Introduction
Cerebral infarction is one of the main causes of
death among adults in China. Between 2004 and 2005, the crude
mortality rate of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases was
136.6/100,000 people, and the standardized mortality rate was
120.1/100,000 people. Among these, intracerebral hemorrhage
accounted for 50.4% of the deaths from cardiovascular and
cerebrovascular disease, followed by cerebral infarction, which
accounted for 24.8% (1). Cerebral
infarction not only reduces quality of life but also imposes a
heavy economic burden on the patient and their family (2). The current treatment methods for
cerebral infarction primarily include interventional therapy,
surgery and drug treatment. A survey of 408 elderly patients with
hemiplegia due to acute ischemic stroke revealed that their
standardized scores on the Stroke-Specific Quality of Life Scale 1
month after discharge were (56.30±5.21)%, only reaching a moderate
level; the actual scores were even lower at (136.35±5.38),
indicating suboptimal functional recovery following cerebral
infarction injury (2).
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult SCs with
self-renewal and multi-directional differentiation potential, and
come from a range of sources, including bone marrow, fat, umbilical
cord and other tissue. MSCs exhibit low immunogenicity and easy
in vitro culture expansion, and have demonstrated potential
therapeutic value in the treatment of various diseases including
cerebral infarction, Parkinson's disease, arthritis, spinal cord
and sciatic nerve injury (3). SC
therapy plays multiple roles in ischemic cerebral infarction,
including neuroprotection through reducing apoptosis and
inflammation, promoting angiogenesis and endogenous neurogenesis,
modulating immune responses, and potentially differentiating into
neural cells to replace damaged tissue. Clinical studies on
mesenchymal SC (MSC) transplantation for ischemic cerebral
infarction have been conducted, confirming its safety and
feasibility in both the acute and chronic phases; preliminary
evidence indicates that motor function recovery can be improved
through various administration routes, such as intravenous,
intra-arterial, and intracerebral methods (4,5). MSC
therapy may be an effective method to improve the prognosis of
patients with cerebral infarction. It is helpful for clinicians to
understand the effectiveness and safety of MSCs in the treatment of
cerebral infarction to provide a basis for the feasibility of
future clinical application. The present study focused on the
efficacy and safety of MSCs in the treatment of cerebral
infarction, aiming to provide a novel approach for the treatment of
cerebral infarction in addition to traditional thrombolysis, drug
and rehabilitation treatment. The present study also aimed to
provide a reference for exploring optimized therapeutic protocols
of MSCs for cerebral infarction.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
VIP Information (qikan.cqvip.com), China National Knowledge
Infrastructure (cnki.net), Wanfang Data (wanfangdata.com.cn/index.html), PubMed
(pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), Cochrane
Library (cochranelibrary.com) and Web of
Science (https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/) were searched from
the establishment of the database to October 2024 for studies on
the treatment of cerebral infarction with MSCs. The Chinese
literature search terms were as follows: ‘Mesenchymal stem cells’,
‘stem cells’, ‘mesenchymal cells’, ‘cerebral infarction’, ‘ischemic
stroke’, ‘stroke’, ‘stroke’, ‘randomized controlled trial’, ‘RCT’,
‘randomized’. English literature search terms included ‘mesenchymal
stem cell’, ‘stem cell’, ‘cerebral infarction’, ‘stroke’ and
‘randomized controlled trial’.
Inclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows: i) Randomized
controlled trials, with or without blinding; ii) patients meeting
the diagnostic criteria for cerebral infarction; iii) use of MSC
treatment, or MSCs combined with other treatments (such as drug or
rehabilitation therapy); iv) use of other treatment as a control
group (such as conventional drug therapy, rehabilitation, placebo);
v) studies reporting National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
score (NIHSS) (6), Fugl-Meyer
Assessment (FMA) (7), Functional
Independence Measure (FIM) (8),
Barthel Index(BI) (9), modified
Rankin scale score (mRS) (10),
adverse events or adverse reactions following treatment (such as
infection, immune response, tumor formation); vi) studies with
complete original data that can be directly or indirectly extracted
for analysis (mean, standard deviation, sample size) and vii)
studies written in Chinese and English. There were no restrictions
on age, sex or ethnicity of patients.
Exclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria were as follows: i) Retrospective
studies, case reports, reviews, meta-analyses, conference abstracts
and other non-randomized controlled trials; ii) animal studies,
in vitro experiments or non-clinical studies; iii) lack of
control group or non-randomized grouping; iv) high risk of bias
(unclear randomization methods, inadequate allocation concealment);
v) incomplete data regarding outcome indicators and inability to
extract data for primary or secondary outcomes and vi) unavailable
full text.
Literature screening
Studies were checked for plagiarism, then the titles
and abstracts of the literature were read for preliminary screening
according to the aforementioned criteria. Duplicate articles were
removed. For articles with duplicate data, the study containing the
most complete data was retained.
Data extraction
Excel (Version 12.1.0.24034, wps.cn) was used
to extract data as follows: Cell type, transplantation method,
intervention, sample size, age, sex, follow-up time, outcome
indicators and adverse reactions. For missing data, it was
attempted to contact the authors of the original study for complete
information. Studies for which missing data could not be obtained
were excluded.
Quality assessment
The risk assessment was performed using the bias
assessment tools recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration
(11). The assessment contents
included randomization methods, allocation concealment, blinding,
blinded assessment of study outcomes, integrity of outcome data,
selective reporting of study results and other sources. Risk of
bias was reported as high, low or unclear.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4.1
(https://www.cochrane.org) and Stata16.0
(https://www.stata.com) software. Among the
continuous variables, the mean difference (MD) was used as the
effect size for those with the same measurement method and unit,
and the odds ratio (OR) was used as the effect size for dichotomous
variables, both of which were expressed as 95%CI. Heterogeneity was
analysed using the Pearson χ2 and I2 tests,
with P>0.1 indicating no heterogeneity and P<0.1 indicating
heterogeneity. I2=0 means studies are completely
homogeneous, and I2 >50% means that there is
significant heterogeneity; If there was no significant
heterogeneity between studies, a fixed-effect model was used for
analysis, and a random-effects model was used after excluding
significant sources of heterogeneity. P≤0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference. Sources of
heterogeneity were investigated using sensitivity and subgroup
analyses. Subgroup analyses were performed for cell type,
transplantation method and length of follow-up for the primary
outcome measures.
Publication bias analysis
RevMan 5.4.1 software was used to draw the funnel
plot and assess the presence of publication bias by observing the
symmetry of the funnel plot. If the funnel plot presents a
symmetrical inverted funnel shape, it suggests a low risk of
publication bias; if the funnel plot shows an obvious asymmetry, it
indicates the existence of potential publication bias. Stata 16.0
software was used to conduct Egger's test. P<0.05 was considered
to indicate statistically significant publication bias.
Results
Included studies
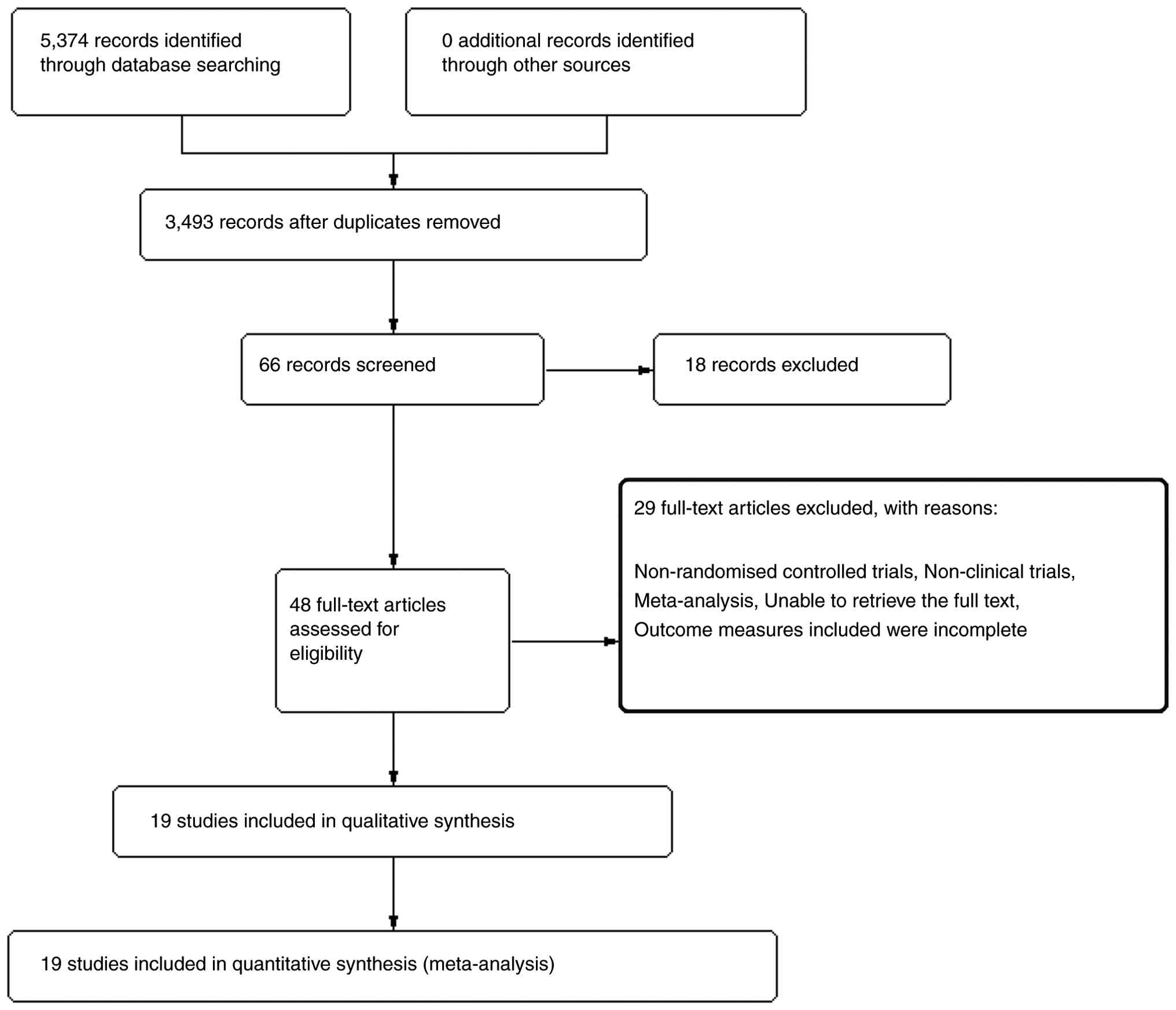
A total of 5,374 articles were retrieved initially.
After duplicate checking, 3,493 articles were included. After
reading the titles and abstracts of the articles, 66 articles were
included for full-text assessment. A total of 18 articles that did
not meet the requirements were excluded, and 48 articles were
included for full-text reading. After excluding 29 articles during
full-text reading, 19 articles (12-30)
were included (Fig. 1). Of these,
13 were in Chinese (14,15,19-21,23-30)
and six were in English (12,13,16-18,22).
All studies described the baseline comparability between the
experimental group and the control group. The intervention measures
were primarily MSCs + conventional treatment vs. conventional
treatment. The total sample size was 1,366 cases, with 697 cases in
the experimental group and 669 cases in the control group (Table I).
 | Table IStudy characteristics. |
Table I
Study characteristics.
| | | Intervention | Age, years | |
|---|
| First author,
year | Cell type | Transplantation
method | Interval | Tx time, days | E | C | E | C | Follow-up time,
months | Outcome
measures | Adverse
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Wang et al,
2014 | BMSC | Not reported | 30-60 days | Not reported | BMSC + con | Con | 56.3 | 56.3 (median) | 1 and 6 | FIM | No adverse
effects | (21) |
| Tian et al,
2018 | UBMSC | 22 LP; 23 IV | 14-30 days | 30 | UBMSC + con | Con | 62.2± 2.1 | 60.6±1.7
(mean) | 1, 2 and 3 | NIHSS; FMA | Not reported | (14) |
| Zhou et al,
2018 | UBMSC | LP | 1 year | 21 | UBMSC + con | Con | 56.3± 5.3
(mean) | 56.3±5.2
(mean) | 12 | BI; FIM | Fever, rash | (15) |
| Xiao et al,
2015 | UBMSC | LP | 1-13 years | Not reported | UBMSC + con | Con | 51.9± 5.2
(mean) | 52.3±5.0
(mean) | 6 | FIM | Not reported | (19) |
| Xie et al,
2014 | BMSC | LP | 7 days | 14 | BMSC + con | Con | 51.4±7.2
(mean) | 53.7±6.1
(mean) | 3 and 6 | NIHSS; BI | Fever;
headache | (20) |
| Hu et al,
2013 | UCMSC | LP + IV | 1-72 months | NA | UBMSC + con | Con | 60.8±15.2
(mean) | 59.2±13.8
(mean) | 0.25, 1, 3 | FMA; FIM | Fever; dizziness
and headache; backache | (26) |
| Liu et al,
2014 | BMSC | LP | 1-21 days | 20~40 | BMSC + con | Con | 55.3±3.6
(mean) | 56.8±4.3
(mean) | 1 and 3 FMA | NIHSS; | No adverse
effects | (23) |
| Feng et al,
2014 | UBMSC | 20 LP; 30 IV | 14-30 days | 30 | UBMSC + con | Con | 61.4±11.3
(mean) | 60.2±11.8
(mean) | 1, 2, 3 s | NIHSS; FMA | Fever | (24) |
| Wang et al,
2013 | UBMSC | IV | Not reported | 7~10 | UBMSC + con | Con | 62.6±7.1
(mean) | 62.2±6.3
(mean) | 0.5 | FMA | No adverse
effects | (25) |
| Chen et al,
2012 | BMSC | LP | 1-12 months | 14 | BMSC + con | Con | 49.3±20.8
(mean) | 57.3±9.5
(mean) | 6 | NIHSS | Fever;
headache | (28) |
| Chen WD et
al, 2012 | BMSC | LP + IV | Not reported | Not reported | BMSC + con | Con | 45.9±10.9
(mean) | 45.9±10.9
(mean) | 1, 3, 5 | FMA; FIM | No adverse
effects | (29) |
| Meng et al,
2009 | BMSC | IV | 42 days | Not reported | BMSC + con | Con | 52.7±7.9
(mean) | 52.9±8.3
(mean) | 1 month, 3 and
6 | FMA; FIM | Fever;
headache | (30) |
| He et al,
2012 | BMSC | IV | Not reported | Not reported | BMSC + con | Con | 56.4±7.9 | 54.3±8.7
(mean) | 3 | NIHSS; BI | Not reported | (27) |
| Fang et al,
2019 | BMSC | IV | 7 days | Not reported | BMSC | Pbo | 49.4±10.8
(mean) | 52.8±14.9
(mean) | 3, 6, 12 48 | NIHSS; BI; mRS | No adverse
effects | (13) |
| Chung et al,
2021 | BMSC | IV | 5-89 days | NA | BMSC + con | Con | 63.0±14.3
(mean) | 64.2±13.2 | 3 months | mRS | No adverse
effects | (12) |
| Hess et al,
2017 | BMSC | IV | 1-2 days | 1h | BMSC | Pbo | 61.8 (median) | 62.6 (medin) | 12 | NIHSS; BI; mRS | Halitosis; fever,
and nausea vomiting | (18) |
| Prasad et
al, 2014 | BMSC | IV | 7-30 days | NA | BMSC + con | Con | 50.7±11.6
(mean) | 52.5±12.1
(mean) | 12 | NIHSS; BI; mRS | Epilepsy | (22) |
| Jin et al,
2017 | BMSC | LP | Not reported | NA | BMSC + con | Con | 50.8±17.4
(mean) | 53.1±13.0
(mean) | 84 | NIHSS; BI; FMA;
FIM; mRS | Fever | (17) |
| Bhatla et
al, 2018 | BMSC | IA | 0-14 days | 10 min | BMSC + con | Con | 57.0±12.2
(mean) | 66.0±7.3
(mean) | 6 | NIHSS; mRS | No adverse
effects | (16) |
Outcome measures of the included
studies
Among outcome indicators, the data successfully
extracted for the BI (18) and mRS
(13) indicators were insufficient,
each corresponding to only one study, therefore these were not
analyzed. The outcome indicators included in the analysis of this
study are NIHSS, FMA, and FIM. All included studies used NIHSS to
assess the degree of neurological deficit. The NIHSS score ranges
from 0 to 42, with higher scores indicating more severe
neurological deficit. All included studies used FMA to assess motor
function recovery. The total FMA score ranges from 0 to 100, with
higher scores indicating better motor function. FIM was used in all
studies to assess functional independence. The FIM score ranges
from 18 to 126 points, with higher scores indicating better
functional independence. Assessment time points include baseline
and post-treatment. NIHSS, FMA and FIM score data were extracted by
two independent investigators.
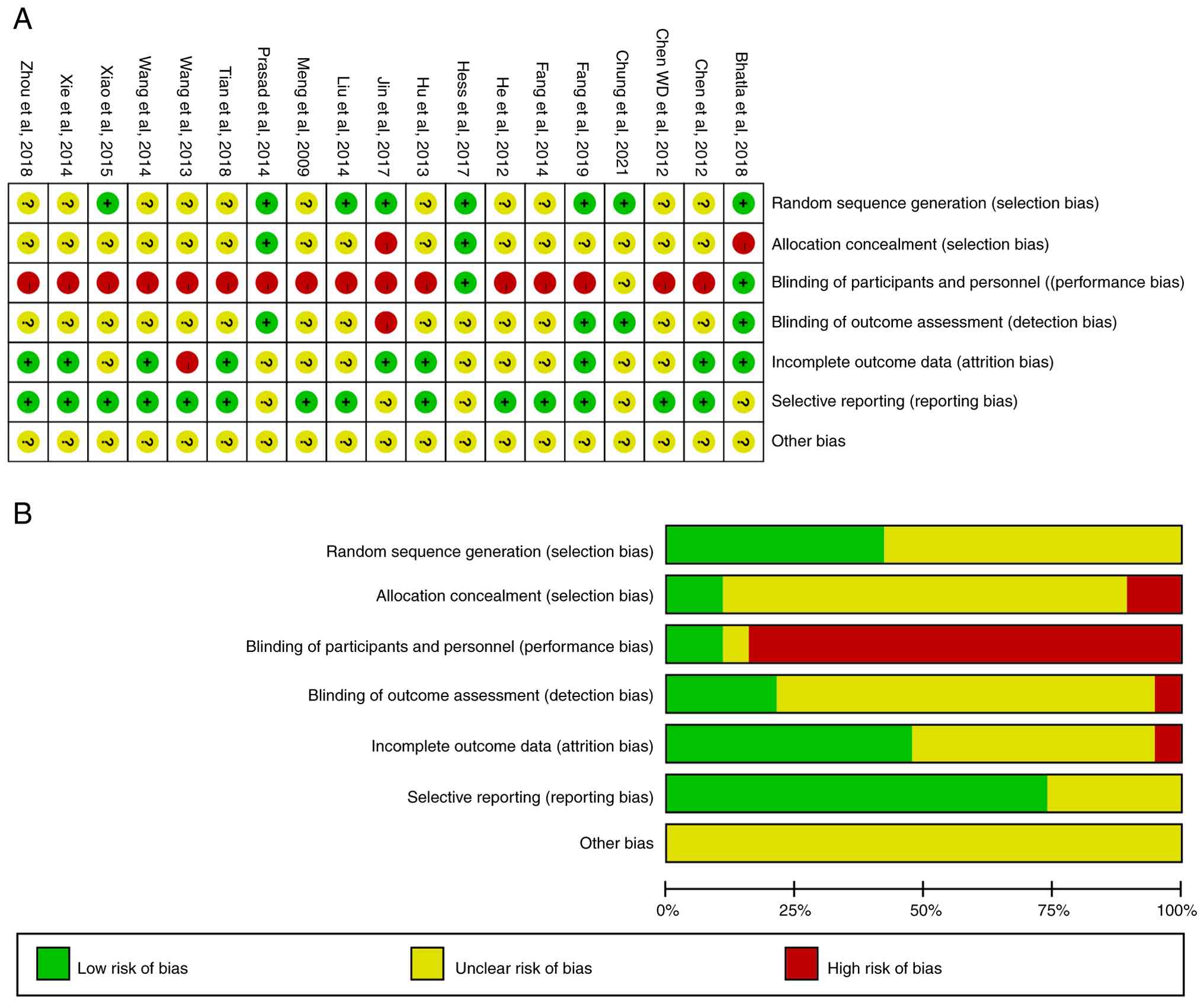
Risk of bias of included studies
The included studies were randomized controlled
trials, and the risk of bias of the included studies was primarily
due to blinding after randomization (Fig. 2).
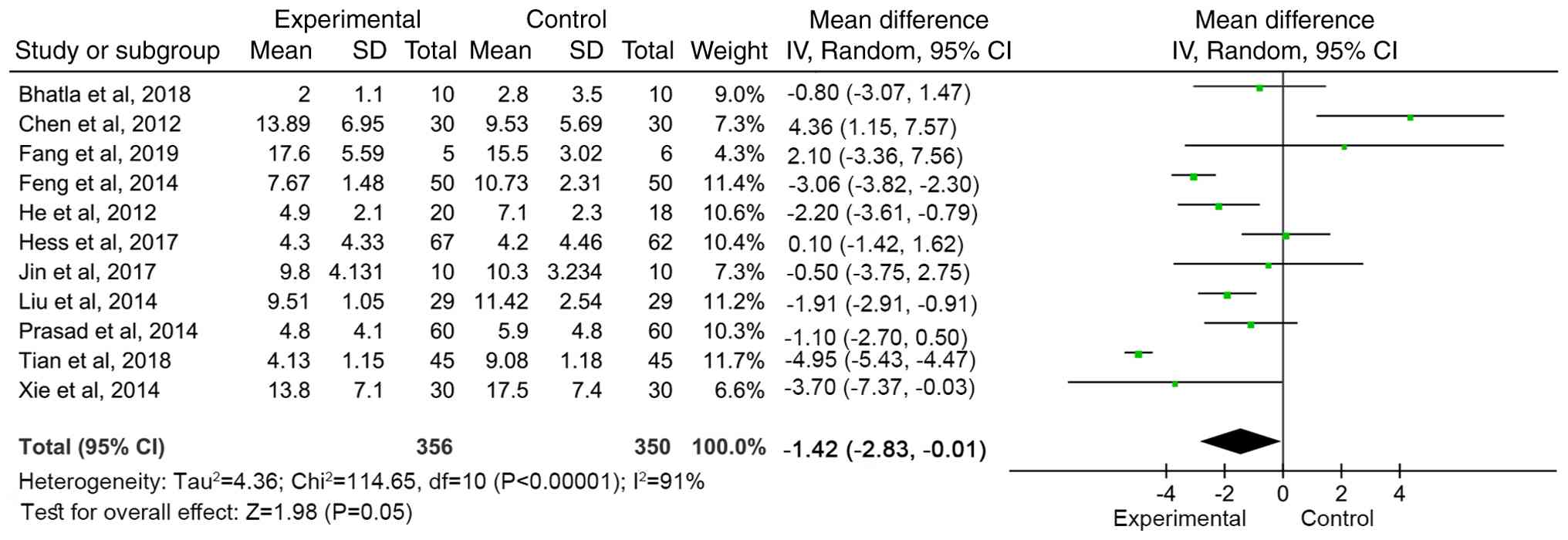
Meta-analysis of NIHSS score
A total of 11 articles (13,14,16-18,20,22,24,27,28)
reported the NIHSS scores of neurological deficit in patients
before and after treatment. The qualitative test
(I2=91%, P<00001) showed heterogeneity, so a random
effects model was used for meta-analysis. The combined effect size
[Weighted Mean Difference WMD=-1.42 (95%CI: -2.83 to -0.01, Z=1.98,
P=0.05)] demonstrated the NIHSS score of the MSC treatment group
was significantly lower than that of the control group, indicating
that MSC therapy decreased the degree of neurological deficit of
patients and had a positive effect on improving the neurological
function of patients (Fig. 3).
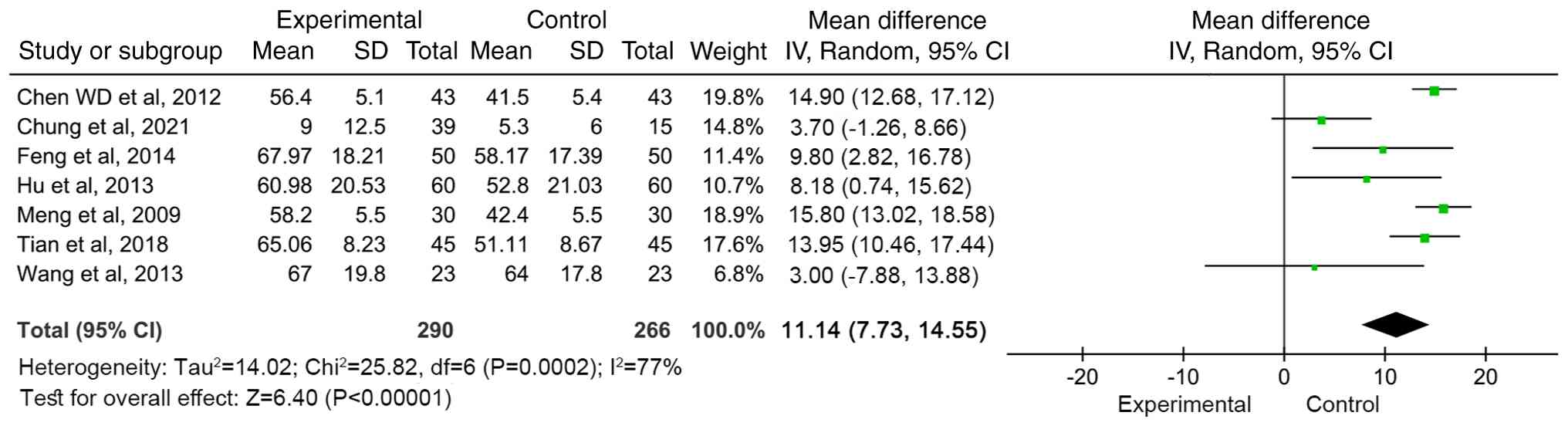
Meta-analysis of motor function score
(FMA)
A total of seven articles (12,14,24,26,29,30)
reported the motor function scores before and after treatment. The
results were heterogeneous (I2=77%, P=0.0002), so a
random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The combined
effect size [WMD=11.14 (95%CI: 7.73-14.55, Z=6.40; P<0.00001)]
indicated that compared with conventional treatment, MSC treatment
significantly improved motor function scores (Fig. 4).
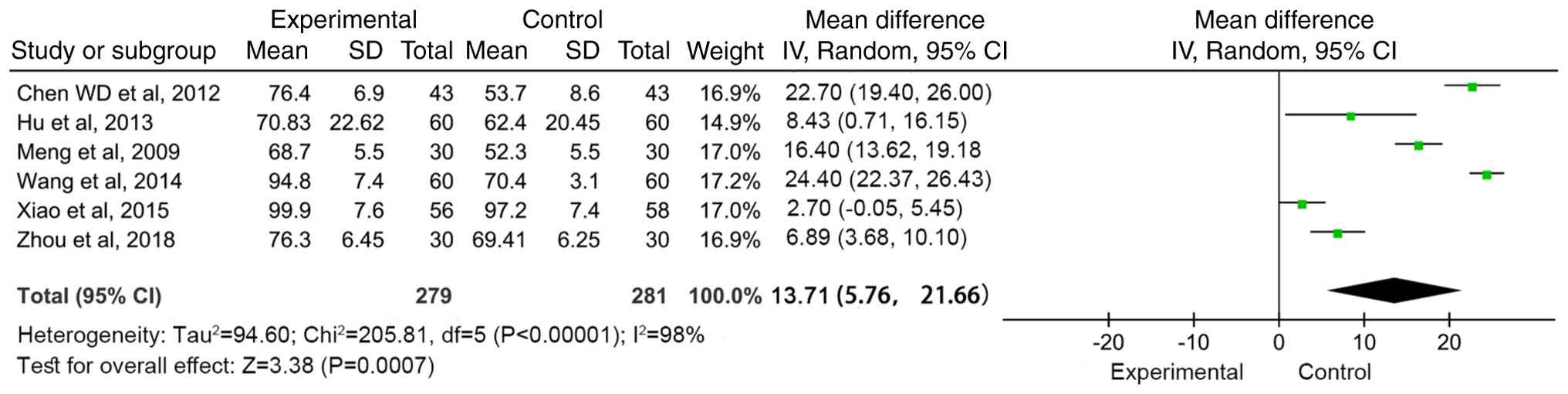
Meta-analysis of functional
independence score (FIM)
A total of six articles (15,19,21,26,29,30)
reported the functional independence score before and after
treatment. The results were heterogeneous (I2=98%,
P<0.00001), so a random effects model was used for
meta-analysis. The combined effect size [WMD=13.71 (95%CI:
5.76-21.66, Z=3.38; P=0.0007)] indicated that compared with
conventional treatment, MSC treatment significantly improved the
functional independence score (Fig.
5).
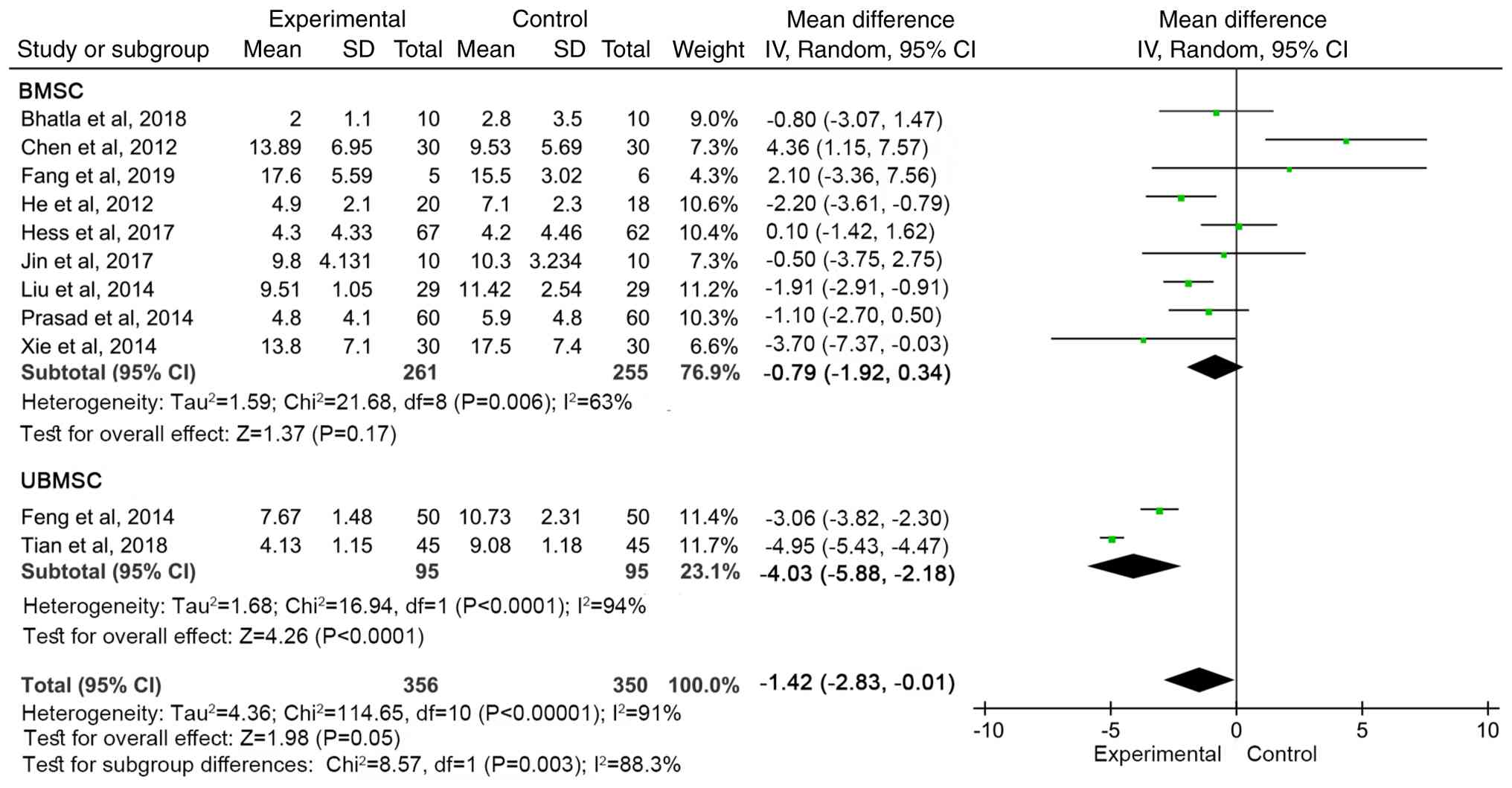
Subgroup analysis
For the primary outcome, NIHSS, subgroup analyses
were performed based on cell type, transplantation modality and
follow-up time. In addition, among the 11 studies (13,14,16-18,20,22,24,27,28)
with outcomes including NIHSS, bone marrow MSCs were all autologous
[Hess et al (18) did not
mention the source]. The number of cells was
3.0-5.0x106/kg (28),
5x106/kg (Fang et al, 2019) (13), 1x107/kg (Liu et
al) (23), and not mentioned in
the remaining studies. In research on umbilical cord MSCs, one
study indicated that the source of the cells was Shenzhen Baker
Biotechnology Co., Ltd., with a cell count of 3x107/kg
(24), while another study
(14) did not mention the source or
quantity of the cells.
The improvement in NIHSS was more significant in the
UBMSC group (WMD=-4.03, 95% CI: -5.88 to -2.18, P<0.0001), while
the effect was weaker in the BMSC group (WMD=-0.79, 95% CI: -1.92
to 0.34, P=0.17; Fig. 6). There was
a significant difference between the groups (P=0.05).
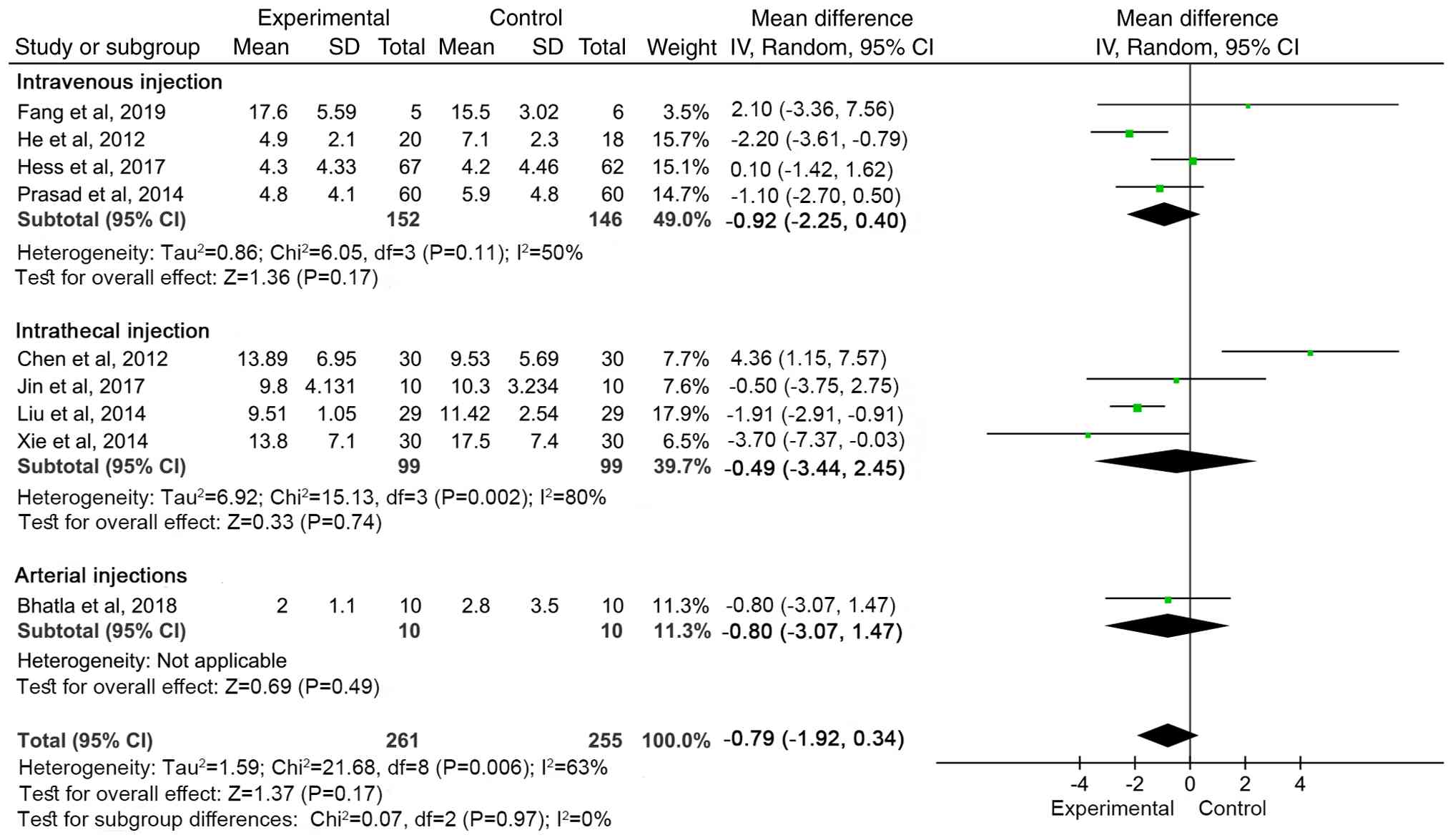
There was no significant difference in NIHSS between
the groups based on transplantation method (total effect size
P=0.17; Fig. 7). Follow-up period
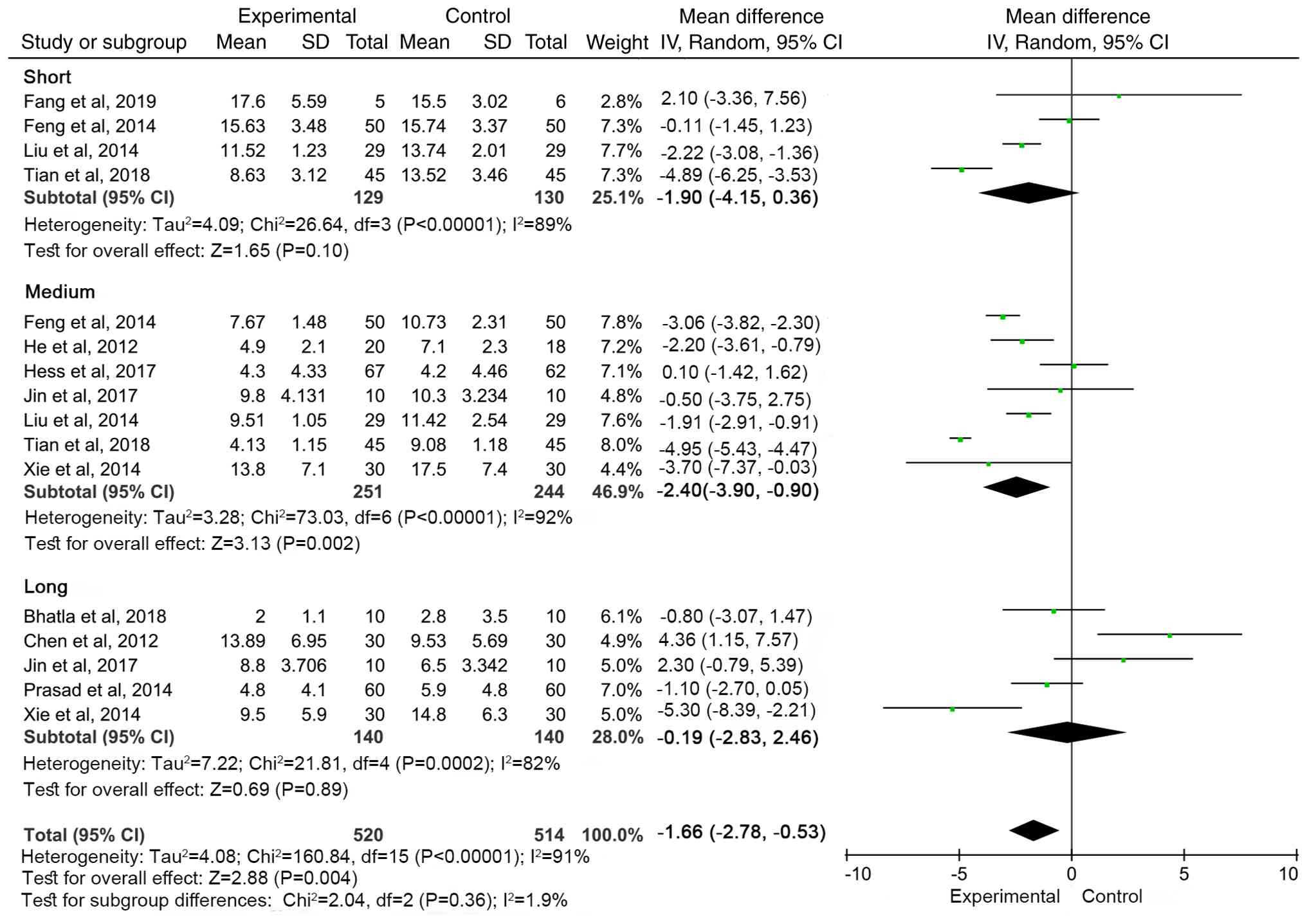
was divided as follows: Short-term, <3 months; medium-term, 3-6
months and long-term, >6 months. The MSC group showed the most
significant improvement in NIHSS scores at 3-6 months follow-up
(WMD=-2.40, 95% CI: -3.90 to -0.90, P=0.002). There was no
significant difference between the treatment and control groups
during short- and long-term follow-up (Fig. 8).
Safety analysis
A total of nine studies (15,17,18,20,22,24,26,28,30)
reported adverse effects such as low-grade fever, dizziness,
headache, backache, depression, urinary and respiratory tract
infection and rash; seven studies (12,13,16,21,23,25,29)
reported no adverse reactions, and three studies (14,19,27)
did not mention adverse reactions.
Sensitivity analysis
To assess the impact of studies at high risk of bias
on the results of meta-analysis, sensitivity analyses were
performed and excluded the only study with a high risk of bias
(Tian et al) (14).
Heterogeneity was significantly reduced after exclusion of the
aforementioned study (I², 91 vs. 75%), and the overall effect size
changed from -1.42 (95% CI: -2.83 to -0.01, Z=1.98, P=0.05) to
-1.11 (95%CI: -2.22 to 0.01, Z=1.94, P=0.05). Although there was a
slight change in the effect size, there was no notable change in
its direction and significance, indicating that the results of the
meta-analysis were robust.
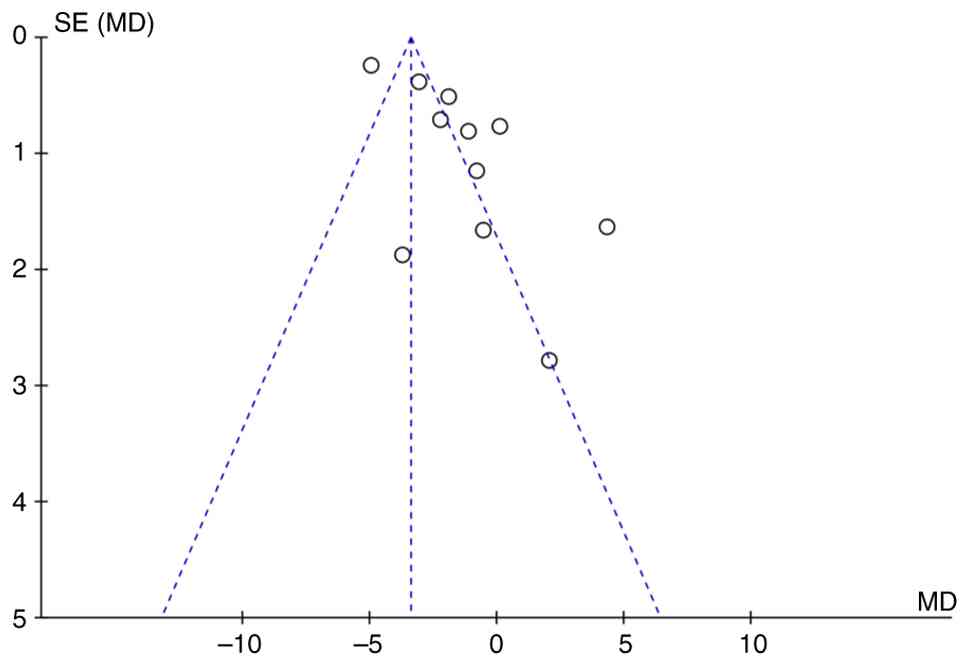
Publication bias analysis
Funnel plots were used to test the publication bias
of the primary outcome, NIHSS (Fig.
9). Funnel plots showed notable asymmetry, suggesting some
publication bias. For more robust analysis of publication bias,
Egger's test was performed for NIHSS, which showed no significant
publication bias (P=0.461).
Discussion
MSCs originate from tissue such as bone marrow,
adipose tissue and umbilical cord. Bone marrow MSCs have relative
ease of procurement. Nevertheless, as the donor age advances, the
proliferative, self-renewal and differentiation capabilities of
bone marrow MSCs decrease, thereby giving rise to disparities in
the efficacy of SC treatment (31,32).
By contrast, adipose and umbilical cord MSCs are not subject to
such constraints. Umbilical cord MSCs exhibit the advantages of
rapid proliferation and high differentiation potential (33,34).
Cortical MSCs are derived from cortical bone. They have a stronger
ability to differentiate into osteoblasts. They are mainly used in
bone regeneration and orthopedics. Compared with bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells, research on cortical MSCs is relatively
limited (35,36). MSCs have demonstrated potential in
the treatment of a number of diseases, including ischemic cerebral
infarction, myocardial ischemia, multiple sclerosis, idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,
osteoarthritis, acute kidney injury and inflammatory bowel disease
(37). SC therapy serves multiple
roles in ischemic cerebral infarction, such as neural repair,
vascular regeneration, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic
effects. MSCs traverse the blood-brain barrier to reach the
ischemic regions of the brain (38). They serve a number of functions such
as mitigating inflammatory responses, substituting for nerve cells
that have undergone ischemic apoptosis, secreting neurotrophic
factors, facilitating the repair of blood vessels within the brain
and diminishing cell apoptosis (28-32,39-43).
Compared with traditional treatment, MSCs improve the symptoms of
neurological deficit and ability to perform daily living
activities. The present study have shown that patients treated with
MSCs have better recovery of limb motor and language function than
those treated with conventional treatment. However, its
effectiveness is affected by a variety of factors, such as the
source of the cell, the mode of administration and the timing of
treatment.
Although one study demonstrated high risk of bias
(14), sensitivity analyses
suggested a limited effect on the overall results. Future studies
should focus on the implementation of randomization procedures,
allocation concealment and blinding to improve the quality of
studies.
In clinical trials, NIHSS, FMA, and FIM are commonly
used to assess cerebral infarction (6-8).
The present study showed that MSC therapy could improve FMA score
and FIM score. The NIHSS score results show that the effect sizes
of Chen et al (28) and Fang
et al's study (13) are both
located to the right of the null line in the forest plot, which has
a certain impact on the combined effect results. For Chen et
al's study (28), the abnormal
effect size may be due to differences in the NIHSS scoring method
and the culture conditions of mesenchymal stem cells; for Fang
et al's study (13), it is
considered to be caused by the small sample size. After excluding
the study with the greatest impact on the results (Chen et
al) (28), the pooled effect
size WMD=-1.91 (95%CI: -3.25 to -0.57, Z=2.79, P=0.005). This meant
that the MSC treatment group demonstrated lower NIHSS score than
the control group, indicating that MSC therapy can reduce the
degree of neurological deficit and have a positive effect on
improving the neurological function of patients. Sensitivity
analysis suggested that the Tian et al (14) may be one of the main sources of
heterogeneity. Heterogeneity was significantly decreased after the
study was excluded, but the overall effect size remained
significant, supporting the positive effect of MSC treatment in
patients with cerebral infarction. However, the presence of high
heterogeneity suggests that future studies should focus on
standardised patient selection, intervention and follow-up time to
reduce heterogeneity and improve the reliability of results. In
conclusion, MSC transplantation can improve neurological and motor
function in patients with ischemic cerebral infarction. This
heterogeneity may be due to differences in patient characteristics,
SC source and treatments, details of interventions, and length of
follow-up between studies.
Among the studies included, nine reported adverse
reactions (15,17,18,20,22,24,26,28,30).
The adverse reactions included low-grade fever, dizziness,
headache, back pain, depression, urinary and respiratory tract
infections, and rash, all of which resolved spontaneously or after
treatment. The most common adverse reactions were fever and
headache, and there were no serious adverse reactions such as to
tumorigenicity or toxicity. MSCs have a high safety profile in the
treatment of cerebral infarction. However, in the future, it is
necessary to continue to pay attention to the potential risks, such
as abnormal cell proliferation and immune-related problems. Safety
of MSCs from different sources, preparation processes and
administration methods may vary, which needs to monitored and
evaluated in clinical applications.
Among the 11 studies included that involved NIHSS
scores (13,14,16-18,20,22,24,27,28),
six fell outside the 95% confidence interval of the funnel plot
(14,16,22-24,29),
which may be attributed to heterogeneity among the studies and
differences in sample sizes. Small-sample studies are prone to
large sampling errors, leading to significant fluctuations in
effect size estimates, exacerbating differences between results
from small- and large-sample studies and increasing overall
heterogeneity, thereby causing funnel plot asymmetry. Additionally,
small-sample studies are more likely to yield negative results,
while journals tend to publish positive findings, which further
contributes to publication bias. and MSCs from bone marrow are the
most widely used. Lumbar puncture, the method of obtaining cells,
is an invasive operation, which not only causes pain and infection
risk to patients, but also raises the threshold for clinical
development. MSCs derived from the umbilical cord are easy to
obtain and have high proliferative and differentiation
capabilities. Unlike bone marrow-derived MSCs, those from the
umbilical cord do not require a bone marrow puncture, avoiding
invasive procedures. Due to the lack of clinical studies using
umbilical cord MSCs, more research is needed in the future to
determine the optimal source of MSCs. Due to the complexity and
heterogeneity of the studies, it was not possible to draw
definitive conclusions. Due to limited data and different
transplantation routes, it was difficult for each subgroup sample
to fully represent the overall characteristics, which may interfere
with the effect estimation and weaken the reliability of the
results.
MSCs are transplanted in a variety of ways,
including stereotactic implantation or craniotomy for direct
injection into the brain parenchyma, intravenous infusion and
arterial and transarachnoid injection (4,5,40,43).
The most common method of transplantation is intravenous infusion.
Compared with intracerebral injection, intravenous infusion is
simpler to perform, carries lower risk, involves less invasiveness
and avoids damage to normal brain tissue caused by direct
injection. However, some studies have shown that intravenous
administration can reduce efficacy to some extent (5). Cells need to pass through the systemic
circulation and blood-brain barrier to reach the brain. Directed
transplantation in the brain is most effective, but normal brain
tissue may be damaged during implantation (4). Craniotomy is generally not accepted by
patients. Intrathecal injection has been used to inject stem cell
suspension into the subarachnoid space through lumbar puncture, so
SCs can circulate with cerebrospinal fluid to the surface of the
brain. This method has the advantage of being minimally invasive
and can partially overcome the physiological limitations of the
blood-brain barrier, allowing the cells to be closer to central
nervous system targets; lumbar puncture has a low probability of
infection and the risk of cerebrospinal fluid leakage; therefore,
clinical use needs to balance the benefits and safety (44). The present study found no
significant differences between intravenous infusion, arterial
injection and intrathecal injection. In clinical studies, the
design of transplantation modalities is highly heterogeneous, such
as the number of cells transplanted and whether cerebrospinal fluid
is replaced by intrathecal injection, and the number of included
studies is small, which may affect the results. More research is
needed in the future to compare the efficacy of transplantation
methods. This may be due to the small number of included studies
and the inconsistency in the design of transplantation modalities.
More research is needed to determine the optimal transplantation
modality.
The efficacy of MSCs varies depending on the length
of follow-up. MSCs may exert neuroprotective effects in the early
stages because of their ability to combat toxic and inflammatory
responses. The present study demonstrated MSC therapy improved
NIHSS score more than conventional therapy during the medium-term
follow-up period, and there was no significant difference between
the treatment and control groups during the short- and long-term
follow-up. However, the high degree of heterogeneity between
studies limits the generalizability of the results. However, the
high degree of heterogeneity between studies limits the
generalizability of the results. Future studies should standardize
MSC treatment regimens, patient selection criteria and outcome
measures to decrease heterogeneity and provide more reliable
evidence. Due to incomplete data, subgroup analyses were not
performed for age, cerebral infarction severity and duration of
cell transplantation.
The present study did not conduct subgroup analysis
by age because most of the patients were aged 50-60 years. It was
not possible to assess the severity of cerebral infarction due to
incomplete data. It was difficult to analyze the differences in
treatment outcomes between different transplantation times, as only
two studies (16,18) accurately recorded the timing of cell
transplantation. The time of cerebral infarction onset in patients
ranged from 1-2 days to 1-12 months. Patients with cerebral
infarction onset of 1-12 months include those with onset of 1-2
days. However, we cannot obtain more detailed timing data from each
study, so we are unable to perform subgroup analysis based on the
duration since cerebral infarction onset. Due to the scarcity of
data, the present study did not further analyze the source of cells
and the number of cells transplanted.
The present study had limitations. Only six
databases were searched, and the included articles were in Chinese
and English, which presents risk of bias. Second, most studies did
not have placebo-controlled trials, did not blind participants and
treatment regimens and did not report allocation concealment.
Although studies were consistent in terms of participants,
intervention and outcome measures, providing a relatively
homogeneous basis for subsequent meta-analysis, there may still be
differences in terms of patient characteristics, SC-related
treatments, SC transplant dose and follow-up time, resulting in
heterogeneity in subsequent analyses. Additionally, the literature
search for this study has certain limitations. Some of the included
studies, particularly those published in Chinese, are not indexed
in common international databases but can be accessed through
specialized Chinese academic databases. This may affect the
accessibility of this portion of the evidence for non-Chinese
researchers, however these studies are available upon request. To
assess the efficacy and safety of MSCs in the treatment of cerebral
infarction, more high-quality studies are needed, including
large-sample, multicenter randomized controlled trials that follow
scientific norms to minimize the impact of publication bias.
In conclusion, MSC transplantation can improve the
neurological function and motor function of patients with ischemic
cerebral infarction and the safety is high. Due to the small sample
size of the included studies, the quality of the articles was not
high and there was a risk of bias. Therefore, in the future,
large-sample, multi-center and rigorously designed clinical trials
are needed to validate the present data.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by Scientific Research
Fund of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (grant no.
GJJ190802), Ganzhou Science and Technology Innovation Talent Plan
(grant no. 202101094460), The Open Project of Key Laboratory of
Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular
Diseases of Educational Ministry in Gannan Medical University
(grant no. XN202011), Graduate Innovation Project of Hunan
University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (grant nos. 2024CX132,
2025CX189 and 2025CX196) and Natural Science Foundation of Hu Nan
Province (grant nos. 2023JJ30362 and 2025JJ40099).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study, and studies
cited which are published in Chinese may be requested from the
corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
YJ, QC, YY, YX, XH and YL wrote the manuscript. YJ,
QC and YY performed the literature review. YL and XH collected the
data. YJ and YL confirm the authenticity of all the raw data, YJ,
YX and XH analyzed the data. YL and QC designed the study and
reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the
final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Jiang Y, Li XY, Hu N, Huang ZJ and Wu F:
Epidemiologic characteristics of cerebrovascular disease mortality
in China, 2004-2005. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 44:293–297.
2010.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Chen Y, Gu SL and Wang QQ: Status quo and
influencing factors of quality of life in elderly patients with
acute ischemic stroke hemiplegia after discharge. Chin J Mult Organ
Dis Elderly. 23:194–197. 2024.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=7111730250&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
3
|
Li Y, Hu G and Cheng Q: Implantation of
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for ischemic stroke:
Perspectives and challenges. Front Med. 9:20–29. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Banerjee S, Williamson DA, Habib N and
Chataway J: The potential benefit of stem cell therapy after
stroke: An update. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 8:569–580.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kuroda S: Current opinion of bone marrow
stromal cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Neurol Med Chir
(Tokyo). 56:293–301. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Goldstein LB and Samsa GP: Reliability of
the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale. Extension to
non-neurologists in the context of a clinical trial. Stroke.
28:307–310. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fugl-Meyer AR, Jääskö L, Leyman I, Olsson
S and Steglind S: The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. a method
for evaluation of physical performance. Scand J Rehabil Med.
7:13–31. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Granger CV, Cotter AC, Hamilton BB and
Fiedler RC: Functional assessment scales: A study of persons after
stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 74:133–138. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hopman-Rock M, van Hirtum H, de Vreede P
and Freiberger E: Activities of daily living in older
community-dwelling persons: A systematic review of psychometric
properties of instruments. Aging Clin Exp Res. 31:917–925.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Saver JL, Chaisinanunkul N, Campbell BCV,
Grotta JC, Hill MD, Khatri P, Landen J, Lansberg MG,
Venkatasubramanian C and Albers GW: XIth Stroke Treatment Academic
Industry Roundtable. Standardized nomenclature for modified rankin
scale global disability outcomes: Consensus recommendations from
stroke therapy academic industry roundtable XI. Stroke.
52:3054–3062. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA, et
al: The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343(d5928)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chung JW, Chang WH, Bang OY, Moon GJ, Kim
SJ, Kim SK, Lee JS, Sohn SI and Kim YH: STARTING-2 Collaborators.
Efficacy and safety of intravenous mesenchymal stem cells for
ischemic stroke. Neurology. 96:e1012–e1023. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fang J, Guo Y, Tan S, Li Z, Xie H, Chen P,
Wang K, He Z, He P, Ke Y, et al: Autologous endothelial progenitor
cells transplantation for acute ischemic stroke: A 4-year follow-up
study. Stem Cells Transl Med. 8:14–21. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tian LP, Wang JJ and Zhao KL: Observation
of the clinical effect of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal
stem cells in the treatment of cerebral infarction. Chin J Clin
Ration Drug Use. 11:109–110. 2018.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=676508155.
|
|
15
|
Zhou J: Clinical efficacy of cord blood
stem cell transplantation in improving functional independence in
stroke patients. Neural Inj Funct Reconstr. 13:42–43. 2018.(In
Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=7000552239&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
16
|
Bhatia V, Gupta V, Khurana D, Sharma RR
and Khandelwal N: Randomized Assessment of the safety and efficacy
of intra-arterial infusion of autologous stem cells in subacute
ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 39:899–904. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jin Y, Ying L, Yu G and Nan G: Analysis of
the long-term effect of bone marrow mononuclear cell
transplantation for the treatment of cerebral infarction. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 10:3059–3068. 2017.
|
|
18
|
Hess DC, Wechsler LR, Clark WM, Savitz SI,
Ford GA, Chiu D, Yavagal DR, Uchino K, Liebeskind DS, Auchus AP, et
al: Safety and efficacy of multipotent adult progenitor cells in
acute ischaemic stroke (MASTERS): A randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 16:360–368.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xiao HX: Clinical efficacy of stem cell
transplantation in stroke. Medical Recapitulate. 21:1875–1876.
2015.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=665002239.
|
|
20
|
Xie XF, Liu SY, Jin GH, Qu XH, Zhang KN
and Wu XM: Clinical analysis of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell transplantation for treatment of cerebral infarction. Lab
Med Clin. 11:2955–2957. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Zhang Z, Jia FR and Yang H: A
clinical study on treatment of cerebral infarction using autologous
marrow mesenchymal stem cells intervening transplantation. Jilin
Med. 35:237–239. 2014.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=48441187&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
22
|
Prasad K, Sharma A, Garg A, Mohanty S,
Bhatnagar S, Johri S, Singh KK, Nair V, Sarkar RS, Gorthi SP, et
al: Intravenous autologous bone marrow mononuclear stem cell
therapy for ischemic stroke: A multicentric, randomized trial.
Stroke. 45:3618–3624. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu DH, Han BJ, Hong SS, Wang QG, Du CY,
Gao H, Han LX, Wan MR and Ye Y: Transplanting autologous
mesenchymal nerve stem cells in the treatment of cerebral
infarction. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil. 36:425–428. 2014.(In Chinese).
https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=50201705&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
24
|
Feng TG, Li L and Zhou J: Clinical
efficacy study of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells
in the treatment of cerebral infarction. PJCCPVD. 22:28–30.
2014.
|
|
25
|
Wang XH, Wang SP, Xu GX, Ma SB, Wang T and
Zou SF: Short-term efficacy of umbilical cord blood nucleated cells
in treatment of cerebral infarction sequelae. Transl Med J.
2:332–335. 2013.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=48118583&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
26
|
Hu Q, Cao MY, Li RF, Jiang HW and Ge LT:
Safety and efficacy on the treatment of cerebral infarction with
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Med J Wuhan Univ. 34:57–70.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=44536233&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
27
|
He ZD: Study on the mechanism of bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation to improve
neurological function in patients with cerebral infarctionf.
Asia-Pacific Tradit Med. 8:126–127. 2012.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=44178016&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
28
|
Chen WM, Zou QY, Lu JJ, Hu YX, Hu QL, Li
ZG and Zeng ZL: Reinfusion of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells for treatment of stroke in 30 cases. Chin J Tissue Eng
Res. 16:6071–6075. 2012.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=43200003&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
29
|
Chen WD, Li JT, Zhang XB, Zhao H, Li W,
Yang SQ, Lu GZ, Li D and He L: Clinical analysis of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral infarction.
Jilin Med. 33(4522)2012.(In Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=42844101&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
30
|
Meng XG, Zhu SW, Gao H, Li YZ, Shi Q, Hou
HS and Li D: Treatment of cerebral infarction using autologous
marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation:A six-month
follow-up. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 13:6374–6378. 2009.(In
Chinese). https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=31368833&from=Qikan_Search_Index.
|
|
31
|
Wen YL, Yun JC, Phil HL, Huh K, Kang YM,
Kim HS, Ahn YH, Lee G and Bang OY: Mesenchymal stem cells for
ischemic stroke: Changes in effects after ex vivo culturing. Cell
Transplant. 17:1045–1059. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bonab MM, Alimoghaddam K, Talebian F,
Ghaffari SH, Ghavamzadeh A and Nikbin B: Aging of mesenchymal stem
cell in vitro. BMC Cell Biol. 7(14)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lin YC, Ko TL, Shih YH, Lin MY, Fu TW,
Hsiao HS, Hsu JY and Fu YS: Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells
promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 42:2045–2053.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hsieh JY, Wang HW, Chang SJ, Liao KH, Lee
IH, Lin WS, Wu CH, Lin WY and Cheng SM: Mesenchymal stem cells from
human umbilical cord express preferentially secreted factors
related to neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. PLoS
One. 8(e72604)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang Q, Huang C, Zeng F, Xue M and Zhang
X: Activation of the Hh pathway in periosteum-derived mesenchymal
stem cells induces bone formation in vivo: Implication for
postnatal bone repair. Am J Pathol. 177:3100–3111. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fernandez-Moure JS, Corradetti B, Chan P,
Van Eps JL, Janecek T, Rameshwar P, Weiner BK and Tasciotti E:
Enhanced osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells from
cortical bone: A comparative analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther.
6(203)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bateman ME, Strong AL, Gimble JM and
Bunnell BA: Concise review: Using fat to fight disease: A
systematic review of nonhomologous adipose-derived stromal/stem
cell therapies. Stem Cells. 36:1311–1328. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang CY, Fei YP, Xu CS, Zhao Y and Pan Y:
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate neurological deficits
and blood-brain barrier dysfunction after intracerebral hemorrhage
in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:4715–4724. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim YJ, Park HJ, Lee G, Bang OY, Ahn YH,
Joe E, Kim HO and Lee PH: Neuroprotective effects of human
mesenchymal stem cells on dopaminergic neurons through
anti-inflammatory action. Glia. 57:13–23. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Oh SH, Choi C, Chang DJ, Shin DA, Lee N,
Jeon I, Sung JH, Lee H, Hong KS, Ko JJ and Song J: Early
neuroprotective effect with lack of long-term cell replacement
effect on experimental stroke after intra-arterial transplantation
of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy.
17:1090–1103. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Leu S, Lin YC, Yuen CM, Yen CH, Kao YH,
Sun CK and Yip HK: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells markedly
attenuate brain infarct size and improve neurological function in
rats. J Transl Med. 8(63)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ryu B, Sekine H, Homma J, Kobayashi T,
Kobayashi E, Kawamata T and Shimizu T: Allogeneic adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cell sheet that produces neurological improvement
with angiogenesis and neurogenesis in a rat stroke model. J
Neurosurg. 132:442–455. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhou L, Wang J, Huang J, Song X, Wu Y,
Chen X, Tan Y and Yang Q: The role of mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation for ischemic stroke and recent research
developments. Front Neurol. 13(1000777)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Miao X, Wu X and Shi W: Umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells in neurological disorders: A clinical study.
Indian J Biochem Biophys. 52:140–146. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|