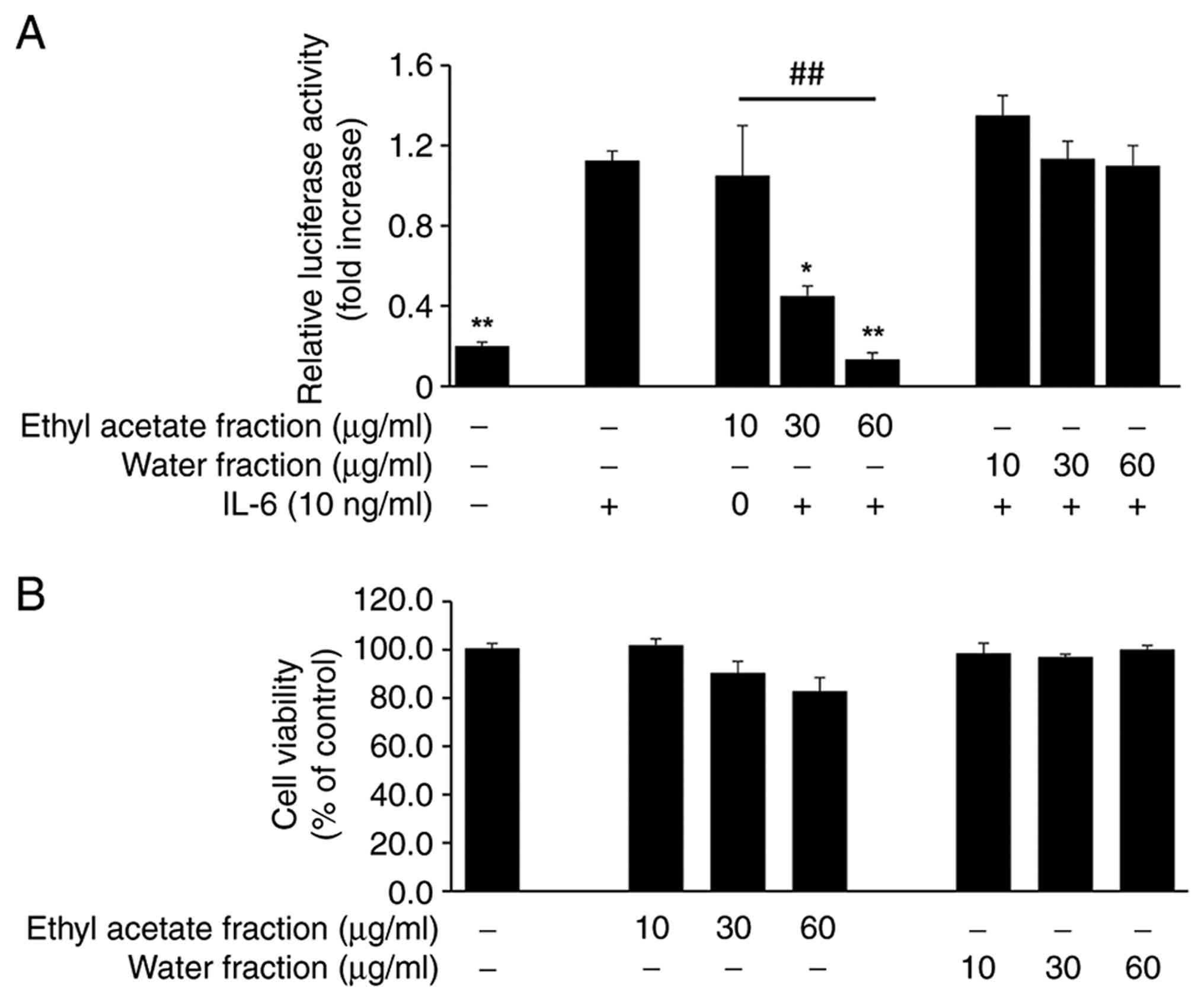
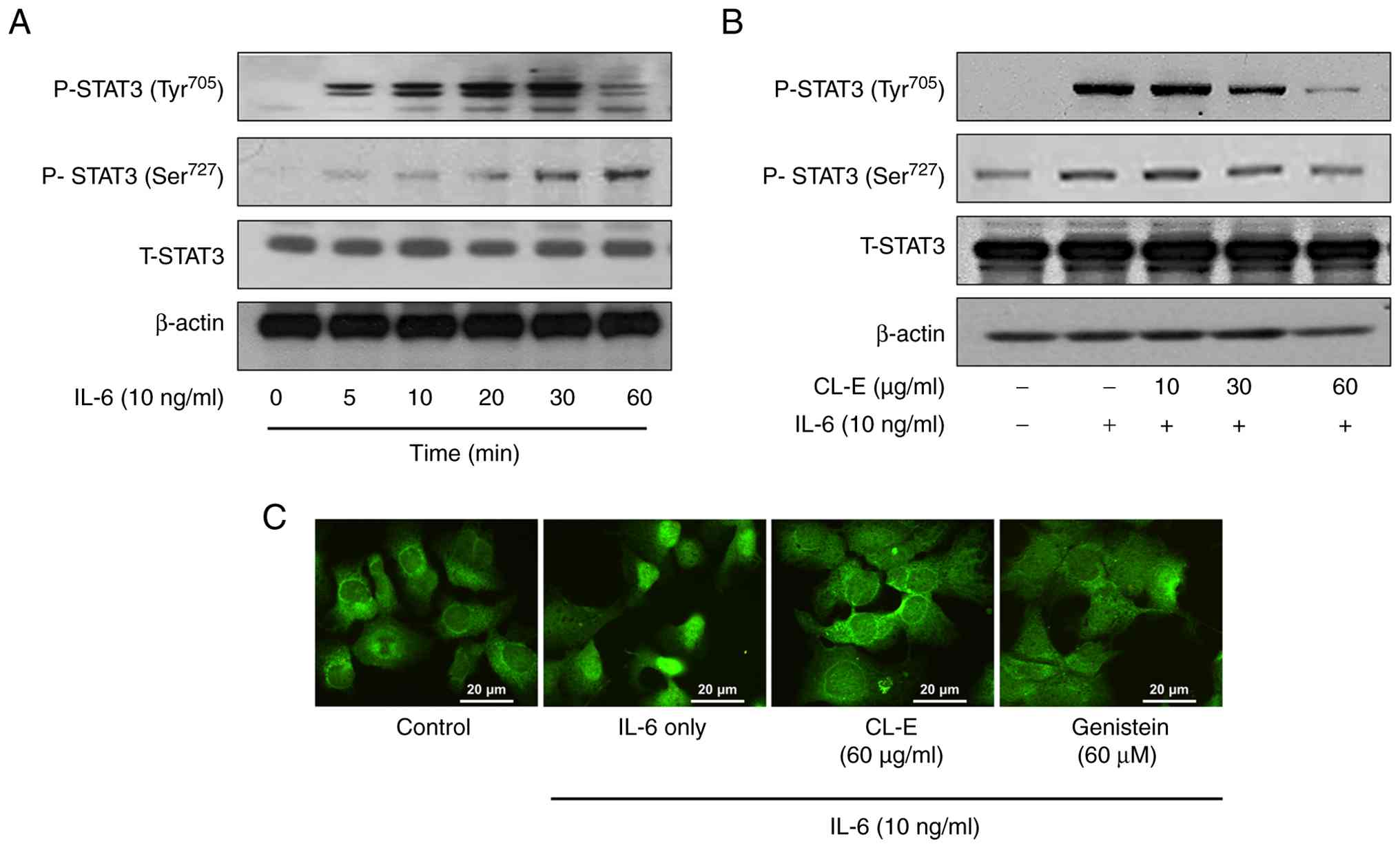
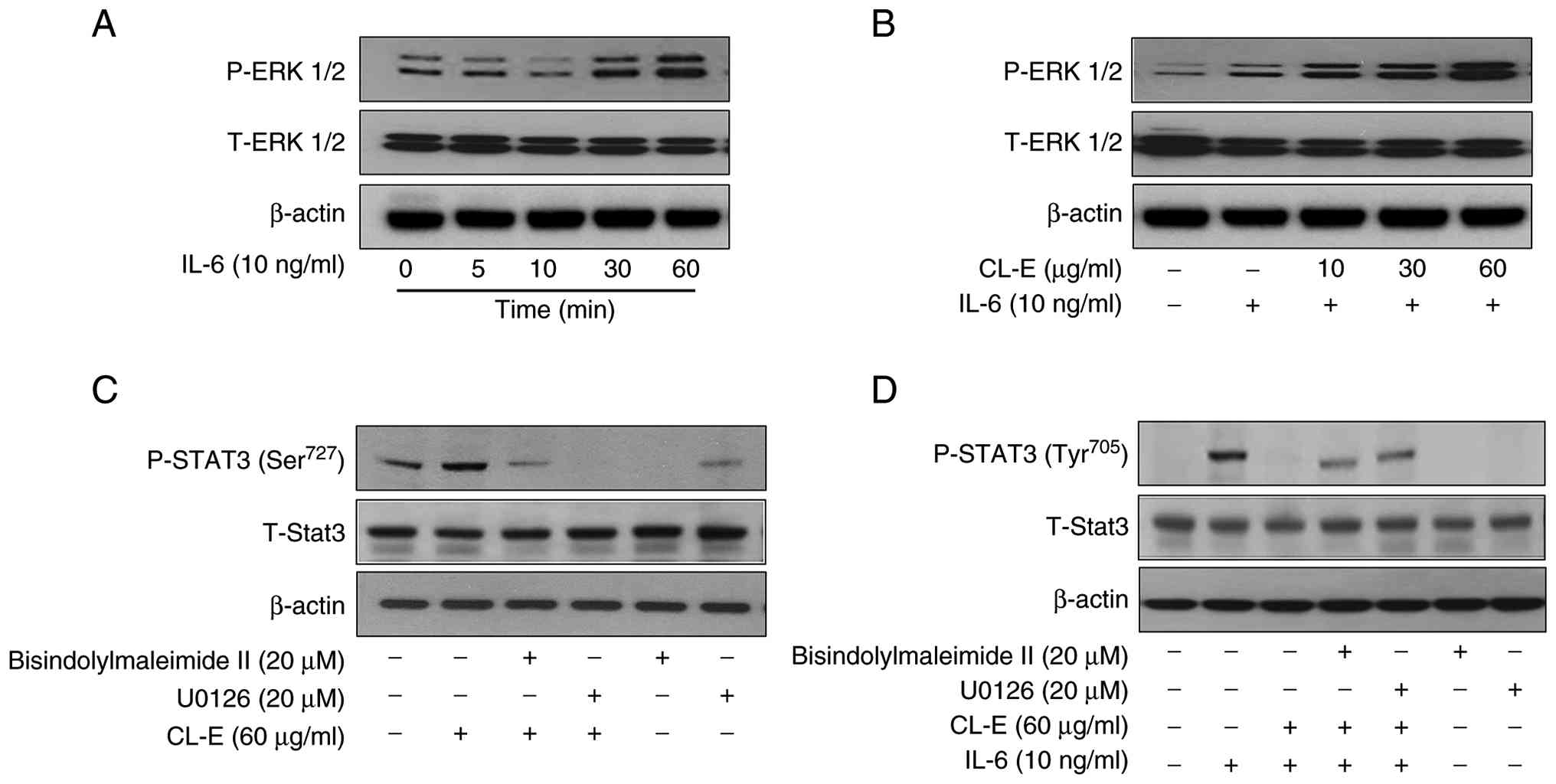
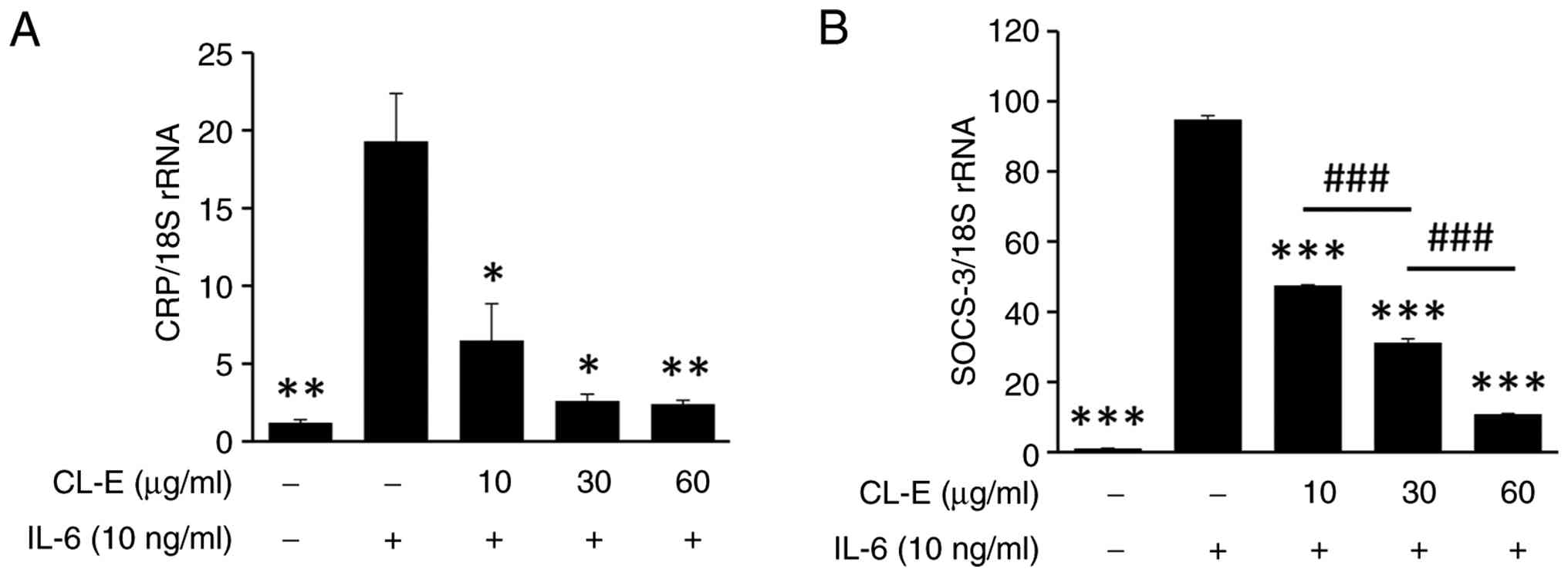
|
1
|
Strassmann G, Masui Y, Chizzonite R and
Fong M: Mechanisms of experimental cancer cachexia. Local
involvement of IL-1 in colon-26 tumor. J Immunol. 150:2341–2345.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kishimoto T: Interleukin-6: From basic
science to medicine-40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol.
23:1–21. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lütticken C, Wegenka UM, Yuan J, Buschmann
J, Schindler C, Ziemiecki A, Harpur AG, Wilks AF, Yasukawa K, Taga
T, et al: Association of transcription factor APRF and protein
kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130.
Science. 263:89–92. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ihle JN: STATs: Signal transducers and
activators of transcription. Cell. 84:331–334. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sebti SM and Der CJ: Opinion: Searching
for the elusive targets of farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:945–951. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Darnell JE Jr: STATs and gene regulation.
Science. 277:1630–1635. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Aaronson DS and Horvath CM: A road map for
those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 296:1653–1655.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar
KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S and Sung B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and
cancer: How intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1171:59–76. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns
HM, Müller-Newen G and Schaper F: Principles of interleukin
(IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J.
374:1–20. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang D, Sun M, Samols D and Kushner I:
STAT3 participates in transcriptional activation of the C-reactive
protein gene by interleukin-6. J Biol Chem. 271:9503–9509.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nishiyama T, Mae T, Kishida H, Tsukagawa
M, Mimaki Y, Kuroda M, Sashida Y, Takahashi K, Kawada T, Nakagawa K
and Kitahara M: Curcuminoids and sesquiterpenoids in turmeric
(Curcuma longa L.) suppress an increase in blood glucose
level in type 2 diabetic KK-Ay mice. J Agric Food Chem. 53:959–963.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Asai A, Nakagawa K and Miyazawa T:
Antioxidative effects of turmeric, rosemary and capsicum extracts
on membrane phospholipid peroxidation and liver lipid metabolism in
mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 63:2118–2122. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Samaha HS, Kelloff GJ, Steele V, Rao CV
and Reddy BS: Modulation of apoptosis by sulindac, curcumin,
phenylethyl-3-methylcaffeate, and 6-phenylhexyl isothiocyanate:
Apoptotic index as a biomarker in colon cancer chemoprevention and
promotion. Cancer Res. 57:1301–1305. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jayaprakasha GK, Jena BS, Negi PS and
Sakariah KK: Evaluation of antioxidant activities and
antimutagenicity of turmeric oil: A byproduct from curcumin
production. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 57:828–835. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hong CH, Noh MS, Lee WY and Lee SK:
Inhibitory effects of natural sesquiterpenoids isolated from the
rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria on prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide
production. Planta Med. 68:545–547. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pothitirat W and Gritsanapan W: Variation
of bioactive components in Curcuma longa in Thailand. Curr
Sci. 91:1397–1400. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Bhardwaj KS, Bhardwaj RS, Ranjeet D and
Ganesh N: Curcuma longa leaves exhibits a potential
antioxidant, antibacterial and immunomodulating properties. Int J
Phytomed. 3:270–278. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Abida Y, Tabassum F, Zaman S, Chhabi SB
and Islam N: Biological screening of Curcuma longa L. for
insecticidal and repellent potentials against Tribolium castaneum
(Herbst) adults. Univ J Zool Rajshahi Univ. 28:69–71. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Kim DW, Lee SM, Woo HS, Park JY, Ko BS,
Heo JD, Ryu YB and Lee WS: Chemical constituents and
anti-inflammatory activity of the aerial parts of Curcuma
longa. J Funct Foods. 26:485–493. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Ahn D, Lee EB, Ahn MS, Lim HW, Xing MM,
Tao C, Yang JH and Kim DK: Antioxidant constituents of the aerial
parts of Curcuma longa Kor. J Pharmacogn. 43:274–278.
2012.
|
|
21
|
Jiang CL, Tsai SF and Lee SS: Flavonoids
from Curcuma longa leaves and their NMR assignments. Nat
Prod Commun. 10:63–66. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SJ, Jang HJ, Kim Y, Oh HM, Lee S, Jung
K, Kim YH, Lee WS, Lee SW and Rho MC: Inhibitory effects of
IL-6-induced STAT3 activation of bio-active compounds derived from
Salvia plebeia R.Br. Process Biochem. 51:2222–2229.
2016.
|
|
23
|
Li HC and Zhang GY: Inhibitory effect of
genistein on activation of STAT3 induced by brain
ischemia/reperfusion in rat hippocampus. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
24:1131–1136. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sengupta TK, Talbot ES, Scherle PA and
Ivashkiv LB: Rapid inhibition of interleukin-6 signaling and Stat3
activation mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:11107–11112. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT
and Saltiel AR: PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation
of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J
Biol Chem. 270:27489–27494. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dudley DT, Pang L, Decker SJ, Bridges AJ
and Saltiel AR: A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated
protein kinase cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:7686–7689.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Müller-Newen G,
Schaper F and Graeve L: Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling
through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J. 334:297–314.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ochrietor JD, Harrison KA, Zahedi K and
Mortensen RF: Role of STAT3 and C/EBP in cytokine-dependent
expression of the mouse serum amyloid P-component (SAP) and
C-reactive protein (CRP) genes. Cytokine. 12:888–899.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang D, Jiang SL, Rzewnicki D, Samols D
and Kushner I: The effect of interleukin-1 on C-reactive protein
expression in Hep3B cells is exerted at the transcriptional level.
Biochem J. 310:143–148. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lim HJ, Jang HJ, Bak SG, Lee S, Lee SW,
Lee KM, Lee SJ and Rho MC: In vitro inhibitory effects of cirsiliol
on IL-6-induced STAT3 activation through anti-inflammatory
activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 29:1586–1592. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chang JS, Lee SW, Kim MS, Yun BR, Park MH,
Lee SG, Park SJ, Lee WS and Rho MC: Manassantin A and B from
Saururus chinensis inhibit interleukin-6-induced signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation in Hep3B
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 115:84–88. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chang JS, Lee SW, Park MH, Kim MS, Hudson
BI, Park SJ, Lee WS and Rho MC: Kansuinine A and Kansuinine B from
Euphorbia kansui L. inhibit IL-6-induced Stat3 activation.
Planta Med. 76:1544–1549. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hodge DR, Hurt EM and Farrar WL: The role
of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer.
41:2502–2512. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chung J, Uchida E, Grammer TC and Blenis
J: STAT3 serine phosphorylation by ERK-dependent and -independent
pathways negatively modulates its tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol
Cell Biol. 17:6508–6516. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Stancato LF, Sakatsume M, David M, Dent P,
Dong F, Petricoin EF, Krolewski JJ, Silvennoinen O, Saharinen P,
Pierce J, et al: Beta interferon and oncostatin M activate Raf-1
and mitogen-activated protein kinase through a JAK1-dependent
pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 17:3833–3840. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Beadling C, Ng J, Babbage JW and Cantrell
DA: Interleukin-2 activation of STAT5 requires the convergent
action of tyrosine kinases and a serine/threonine kinase pathway
distinct from the Raf1/ERK2 MAP kinase pathway. EMBO J.
15:1902–1913. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee HK, Jung J, Lee SH, Seo SY, Suh DJ and
Park HT: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation is
required for serine 727 phosphorylation of STAT3 in Schwann cells
in vitro and in vivo. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 13:161–168.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Terstegen L, Gatsios P, Bode JG, Schaper
F, Heinrich PC and Graeve L: The inhibition of
interleukin-6-dependent STAT activation by mitogen-activated
protein kinases depends on tyrosine 759 in the cytoplasmic tail of
glycoprotein 130. J Biol Chem. 275:18810–18817. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pepys MB and Hirschfield GM: C-reactive
protein: A critical update. J Clin Invest. 111:1805–1812.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ridker PM: From C-reactive protein to
interleukin-6 to interleukin-1: Moving upstream to identify novel
targets for atheroprotection. Circ Res. 118:145–156.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yasukawa H, Ohishi M, Mori H, Murakami M,
Chinen T, Aki D, Hanada T, Takeda K, Akira S, Hoshijima M, et al:
IL-6 induces an anti-inflammatory response in the absence of SOCS3
in macrophages. Nat Immunol. 4:551–556. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
El Kasmi KC, Holst J, Coffre M, Mielke L,
de Pauw A, Lhocine N, Smith AM, Rutschman R, Kaushal D, Shen Y, et
al: General nature of the STAT3-activated anti-inflammatory
response. J Immunol. 177:7880–7888. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jang HJ, Park EJ, Lee SJ, Lim HJ, Jo JH,
Lee SW and Rho MC: Diarylheptanoids from Curcuma phaeocaulis
suppress IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Planta Med. 85:94–102.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Rajasingh J, Raikwar HP, Muthian G,
Johnson C and Bright JJ: Curcumin induces growth-arrest and
apoptosis in association with the inhibition of constitutively
active JAK-STAT pathway in T cell leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 340:359–368. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Saydmohammed M, Joseph D and Syed V:
Curcumin suppresses constitutive activation of STAT-3 by
up-regulating protein inhibitor of activated STAT-3 (PIAS-3) in
ovarian and endometrial cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 110:447–456.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|