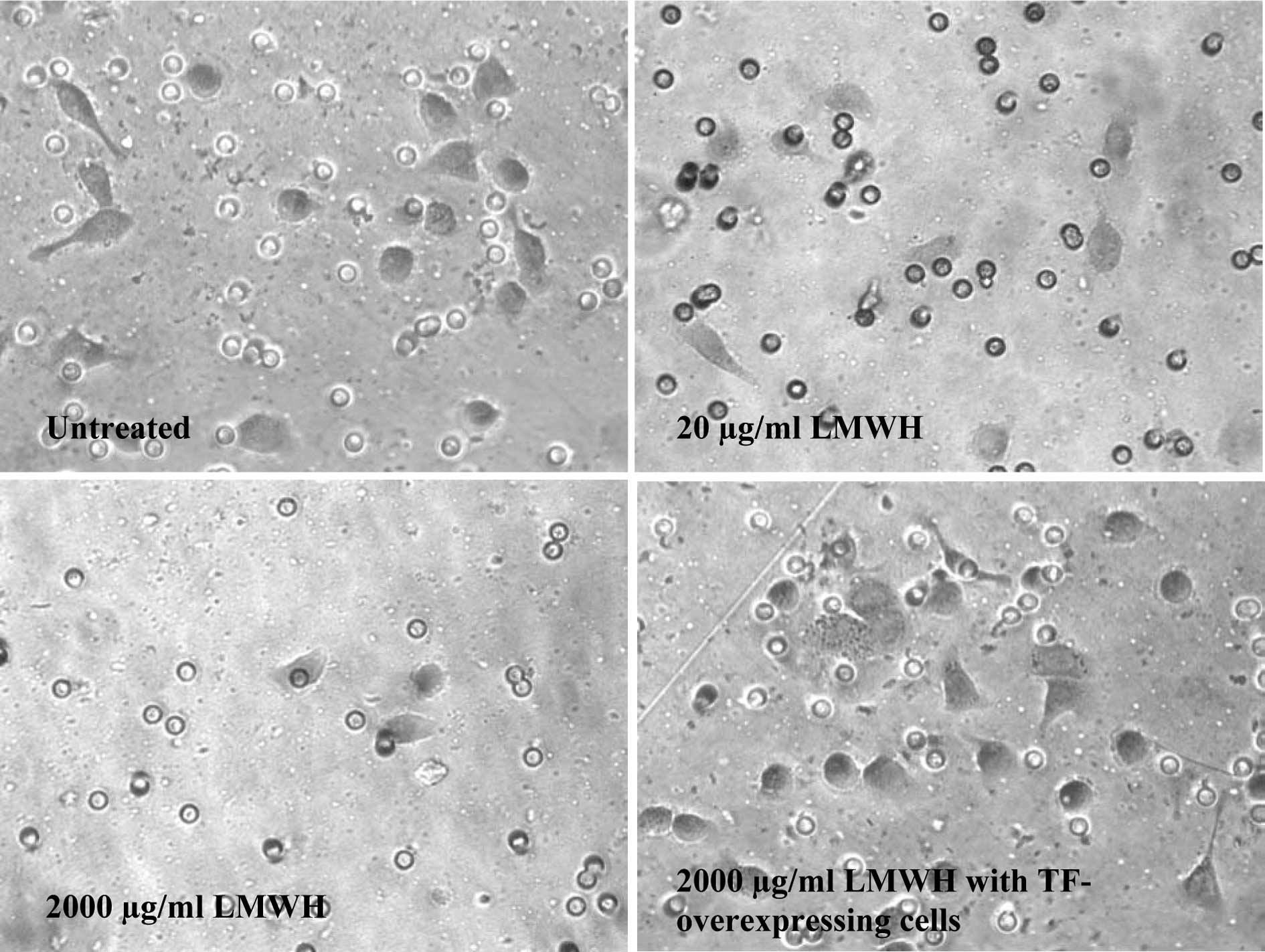
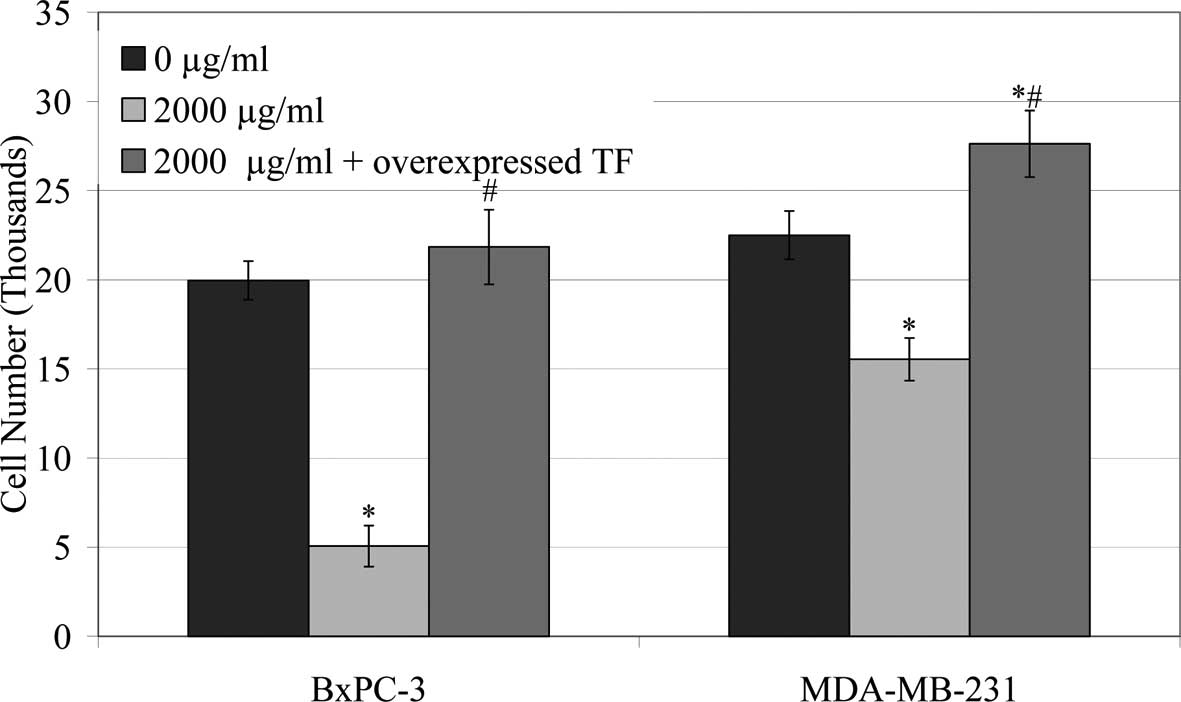
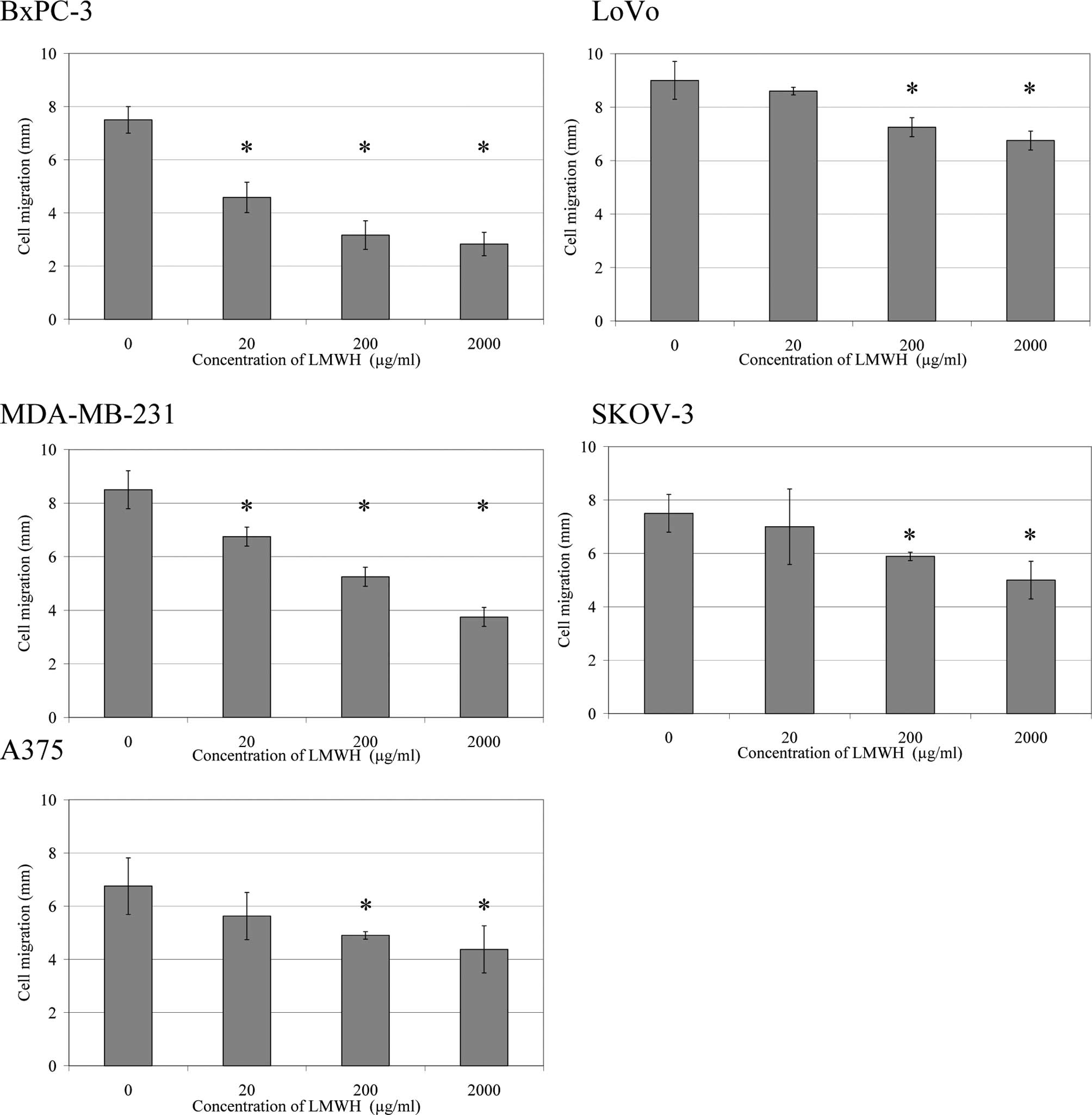
|
1.
|
Kakkar AK, Lemoine NR, Scully MF, Tebbutt
S and Williamson RC: Tissue factor expression correlates with
histological grade in human pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg.
82:1101–1104. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Khorana AA, Ahrendt SA, Ryan CK, Francis
CW, Hruban RH, Hu YC, Hostetter G, Harvey J and Taubman MB: Tissue
factor expression, angiogenesis, and thrombosis in pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2870–2875. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Gessler F, Voss V, Dützmann S, Seifert V,
Gerlach R and Kögel D: Inhibition of tissue
factor/protease-activated receptor-2 signaling limits
proliferation, migration and invasion of malignant glioma cells.
Neuroscience. 165:1312–1322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Jiang X, Zhu S, Panetti TS and Bromberg
ME: Formation of tissue factor-factor VIIa-factor Xa complex
induces activation of the mTOR pathway which regulates migration of
human breast cancer cells. Thromb Haemost. 100:127–133. 2008.
|
|
5.
|
Siegbahn A, Johnell M, Sorensen BB,
Petersen LC and Heldin CH: Regulation of chemotaxis by the
cytoplasmic domain of tissue factor. Thromb Haemost. 93:27–34.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Dorfleutner A, Hintermann E, Tarui T,
Takada Y and Ruf W: Cross-talk of integrin alpha3beta1 and tissue
factor in cell migration. Mol Biol Cell. 15:4416–4425. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Sato Y, Kataoka H, Asada Y, Marutsuka K,
Kamikubo Y, Koono M and Sumiyoshi A: Overexpression of tissue
factor pathway inhibitor in aortic smooth muscle cells inhibits
cell migration induced by tissue factor/factor VIIa complex. Thromb
Res. 94:401–406. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Khorana AA and Fine RL: Pancreatic cancer
and thromboembolic disease. Lancet Oncol. 5:655–663. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Kakkar AK and Williamson RC: Prevention of
venous thromboembolism in cancer using low-molecular-weight
heparins. Haemostasis. 27(Suppl 1): 32–37. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Maraveyas A, Ettelaie C, Echrish H, Li C,
Gardiner E, Greenman J and Madden L: Weight-adjusted dalteparin for
prevention of vascular thromboembolism in advanced pancreatic
cancer patients decreases serum tissue factor and serum-mediated
induction of cancer cell invasion. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis.
21:452–458. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Icli F, Akbulut H, Utkan G, Yalcin B,
Dincol D, Isikdogan A, Demirkazik A, Onur H, Cay F and Büyükcelik
A: Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) increases the efficacy of
cisplatinum plus gemcitabine combination in advanced pancreatic
cancer. J Surg Oncol. 95:507–512. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Von Delius S, Ayvaz M, Wagenpfeil S, Eckel
F, Schmid RM and Lersch C: Effect of low-molecular-weight heparin
on survival in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Thromb Haemost. 98:434–439. 2007.
|
|
13.
|
Gori AM, Pepe G, Attanasio M, Falciani M,
Abbate R, Prisco D, Fedi S, Giusti B, Brunelli T, Giusti B,
Brunelli T, Comeglio P, Gensini GF and Neri Serneri GG: Tissue
factor reduction and tissue factor pathway inhibitor release after
heparin administration. Thromb Haemost. 81:589–593. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Li C, Colman LM, Collier ME, Dyer CE,
Greenman J and Ettelaie C: Tumour-expressed tissue factor inhibits
cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 55:1301–1308.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ettelaie C, Su S, Li C and Collier ME:
Tissue factor-containing microparticles released from mesangial
cells in response to high glucose and AGE induce tube formation in
microvascular cells. Microvasc Res. 76:152–160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Zhang JQ, Wan YL, Liu YC, Wang X, Tang JQ,
Wu T, Zhu J and Pan YS: The FVIIa-tissue factor complex induces the
expression of MMP7 in LOVO cells in vitro. Int J Colorectal Dis.
23:971–978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Tang JQ, Wan YL, Liu YC, Rong L, Wang X,
Wu T, Pan YS, Ye JM, Yao HW and Zhu J: Role of tissue factor in the
invasion of cultured human colon carcinoma cells and its
correlation with matrix metalloproteinases. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.
37:265–268. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|