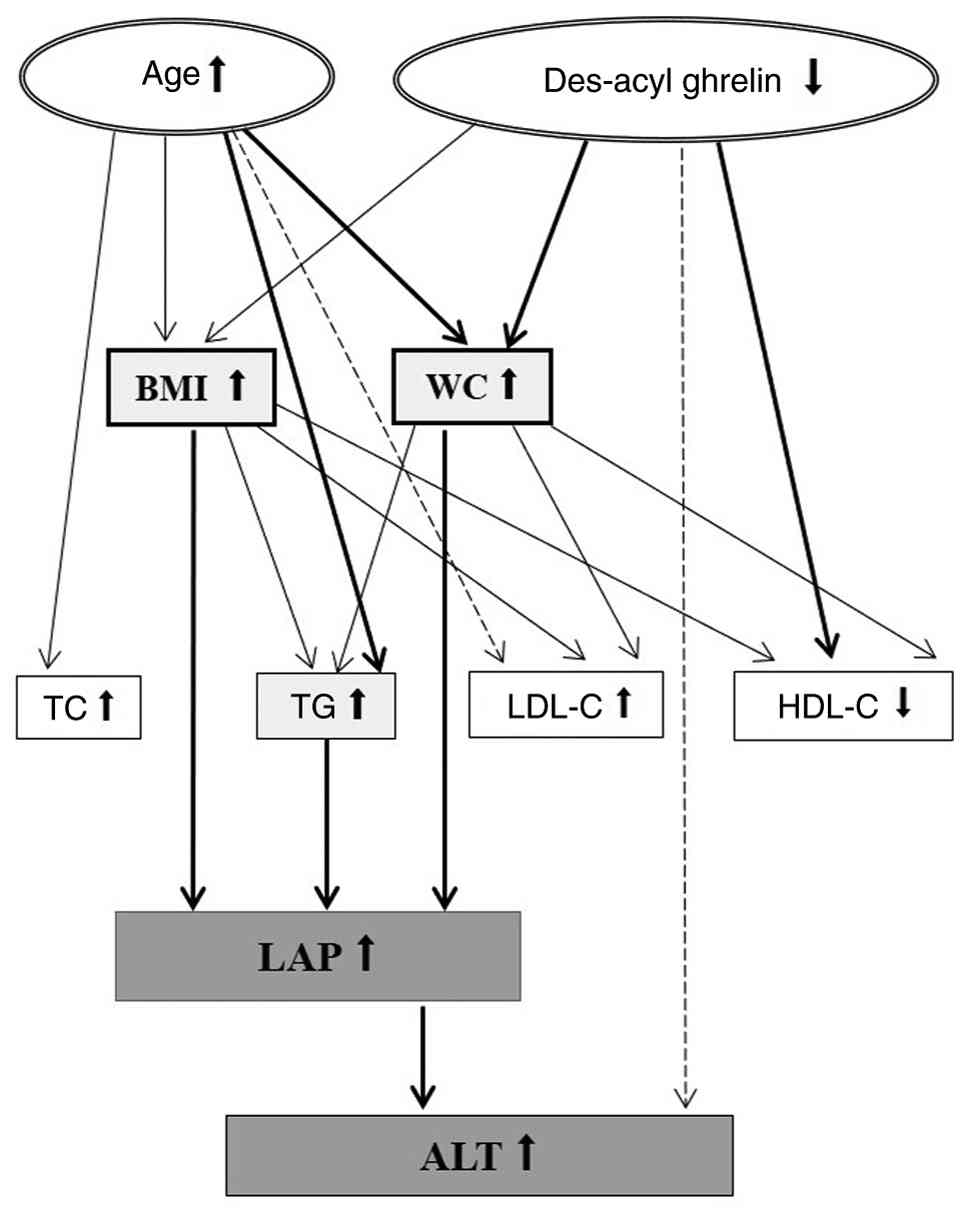
|
1
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes
(EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO).
EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines on the management of
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
Obes Facts. 17:374–444. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Eslam M, Fan JG, Yu ML, Wong VW, Cua IH,
Liu CJ, Tanwandee T, Gani R, Seto WK, Alam S, et al: The Asian
Pacific association for the study of the liver clinical practice
guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic
dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int.
19:261–301. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen CH, Huang MH, Yang JC, Nien CK, Yang
CC, Yeh YH and Yueh SK: Prevalence and risk factors of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease in an adult population of Taiwan: Metabolic
significance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese
adults. J Clin Gastroenterol. 40:745–752. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang WS, Wahlqvist ML, Hsu CC, Chang HY,
Chang WC and Chen CC: Age- and gender-specific population
attributable risks of metabolic disorders on all-cause and
cardiovascular mortality in Taiwan. BMC Public Health.
12(111)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Health Promotion Administration, Ministry
of Health and Welfare: Report on the Changes in National
Nutritional and Health Status 2017-2020: Survey on Changes in
National Nutritional and Health Status, 2022 (In Chinese).
https://www.hpa.gov.tw/EngPages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=3999&pid=15562.
|
|
6
|
Chen CY, Fujimiya M, Laviano A, Chang FY,
Lin HC and Lee SD: Modulation of ingestive behavior and
gastrointestinal motility by ghrelin in diabetic animals and
humans. J Chin Med Assoc. 73:225–229. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen CY and Tsai CY: From endocrine to
rheumatism: Do gut hormones play roles in rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:205–212. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen CY, Asakawa A, Fujimiya M, Lee SD and
Inui A: Ghrelin gene products and the regulation of food intake and
gut motility. Pharmacol Rev. 61:430–481. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Iwakura H, Ensho T and Ueda Y:
Desacyl-ghrelin, not just an inactive form of ghrelin? A review of
current knowledge on the biological actions of desacyl-ghrelin.
Peptides. 167(171050)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gong Y, Qiu B, Zheng H, Li X, Wang Y, Wu
M, Yan M and Gong Y: Unacylated ghrelin attenuates acute liver
injury and hyperlipidemia via its anti-inflammatory and
anti-oxidative activities. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
27(49)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim H, Ranjit R, Claflin DR, Georgescu C,
Wren JD, Brooks SV, Miller BF and Ahn B: Unacylated ghrelin
protects against age-related loss of muscle mass and contractile
dysfunction in skeletal muscle. Aging Cell.
23(e14323)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Koliaki C, Liatis S, Dalamaga M and
Kokkinos A: The implication of gut hormones in the regulation of
energy homeostasis and their role in the pathophysiology of
obesity. Curr Obes Rep. 9:255–271. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tarantino G and Balsano C:
Gastrointestinal peptides and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 27:11–15. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bakar RB, Reimann F and Gribble FM: The
intestine as an endocrine organ and the role of gut hormones in
metabolic regulation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:784–796.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Alexander CM, Landsman PB and Grundy SM:
The influence of age and body mass index on the metabolic syndrome
and its components. Diabetes Obes Metab. 10:246–250.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Baneu P, Văcărescu C, Drăgan SR, Cirin L,
Lazăr-Höcher AI, Cozgarea A, Faur-Grigori AA, Crișan S, Gaiță D,
Luca CT and Cozm D: The Triglyceride/HDL ratio as a surrogate
biomarker for insulin resistance. Biomedicines.
12(1493)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen CY, Lee WJ, Asakawa A, Fujitsuka N,
Chong K, Chen SC, Lee SD and Inui A: Insulin secretion and
interleukin-1β dependent mechanisms in human diabetes remission
after metabolic surgery. Curr Med Chem. 20:2374–2388.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ebrahimi M, Seyedi SA, Nabipoorashrafi SA,
Rabizadeh S, Sarzaeim M, Yadegar A, Mohammadi F, Bahri RA, Pakravan
P, Shafiekhani P, et al: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) index for
the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis.
22(41)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chiang JK and Koo M: Lipid accumulation
product: A simple and accurate index for predicting metabolic
syndrome in Taiwanese people aged 50 and over. BMC Cardiovasc
Disord. 12(78)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lockie S, Lyons K, Lawrence G and Grice J:
Choosing organics: A path analysis of factors underlying the
selection of organic food among Australian consumers. Appetite.
43:135–146. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Senn TE, Espy KA and Kaufmann PM: Using
path analysis to understand executive function organization in
preschool children. Dev Neuropsychol. 26:445–464. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bilson J, Sethi JK and Byrne CD:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multi-system disease
influenced by ageing and sex, and affected by adipose tissue and
intestinal function. Proc Nutr Soc. 81:146–161. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Muratsu J, Kamide K, Fujimoto T, Takeya Y,
Sugimoto K, Taniyama Y, Morishima A, Sakaguchi K, Matsuzawa Y and
Rakugi H: The combination of high levels of adiponectin and insulin
resistance are affected by aging in non-obese old peoples. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12(805244)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yuan Q, Wang H, Gao P, Chen W, Lv M, Bai S
and Wu J: Prevalence and risk factors of metabolic-associated fatty
liver disease among 73,566 individuals in Beijing, China. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 19(2096)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Delhanty PJ, Neggers SJ and van der Lely
AJ: Mechanisms in endocrinology: Ghrelin: The differences between
acyl- and des-acyl ghrelin. Eur J Endocrinol. 167:601–608.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shimada T, Furuta H, Doi A, Ariyasu H,
Kawashima H, Wakasaki H, Nishi M, Sasaki H and Akamizu T: Des-acyl
ghrelin protects microvascular endothelial cells from oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis through sirtuin 1 signaling pathway.
Metabolism. 63:469–474. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cappellari GG, Zanetti M, Semolic A, Vinci
P, Ruozi G, Falcione A, Filigheddu N, Guarnieri G, Graziani A,
Giacca M and Barazzoni R: Unacylated ghrelin reduces skeletal
muscle reactive oxygen species generation and inflammation and
prevents high-fat diet-induced hyperglycemia and whole-body insulin
resistance in rodents. Diabetes. 65:874–886. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Agosti E, De Feudis M, Angelino E, Belli
R, Teixeira MA, Zaggia I, Tamiso E, Raiteri T, Scircoli A, Ronzoni
F, et al: Both ghrelin deletion and unacylated ghrelin
overexpression preserve muscles in aging mice. Aging (Albany NY).
12:13939–13957. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yuan F, Zhang Q, Dong H, Xiang X, Zhang W,
Zhang Y and Li Y: Effects of des-acyl ghrelin on insulin
sensitivity and macrophage polarization in adipose tissue. J Transl
Int Med. 9:84–97. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Alharbi S: Exogenous administration of
unacylated ghrelin attenuates hepatic steatosis in high-fat
diet-fed rats by modulating glucose homeostasis, lipogenesis,
oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed
Pharmacother. 151(113095)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ahmad MA, Karavetian M, Moubareck CA, Wazz
G, Mahdy T and Venema K: The association between peptide hormones
with obesity and insulin resistance markers in lean and obese
individuals in the United Arab Emirates. Nutrients.
14(1271)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cho YH, Lee SY, Jeong DW, Cho AR, Jeon JS,
Kim YJ, Lee JG, Yi YH, Tak YJ, Hwang HR, et al: Metabolic syndrome
is associated with lower plasma levels of desacyl ghrelin and total
ghrelin in asymptomatic middle-aged Korean men. J Obes Metab Syndr.
26:114–121. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Amitani M, Amitani H, Cheng KC, Kairupan
TS, Sameshima N, Shimoshikiryo I, Mizuma K, Rokot NT, Nerome Y,
Owaki T, et al: The role of ghrelin and ghrelin signaling in aging.
Int J Mol Sci. 18(1511)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ezquerro S, Mocha F, Frühbeck G,
Guzmán-Ruiz R, Valentí V, Mugueta C, Becerril S, Catalán V,
Gómez-Ambrosi J, Silva C, et al: Ghrelin reduces TNF-α-induced
human hepatocyte apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis: Role in
obesity-associated NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 104:21–37.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ezquerro S, Méndez-Giménez L, Becerril S,
Moncada R, Valentí V, Catalán V, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Frühbeck G and
Rodríguez A: Acylated and desacyl ghrelin are associated with
hepatic lipogenesis, β-oxidation and autophagy: Role in NAFLD
amelioration after sleeve gastrectomy in obese rats. Sci Rep.
6(39942)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zang P, Yang CH, Liu J, Lei HY, Wang W,
Guo QY, Lu B and Shao JQ: Relationship between acyl and desacyl
ghrelin levels with insulin resistance and body fat mass in type 2
diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 15:2763–2770.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Delhanty PJ, Sun Y, Visser JA, van
Kerkwijk A, Huisman M, van Ijcken WF, Swagemakers S, Smith RG,
Themmen AP and van der Lely AJ: Unacylated ghrelin rapidly
modulates lipogenic and insulin signaling pathway gene expression
in metabolically active tissues of GHSR deleted mice. PLoS One.
5(e11749)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu X, Guo Y, Li Z and Gong Y: The role of
acylated ghrelin and unacylated ghrelin in the blood and
hypothalamus and their interaction with nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 23:1191–1196. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Asakawa A, Inui A, Fujimiya M, Sakamaki R,
Shinfuku N, Ueta Y, Meguid MM and Kasuga M: Stomach regulates
energy balance via acylated ghrelin and desacyl ghrelin. Gut.
54:18–24. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ariyasu H, Takaya K, Iwakura H, Hosoda H,
Akamizu T, Arai Y, Kangawa K and Nakao K: Transgenic mice
overexpressing des-acyl ghrelin show small phenotype.
Endocrinology. 146:355–364. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rodríguez A, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Catalán V,
Rotellar F, Valentí V, Silva C, Mugueta C, Pulido MR, Vázquez R,
Salvador J, et al: The ghrelin O-acyltransferase-ghrelin system
reduces TNF-α-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human visceral
adipocytes. Diabetologia. 55:3038–3050. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lv P, Li H, Li X, Wang X, Yu J and Gong Y:
Intestinal perfusion of unacylated ghrelin alleviated metabolically
associated fatty liver disease in rats via a central glucagon-like
peptide-1 pathway. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
326:G643–G658. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Pei XM, Yung BY, Yip SP, Chan LW, Wong CS,
Ying M and Siu PM: Protective effects of desacyl ghrelin on
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Diabetol. 52:293–306. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Long MT, Pedley A, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U,
Ma J, Loomba R, Chung RT and Benjamin EJ: A simple clinical model
predicts incident hepatic steatosis in a community-based cohort:
The Framingham heart study. Liver Int. 38:1495–1503.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Mumusoglu S and Yildiz BO: Metabolic
syndrome during menopause. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 17:595–603.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
de Mutsert R, Gast K, Widya R, de Koning
E, Jazet I, Lamb H, le Cessie S, de Roos A, Smit J, Rosendaal F and
den Heijer M: Associations of abdominal subcutaneous and visceral
fat with insulin resistance and secretion differ between men and
women: The Netherlands epidemiology of obesity study. Metab Syndr
Relat Disord. 16:54–63. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Smith A, Woodside B and Abizaid A: Ghrelin
and the control of energy balance in females. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13(904754)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
de Souza GO, Wasinski F and Donato J Jr:
Characterization of the metabolic differences between male and
female C57BL/6 mice. Life Sci. 301(120636)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|