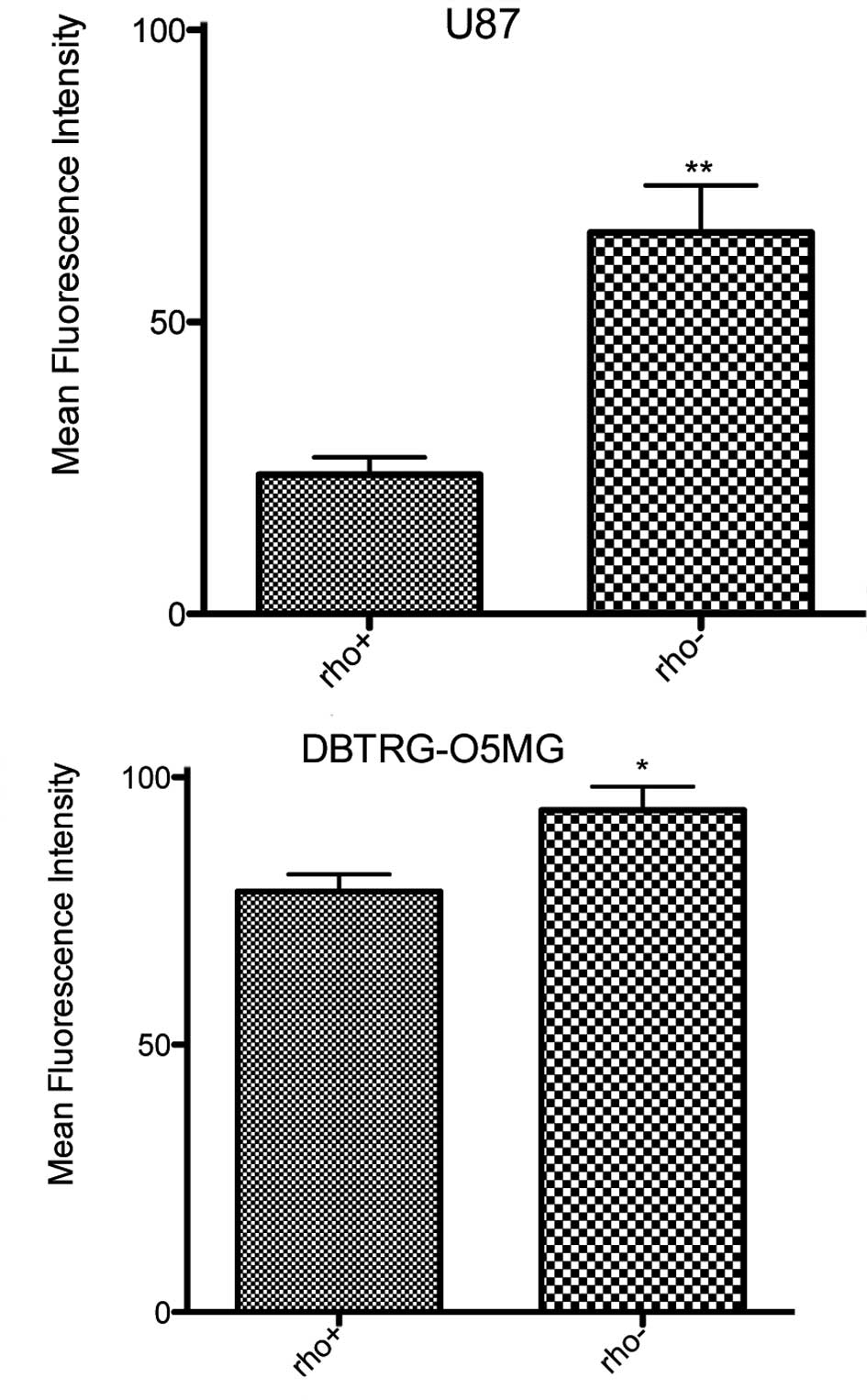
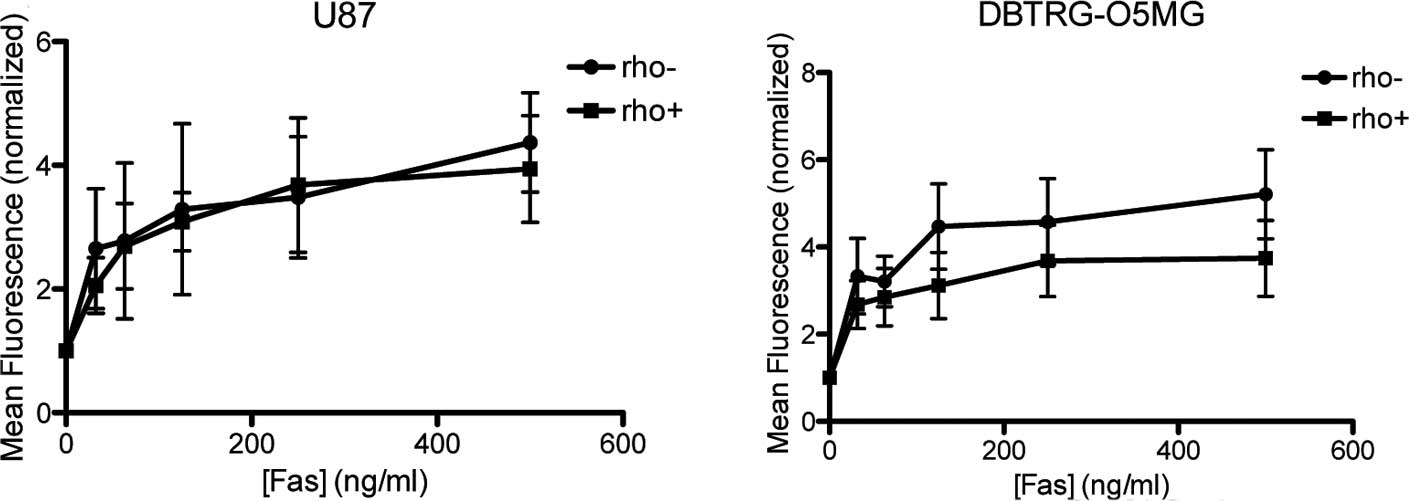
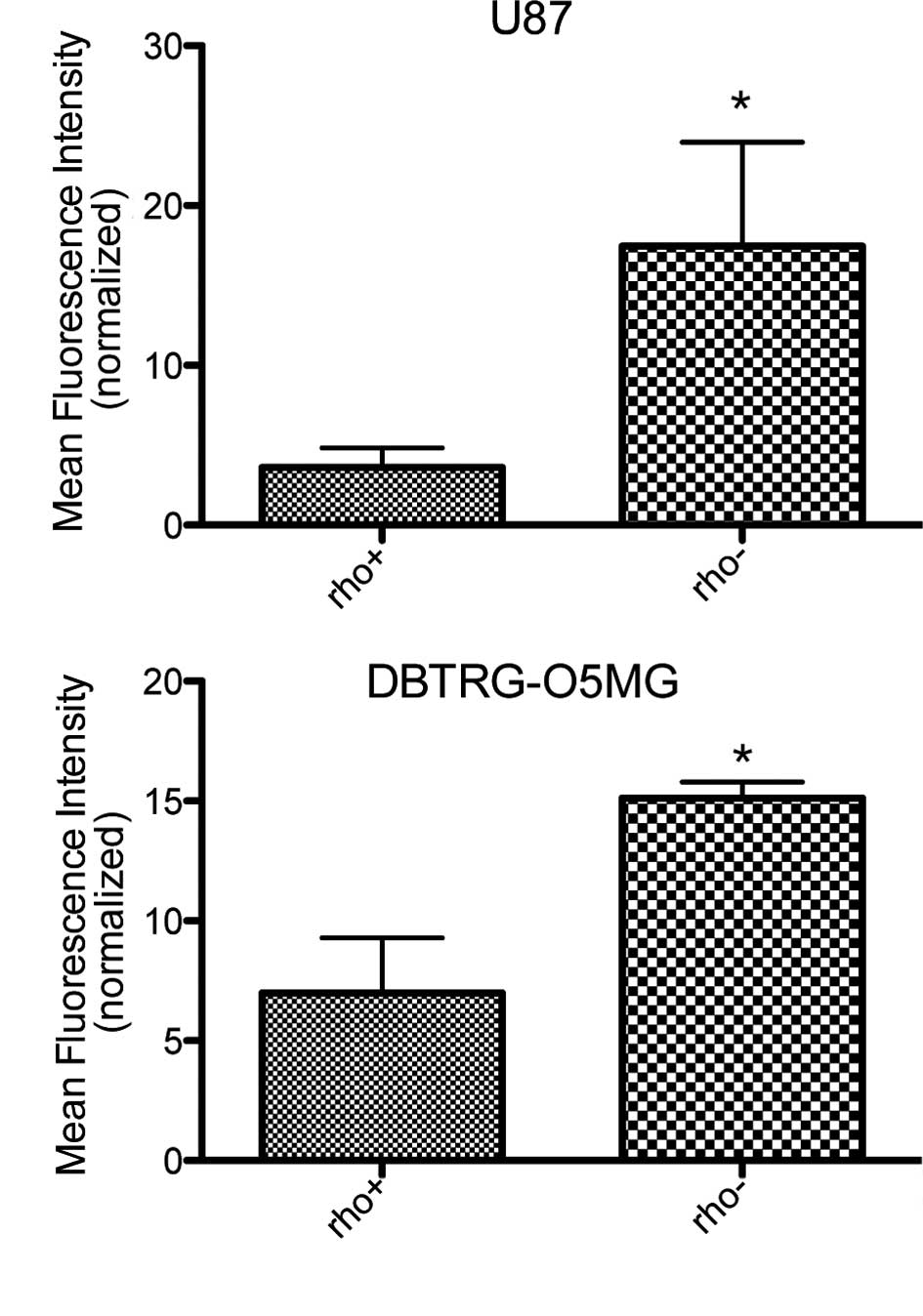
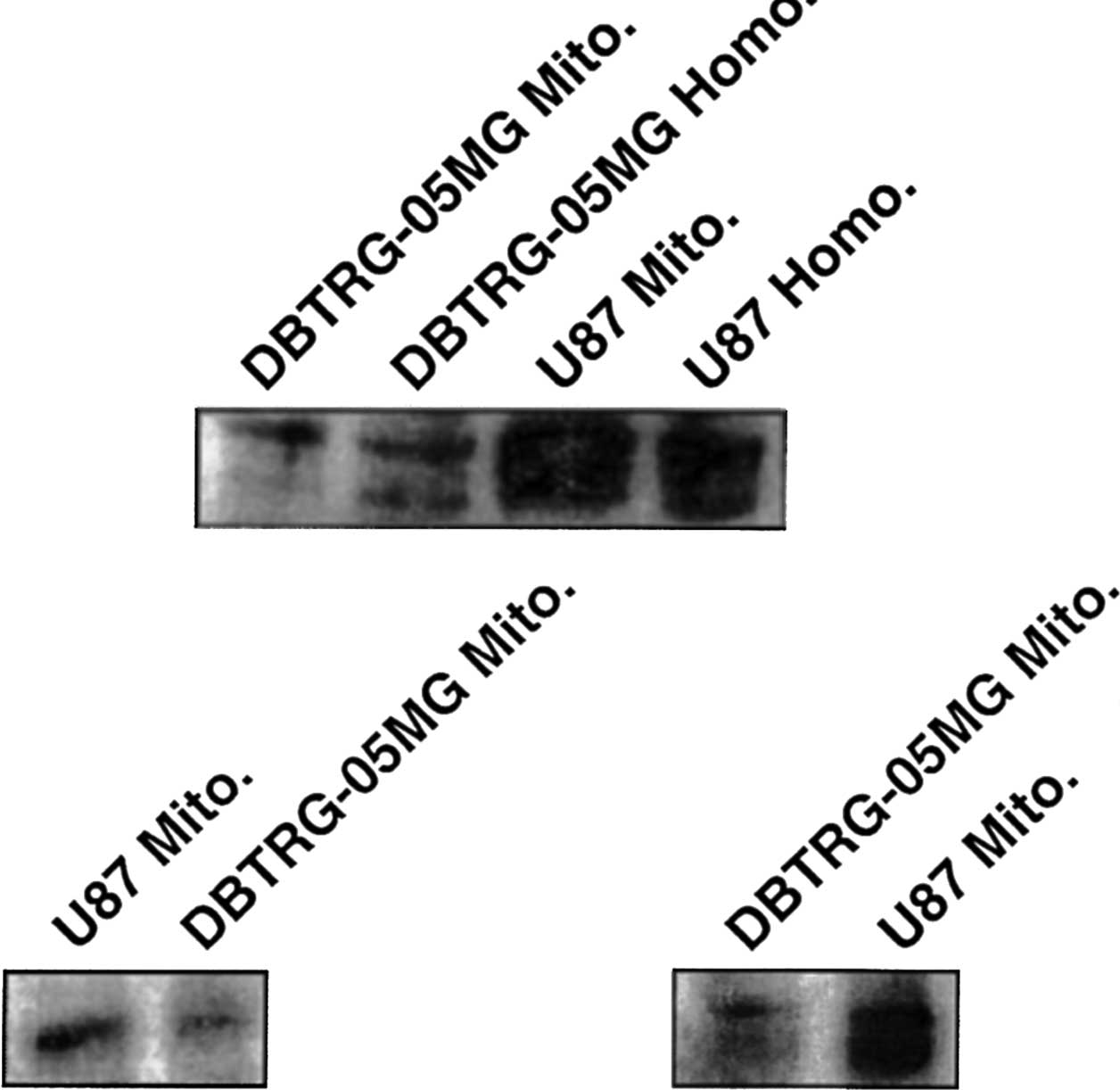
|
1.
|
Henkart PA and Grinstein S: Apoptosis:
mitochondria resurrected? J Exp Med. 183:1293–1295. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kroemer G, Zamzami N and Susin SA:
Mitochondrial control of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 18:44–51. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Cavalli LR and Liang BC: Mutagenesis,
tumorigenicity and apoptosis: are the mitochondria involved? Mutat
Res. 398:19–26. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Newmeyer DD, Farschon DM and Reed JC:
Cell-free apoptosis in Xenopus egg extracts: inhibition by Bel-2
and requirement for an organelle fraction enriched in mitochondria.
Cell. 79:353–364. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Vayssiere JL, Petit PX, Risler Y and
Mignotte B: Commitment to apoptosis is associated with changes in
mitochondrial biogenesis and activity in cell lines conditionally
immortalized with simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:11752–11756. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Cossarizza A, Franceschi C, Monti D, et
al: Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine in tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in U937 cells: the role of
mitochondria. Exp Cell Res. 220:232–240. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Petit PX, Lecoeur H, Zorn E, et al:
Alterations in mitochondrial structure and function are early
events of dexamethasone-induced thymocyte apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
130:157–167. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Castedo M, Macho A, Zamzani N, et al:
Mitochondrial perturbations define lymphocytes undergoing apoptotic
depletion in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 25:3277–3284. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, et al:
Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and
generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell
death. J Exp Med. 182:367–377. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, et al:
Mitochondrial control of nuclear apoptosis. J Exp Med.
183:1533–1544. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kamiike W, et al:
Bcl-2 blocks loss of mitochondrial membrane potential while ICE
inhibitors act at a different step during inhibition of death
induced by respiratory chain inhibitors. Oncogene. 13:21–29.
1996.
|
|
13.
|
Susin SA, Zamzami N, Castedo M, et al:
Bcl-2 inhibits the mitochondrial release of an apoptogenic
protease. J Exp Med. 184:1331–1341. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, et al:
Inhibitors of permeability transition interfere with the disruption
of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential during apoptosis. FEBS
Lett. 384:53–57. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Boise LH and Thompson CB: Bcl-x(L) can
inhibit apoptosis in cells that have undergone Fas-induced protease
activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3759–3764. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Kroemer G: The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and
its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med. 3:614–620. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Stuart RA and Neupert W: Apocytochrome c:
an exceptional mitochondrial precursor protein using an exceptional
import pathway. Biochimie. 72:115–121. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Mancini M, Nicholson DW, Roy S, et al: The
caspase-3 precursor has a cytosolic and mitochondrial distribution:
implications for apoptotic signaling. J Cell Biol. 140:1485–1495.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzani N, et al:
Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing
factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzani N, et al:
Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic
process. J Exp Med. 189:381–394. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
D'Amelio M, Tino E and Cecconi F: The
apoptosome emerging insights and new potential targets for drug
design. Pharm Res. 25:740–751. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Bossy-Wetzel E, Newmeyer DD and Green DR:
Mitochondrial cytochrome c release in apoptosis occurs upstream of
DEVD-specific caspase activation and independently of mitochondrial
transmembrane depolarization. EMBO J. 17:37–49. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Suzuki A, Tsutomi Y, Yamamoto N, Shibutani
T and Akahane K: Mitochondrial regulation of cell death:
mitochondria are essential for procaspase 3-p21 complex formation
to resist Fas-mediated cell death. Mol Cell Biol. 19:3842–3847.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AM, et al:
Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of
apoptosis. Science. 245:301–305. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Leithauser F, Dhein J, Mechtersheimer G,
et al: Constitutive and induced expression of APO-1, a new member
of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor
superfamily, in normal and neoplastic cells. Lab Invest.
69:415–429. 1993.
|
|
27.
|
Moller P, Koretz K, Leithauser F, et al:
Expression of APO-1 (CD95), a member of the NGF/TNF receptor
superfamily, in normal and neoplastic colon epithelium. Int J
Cancer. 57:371–377. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Weller M, Malipiero U, Rensing-Ehl A, Barr
PJ and Fontana A: Fas/APO-1 gene transfer for human malignant
glioma. Cancer Res. 55:2936–2944. 1955.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Nagata S and Golstein P: The Fas death
factor. Science. 267:1449–1456. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
French LE, Hahne M, Viard I, et al: Fas
and Fas ligand in embryos and adult mice: ligand expression in
several immune-privileged tissues and coexpression in adult tissues
characterized by apoptotic cell turnover. J Cell Biol. 133:335–343.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Houghton JA, Harwood FG, Gibson AA and
Tillman DM: The fas signaling pathway is functional in colon
carcinoma cells and induces apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res.
3:2205–2209. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Mahmood Z and Shulka Y: Death receptors:
targets for cancer therapy. Exp Cell Res. 316:887–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Itoh N and Nagata S: A novel protein
domain required for apoptosis. Mutational analysis of human Fas
antigen. J Biol Chem. 268:10932–10937. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Cheng J, Zhou T, Liu C, et al: Protection
from Fas-mediated apoptosis by a soluble form of the Fas molecule.
Science. 263:1759–1762. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Sato T, Irie S, Kitada S and Reed JC:
FAP-1: a protein tyrosine phosphatase that associates with Fas.
Science. 268:411–415. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Hughes SJ, Nambu Y, Soldes OS, et al:
Fas/APO-1 (CD95) is not translocated to the cell membrane in
esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 57:5571–5578.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Irmler M, Thorne M, Hahne M, et al:
Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature.
388:190–195. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Rokhlin OW, Bishop GA, Hostager BS, et al:
Fas-mediated apoptosis in human prostatic carcinoma cell lines.
Cancer Res. 57:1758–1768. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Tillman DM, Harwood FG, Gibson AA and
Houghton JA: Expression of genes that regulate Fas signalling and
Fas-mediated apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. Cell Death Differ.
5:450–457. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Owen-Schaub LB, Radinsky R, Kruzel E,
Berry K and Yonehara S: Anti-Fas on nonhematopoietic tumors: levels
of Fas/APO-1 and bcl-2 are not predictive of biological
responsiveness. Cancer Res. 54:1580–1586. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Holmstrom TH, Tran SE, Johnson VL, et al:
Inhibition of mitogen-activated kinase signaling sensitizes HeLa
cells to Fas receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
19:5991–6002. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, et al:
Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J. 17:1675–1687.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Heerdt BG, Houston MA and Augenlicht LH:
Short-chain fatty acid-initiated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of
colonic epithelial cells is linked to mitochondrial function. Cell
Growth Differ. 8:523–532. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Jacobson MD, Burne JF, King MP, et al:
Bcl-2 blocks apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Nature.
361:365–369. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Jacobson MD and Raff MC: Programmed cell
death and Bcl-2 protection in very low oxygen. Nature. 374:814–816.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kosaka H, et al:
Prevention of hypoxia-induced cell death by Bcl-2 and Bel-xL.
Nature. 374:811–813. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Gamen S, Anel A, Montoya J, et al:
mtDNA-depleted U937 cells are sensitive to TNF and Fas-mediated
cytotoxicity. FEBS Lett. 376:15–18. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Marchetti P, Susin SA, Decaudin D, et al:
Apoptosis-associated derangement of mitochondrial function in cells
lacking mitochondrial DNA. Cancer Res. 56:2033–2038.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Schulze-Osthoff K, Beyaert R, Vandevoorde
V, Haegeman G and Fiers W: Depletion of the mitochondrial electron
transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of
TNF. EMBO J. 12:3095–3104. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Cavalli LR, Varella-Garcia M and Liang BC:
Diminished tumorigenic phenotype after depletion of mitochondrial
DNA. Cell Growth Differ. 8:1189–1198. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Liang BC and Ullyatt E: Increased
sensitivity to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum induced apoptosis with
mitochondrial DNA depletion. Cell Death Differ. 5:694–701. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Liang BC and Ullyatt E: Chemosensitization
of glioblastoma cells to bis-dichloroethyl nitrosourea with
tyrphostin AG17. Clin Cancer Res. 4:773–781. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
King MP and Attardi G: Isolation of human
cell lines lacking mitochondrial DNA. Methods Enzymol. 264:304–313.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC,
Grignani F and Riccardi C: A rapid and simple method for measuring
thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow
cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 139:271–279. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson
EK, Schumacker PT and Thompson CB: Bcl-xL regulates the membrane
potential and volume homeostasis of mitochondria. Cell. 91:627–637.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland
NG, Jenkins NA and Nagata S: Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice
explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis.
Nature. 356:314–317. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57.
|
Nagata S and Suda T: Fas and Fas ligand:
1pr and gld mutations. Immunol Today. 16:39–43. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58.
|
Wong GH and Goeddel DV: Fas antigen and
p55 TNF receptor signal apoptosis through distinct pathways. J
Immunol. 152:1751–1755. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Shima Y, Nishimoto N, Ogata A, et al:
Myeloma cells express Fas antigen/APO-1 (CD95) but only some are
sensitive to anti-Fas antibody resulting in apoptosis. Blood.
85:757–764. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Westendorf JJ, Lammert JM and Jelinek DF:
Expression and function of Fas (APO 1/CD95) in patient myeloma
cells and myeloma cell lines. Blood. 85:3566–3576. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Danielson SR, Wong A, Carelli V,
Martinuzzi A, Schapira AH and Cortopassi GA: Cells bearing
mutations causing Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy are
sensitized to Fas-Induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:5810–5815.
2002.
|
|
62.
|
Raisova M, Hossini AM, Eberle J, Riebeling
C, Wieder T, Sturm I, Daniel PT, Orfanos CE and Geilen CC: The
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio determines the susceptibility of human melanoma
cells to CD95/Fas-mediated apoptis. J Invest Dermatol. 117:333–340.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Maas C, Verbrugge I, De Vries E, Savich G,
van de Kooij LW, Tait SW and Borst J: Smac/DIABLO release from
mitochondria and XIAP inhibition are essential to limit
clonogencity of Type I tumor cells after TRAIL receptor
stimulation. Cell Death Differ. 17:1613–1623. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH and Debatin
KM: Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/FAS) receptor/ligand system in
drug-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Nat Med. 2:574–577. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Matsumoto Y, Hayakawa A, Tamada Y, Mori H
and Ohashi M: Upregulated expression of Fas antigen on cultured
human keratinocytes with induction of apoptosis by cisplatin. Arch
Dermatol Res. 288:267–279. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Fulda S, Sieverts H, Friesen C, Herr I and
Debatin KM: The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) system mediates drug-induced
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 57:3823–3829.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Muller M, Strand S, Hug H, et al:
Drug-induced apoptosis in hepatoma cells is mediated by the CD95
(APO-1/Fas) receptor/ligand system and involves activation of
wild-type p53. J Clin Invest. 99:403–413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Eischen CM, Kottke TJ, Martins LM, et al:
Comparison of apoptosis in wild-type and Fas-resistant cells:
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis is not dependent on Fas/Fas ligand
interactions. Blood. 90:935–943. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Villunger A, Egle A, Kos M, et al:
Drug-induced apoptosis is associated with enhanced Fas (Apo-1/CD95)
ligand expression but occurs independently of' Fas (Apo-1/CD95)
signaling in human T-acute lymphatic leukemia cells. Cancer Res.
57:3331–3334. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Verbrugge I, Maas C, Heijkoop M, Verheij
and Borst J: Radiation and anticancer drugs can facilitate
mitochondrial bypass by CD95/FAS via c-FLIP downregulation. Cell
Death Differ. 17:551–561. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Asoh S, Mori T, Hayashi J and Ohta S:
Expression of the apoptosis-mediator Fas is enhanced by
dysfunctional mitochondria. J Biochem. 120:600–607. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|