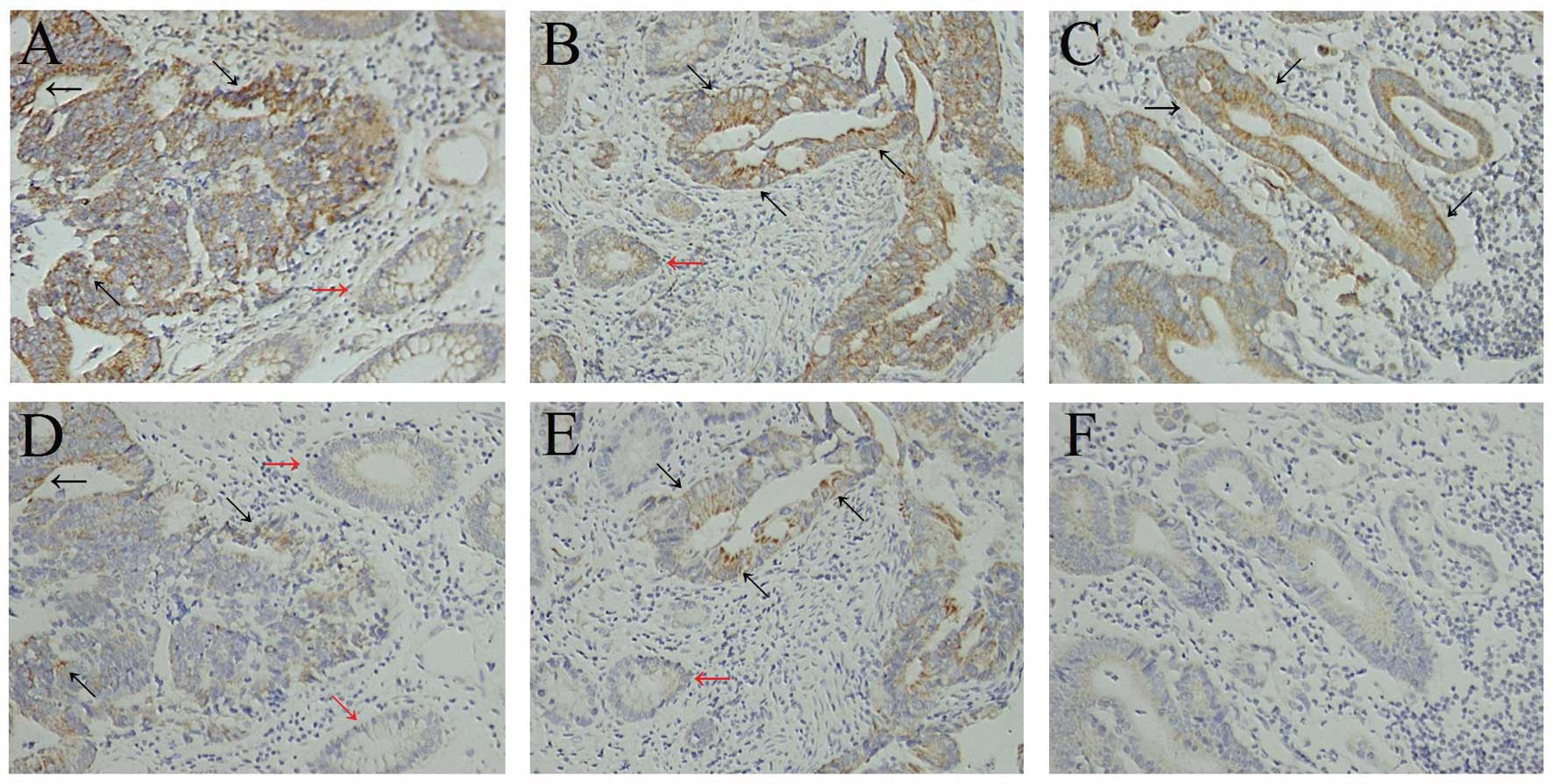
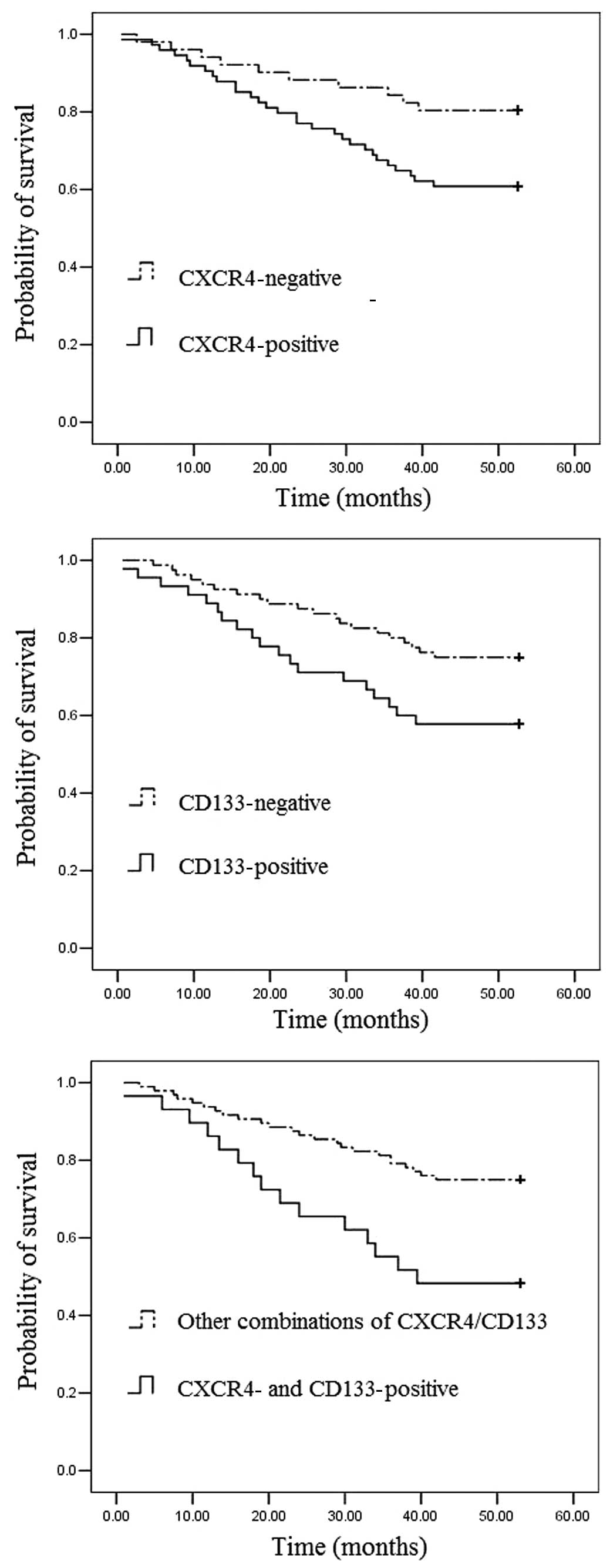
|
1.
|
Weir HK, Thun MJ, Hankey BF, et al: Annual
report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2000, featuring
the uses of surveillance data for cancer prevention and control. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 95:1276–1299. 2003.
|
|
2.
|
Singh R, Lillard JW Jr and Singh S:
Chemokines: key players in cancer progression and metastasis. Front
Biosci (Schol Ed). 3:1569–1582. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Liekens S, Schols D and Hatse S:
CXCL12-CXCR4 axis in angiogenesis, metastasis and stem cell
mobilization. Curr Pharm Des. 16:3903–3920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Arya M, Patel HR and Williamson M:
Chemokines: key players in cancer. Curr Med Res Opin. 19:557–564.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Ali S and Lazennec G: Chemokines: novel
targets for breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:401–420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Murdoch C: CXCR4: chemokine receptor
extraordinaire. Immunol Rev. 177:175–184. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Lutz M, Belperio
JA, Keane MP and Strieter RM: The stromal derived
factor-1/CXCL12-CXC chemokine receptor 4 biological axis in
non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
167:1676–1686. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kawamata H, Furihata T, Omotehara F, et
al: Identification of genes differentially expressed in a newly
isolated human metastasizing esophageal cancer cell line, T.Tn-AT1,
by cDNA microarray. Cancer Sci. 94:699–706. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA and Mercurio AM:
Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma
invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine
receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res. 62:7203–7206. 2002.
|
|
10.
|
Kijima T, Maulik G, Ma PC, et al:
Regulation of cellular proliferation, cytoskeletal function, and
signal transduction through CXCR4 and c-Kit in small cell lung
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:6304–6311. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Gao Z, Wang X, Wu K, Zhao Y and Hu G:
Pancreatic stellate cells increase the invasion of human pancreatic
cancer cells through the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 axis.
Pancreatology. 10:186–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Guleng B, Tateishi K, Ohta M, et al:
Blockade of the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 axis attenuates
in vivo tumor growth by inhibiting angiogenesis in a vascular
endothelial growth factor-independent manner. Cancer Res.
65:5864–5871. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Koshiba T, Hosotani R, Miyamoto Y, et al:
Expression of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and CXCR4 ligand
receptor system in pancreatic cancer: a possible role for tumor
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3530–3535. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Van der Meulen AA, Biber K, Lukovac S, et
al: The role of CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL)12-CXC chemokine
receptor (CXCR)4 signalling in the migration of neural stem cells
towards a brain tumour. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 35:579–591.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Li W, Gomez E and Zhang Z:
Immunohistochemical expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1
(SDF-1) and CXCR4 ligand receptor system in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 26:527–533. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chen GS, Yu HS, Lan CC, et al: CXC
chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression enhances tumorigenesis and
angiogenesis of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 154:910–918.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Barbero S, Bonavia R, Bajetto A, et al:
Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha stimulates human glioblastoma
cell growth through the activation of both extracellular
signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and Akt. Cancer Res. 63:1969–1974.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zeelenberg IS, Ruuls-Van Stalle L and Roos
E: The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is required for outgrowth of colon
carcinoma micrometastases. Cancer Res. 63:3833–3839.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kato M, Kitayama J, Kazama S and Nagawa H:
Expression pattern of CXC chemokine receptor-4 is correlated with
lymph node metastasis in human invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast
Cancer Res. 5:144–150. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Uchida D, Begum NM, Almofti A, et al:
Possible role of stromal-cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 signaling on
lymph node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Cell
Res. 290:289–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Todaro M, Francipane MG, Medema JP and
Stassi G: Colon cancer stem cells: promise of targeted therapy.
Gastroenterology. 138:2151–2162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Boman BM and Wicha MS: Cancer stem cells:
a step toward the cure. J Clin Oncol. 26:2795–2799. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Wang J, Guo LP, Chen LZ, Zeng YX and Lu
SH: Identification of cancer stem cell-like side population cells
in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res.
67:3716–3724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Horst D, Kriegl L, Engel J, Kirchner T and
Jung A: Prognostic significance of the cancer stem cell markers
CD133, CD44, and CD166 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Invest.
27:844–850. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
O’Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
et al: Identification and expansion of human
colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature. 445:111–115. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Murat A, Migliavacca E, Gorlia T, et al:
Stem cell-related ‘self-renewal’ signature and high epidermal
growth factor receptor expression associated with resistance to
concomitant chemoradiotherapy in glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
26:3015–3024. 2008.
|
|
29.
|
Hambardzumyan D, Squatrito M and Holland
EC: Radiation resistance and stem-like cells in brain tumors.
Cancer Cell. 10:454–456. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N,
Radovanovic I and Ruiz i Altaba A: HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling
regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and
tumorigenicity. Curr Biol. 17:165–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Hambardzumyan D, Becher OJ and Holland EC:
Cancer stem cells and survival pathways. Cell Cycle. 7:1371–1378.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, et al: Glioma
stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of
the DNA damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Griguer CE, Oliva CR, Gobin E, et al:
CD133 is a marker of bioenergetic stress in human glioma. PLoS One.
3:e36552008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, et al:
Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem
cell population. Cell Death Differ. 15:504–514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Ma S, Chan KW, Hu L, et al: Identification
and characterization of tumorigenic liver cancer stem/progenitor
cells. Gastroenterology. 132:2542–2556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED, et al:
AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and progenitor
cells. Blood. 90:5002–5012. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Monzani E, Facchetti F, Galmozzi E, et al:
Melanoma contains CD133 and ABCG2 positive cells with enhanced
tumourigenic potential. Eur J Cancer. 43:935–946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Wright MH, Calcagno AM, Salcido CD,
Carlson MD, Ambudkar SV and Varticovski L: Brca1 breast tumors
contain distinct CD44+/CD24− and
CD133+ cells with cancer stem cell characteristics.
Breast Cancer Res. 10:R102008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Boman BM and Huang E: Human colon cancer
stem cells: a new paradigm in gastrointestinal oncology. J Clin
Oncol. 26:2828–2838. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Matsumoto K, Shariat SF, Ayala GE, Rauen
KA and Lerner SP: Loss of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor
expression is associated with features of aggressive bladder
cancer. Urology. 66:441–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Brabletz T, Jung A, Spaderna S, Hlubek F
and Kirchner T: Opinion: migrating cancer stem cells - an
integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:744–749. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Terauchi M, Ino K,
Nawa A and Kikkawa F: Involvement of SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 axis in the
enhanced peritoneal metastasis of epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int
J Cancer. 122:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Schrader AJ, Lechner O, Templin M, et al:
CXCR4/CXCL12 expression and signalling in kidney cancer. Br J
Cancer. 86:1250–1256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Sasaki K, Natsugoe S, Ishigami S, et al:
Expression of CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 correlates with lymph
node metastasis in submucosal esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol.
97:433–438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Kim J, Takeuchi H, Lam ST, et al:
Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in colorectal cancer patients
increases the risk for recurrence and for poor survival. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2744–2753. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Schimanski CC, Schwald S, Simiantonaki N,
et al: Effect of chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7 on the
metastatic behavior of human colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:1743–1750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Ottaiano A, Franco R, Aiello Talamanca A,
et al: Overexpression of both CXC chemokine receptor 4 and vascular
endothelial growth factor proteins predicts early distant relapse
in stage II–III colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
12:2795–2803. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Todaro M, Alea MP, Di Stefano AB, et al:
Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and resist cell death
by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell. 1:389–402. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Horst D, Kriegl L, Engel J, Kirchner T and
Jung A: CD133 expression is an independent prognostic marker for
low survival in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:1285–1289. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Kojima M, Ishii G, Atsumi N, Fujii S,
Saito N and Ochiai A: Immunohistochemical detection of CD133
expression in colorectal cancer: a clinicopathological study.
Cancer Sci. 99:1578–1583. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Li CY, Li BX, Liang Y, et al: Higher
percentage of CD133+ cells is associated with poor
prognosis in colon carcinoma patients with stage IIIB. J Transl
Med. 7:562009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Ong CW, Kim LG, Kong HH, et al: CD133
expression predicts for non-response to chemotherapy in colorectal
cancer. Mod Pathol. 23:450–457. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Corbeil D, Röper K, Hellwig A, et al: The
human AC133 hematopoietic stem cell antigen is also expressed in
epithelial cells and targeted to plasma membrane protrusions. J
Biol Chem. 275:5512–5520. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, et al: Analysis of
gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer
stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Florek M, Haase M, Marzesco AM, et al:
Prominin-1/CD133, a neural and hematopoietic stem cell marker, is
expressed in adult human differentiated cells and certain types of
kidney cancer. Cell Tissue Res. 319:15–26. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Pfenninger CV, Roschupkina T, Hertwig F,
et al: CD133 is not present on neurogenic astrocytes in the adult
subventricular zone, but on embryonic neural stem cells, ependymal
cells, and glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:5727–5736. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Weigmann A, Corbeil D, Hellwig A and
Huttner WB: Prominin, a novel microvilli-specific polytopic
membrane protein of the apical surface of epithelial cells, is
targeted to plasmalemmal protrusions of non-epithelial cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:12425–12430. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58.
|
Shmelkov SV, Butler JM, Hooper AT, et al:
CD133 expression is not restricted to stem cells, and both
CD133+ and CD133− metastatic colon cancer
cells initiate tumors. J Clin Invest. 118:2111–2120.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|