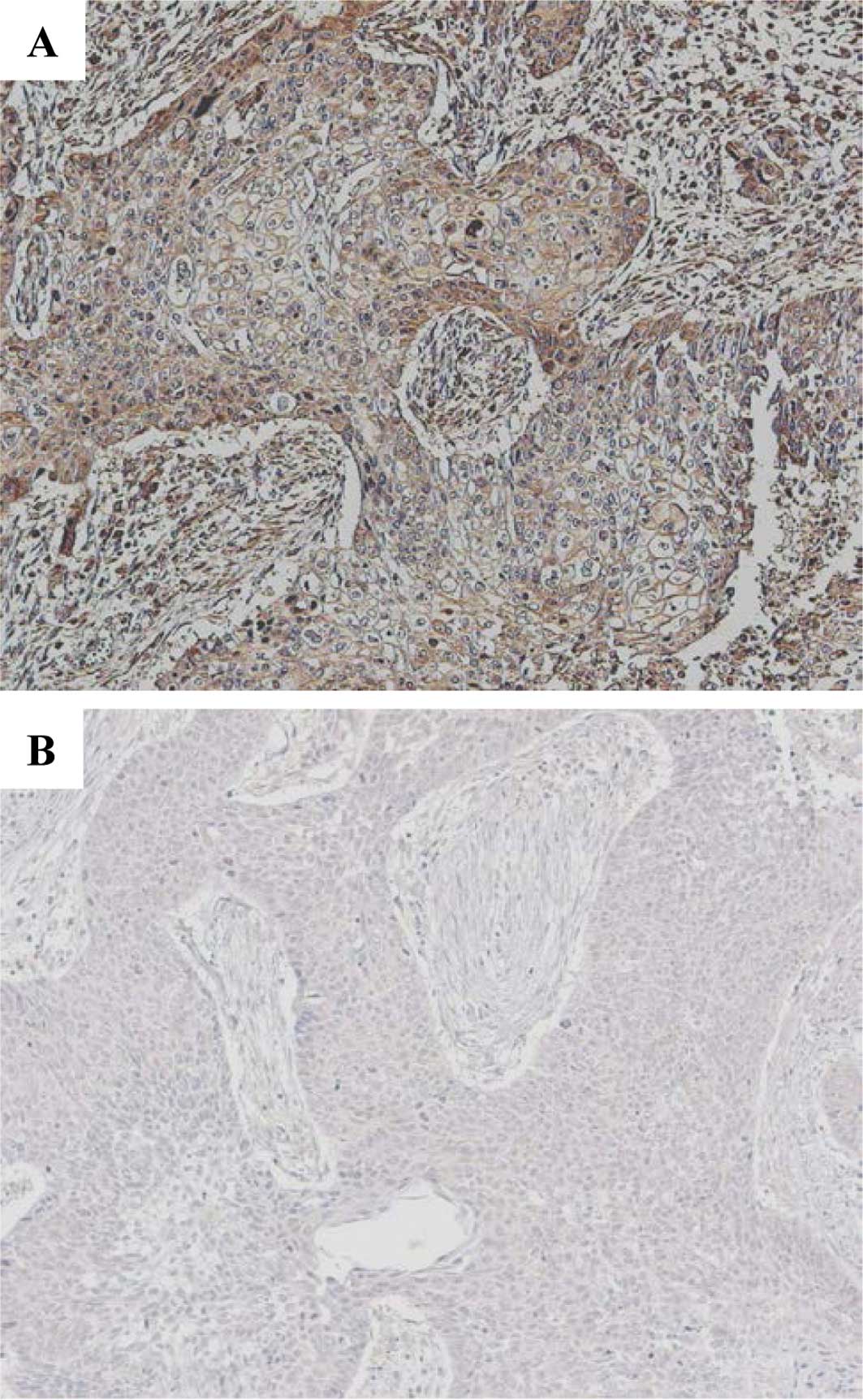
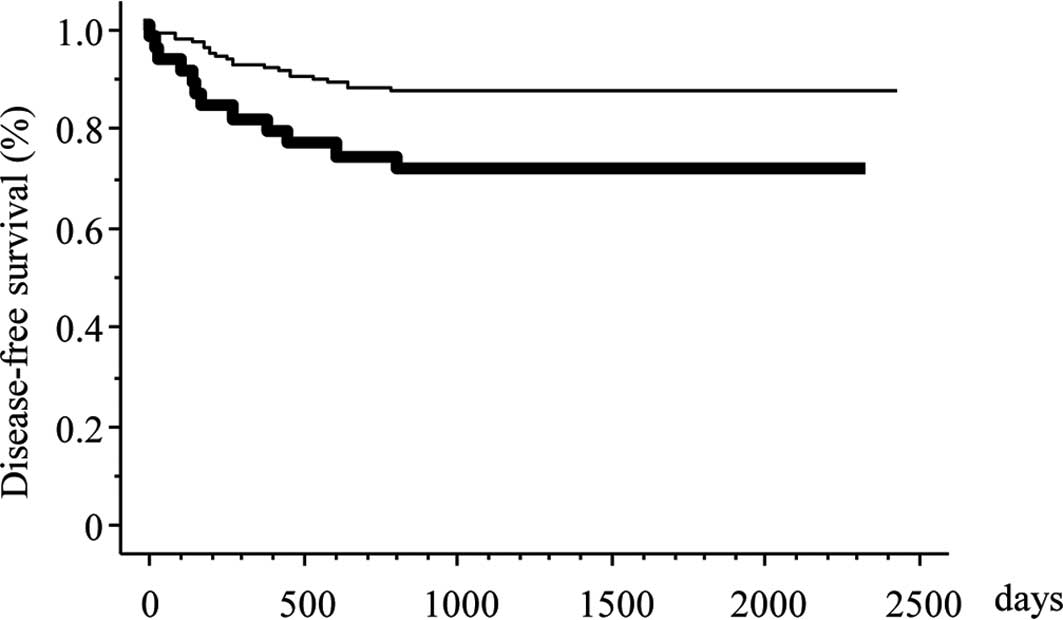
|
1.
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Janssen-Heijnen ML and Coebergh JW: Trends
in incidence and prognosis of the histological subtypes of lung
cancer in North America, Australia, New Zealand and Europe. Lung
Cancer. 31:123–137. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Goya T, Asamura H, Yoshimura H, Kato H,
Shimokata K, Tsuchiya R, Sohara Y, Miya T and Miyaoka E: The
Japanese Joint Committee of Lung Cancer Registry Prognosis of 6644
resected non-small cell lung cancers in Japan: a Japanese lung
cancer registry study. Lung Cancer. 50:227–234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV, et
al: Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the
LACE Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol. 26:3552–3559. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Kato H, Ichinose Y and Ohta M, Hata E,
Tsubota N, Tada H, Watanabe Y, Wada H, Tsuboi M, Hamajima N and
Ohta M: Japan Lung Cancer Research Group on Postsurgical Adjuvant
Chemotherapy. A randomized trial of adjuvant chemotherapy with
uracil-tegafur for adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med.
350:1713–1721. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A
and Friend KE: The effects of insulin-like growth factors on
tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 21:215–244. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
LeRoith D and Roberts CT Jr: The
insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett.
195:127–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Merrick DT, Dziadziuszko R, Szostakiewicz
B, Szymanowska A, Rzyman W, Jassem E, Jassem J, Franklin WA, Bunn
PA and Hirsch FR: High insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF
1R) expression is associated with poor survival in surgically
treated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. J Clin Oncol.
25:75502007.
|
|
9.
|
Vallières E, Shepherd FA, Crowley J, van
Houtte P, Postmus PE, Carney D, Chansky K, Shaikh Z and Goldstraw
P: International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee and Participating Institutions. The
IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals regarding the
relevance of TNM in the pathologic staging of small cell lung
cancer in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM
classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 4:1049–1059.
2009.
|
|
10.
|
Onitsuka T, Uramoto H, Nose N, Takenoyama
M, Hanagiri T, Sugio K and Yasumoto K: Acquired resistance to
gefitinib: the contribution of mechanisms other than the T790M,
MET, and HGF status. Lung Cancer. 68:198–203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Yamashita T, Uramoto H, Onitsuka T, Ono K,
Baba T, So T, So T, Takenoyama M, Hanagiri T, Oyama T and Yasumoto
K: Association between lymphangiogenesis-/micrometastasis- and
adhesion-related molecules in resected stage I NSCLC. Lung Cancer.
70:320–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Chang MH, Lee J, Han J, Park YH, Ahn JS,
Park K and Ahn MJ: Prognostic role of insulin-like growth factor
receptor-1 expression in small cell lung cancer. APMIS.
117:861–869. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Onitsuka T, Uramoto H, Ono K, Takenoyama
M, Hanagiri T, Oyama T, Izumi H, Kohno K and Yasumoto K:
Comprehensive molecular analyses of lung adenocarcinoma with regard
to the epidermal growth factor receptor, K-ras, MET, and hepatocyte
growth factor status. J Thorac Oncol. 5:591–596. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Shimokawa H, Uramoto H, Onitsuka T, Iwata
T, Nakagawa M, Ono K and Hanagiri T: TS expression predicts
postoperative recurrence in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung
Cancer. Oct. 21–2010, (E-pub ahead of print).
|
|
15.
|
Ludovini V, Bellezza G, Pistola L, et al:
High coexpression of both insulin-like growth factor receptor-1
(IGFR-1) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated
with shorter disease-free survival in resected non-small-cell lung
cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 20:842–849. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Uramoto H, Sugio K, Oyama T, Ono K, Sugaya
M, Yoshimatsu T, Hanagiri T, Morita M and Yasumoto K: Epidermal
growth factor receptor mutations are associated with gefitinib
sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer in Japanese. Lung Cancer.
51:71–77. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Cappuzzo F, Toschi L, Tallini G, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR-1) is significantly
associated with longer survival in non-small-cell lung cancer
patients treated with gefitinib. Ann Oncol. 17:1120–1127. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Karp DD, Paz-Ares LG, Novello S, et al:
Phase II study of the anti-insulin-like growth factor type 1
receptor antibody CP-751,871 in combination with paclitaxel and
carboplatin in previously untreated, locally advanced, or
metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:2516–2522.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Cappuzzo F, Tallini G, Finocchiaro G, et
al: Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and
survival in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
patients. Ann Oncol. 21:562–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lee AV, Cui X and Oesterreich S:
Cross-talk among estrogen receptor, epidermal growth factor, and
insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 7:4429–4435. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Gilmore AP, Valentijn AJ, Wang P, Ranger
AM, Bundred N, O'Hare MJ, Wakeling A, Korsmeyer SJ and Streuli CH:
Activation of BAD by therapeutic inhibition of epidermal growth
factor receptor and transactivation by insulin-like growth factor
receptor. J Biol Chem. 277:27643–27650. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Shen YM, Yang XC, Yang C and Shen JK:
Enhanced therapeutic effects for human pancreatic cancer by
application K-ras and IGF-IR antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. World
J Gastroenterol. 14:5176–5185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Scartozzi M, Mandolesi A, Giampieri R, et
al: Insulin-like growth factor 1 expression correlates with
clinical outcome in K-RAS wild-type colorectal cancer patients
treated with cetuximab and irinotecan. Int J Cancer. 127:1941–1947.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|