Introduction
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) have attracted
attention as promising therapeutic tools because they can silence
disease-related genes (1,2). However, siRNAs undergo rapid
degradation by endogenous nucleases after systemic administration.
Additionally, its hydrophilic nature and high molecular weight
restrict penetration into target cell membranes. Therefore,
developing a siRNA delivery system for target sites is crucial for
inducing therapeutic effects (3).
Several siRNA carriers comprising polymers or lipids have been
investigated (4).
Cationic liposomes are widely used for siRNA
delivery (5). The formation of
siRNA lipoplexes, that is, complexes of siRNA and cationic
liposomes, prevents siRNA degradation by nucleases and improves its
transport into the cytoplasm. The cationic characteristics of
lipoplexes induce binding to negatively charged cell surfaces,
improving intracellular delivery. However, after intravenous
injection, cationic lipoplexes non-specifically interact with
negatively charged serum proteins or erythrocytes, forming
aggregates that accumulate mainly in the lungs (6,7).
To reduce non-specific interactions and
agglutination of cationic lipoplexes with blood components,
polyethylene glycol (PEG) modification of lipoplexes has been
explored (8,9). PEG-modified carriers reportedly
improve siRNA stability and retention in the circulation by
inducing steric hindrance and accumulate in the target tissue as a
result of evading lung accumulation. However, PEG modification
frequently inhibits cellular uptake and endosomal escape, resulting
in reduced gene silencing (8,10). As
an alternative to PEG modification, surface modification of
cationic lipoplexes using anionic materials has been investigated.
For example, coating cationic lipoplexes with anionic polymers has
been reported to attenuate electrostatic interactions with blood
components (11-13).
Several biocompatible anionic polymers, such as hyaluronan (HA),
chondroitin sulfate (CS), and polyglutamic acid (PGA), can minimize
the non-specific interaction of cationic lipoplexes with biological
components. Similarly, incorporation of anionic lipids into
cationic lipoplexes can reduce the surface charge through charge
neutralization, thereby decreasing non-specific interactions with
erythrocytes as reported in our previous study (14). Compared with simple charge
neutralization using anionic lipids, anionic polymer coating
provides additional advantages by enabling functional modification
of lipoplexes through polymer structure and functional properties,
such as prolonged circulation and receptor-mediated
interactions.
Previously, our group reported a simple preparation
method for siRNA lipoplexes [modified ethanol injection (MEI)
method], in which the siRNA solution was rapidly mixed with a small
volume of a lipid-ethanol solution, which could be applicable for
in vitro and in vivo siRNA transfections (15,16).
To extend the usefulness and applicability of this preparation
method, we explored the potential of anionic polymer coating on
siRNA lipoplexes prepared by MEI in the current study.
Biocompatible polymers, including HA, CS, and PGA, were used to
coat cationic siRNA lipoplexes prepared using the MEI method. In
addition, the effects of anionic polymer coating of siRNA
lipoplexes on gene knockdown efficiency and biodistribution were
evaluated.
Materials and methods
Materials
1,2-Dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl
sulfate salt (DOTAP) was obtained from Avanti Polar Lipids (now
part of Croda International Plc, Yorkshire, UK).
Dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (DDAB; product name: DC-1-18)
was obtained from Sogo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan).
1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE;
COATSOME® ME-8181) was purchased from NOF Corporation
(Tokyo, Japan). Ultra-low-molecular-weight hyaluronan (HA-UL;
molecular mass: 7.5 kDa), low-molecular-weight HA (HA-L; 16.7 kDa),
medium-molecular-weight HA (HA-M; 215 kDa), and
high-molecular-weight HA (HA-H; 975 kDa) were purchased from
R&D Systems, Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA). Chondroitin sulfate C
sodium salt (CS; average molecular mass: 35 kDa) was purchased from
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corp. (Osaka, Japan). Poly-α-L-glutamic
acid sodium salt (PGA; molecular weight: 20500) was purchased from
Sigma-Aldrich (now part of Merck, Darmstadt, Germany).
siRNAs
Firefly luciferase siRNA (Luc siRNA, target
sequence: hLuc+, GenBank accession no. AY535007.1),
non-silencing control siRNA (Cont siRNA), and cyanine 5-conjugated
Cont siRNA (Cy5-siRNA) were designed as reported previously
(17) and synthesized by
Sigma-Aldrich (Merck). The siRNA sequences were as follows: Luc
siRNA passenger strand, 5 -CCGUGGUGUUCGUGUCUAAGA-3 , and
guide strand, 5 -UUAGACACGAACACCACGGUA-3 ; Cont siRNA
passenger strand, 5 -GUACCGCACGUCAUUCGUAUC-3 , and guide
strand, 5 -UACGAAUGACGUGCGGUACGU-3 . For Cy5-siRNA, Cy5
dye was conjugated at the 5 -end of the passenger strand of
Cont siRNA.
Preparation of anionic polymer-coated
lipoplexes using the MEI method
siRNA lipoplexes were prepared using the MEI method,
as reported previously (15,16).
Briefly, siRNA dispersed in 5% glucose aqueous solution (500 nM
siRNA) was rapidly added to a lipid-ethanol solution containing
DOTAP:DOPE=1:1 (molar ratio) or DDAB:DOPE=1:1 (molar ratio) at a
charge ratio (+:-) of 4:1, followed by incubation for 5 min. The
charge ratio (+:-) of cationic lipids to siRNA was calculated as
the molar ratio of amines in cationic lipids to siRNA phosphate. To
prepare anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes, siRNA lipoplexes were
mixed with an aqueous solution of anionic polymers at charge ratios
(+:-) of cationic lipids to anionic polymers from 1:0.5 to 1:3, and
followed by incubation for 5 min. The charge ratio (+:-) of
cationic lipids to anionic polymers was calculated as the molar
ratio of the carboxylic acid of HA (one negative charge per
disaccharide unit), sulfate and carboxylic acid of CS (two negative
charges per disaccharide unit), and carboxylic acid of PGA (one
negative charge per glutamic acid).
The average particle size and ζ-potential of
lipoplexes were measured using a light-scattering photometer
(ELSZ-2000; Otsuka Electronics Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) at 25˚C
after diluting the dispersion to an appropriate volume with
water.
Cell culture
Human breast cancer MCF-7 cells stably expressing
firefly luciferase (MCF-7-Luc), which were constructed by
transfection of pcDNA3 plasmid containing firefly luciferase
(hLuc+) gene (GenBank no. AY535007.1) derived from
psiCHECK-2 vector (Promega Corporation), were provided by Dr. Kenji
Yamato (University of Tsukuba). Cells were cultured in RPMI-1640
medium (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corp.) supplemented with 10%
heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Waltham, MA, USA) and 1.2 mg/ml G418 (geneticin) sulfate (Santa
Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) at 37˚C in a humidified
incubator with 5% CO2.
Gene silencing of anionic
polymer-coated lipoplexes
In brief, MCF-7-Luc cells were seeded in 6-well
culture plates the day before transfection. Lipoplexes with Luc or
Cont siRNA were prepared as described above, diluted in RPMI-1640
medium supplemented with 10% FBS at a 50 nM siRNA concentration,
and added to the cells for 48 h. Following transfection, luciferase
activity was measured as counts per second (cps)/µg protein using
the luciferase assay system (PicaGene MelioraStar-LT Luminescence
Reagent, Toyo B-Net Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) and Pierce™ BCA
Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Luciferase activity
(%) was calculated relative to the luciferase activity (cps/µg
protein) of untreated cells, as reported previously (9).
Cellular association of siRNA
lipoplexes
Flow cytometry was performed to confirm the cellular
association of lipoplexes. In brief, MCF-7-Luc cells were seeded in
12-well culture plates the day before the experiment. Lipoplexes
with Cy5-siRNA were prepared as described above, diluted in
RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS at a 50 nM siRNA
concentration, and added to the cells. After incubation for 3 h,
the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4),
detached using TrypLE™ Express Enzyme (Gibco™, Thermo Fisher
Scientific), and suspended in PBS containing 0.1% bovine serum
albumin and 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. The association
of Cy5-siRNA with cells was determined by examining the
fluorescence intensity using a BD FACSVerse™ flow cytometer (BD
Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA), as reported previously (18).
Cytotoxicity of siRNA lipoplexes
Briefly, MCF-7-Luc cells were seeded in 96-well
culture plates the day before transfection. Lipoplexes with Cont
siRNA were prepared as described above, diluted in RPMI-1640 medium
supplemented with 10% FBS at a 50 nM siRNA concentration, and added
to the cells. After incubation for 24 h, cell viability was
measured using the WST-8 assay (Cell Counting Kit-8; Dojindo
Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). Cell viability (%) was calculated
relative to the cell viability of untreated cells.
Animals
A total of 42 female BALB/c mice (8 weeks old) were
purchased from Sankyo Labo Service Corporation (Tokyo, Japan) and
maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions.
All animal experiments were conducted according to a
protocol reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and
Use Committee of Hoshi University (Permit No. P24-094).
Effect of anionic polymer-coating on
erythrocyte agglutination with siRNA lipoplexes
Agglutination of erythrocytes with siRNA lipoplexes
was determined as described previously (9). In brief, approximately 0.3 ml of blood
was collected in a single sampling from the jugular vein of one
female BALB/c mouse under inhalation anesthesia with isoflurane (5%
for induction and 2% for maintenance), and the mouse was euthanized
by cervical dislocation. Erythrocytes were separated by
centrifugation at 300 x g for 3 min and resuspended in PBS as a 2%
(v/v) suspension of erythrocyte. siRNA lipoplexes with 2 µg Cont
siRNA were mixed with the prepared erythrocyte suspension.
Subsequently, the mixture was placed on a glass plate and observed
by microscopy.
Biodistribution of anionic
polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes
siRNA lipoplexes with 10 µg Cy5-siRNA were
administered intravenously via the lateral tail vein of BALB/c mice
(n=1 per siRNA lipoplex). One hour post-injection, mice were
euthanized by cervical dislocation under inhalation anesthesia with
isoflurane (5% for induction and 2% for maintenance), and Cy5
fluorescence imaging of tissues was performed using a NightOWL
LB981 NC100 system (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad, Germany),
as reported previously (19).
Images were analyzed using IndiGo2 software (version 2.0.1.0)
provided with the in vivo imaging system (Berthold
Technologies).
Measurement of TNF-α concentration in
mice
siRNA lipoplexes with 10 µg Cont siRNA were
administered intravenously via the lateral tail vein of BALB/c mice
(n=3 per siRNA lipoplex). Based on previous studies (20,21),
approximately 0.3 ml of blood was collected in a single sampling
from the jugular vein of a mouse under inhalation anesthesia with
isoflurane (5% for induction and 2% for maintenance) 2 h after
administration, after which the mouse was euthanized by cervical
dislocation. The blood was centrifuged at 1,000 x g for 10 min to
obtain serum. The concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α
(TNF-α) in serum were determined by enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (LBIS mouse TNF-α ELISA kit, Fujifilm
Wako Shibayagi Corp. Cat # 634-44721), according to the
manufacturer s instructions.
Statistical analysis
The statistical significance of differences between
the means of the two groups was determined using an unpaired t-test
with Welch s correction. For multiple-group comparisons,
statistical significance was determined using one-way analysis of
variance (ANOVA), followed by Dunnett s multiple comparison
test. GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad Software Inc., Boston, MA, USA)
was used for the statistical analyses. Statistical significance was
set at P<0.05.
Results
Size and ζ-potential of anionic
polymer-coated lipoplexes prepared using the MEI method
Previously, cationic siRNA lipoplexes were
successfully prepared using the MEI method (15,16).
In this study, anionic polymers were electrostatically coated with
siRNA lipoplexes to prevent the agglutination of blood components,
such as erythrocytes. The size and ζ-potential of anionic
polymer-coated lipoplexes prepared using the MEI method are shown
in Table I. The charge ratio (+:-)
of cationic lipids to anionic polymers was examined over a range
from 1:0.5 to 1:3. A ratio of 1:2 was selected because not all
anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes exhibited negative surface charge
at ratios below 1:1, suggesting that the coating of lipoplexes may
be insufficient. The average size of siRNA lipoplex composed of
DOTAP/DOPE or DDAB/DOPE without polymer coating (LP-DOTAP and
LP-DDAB, respectively) was 106.1 and 75.1 nm, respectively. Anionic
polymer-coated lipoplexes showed comparable hydrodynamic size
(84.6-141.1 nm). LP-DOTAP and LP-DDAB had positive ζ-potentials
(52.8 and 36.6 mV, respectively). Each anionic polymer-coated
lipoplex exhibited a negative surface charge (from -14.4 to -45.1
mV of ζ-potential), indicating that cationic lipoplexes were
successfully coated with anionic polymers.
 | Table IEffect of anionic polymer coating on
size and ζ-potential of small interfering RNA lipoplexes. |
Table I
Effect of anionic polymer coating on
size and ζ-potential of small interfering RNA lipoplexes.
| Lipoplexes | Lipid
formulation | Polymer
coatinga | Average
sizeb, nm | Polydispersity
index |
ζ-potentialb, mV |
|---|
| LP-DOTAP | DOTAP/DOPE=1:1
(mol:mol) | - | 106.1±2.9 | 0.29±0.01 | 52.8±4.6 |
| LP-DOTAP/HA-UL | | HA-UL | 115.7±0.3 | 0.11±0.02 | -18.0±1.4 |
| LP-DOTAP/HA-L | | HA-L | 140.0±15.3 | 0.26±0.05 | -24.1±1.4 |
| LP-DOTAP/HA-M | | HA-M | 84.6±1.7 | 0.26±0.00 | -26.2±1.7 |
| LP-DOTAP/HA-H | | HA-H | 99.7±5.7 | 0.21±0.00 | -26.3±7.0 |
| LP-DOTAP/CS | | CS | 114.9±2.0 | 0.23±0.01 | -41.4±1.9 |
| LP-DOTAP/PGA | | PGA | 126.9±23.7 | 0.24±0.07 | -45.1±1.7 |
| LP-DDAB | DDAB/DOPE=1:1
(mol:mol) | - | 75.1±5.9 | 0.20±0.06 | 36.6±8.8 |
| LP-DDAB/HA-UL | | HA-UL | 96.4±0.8 | 0.12±0.03 | -14.4±4.1 |
| LP-DDAB/HA-L | | HA-L | 133.3±16.9 | 0.15±0.04 | -26.1±0.3 |
| LP-DDAB/HA-M | | HA-M | 103.1±0.6 | 0.24±0.01 | -24.0±5.4 |
| LP-DDAB/HA-H | | HA-H | 120.8±0.6 | 0.21±0.02 | -27.8±0.6 |
| LP-DDAB/CS | | CS | 141.1±8.7 | 0.22±0.06 | -43.9±1.3 |
| LP-DDAB/PGA | | PGA | 115.0±7.5 | 0.23±0.04 | -43.2±4.2 |
Gene knockdown effect and cellular
association of anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes
To determine the effect of the anionic polymer
coating on gene knockdown, MCF-7-Luc cells were incubated with
lipoplexes of Luc or Cont siRNA, and their luciferase activities
were evaluated (Fig. 1). Both
LP-DOTAP and LP-DDAB with Luc siRNA efficiently suppressed
luciferase activity in MCF-7-Luc cells. Anionic polymer-coated
lipoplexes also suppressed luciferase activity to the same level as
cationic lipoplexes.
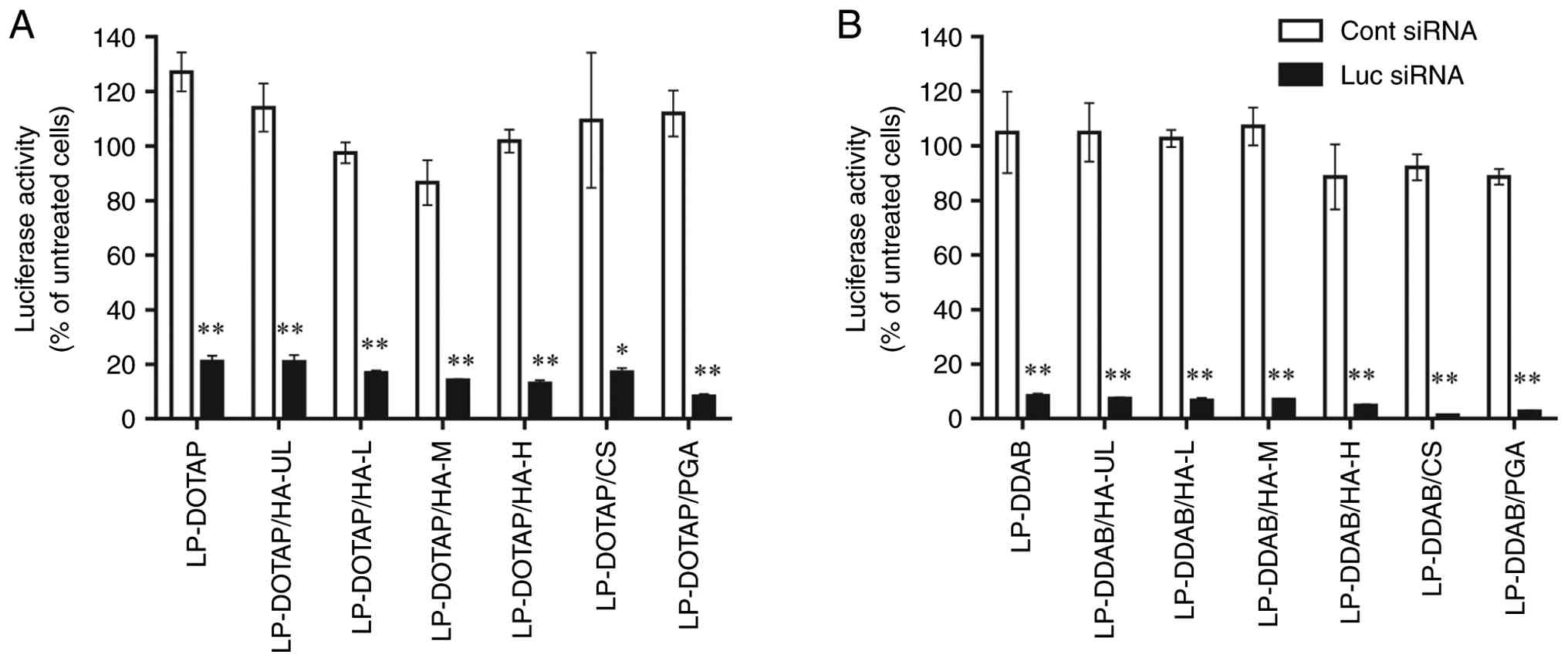 | Figure 1Effect of anionic polymer coating of
siRNA lipoplexes on suppression of luciferase expression in
MCF-7-Luc cells. MCF-7-Luc cells were treated for 48 h with anionic
polymer-coated (A) LP-DOTAP or (B) LP-DDAB at a final Cont or Luc
siRNA concentration of 50 nM. Each value represents the mean ±
standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05,
**P<0.01 compared with Cont siRNA. Cont, control; CS,
chondroitin sulfate; DDAB, dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide;
DOTAP, 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate
salt; HA, hyaluronan; HA-H, high-molecular-weight HA; HA-L,
low-molecular-weight HA; HA-M, medium-molecular-weight HA; HA-UL,
ultra-low-molecular-weight HA; Luc, luciferase; LP, lipoplex; PGA,
polyglutamic acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA. |
Next, we evaluated the cellular association of the
anionic polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes using flow cytometry
(Fig. 2). Representative flow
cytometry histograms are shown in Fig.
S1. The cationic lipoplexes, LP-DOTAP and LP-DDAB, exhibited a
higher cellular association than the anionic polymer-coated
lipoplexes. The mean fluorescence intensity of the HA-coated
lipoplexes decreased slightly as the molecular weight of HA
increased. CS and PGA-coated lipoplexes exhibited lower cellular
association than HA-coated lipoplexes. As shown in Table I, the large negative ζ-potential of
CS- and PGA-coated lipoplexes, compared with that of HA-coated
lipoplexes, may influence the reduced cellular association of
lipoplexes.
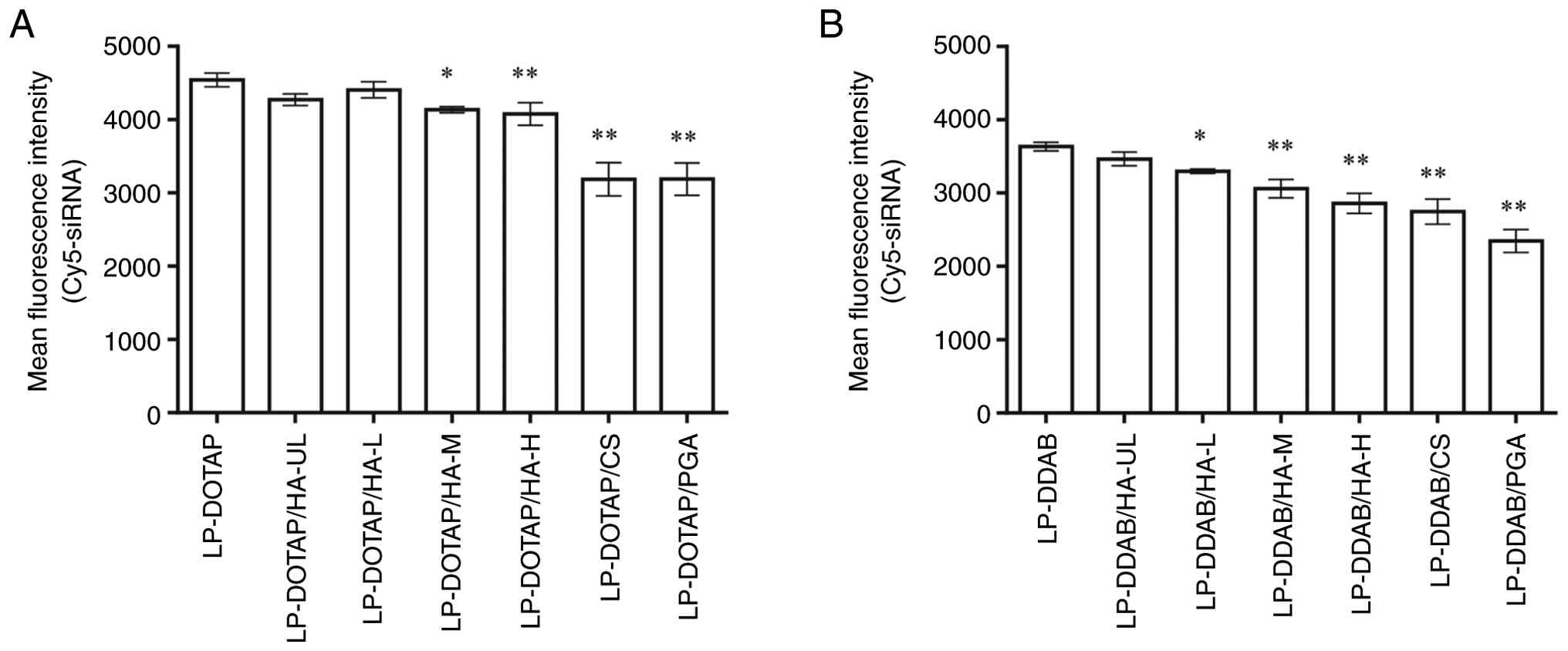 | Figure 2Cellular association of anionic
polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes. MCF-7-Luc cells were treated for 3
h with anionic polymer-coated (A) LP-DOTAP or (B) LP-DDAB at a
final Cy5-siRNA concentration of 50 nM. The association between the
siRNA lipoplexes and cells was determined based on Cy5 fluorescence
using flow cytometry. Each value represents the mean ± standard
deviation (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01
compared with LP-DOTAP or LP-DDAB. CS, chondroitin sulfate; DDAB,
dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide; DOTAP,
1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate salt; HA,
hyaluronan; HA-H, high-molecular-weight HA; HA-L,
low-molecular-weight HA; HA-M, medium-molecular-weight HA; HA-UL,
ultra-low-molecular-weight HA; LP, lipoplex; PGA, polyglutamic
acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA. |
Collectively, these results suggested that anionic
polymer-coating of siRNA lipoplexes decreased the cellular
association but did not affect gene knockdown. Anionic
polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes could effectively deliver siRNAs
into cells.
Cytotoxicity of anionic polymer-coated
lipoplexes
The effect of the anionic polymer coating on the
cytotoxicity of siRNA lipoplexes was examined (Fig. 3). The viability of MCF-7-Luc cells
incubated with all anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes exceeded 85%
of that of the untreated cells. No significant differences in cell
viability were observed compared with untreated cells. These
results suggested that the anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes
exhibited low cytotoxicity toward MCF-7-Luc cells.
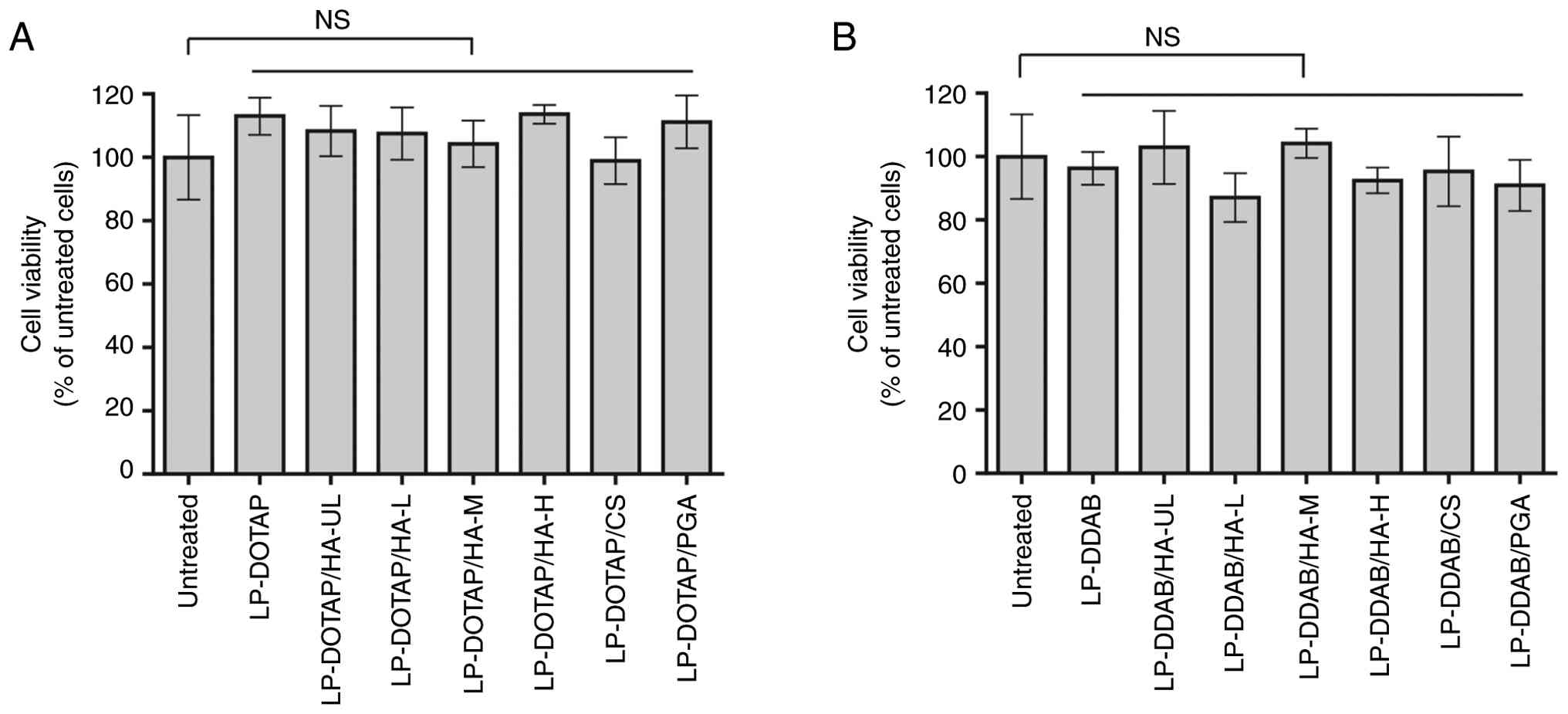 | Figure 3Effect of anionic polymer-coated
siRNA lipoplexes on cell viability. MCF-7-Luc cells were treated
for 24 h with anionic polymer-coated (A) LP-DOTAP or (B) LP-DDAB at
a final control siRNA concentration of 50 nM. Each value represents
the mean ± standard deviation (n=5-6). CS, chondroitin sulfate;
DDAB, dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide; DOTAP,
1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate salt; HA,
hyaluronan; HA-H, high-molecular-weight HA; HA-L,
low-molecular-weight HA; HA-M, medium-molecular-weight HA; HA-UL,
ultra-low-molecular-weight HA; LP, lipoplex; NS, not significant;
PGA, polyglutamic acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA. |
Erythrocyte agglutination with anionic
polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes
Because cationic lipoplexes have a positively
charged surface, they electrostatically interact with negatively
charged biological components, such as erythrocytes. We evaluated
whether the anionic polymer coating of lipoplexes could prevent
agglutination with erythrocytes (Fig.
4). Mixing cationic lipoplexes (LP-DOTAP or LP-DDAB) with
erythrocyte suspensions resulted in large aggregates. Small
aggregates were observed with HA-UL, HA-L, and HA-M-coated
lipoplexes. Conversely, LP-DOTAP/HA-H, LP-DOTAP/CS, LP-DOTAP/PGA,
LP-DDAB/HA-H, LP-DDAB/CS, and LP-DDAB/PGA did not induce
erythrocyte agglutination. These results suggested that HA-H-, CS-,
and PGA-coated lipoplexes of LP-DOTAP and LP-DDAB could prevent
erythrocyte agglutination.
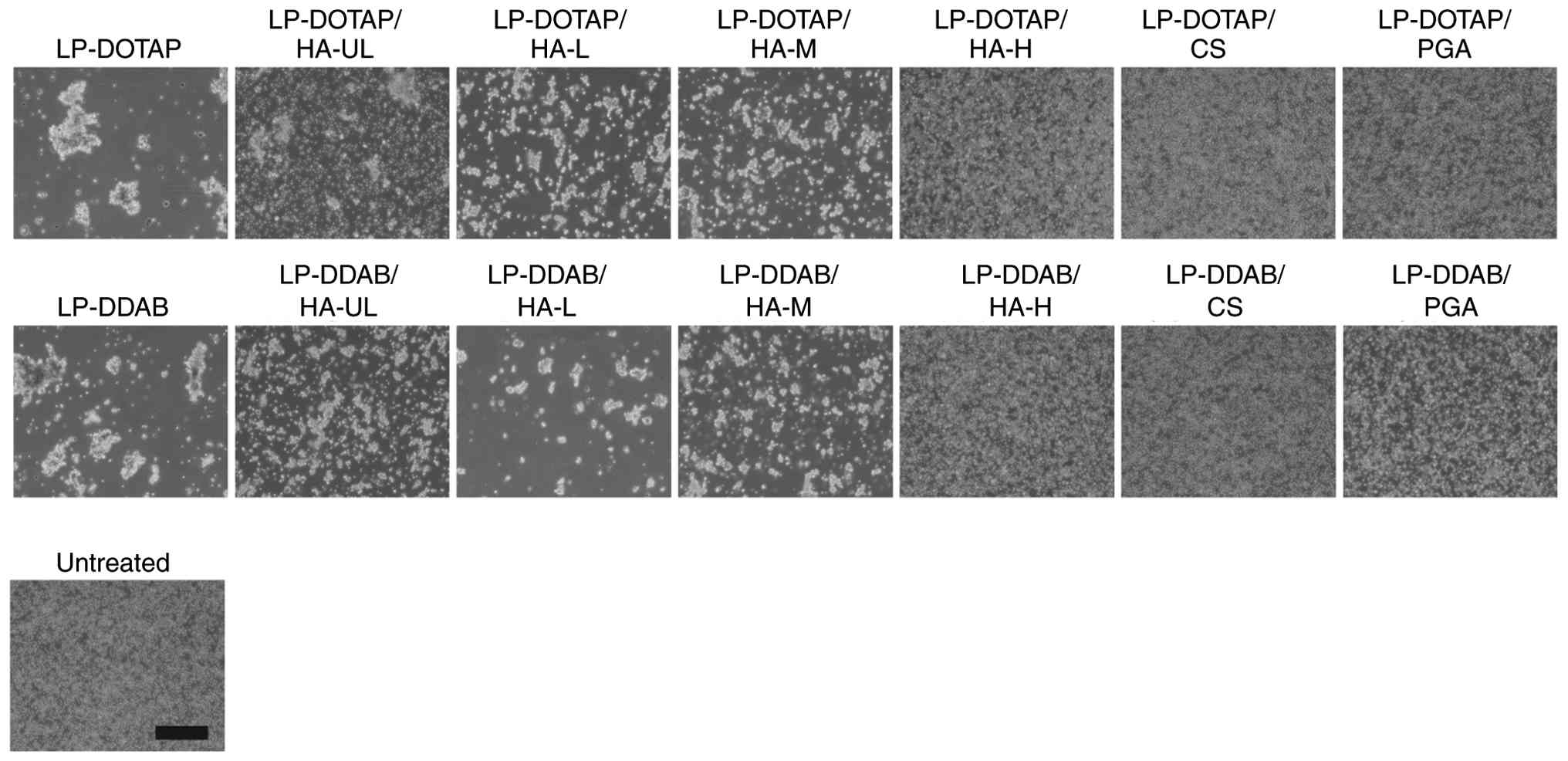 | Figure 4Erythrocyte agglutination with
anionic polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes. Anionic polymer-coated
LP-DOTAP or LP-DDAB with 2 µg control siRNA were added to
erythrocyte suspensions, and agglutination was observed by
microscopy. Scale bar, 200 µm. CS, chondroitin sulfate; DDAB,
dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide; DOTAP,
1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate salt; HA,
hyaluronan; HA-H, high-molecular-weight HA; HA-L,
low-molecular-weight HA; HA-M, medium-molecular-weight HA; HA-UL,
ultra-low-molecular-weight HA; LP, lipoplex; PGA, polyglutamic
acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA. |
Since anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes prevented
erythrocyte agglutination, they may have the potential to reduce
toxicity in vivo. To evaluate the inflammatory response of
lipoplexes, TNF-α concentrations in serum were determined (Fig. S2). Intravenous injection of LP-DDAB
caused a slight increase in serum TNF-α, whereas no elevation was
observed for LP-DDAB/HA-H or LP-DDAB/CS. Therefore, lipoplexes
coated with HA-H or CS are thought to have a higher safety
profile.
Biodistribution of anionic
polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes
Ex vivo imaging was performed to examine the
biodistribution of anionic polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes
(Fig. 5). LP-DOTAP and LP-DDAB were
distributed in the lungs, liver, spleen, and kidneys. As shown in
Fig. 5A, LP-DOTAP/HA-UL largely
accumulated in the lungs. The biodistribution of LP-DOTAP/HA-L and
LP-DOTAP/HA-M was similar to that of LP-DOTAP. The lung
distributions of LP-DOTAP/HA-H, LP-DOTAP/CS, and LP-DOTAP/PGA were
reduced. As shown in Fig. 5B,
LP-DDAB/HA-UL largely accumulated in the lungs, and other HA-coated
LP-DDAB were distributed in the lungs, liver, spleen, and kidneys.
The lung distribution of LP-DDAB/CS and LP-DDAB/PGA was lower than
that of LP-DDAB, whereas the liver distribution of LP-DDAB/CS and
LP-DDAB/PGA was higher than that of LP-DDAB.
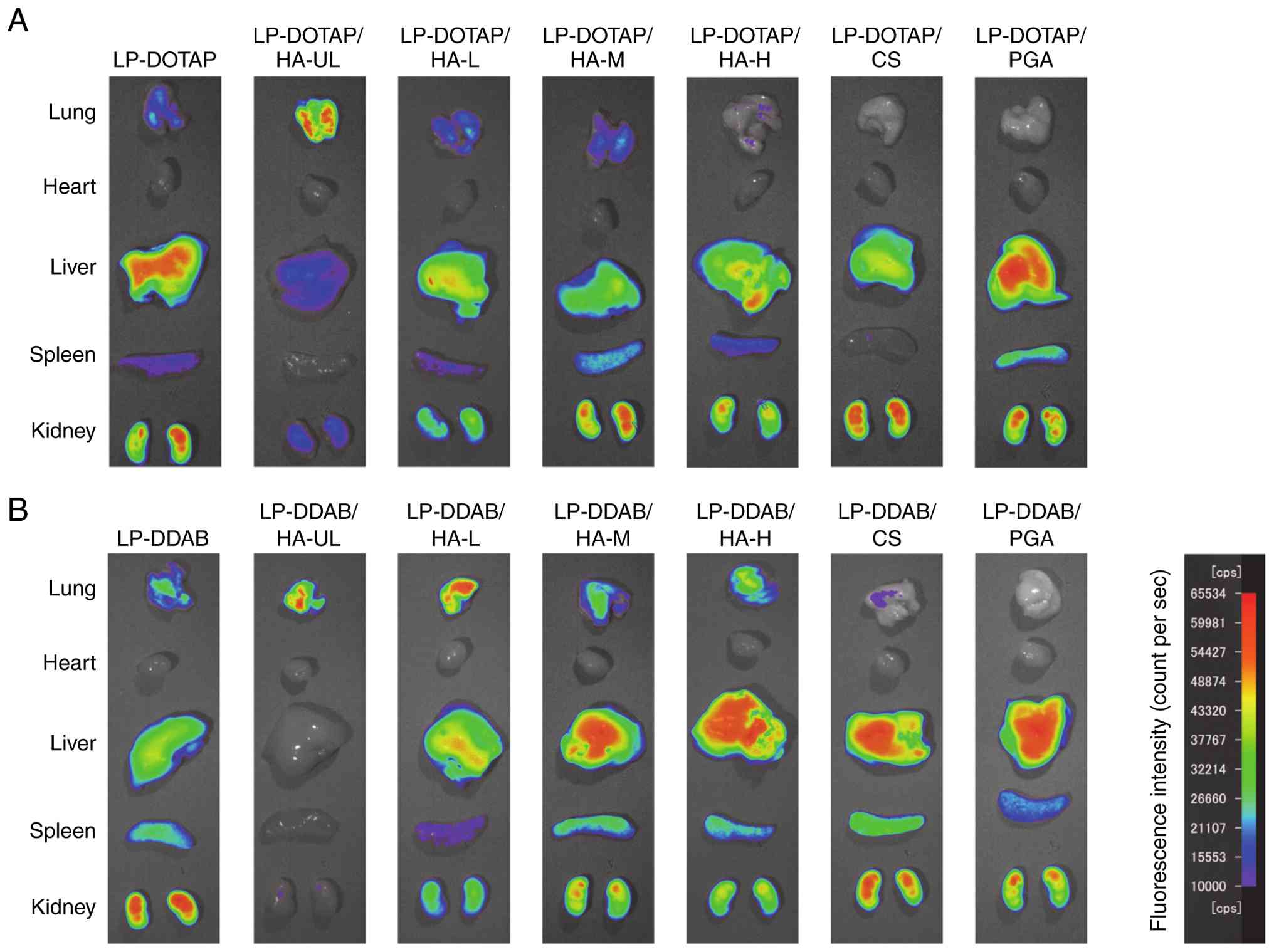 | Figure 5Biodistribution of siRNA in mice 1 h
after intravenous injection of anionic polymer-coated siRNA
lipoplexes. Fluorescence imaging of the tissues was performed 1 h
after injection of mice with anionic polymer-coated (A) LP-DOTAP or
(B) LP-DDAB with 10 µg Cy5-siRNA. Images were obtained from one
mouse for each siRNA lipoplex. The fluorescence intensity was
illustrated using a color-coded scale (red is the maximum, purple
is the minimum). cps, count per sec; CS, chondroitin sulfate; DDAB,
dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide; DOTAP,
1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate salt; HA,
hyaluronan; HA-H, high-molecular-weight HA; HA-L,
low-molecular-weight HA; HA-M, medium-molecular-weight HA; HA-UL,
ultra-low-molecular-weight HA; LP, lipoplex; PGA, polyglutamic
acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA. |
Discussion
In a recent report, our group demonstrated that the
MEI method was convenient for preparing lipoplexes of siRNA and
messenger RNA (mRNA) and that these lipoplexes could exert gene
transfection effects comparable to lipoplexes prepared using the
conventional thin lipid film hydration method (15,22).
In the MEI method, lipoplexes are prepared by mixing an RNA
solution with a lipid-ethanol solution. As shown in Table I, the average size of the lipoplexes
remained small (~100 nm), even after anionic polymer coating,
without mechanical shearing or sonication. Previously, siRNA
lipoplex prepared from cationic liposomes comprising DOTAP and
cholesterol was successfully coated with CS and PGA at a charge
ratio (+:-, cationic lipid:anionic polymer) of 1:1 and 1:1.5,
respectively (23). In the current
study, we established a charge ratio (+:-, cationic lipid:anionic
polymer) of 1:2 and generated lipoplexes with negative
ζ-potentials.
The gene knockdown effect of anionic polymer-coated
siRNA lipoplexes was comparable to that of cationic siRNA
lipoplexes, although the cellular association of anionic
polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes was lower than that of cationic
siRNA lipoplexes (Figs. 1 and
2). In our previous report, we
observed that anionic polymer coating of cationic siRNA lipoplexes
composed of DOTAP/cholesterol resulted in the disappearance of the
in vitro gene knockdown effect (23). The discrepancy in the gene knockdown
effect caused by anionic polymer coating is likely attributable to
the lipid composition of the lipoplexes, since cationic complexes
containing DOPE exhibited a greater gene knockdown effect despite
their low cellular association (24). Namely, the in vitro gene
knockdown effects of siRNA lipoplexes composed of DOTAP/DOPE and
DDAB/DOPE were higher than those of DOTAP/cholesterol and
DDAB/cholesterol, although cellular associations of siRNA
lipoplexes comprising DOTAP/DOPE and DDAB/DOPE were lower than
those of DOTAP/cholesterol and DDAB/cholesterol (24). Recently, Nabar et al
(25) reported that anionic polymer
coating on lipid nanoparticles can alter cellular interactions and
the intracellular trafficking of their cargo (mRNA and plasmid
DNA). Therefore, anionic polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes may
effectively deliver siRNA into cells; however, the intracellular
distribution of siRNA delivered by anionic polymer-coated
lipoplexes needs to be evaluated.
After intravenous injection of cationic lipoplexes,
agglutinates of cationic lipoplexes and erythrocytes are reportedly
entrapped in the highly extended lung capillary (6), which complicates delivery to organs
other than the lungs. PEG modification of the cationic lipoplex
surface decreases accumulation in the lung by avoiding association
with blood components, but PEG-modified lipoplexes lead to low
transfection efficiency (8-10).
To overcome this problem, the use of PEG-lipid derivatives with
cleavable linkers or releasable PEG derivatives has been explored
(9,26). In the current study, we found that
HA-H-, CS-, and PGA-coated lipoplexes prevented erythrocyte
agglutination and exhibited transfection efficiency comparable to
cationic lipoplexes (Figs. 1 and
4). These anionic polymers are
biodegradable, biocompatible, and exhibit low toxicity. Their
structures and charge density of polymers greatly influence the
biodistribution of lipoplexes coated with them. HA has one carboxyl
group per disaccharide unit, CS has a carboxyl group and a sulfate
group per disaccharide unit, and PGA has one carboxyl group per
glutamic acid unit. Because HA has a lower charge density than CS
or PGA, it is not expected to interact strongly with lipoplexes
(11); however, HA-H is likely to
interact more strongly and suppress erythrocyte agglutination.
These differences in charge density and structural features result
in distinct performance among HA-, CS-, and PGA-coated lipoplexes,
particularly in terms of coating strength, erythrocyte
agglutination, and biodistribution behavior. HA and CS are known
ligands for the cell surface receptor CD44, which is overexpressed
in numerous cancers (27,28). The usefulness of CD44 targeting by
these polymers has been reported previously (29,30).
Regarding HA, negatively charged lipoplexes were formed with all
molecular weights used for coating; however, the tendency to
aggregate with erythrocytes varied depending on the molecular
weight of HA (Fig. 4). Previous
reports suggested that molecular weight and grafting density of HA
on nanoparticles influenced the blood circulation time or receptor
recognition of nanoparticles (31-34).
Therefore, HA-H-coated lipoplexes are considered to have the
potential to reduce non-specific interactions, thereby improving
their stability in vivo while maintaining affinity for
target receptors. In the case of PGA, the tumor- or liver-targeting
properties have been reported previously (23,35-37).
It is important to evaluate the tumor- or liver-targeting efficacy
of anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes prepared using the MEI method
in the future.
Lipoplexes which form aggregates with erythrocytes
tend to accumulate in the lungs, the first capillary bed they pass
through (6,7). Aggregation with erythrocytes was
observed for both cationic lipoplexes (LP-DOTAP and LP-DDAB) and
those coated with HA-UL, HA-L or HA-M (Fig. 4), but not all lipoplexes accumulated
in the lungs (Fig. 5). This
discrepancy might be explained by differences in the stability of
the aggregates, which may induce dissociation of lipoplexes from
erythrocyte. It has been reported that the surface chemistry of
nanoparticles influenced the composition of the protein corona,
thereby affecting their organ tropism (38). Nanoparticles containing DOTAP have
been reported to form a protein corona enriched in vitronectin,
which binds to αvβ3 integrin highly expressed
in lung epithelium (38,39); however, in this study, LP-DOTAP
exhibited higher accumulation in the liver. It might be because the
lipoplex prepared in 5% glucose solution using the MEI method has
different morphology or surface properties. Further studies are
needed to clarify these mechanisms.
Anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes (especially CS- or
PGA-coated lipoplexes) altered the biodistribution of the siRNAs
(Fig. 5). However, the accumulation
of siRNA lipoplexes does not consistently correlate with the gene
knockdown effect in vivo (24,40).
Previous studies have shown that siRNA lipoplexes coated with CS or
PGA accumulate in the liver, but that only PGA-coated lipoplexes
can suppress the mRNA level of the hepatic target gene (23). Furthermore, it has been reported
that sequential intravenous administration of CS followed by
cationic lipoplexes results in siRNA accumulation in the liver and
subsequent suppression of the hepatic target gene (41). A limitation of the present study is
the absence of quantitative biodistribution data. Because
fluorescence imaging offers qualitative visualization rather than
reliable quantitative measurements (42), the biodistribution profiles of the
lipoplexes could not be discussed quantitatively. Further studies
are required to clarify the relationship between the
biodistribution of anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes and the in
vivo gene knockdown effects.
In conclusion, cationic siRNA lipoplexes were
prepared using the MEI method and successfully coated with anionic
polymers without a loss of transfection efficiency. HA-H-, CS-, and
PGA-coated lipoplexes prevented erythrocyte agglutination, while
decreased lung accumulation and increased liver accumulation were
observed after CS or PGA coating of siRNA lipoplexes. Although
further evaluation is necessary, anionic polymer-coated lipoplexes
prepared using the MEI method could enable siRNA delivery to the
liver or tumor tissues.
Supplementary Material
Representative flow cytometry
histograms. MCF-7-Luc cells were treated for 3 h with anionic
polymer-coated (A) LP-DOTAP or (B) LP-DDAB at a final Cy5-siRNA
concentration of 50 nM. The fluorescence intensity of gate P2 was
quantified and used for the analysis shown in Fig. 2. CS, chondroitin sulfate; DDAB,
dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide; DOTAP,
1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate salt; HA,
hyaluronan; HA-H, high-molecular-weight HA; HA-L,
low-molecular-weight HA; HA-M, medium-molecular-weight HA; HA-UL,
ultra-low-molecular-weight HA; LP, lipoplex; PGA, polyglutamic
acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
TNF-α levels in serum after
intravenous injection of anionic polymer-coated siRNA lipoplexes.
The concentrations of TNF-α in serum were determined 2 h after
injection of HA-H, CS, or PGA-coated LP-DOTAP or LP-DDAB with 10
μg control siRNA to mice. Each value represents the mean ±
standard deviation of three individual mice (n=3 biological
replicates). CS, chondroitin sulfate; DDAB,
dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide; DOTAP,
1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane methyl sulfate salt; HA-H,
high-molecular-weight hyaluronan; LP, lipoplex; PGA, polyglutamic
acid; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Min Tang, Ms. Yui
Kikuchi, Mr. Rento Suzuki, Ms. Sumire Fukushige and Mr. Kohei Miura
(Department of Molecular Pharmaceutics, Hoshi University,
Shinagawa, Tokyo, Japan) for their assistance with experiments.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors contributions
KK and YH conceived and designed the experiments. KK
conducted the investigation, curated data, performed formal
analysis, prepared the original draft, and wrote, reviewed and
edited the manuscript. KK and YH confirm the authenticity of all
the raw data. All authors have read and approved the final version
of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Institutional
Animal Care and Use Committee of Hoshi University (approval no.
P24-094; Shinagawa, Tokyo, Japan).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Davis ME, Zuckerman JE, Choi CHJ, Seligson
D, Tolcher A, Alabi CA, Yen Y, Heidel JD and Ribas A: Evidence of
RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted
nanoparticles. Nature. 464:1067–1070. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zatsepin TS, Kotelevtsev YV and
Koteliansky V: Lipid nanoparticles for targeted siRNA
delivery-going from bench to bedside. Int J Nanomedicine.
11:3077–3086. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yan Y, Liu XY, Lu A, Wang XY, Jiang LX and
Wang JC: Non-viral vectors for RNA delivery. J Control Release.
342:241–279. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang S, Zhi D and Huang L: Lipid-based
vectors for siRNA delivery. J Drug Target. 20:724–735.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Simberg D, Weisman S, Talmon Y, Faerman A,
Shoshani T and Barenholz Y: The role of organ vascularization and
lipoplex-serum initial contact in intravenous murine lipofection. J
Biol Chem. 278:39858–39865. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Eliyahu H, Servel N, Domb AJ and Barenholz
Y: Lipoplex-induced hemagglutination: Potential involvement in
intravenous gene delivery. Gene Ther. 9:850–858. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Buyens K, De Smedt SC, Braeckmans K,
Demeester J, Peeters L, van Grunsven LA, de Mollerat du Jeu X,
Sawant R, Torchilin V, Farkasova K, et al: Liposome based systems
for systemic siRNA delivery: Stability in blood sets the
requirements for optimal carrier design. J Control Release.
158:362–370. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hattori Y, Tamaki K, Sakasai S, Ozaki KI
and Onishi H: Effects of PEG anchors in PEGylated siRNA lipoplexes
on in vitro gene-silencing effects and siRNA biodistribution
in mice. Mol Med Rep. 22:4183–4196. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hatakeyama H, Akita H and Harashima H: A
multifunctional envelope type nano device (MEND) for gene delivery
to tumours based on the EPR effect: A strategy for overcoming the
PEG dilemma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 63:152–160. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hattori Y, Yamasaku H and Maitani Y:
Anionic polymer-coated lipoplex for safe gene delivery into tumor
by systemic injection. J Drug Target. 21:639–647. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fukushige K, Tagami T and Ozeki T: The
offset effect of a hyaluronic acid coating to cationic carriers
containing siRNA: Alleviated cytotoxicity and retained gene
silencing in vitro. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 39:435–441. 2017.
|
|
13
|
Qian Y, Liang X, Yang J, Zhao C, Nie W,
Liu L, Yi T, Jiang Y, Geng J, Zhao X and Wei X: Hyaluronan reduces
cationic liposome-induced toxicity and enhances the antitumor
effect of targeted gene delivery in mice. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 10:32006–32016. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hattori Y, Kurihara A and Shinkawa M:
Assessment of anionic siRNA lipoplexes prepared via modified
ethanol injection for tumor cell delivery. Biomed Rep.
24(12)2026.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hattori Y, Saito H, Nakamura K, Yamanaka
A, Tang M and Ozaki KI: In vitro and in vivo transfections using
siRNA lipoplexes prepared by mixing siRNAs with a lipid-ethanol
solution. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 75(103635)2022.
|
|
16
|
Hattori Y, Tang M, Suzuki H, Hattori A,
Endo S, Ishii A, Aoki A, Ezaki M and Sakai H: Optimization of
transfection into cultured cells with siRNA lipoplexes prepared
using a modified ethanol injection method. J Drug Deliv Sci
Technol. 99(106000)2024.
|
|
17
|
Hattori Y, Tang M, Aoki A, Ezaki M, Sakai
H and Ozaki KI: Effect of the combination of cationic lipid and
phospholipid on gene-knockdown using siRNA lipoplexes in breast
tumor cells and mouse lungs. Mol Med Rep. 28(180)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hattori Y and Shimizu R: Effective mRNA
transfection of tumor cells using cationic triacyl lipid-based mRNA
lipoplexes. Biomed Rep. 22(25)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hattori Y, Tamaki K, Ozaki KI, Kawano K
and Onishi H: Optimized combination of cationic lipids and neutral
helper lipids in cationic liposomes for siRNA delivery into the
lung by intravenous injection of siRNA lipoplexes. J Drug Deliv Sci
Technol. 52:1042–1050. 2019.
|
|
20
|
Whitmore M, Li S and Huang L: LPD
lipopolyplex initiates a potent cytokine response and inhibits
tumor growth. Gene Ther. 6:1867–1875. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hattori Y, Arai S, Kikuchi T, Ozaki KI,
Kawano K and Yonemochi E: Therapeutic effect for liver-metastasized
tumor by sequential intravenous injection of anionic polymer and
cationic lipoplex of siRNA. J Drug Target. 24:309–317.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hattori Y, Tang M, Sato J, Tsuiji M and
Kawano K: Evaluation of mRNA lipoplexes prepared using modified
ethanol injection method as a tumour vaccine. J Drug Target.
32:1267–1277. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura A, Arai S, Nishigaki
M, Ohkura H, Kawano K, Maitani Y and Yonemochi E: In vivo siRNA
delivery system for targeting to the liver by poly-l-glutamic
acid-coated lipoplex. Results Pharm Sci. 4:1–7. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura A, Arai S, Kawano K,
Maitani Y and Yonemochi E: siRNA delivery to lung-metastasized
tumor by systemic injection with cationic liposomes. J Liposome
Res. 25:279–286. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nabar N, Dacoba TG, Covarrubias G,
Romero-Cruz D and Hammond PT: Electrostatic adsorption of
polyanions onto lipid nanoparticles controls uptake, trafficking,
and transfection of RNA and DNA therapies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
121(e2307809121)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang T, Upponi JR and Torchilin VP: Design
of multifunctional non-viral gene vectors to overcome physiological
barriers: Dilemmas and strategies. Int J Nanomedicine. 427:3–20.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lesley J, Hascall VC, Tammi M and Hyman R:
Hyaluronan binding by cell surface CD44. J Biol Chem.
275:26967–26975. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sironen RK, Tammi M, Tammi R, Auvinen PK,
Anttila M and Kosma VM: Hyaluronan in human malignancies. Exp Cell
Res. 317:383–391. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lin WJ and Lee WC: Polysaccharide-modified
nanoparticles with intelligent CD44 receptor targeting ability for
gene delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 13:3989–4002. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dosio F, Arpicco S, Stella B and Fattal E:
Hyaluronic acid for anticancer drug and nucleic acid delivery. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 97:204–236. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Peer D and Margalit R: Tumor-targeted
hyaluronan nanoliposomes increase the antitumor activity of
liposomal Doxorubicin in syngeneic and human xenograft mouse tumor
models. Neoplasia. 6:343–353. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Deng C, Fu Y, Sun X, Gong T and
Zhang Z: Repeated administration of hyaluronic acid coated
liposomes with improved pharmacokinetics and reduced immune
response. Mol Pharm. 13:1800–1808. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mizrahy S, Raz SR, Hasgaard M, Liu H,
Soffer-Tsur N, Cohen K, Dvash R, Landsman-Milo D, Bremer MG,
Moghimi SM and Peer D: Hyaluronan-coated nanoparticles: The
influence of the molecular weight on CD44-hyaluronan interactions
and on the immune response. J Control Release. 156:231–238.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Qhattal HS and Liu X: Characterization of
CD44-mediated cancer cell uptake and intracellular distribution of
hyaluronan-grafted liposomes. Mol Pharm. 8:1233–1246.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Peng SF, Tseng MT, Ho YC, Wei MC, Liao ZX
and Sung HW: Mechanisms of cellular uptake and intracellular
trafficking with chitosan/DNA/poly(γ-glutamic acid) complexes as a
gene delivery vector. Biomaterials. 32:239–248. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kurosaki T, Ueda Y, Kato Y, Nakashima M,
Kitahara T, Sasaki H and Kodama Y: Effect of a novel siRNA delivery
system, siRNA ternary complex, on melanoma lung metastasis. J Drug
Target. 32:848–854. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hattori Y, Arai S, Okamoto R, Hamada M,
Kawano K and Yonemochi E: Sequential intravenous injection of
anionic polymer and cationic lipoplex of siRNA could effectively
deliver siRNA to the liver. Int J Pharm. 476:289–298.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dilliard SA, Cheng Q and Siegwart DJ: On
the mechanism of tissue-specific mRNA delivery by selective organ
targeting nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118(e2109256118)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dilliard SA, Sun Y, Brown MO, Sung YC,
Chatterjee S, Farbiak L, Vaidya A, Lian X, Wang X, Lemoff A and
Siegwart DJ: The interplay of quaternary ammonium lipid structure
and protein corona on lung-specific mRNA delivery by selective
organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles. J Control Release.
361:361–372. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura M, Takeuchi N, Tamaki
K, Ozaki KI and Onishi H: Effect of cationic lipid type in
PEGylated liposomes on siRNA delivery following the intravenous
injection of siRNA lipoplexes. World Acad Sci J. 1:74–85. 2019.
|
|
41
|
Hattori Y, Yoshiike Y, Kikuchi T, Yamamoto
N, Ozaki KI and Onishi H: Evaluation of the injection route of an
anionic polymer for small interfering RNA delivery into the liver
by sequential injection of anionic polymer and cationic lipoplex of
small interfering RNA. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 35:40–49.
2016.
|
|
42
|
Simonsen JB and Kromann EB: Pitfalls and
opportunities in quantitative fluorescence-based nanomedicine
studies-A commentary. J Control Release. 335:660–667.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|



















