Spandidos Publications style
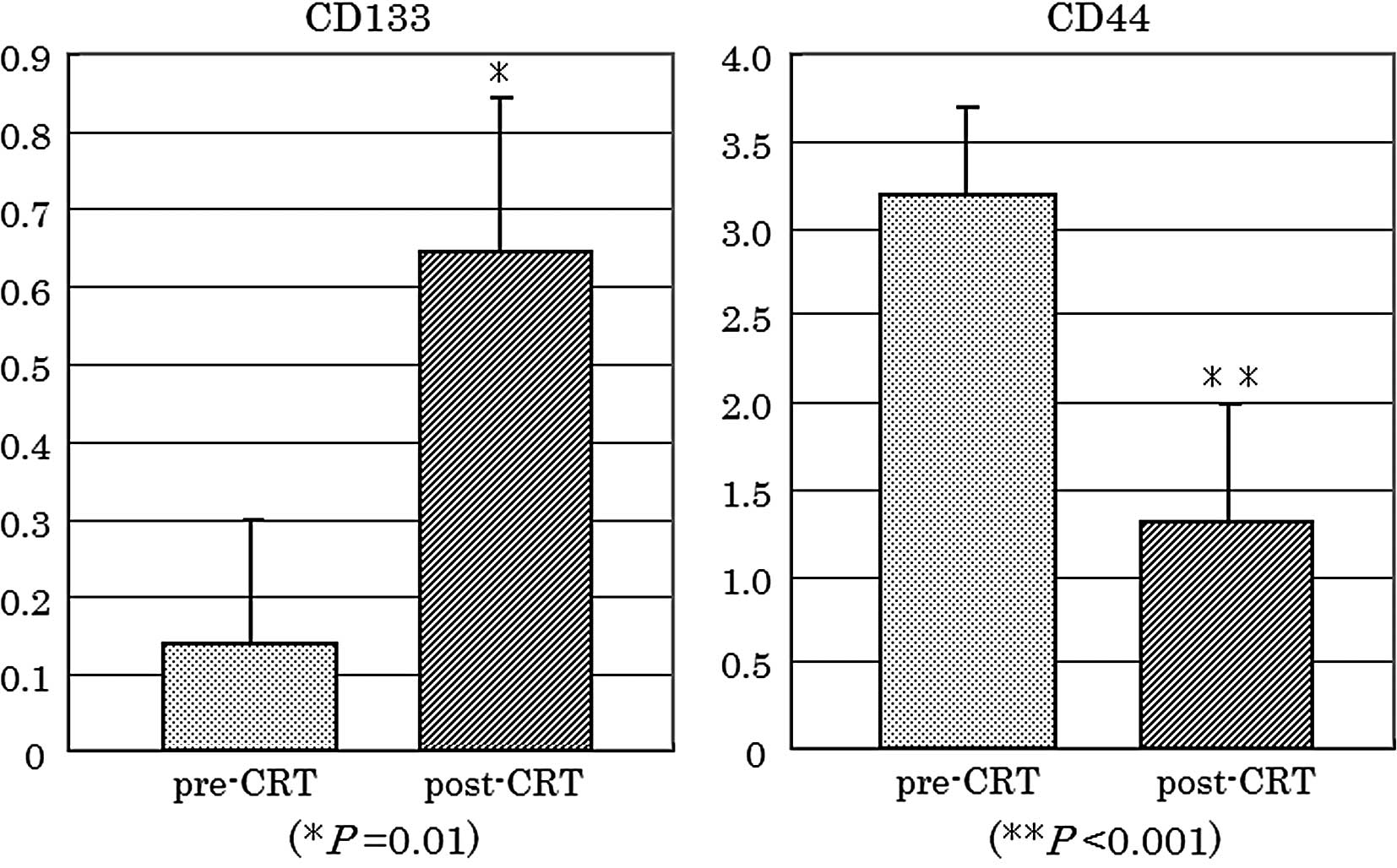
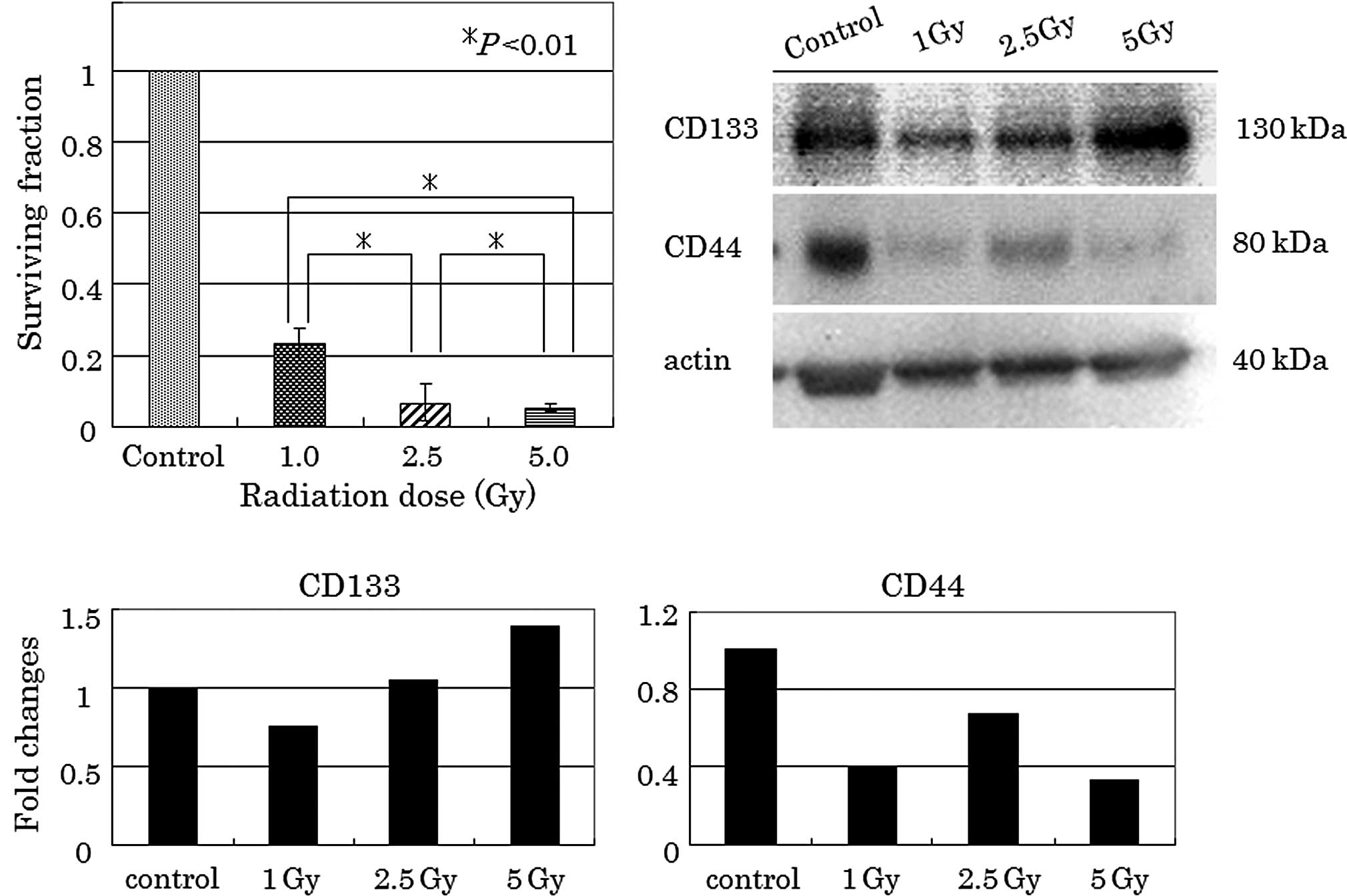
Kawamoto A, Tanaka K, Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Morimoto Y, Fujikawa H, Iwata T, Matsushita K, Yokoe T, Yasuda H, Yasuda H, et al: Clinical significance of radiation-induced CD133 expression in residual rectal cancer cells after chemoradiotherapy. Exp Ther Med 3: 403-409, 2012.
APA
Kawamoto, A., Tanaka, K., Saigusa, S., Toiyama, Y., Morimoto, Y., Fujikawa, H. ... Kusunoki, M. (2012). Clinical significance of radiation-induced CD133 expression in residual rectal cancer cells after chemoradiotherapy. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 3, 403-409. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2011.438
MLA
Kawamoto, A., Tanaka, K., Saigusa, S., Toiyama, Y., Morimoto, Y., Fujikawa, H., Iwata, T., Matsushita, K., Yokoe, T., Yasuda, H., Inoue, Y., Miki, C., Kusunoki, M."Clinical significance of radiation-induced CD133 expression in residual rectal cancer cells after chemoradiotherapy". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 3.3 (2012): 403-409.
Chicago
Kawamoto, A., Tanaka, K., Saigusa, S., Toiyama, Y., Morimoto, Y., Fujikawa, H., Iwata, T., Matsushita, K., Yokoe, T., Yasuda, H., Inoue, Y., Miki, C., Kusunoki, M."Clinical significance of radiation-induced CD133 expression in residual rectal cancer cells after chemoradiotherapy". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 3, no. 3 (2012): 403-409. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2011.438